How wireless technology transforms laryngoscope operations.
JUL 14, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Wireless Laryngoscopy Evolution and Objectives
Wireless laryngoscopy represents a significant advancement in medical technology, transforming the way healthcare professionals perform intubation procedures. The evolution of this technology has been driven by the need for improved visualization, enhanced patient safety, and increased operational efficiency in critical care settings.
Traditionally, laryngoscopes were rigid, wired devices that limited maneuverability and often caused discomfort for patients. The integration of wireless technology into laryngoscopes has marked a pivotal shift in their design and functionality. This transition began in the early 2000s with the introduction of video laryngoscopes, which incorporated small cameras at the blade tip to provide a clear view of the larynx on an external monitor.
The primary objective of wireless laryngoscopy is to overcome the limitations of conventional devices by eliminating cables and enhancing portability. This advancement aims to improve the success rate of first-attempt intubations, reduce the risk of trauma to the patient's airway, and minimize the time required for the procedure, which is crucial in emergency situations.
Wireless laryngoscopes utilize various technologies to transmit video feeds, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and proprietary wireless protocols. These systems typically consist of a handle with a detachable blade, an integrated camera and light source, and a separate display unit. The wireless connectivity allows for greater flexibility in positioning the display, enabling multiple healthcare providers to view the procedure simultaneously.
As the technology continues to evolve, the objectives for wireless laryngoscopy extend beyond mere cable elimination. Current goals include the integration of augmented reality (AR) features to provide real-time guidance during intubation, the development of AI-assisted intubation systems to help identify optimal insertion paths, and the creation of more compact and energy-efficient devices for extended use in various healthcare settings.
The future trajectory of wireless laryngoscopy technology is focused on further miniaturization, improved battery life, and enhanced image quality. There is also a push towards developing disposable wireless blades to reduce the risk of cross-contamination and streamline sterilization processes. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of 5G connectivity to enable remote assistance during difficult intubations, allowing specialists to guide procedures from a distance.
In conclusion, the evolution of wireless laryngoscopy technology has significantly transformed laryngoscope operations, with clear objectives to enhance patient care, improve procedural outcomes, and advance the capabilities of healthcare providers in managing airway interventions.
Traditionally, laryngoscopes were rigