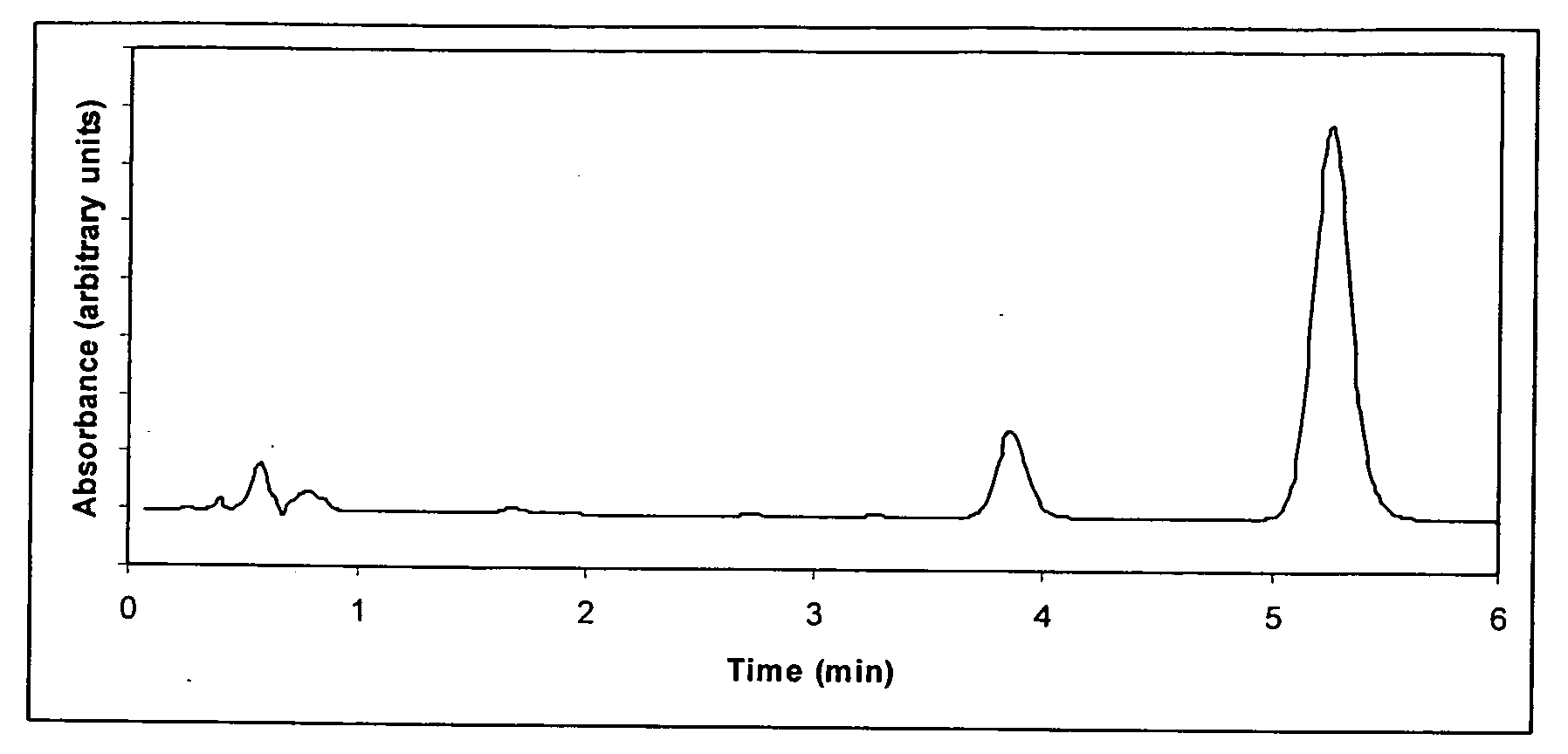
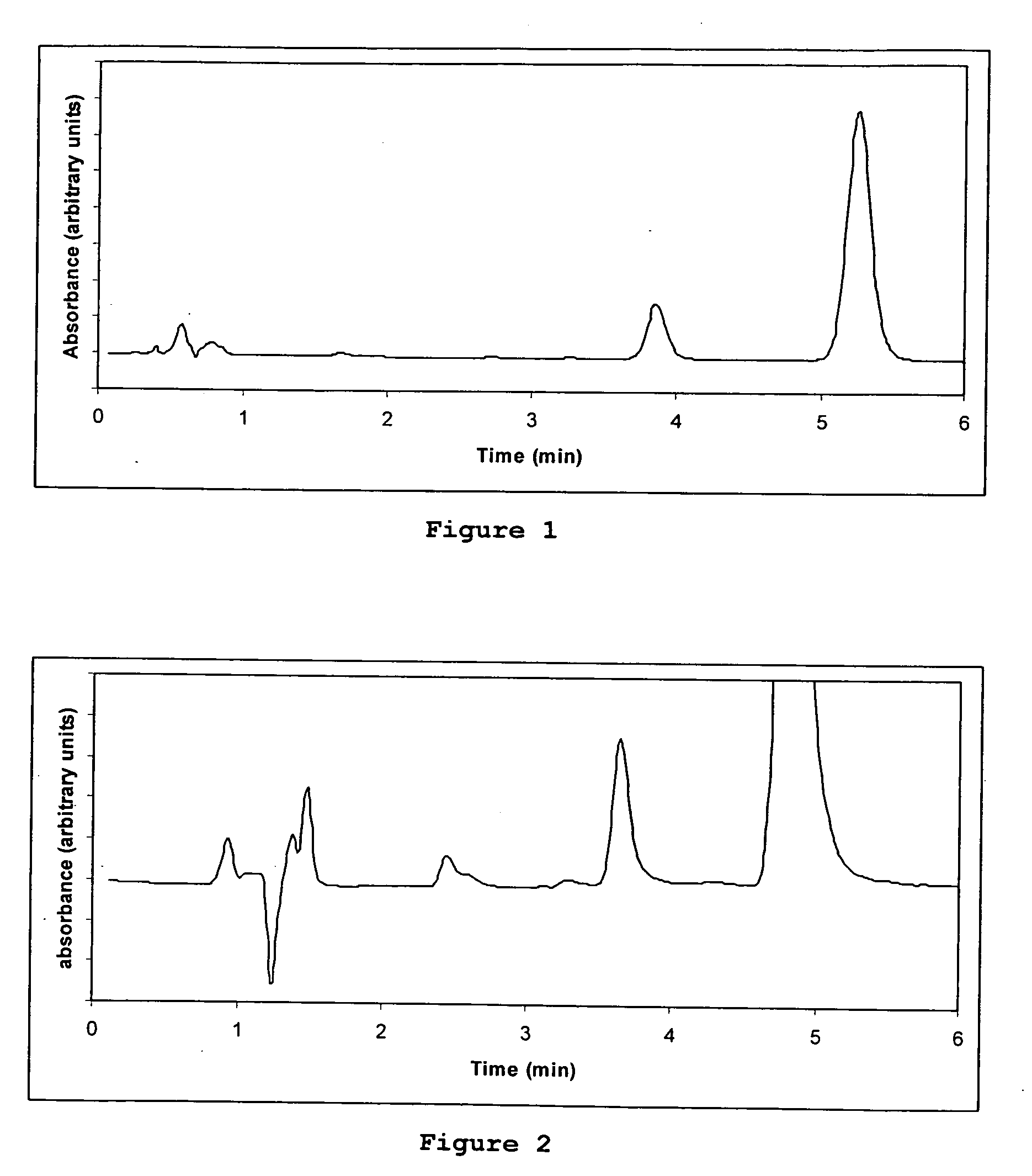
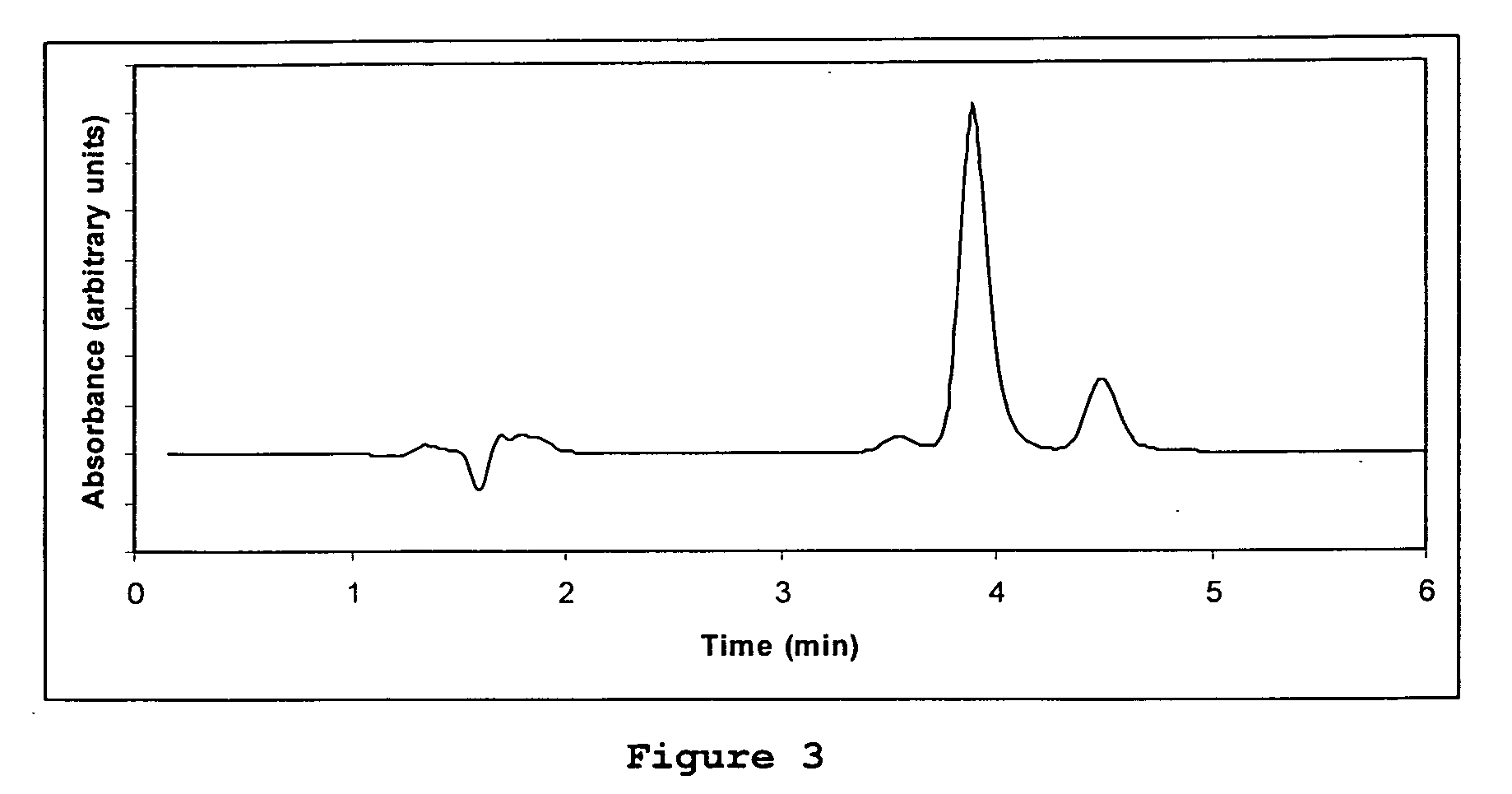
How to Test Luteolin Stability in Storage
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Stability Testing Background and Objectives
Luteolin, a natural flavonoid compound found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has gained significant attention in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries due to its diverse biological activities. These include anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, and neuroprotective properties. The stability of luteolin during storage represents a critical factor affecting its efficacy, bioavailability, and commercial viability in various formulations.
The evolution of luteolin stability research spans several decades, beginning with basic identification and isolation techniques in the 1950s, progressing through analytical method development in the 1970s-1980s, and advancing to sophisticated stability-indicating assays in recent years. Modern research has increasingly focused on understanding the degradation pathways and mechanisms that affect luteolin during storage under various environmental conditions.
Current technological trends in this field include the development of advanced chromatographic techniques coupled with mass spectrometry for precise quantification, real-time stability monitoring systems, and predictive modeling approaches to estimate shelf-life under various storage conditions. Additionally, innovative stabilization technologies such as microencapsulation, nanoformulation, and inclusion complexes have emerged as potential solutions to enhance luteolin stability.
The primary objectives of luteolin stability testing are multifaceted. First, to establish standardized protocols for evaluating luteolin stability across different storage conditions, including temperature, humidity, light exposure, and packaging materials. Second, to identify critical factors influencing degradation rates and mechanisms, enabling the development of effective stabilization strategies. Third, to determine appropriate shelf-life parameters and storage recommendations for luteolin-containing products.
Furthermore, this technical research aims to bridge existing knowledge gaps regarding the impact of formulation excipients on luteolin stability, the formation and toxicological significance of degradation products, and the correlation between chemical stability and biological activity retention. Understanding these aspects is crucial for ensuring consistent quality, safety, and efficacy of luteolin-based products throughout their intended shelf-life.
The expected outcomes of this research include the establishment of robust analytical methods for luteolin stability assessment, identification of optimal storage conditions and packaging materials, development of effective stabilization technologies, and creation of predictive models for accelerated stability testing. These advancements would significantly contribute to the successful commercialization of luteolin-based pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic products with reliable quality and extended shelf-life.
The evolution of luteolin stability research spans several decades, beginning with basic identification and isolation techniques in the 1950s, progressing through analytical method development in the 1970s-1980s, and advancing to sophisticated stability-indicating assays in recent years. Modern research has increasingly focused on understanding the degradation pathways and mechanisms that affect luteolin during storage under various environmental conditions.
Current technological trends in this field include the development of advanced chromatographic techniques coupled with mass spectrometry for precise quantification, real-time stability monitoring systems, and predictive modeling approaches to estimate shelf-life under various storage conditions. Additionally, innovative stabilization technologies such as microencapsulation, nanoformulation, and inclusion complexes have emerged as potential solutions to enhance luteolin stability.
The primary objectives of luteolin stability testing are multifaceted. First, to establish standardized protocols for evaluating luteolin stability across different storage conditions, including temperature, humidity, light exposure, and packaging materials. Second, to identify critical factors influencing degradation rates and mechanisms, enabling the development of effective stabilization strategies. Third, to determine appropriate shelf-life parameters and storage recommendations for luteolin-containing products.
Furthermore, this technical research aims to bridge existing knowledge gaps regarding the impact of formulation excipients on luteolin stability, the formation and toxicological significance of degradation products, and the correlation between chemical stability and biological activity retention. Understanding these aspects is crucial for ensuring consistent quality, safety, and efficacy of luteolin-based products throughout their intended shelf-life.
The expected outcomes of this research include the establishment of robust analytical methods for luteolin stability assessment, identification of optimal storage conditions and packaging materials, development of effective stabilization technologies, and creation of predictive models for accelerated stability testing. These advancements would significantly contribute to the successful commercialization of luteolin-based pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic products with reliable quality and extended shelf-life.
Market Demand Analysis for Stable Luteolin Products
The global market for luteolin and luteolin-containing products has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing consumer awareness of its health benefits and therapeutic potential. The compound's antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and potential anti-cancer properties have positioned it as a valuable ingredient in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, cosmetics, and functional foods.
Market research indicates that the nutraceutical segment currently dominates the luteolin market, with dietary supplements accounting for approximately 45% of total market share. This trend is expected to continue as consumers increasingly seek natural alternatives for health maintenance and disease prevention. The pharmaceutical industry follows closely, with growing interest in luteolin's potential applications in cancer therapy, neuroprotection, and cardiovascular health.
A critical factor influencing market demand is product stability. Consumers and manufacturers alike are increasingly concerned about the shelf-life and efficacy of luteolin products throughout their storage period. Market surveys reveal that over 70% of consumers consider stability and potency retention as "very important" factors when purchasing natural bioactive compounds. This has created a substantial demand for stable luteolin formulations that can maintain their biological activity during storage.
Regional analysis shows that North America and Europe currently lead the market for stable luteolin products, primarily due to advanced regulatory frameworks and higher consumer awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, with China and India at the forefront of both production and consumption. This growth is attributed to the region's traditional use of luteolin-containing herbs in medicine and increasing disposable income.
Industry forecasts project the global market for stable luteolin products to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.2% over the next five years. This growth trajectory is supported by expanding applications in personalized nutrition, anti-aging products, and preventive healthcare solutions. The market value is expected to reach significant levels by 2028, driven by technological advancements in stabilization techniques and delivery systems.
Consumer preference analysis reveals a growing demand for transparent information regarding stability testing methods and shelf-life data. Manufacturers who can demonstrate superior stability profiles through rigorous testing protocols are gaining competitive advantages in the marketplace. Additionally, there is increasing interest in environmentally friendly stabilization methods that avoid synthetic preservatives, aligning with the broader trend toward sustainable and clean-label products.
Market research indicates that the nutraceutical segment currently dominates the luteolin market, with dietary supplements accounting for approximately 45% of total market share. This trend is expected to continue as consumers increasingly seek natural alternatives for health maintenance and disease prevention. The pharmaceutical industry follows closely, with growing interest in luteolin's potential applications in cancer therapy, neuroprotection, and cardiovascular health.
A critical factor influencing market demand is product stability. Consumers and manufacturers alike are increasingly concerned about the shelf-life and efficacy of luteolin products throughout their storage period. Market surveys reveal that over 70% of consumers consider stability and potency retention as "very important" factors when purchasing natural bioactive compounds. This has created a substantial demand for stable luteolin formulations that can maintain their biological activity during storage.
Regional analysis shows that North America and Europe currently lead the market for stable luteolin products, primarily due to advanced regulatory frameworks and higher consumer awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, with China and India at the forefront of both production and consumption. This growth is attributed to the region's traditional use of luteolin-containing herbs in medicine and increasing disposable income.
Industry forecasts project the global market for stable luteolin products to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.2% over the next five years. This growth trajectory is supported by expanding applications in personalized nutrition, anti-aging products, and preventive healthcare solutions. The market value is expected to reach significant levels by 2028, driven by technological advancements in stabilization techniques and delivery systems.
Consumer preference analysis reveals a growing demand for transparent information regarding stability testing methods and shelf-life data. Manufacturers who can demonstrate superior stability profiles through rigorous testing protocols are gaining competitive advantages in the marketplace. Additionally, there is increasing interest in environmentally friendly stabilization methods that avoid synthetic preservatives, aligning with the broader trend toward sustainable and clean-label products.
Current Challenges in Luteolin Stability Assessment
Despite significant advancements in analytical techniques, assessing luteolin stability during storage presents numerous complex challenges that impede accurate and reliable testing. One fundamental difficulty lies in the inherent chemical instability of luteolin, which readily undergoes oxidation, isomerization, and degradation when exposed to environmental factors such as light, oxygen, temperature fluctuations, and humidity. These reactions can occur simultaneously through multiple pathways, creating a complex degradation profile that is difficult to monitor comprehensively.
The lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for luteolin stability assessment represents another significant obstacle. Current methodologies often borrow techniques from general flavonoid analysis, which may not adequately address the unique physicochemical properties and degradation mechanisms specific to luteolin. This inconsistency in testing approaches makes cross-study comparisons challenging and hinders the establishment of universal stability parameters.
Analytical sensitivity limitations pose additional challenges, particularly when measuring luteolin in complex matrices or at low concentrations. Many conventional detection methods struggle to differentiate between parent luteolin and its structurally similar degradation products or isomers, potentially leading to inaccurate stability assessments. The formation of these degradation products often occurs at concentrations near detection limits, further complicating accurate quantification.
Matrix effects represent a substantial hurdle in stability testing, especially when luteolin is incorporated into various formulations, supplements, or food products. Components within these matrices can interact with luteolin, either accelerating degradation through catalytic effects or providing protective mechanisms through antioxidant networks. These complex interactions are difficult to predict and control in stability studies.
Time-dependent stability assessment presents practical challenges for researchers and manufacturers. Real-time stability studies require extended periods, which delays product development and market entry. While accelerated stability testing offers a potential solution, the correlation between accelerated and real-time conditions remains questionable for luteolin due to its complex degradation kinetics that may not follow simple Arrhenius relationships.
The absence of well-characterized reference standards for luteolin degradation products further complicates stability assessment. Without these standards, identifying and quantifying specific degradation pathways becomes problematic, limiting the comprehensive understanding of stability profiles. This gap in reference materials particularly affects the validation of analytical methods for stability-indicating assays.
Regulatory uncertainty adds another layer of complexity, as different regions maintain varying requirements for stability testing of natural compounds like luteolin. This regulatory inconsistency creates confusion regarding acceptable testing methodologies, stability specifications, and shelf-life determination approaches for luteolin-containing products.
The lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for luteolin stability assessment represents another significant obstacle. Current methodologies often borrow techniques from general flavonoid analysis, which may not adequately address the unique physicochemical properties and degradation mechanisms specific to luteolin. This inconsistency in testing approaches makes cross-study comparisons challenging and hinders the establishment of universal stability parameters.
Analytical sensitivity limitations pose additional challenges, particularly when measuring luteolin in complex matrices or at low concentrations. Many conventional detection methods struggle to differentiate between parent luteolin and its structurally similar degradation products or isomers, potentially leading to inaccurate stability assessments. The formation of these degradation products often occurs at concentrations near detection limits, further complicating accurate quantification.
Matrix effects represent a substantial hurdle in stability testing, especially when luteolin is incorporated into various formulations, supplements, or food products. Components within these matrices can interact with luteolin, either accelerating degradation through catalytic effects or providing protective mechanisms through antioxidant networks. These complex interactions are difficult to predict and control in stability studies.
Time-dependent stability assessment presents practical challenges for researchers and manufacturers. Real-time stability studies require extended periods, which delays product development and market entry. While accelerated stability testing offers a potential solution, the correlation between accelerated and real-time conditions remains questionable for luteolin due to its complex degradation kinetics that may not follow simple Arrhenius relationships.
The absence of well-characterized reference standards for luteolin degradation products further complicates stability assessment. Without these standards, identifying and quantifying specific degradation pathways becomes problematic, limiting the comprehensive understanding of stability profiles. This gap in reference materials particularly affects the validation of analytical methods for stability-indicating assays.
Regulatory uncertainty adds another layer of complexity, as different regions maintain varying requirements for stability testing of natural compounds like luteolin. This regulatory inconsistency creates confusion regarding acceptable testing methodologies, stability specifications, and shelf-life determination approaches for luteolin-containing products.
Established Methodologies for Luteolin Stability Testing
01 Stabilization methods for luteolin formulations
Various methods can be employed to enhance the stability of luteolin in formulations. These include encapsulation techniques, use of antioxidants, pH adjustment, and incorporation of specific excipients that prevent degradation. These stabilization methods help to maintain the bioactivity of luteolin during storage and extend the shelf life of products containing this flavonoid.- Stabilization methods for luteolin: Various methods can be employed to enhance the stability of luteolin, including encapsulation techniques, addition of antioxidants, and formation of complexes with cyclodextrins. These approaches protect luteolin from degradation due to environmental factors such as light, heat, and oxidation. Encapsulation in liposomes or nanoparticles can significantly improve the stability profile of luteolin while maintaining its bioactivity.
- pH control for luteolin stability: The stability of luteolin is highly dependent on pH conditions. Research indicates that luteolin exhibits optimal stability in slightly acidic to neutral pH environments (pH 5-7), while alkaline conditions accelerate its degradation. Buffering systems and pH adjusters can be incorporated into luteolin formulations to maintain the optimal pH range, thereby extending shelf life and preserving bioactivity of the compound.
- Thermal stability enhancement of luteolin: Improving the thermal stability of luteolin is crucial for its application in various products. Techniques such as co-crystallization with stabilizing agents, addition of thermal protectants, and modification of the molecular structure can enhance luteolin's resistance to heat-induced degradation. These approaches allow luteolin to maintain its structural integrity and functional properties even when exposed to elevated temperatures during processing or storage.
- Light and oxidation protection for luteolin: Luteolin is susceptible to degradation when exposed to light and oxidative conditions. Protective measures include packaging in opaque containers, incorporation of UV blockers, and addition of antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin E, or butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT). These strategies prevent photo-oxidation and free radical-induced degradation, thereby preserving the stability and efficacy of luteolin in various formulations.
- Formulation approaches for luteolin delivery and stability: Specialized formulation approaches can significantly improve luteolin stability while enhancing its bioavailability. These include development of solid dispersions, microemulsions, and nanostructured lipid carriers. Additionally, freeze-drying techniques and the use of compatible excipients can protect luteolin from degradation during storage. These formulation strategies not only improve stability but also enhance the therapeutic efficacy of luteolin-containing products.
02 Luteolin derivatives with improved stability
Chemical modifications of luteolin can lead to derivatives with enhanced stability profiles. These derivatives maintain the beneficial properties of luteolin while being less susceptible to oxidation, hydrolysis, or photodegradation. The structural modifications typically involve protecting vulnerable hydroxyl groups or introducing stabilizing moieties that shield the molecule from degradative processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulation techniques for preserving luteolin activity
Specific formulation techniques can be employed to preserve the activity of luteolin in various product forms. These include solid dispersion technologies, liposomal formulations, nanoparticle systems, and controlled-release mechanisms. Such approaches protect luteolin from environmental factors that could compromise its stability while potentially enhancing its bioavailability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental factors affecting luteolin stability
Luteolin stability is significantly influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, light exposure, oxygen, and humidity. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing appropriate storage conditions and packaging solutions. Research has shown that luteolin is particularly sensitive to alkaline conditions, elevated temperatures, and UV radiation, which can accelerate its degradation through oxidation and structural rearrangement.Expand Specific Solutions05 Synergistic stabilization of luteolin with other compounds
Combining luteolin with certain other compounds can create synergistic stabilization effects. These combinations may include other flavonoids, vitamins, amino acids, or specific plant extracts that enhance the overall stability of formulations. The synergistic approach not only improves stability but can also enhance the therapeutic efficacy of luteolin-containing products through complementary biological activities.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Phytochemical Stability Research
The luteolin stability testing market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for natural antioxidants in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. The market size is expanding as research into flavonoid stability gains importance for product development and quality control. Technologically, stability testing methods are moderately mature but evolving, with companies like Merck Patent GmbH and Croda International leading analytical innovation. Pharmaceutical players including Concert Pharmaceuticals, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, and Hanmi Pharmaceutical are advancing storage stability protocols, while chemical specialists such as Kemira Oyj and Sanyo Chemical Industries contribute expertise in stabilization technologies. Academic institutions like Shanghai Normal University collaborate with industry to develop standardized testing methodologies for this increasingly important bioactive compound.
Merck Patent GmbH
Technical Solution: Merck has developed a comprehensive stability testing protocol for luteolin that incorporates multiple protective mechanisms. Their approach includes microencapsulation technology using cyclodextrins to create inclusion complexes that shield luteolin from oxidative degradation and light exposure. The company employs specialized antioxidant systems combining both water-soluble and lipid-soluble components (including ascorbic acid derivatives and tocopherols) that work synergistically to prevent oxidation. Merck's stability testing protocols involve accelerated aging studies under controlled temperature and humidity conditions (40°C/75% RH), with regular HPLC analysis to monitor degradation products. They've also developed specialized packaging solutions with oxygen scavengers and UV-protective materials to extend shelf life during commercial storage. Their research has demonstrated that proper stabilization can maintain >90% of luteolin content over 24 months under recommended storage conditions.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining multiple protection mechanisms; extensive analytical capabilities for detecting degradation products; global research network allowing for varied storage condition testing. Weakness: Higher production costs associated with complex stabilization systems; some stabilization methods may affect bioavailability in final formulations.
Guizhou Yibai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Guizhou Yibai Pharmaceutical has pioneered a Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) inspired approach to luteolin stability testing, focusing on natural preservation methods. Their technology combines luteolin with compatible natural compounds from traditional Chinese herbs that act as stability enhancers. The company utilizes a proprietary freeze-drying process that removes moisture while preserving molecular integrity, followed by vacuum sealing in specialized packaging materials that block both oxygen and light penetration. Their stability protocol includes testing at various temperature points (4°C, 25°C, and 40°C) with regular analysis using both HPLC and mass spectrometry to identify degradation pathways. The company has developed a unique "fingerprinting" method that monitors not just luteolin content but also its interaction with other bioactive compounds in complex formulations. Their research indicates that their natural preservation system can maintain luteolin stability for up to 36 months when stored properly, with degradation rates below 5% annually.
Strengths: Integration of traditional knowledge with modern analytical techniques; specialized expertise in plant-derived compounds; cost-effective natural preservation methods. Weaknesses: Standardization challenges when using natural stabilizers; potential batch-to-batch variation in stabilization effectiveness; limited application to certain formulation types.
Critical Analytical Techniques for Luteolin Degradation Studies
Topical composition
PatentActiveUS20190358151A1
Innovation
- A composition comprising a polyaphron dispersion with a continuous and discontinuous phase, incorporating vitamin D or vitamin D analogues and corticosteroids, which enhances dermal diffusion and stability, allowing for lower active agent concentrations and reduced skin irritation, while maintaining stability at elevated temperatures without the need for heating.
Topical composition
PatentActiveUS20080234239A1
Innovation
- A composition comprising a polyaphron dispersion with a continuous and discontinuous phase, incorporating vitamin D or vitamin D analogues and corticosteroids, which enhances dermal diffusion and stability, allowing for lower active agent concentrations and reduced skin irritation, while maintaining effective treatment at room temperature without the need for heating.
Regulatory Requirements for Flavonoid Stability Testing
The regulatory landscape for flavonoid stability testing, particularly for compounds like luteolin, is governed by multiple international and regional frameworks. The FDA in the United States requires comprehensive stability data for botanical drug products under 21 CFR Part 211, with specific guidelines outlined in ICH Q1A(R2) for stability testing of new drug substances and products. These regulations mandate testing under various storage conditions, including accelerated, intermediate, and long-term scenarios, with defined temperature and humidity parameters.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) enforces similar requirements through its "Guideline on Quality of Herbal Medicinal Products/Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products," which specifically addresses natural compounds like flavonoids. This guideline emphasizes the need for stability-indicating analytical methods that can effectively distinguish between degradation products and the active compound.
For dietary supplements containing luteolin, the FDA's Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations under 21 CFR Part 111 apply, requiring manufacturers to establish product specifications including stability parameters. These regulations necessitate validated analytical methods for determining shelf life and appropriate storage conditions.
The International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines provide the most comprehensive framework for stability testing protocols. ICH Q1B specifically addresses photostability testing, which is particularly relevant for flavonoids like luteolin that are known to be sensitive to light. Additionally, ICH Q2(R1) outlines validation parameters for analytical procedures used in stability testing, including specificity, accuracy, precision, and robustness.
Japan's Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) follows similar guidelines but has additional requirements for natural products, particularly regarding the identification and quantification of degradation products. These regulations emphasize the importance of developing stability-indicating methods that can detect changes in not only the active compound but also its potential degradation pathways.
WHO guidelines for stability testing of pharmaceutical products containing herbal drugs provide a global perspective, particularly relevant for international distribution of luteolin-containing products. These guidelines recommend stability testing under conditions representative of the intended market, acknowledging the variability in climate zones worldwide.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks requires implementing validated analytical methods, typically HPLC or UPLC coupled with appropriate detection systems, to monitor luteolin content and potential degradation products throughout the product's shelf life. Documentation of these stability studies must be comprehensive and follow the specific reporting formats required by each regulatory body.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) enforces similar requirements through its "Guideline on Quality of Herbal Medicinal Products/Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products," which specifically addresses natural compounds like flavonoids. This guideline emphasizes the need for stability-indicating analytical methods that can effectively distinguish between degradation products and the active compound.
For dietary supplements containing luteolin, the FDA's Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations under 21 CFR Part 111 apply, requiring manufacturers to establish product specifications including stability parameters. These regulations necessitate validated analytical methods for determining shelf life and appropriate storage conditions.
The International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines provide the most comprehensive framework for stability testing protocols. ICH Q1B specifically addresses photostability testing, which is particularly relevant for flavonoids like luteolin that are known to be sensitive to light. Additionally, ICH Q2(R1) outlines validation parameters for analytical procedures used in stability testing, including specificity, accuracy, precision, and robustness.
Japan's Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) follows similar guidelines but has additional requirements for natural products, particularly regarding the identification and quantification of degradation products. These regulations emphasize the importance of developing stability-indicating methods that can detect changes in not only the active compound but also its potential degradation pathways.
WHO guidelines for stability testing of pharmaceutical products containing herbal drugs provide a global perspective, particularly relevant for international distribution of luteolin-containing products. These guidelines recommend stability testing under conditions representative of the intended market, acknowledging the variability in climate zones worldwide.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks requires implementing validated analytical methods, typically HPLC or UPLC coupled with appropriate detection systems, to monitor luteolin content and potential degradation products throughout the product's shelf life. Documentation of these stability studies must be comprehensive and follow the specific reporting formats required by each regulatory body.
Environmental Factors Affecting Luteolin Shelf-life
Luteolin stability is significantly influenced by various environmental factors during storage, with temperature being one of the most critical parameters. Research indicates that luteolin degradation accelerates considerably at temperatures above 25°C, with degradation rates approximately doubling with every 10°C increase. Refrigerated storage (2-8°C) substantially extends shelf-life, while freezing conditions (-20°C) can preserve stability for extended periods, though repeated freeze-thaw cycles may compromise molecular integrity.
Light exposure represents another major destabilizing factor, as luteolin is highly susceptible to photodegradation. Studies demonstrate that UV light exposure can reduce luteolin content by up to 40% within just 72 hours of continuous exposure. Even standard indoor lighting conditions can cause gradual degradation, necessitating amber or opaque containers for proper storage.
Humidity levels directly impact luteolin stability through hydrolysis mechanisms. Relative humidity exceeding 60% significantly accelerates degradation processes, particularly when combined with elevated temperatures. This synergistic effect between temperature and humidity creates particularly challenging storage conditions in tropical or subtropical environments.
Oxygen exposure triggers oxidative degradation pathways in luteolin, forming various oxidation products that diminish both purity and bioactivity. Research indicates that oxygen-induced degradation follows first-order kinetics, with degradation rates proportional to oxygen concentration. Vacuum packaging or nitrogen-flushing techniques have demonstrated effectiveness in minimizing oxidative damage during storage periods.
pH conditions represent another critical factor, with luteolin exhibiting optimal stability in slightly acidic environments (pH 5.5-6.5). Alkaline conditions (pH > 7.5) dramatically accelerate degradation through base-catalyzed reactions, while strongly acidic environments (pH < 4.0) can also compromise stability through different degradation mechanisms.
Container material selection significantly impacts luteolin shelf-life. Studies show that certain plastics may absorb luteolin or leach compounds that catalyze degradation. Glass containers, particularly amber glass, generally provide superior protection against environmental factors. Metal containers should be avoided due to potential catalytic effects on oxidation processes.
Formulation components, including excipients, solvents, and other active ingredients, can either enhance or compromise luteolin stability. Certain antioxidants (vitamin C, vitamin E) demonstrate synergistic protective effects, while some preservatives may accelerate degradation through chemical interactions. Comprehensive compatibility testing is essential when developing multi-component formulations containing luteolin.
Light exposure represents another major destabilizing factor, as luteolin is highly susceptible to photodegradation. Studies demonstrate that UV light exposure can reduce luteolin content by up to 40% within just 72 hours of continuous exposure. Even standard indoor lighting conditions can cause gradual degradation, necessitating amber or opaque containers for proper storage.
Humidity levels directly impact luteolin stability through hydrolysis mechanisms. Relative humidity exceeding 60% significantly accelerates degradation processes, particularly when combined with elevated temperatures. This synergistic effect between temperature and humidity creates particularly challenging storage conditions in tropical or subtropical environments.
Oxygen exposure triggers oxidative degradation pathways in luteolin, forming various oxidation products that diminish both purity and bioactivity. Research indicates that oxygen-induced degradation follows first-order kinetics, with degradation rates proportional to oxygen concentration. Vacuum packaging or nitrogen-flushing techniques have demonstrated effectiveness in minimizing oxidative damage during storage periods.
pH conditions represent another critical factor, with luteolin exhibiting optimal stability in slightly acidic environments (pH 5.5-6.5). Alkaline conditions (pH > 7.5) dramatically accelerate degradation through base-catalyzed reactions, while strongly acidic environments (pH < 4.0) can also compromise stability through different degradation mechanisms.
Container material selection significantly impacts luteolin shelf-life. Studies show that certain plastics may absorb luteolin or leach compounds that catalyze degradation. Glass containers, particularly amber glass, generally provide superior protection against environmental factors. Metal containers should be avoided due to potential catalytic effects on oxidation processes.
Formulation components, including excipients, solvents, and other active ingredients, can either enhance or compromise luteolin stability. Certain antioxidants (vitamin C, vitamin E) demonstrate synergistic protective effects, while some preservatives may accelerate degradation through chemical interactions. Comprehensive compatibility testing is essential when developing multi-component formulations containing luteolin.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!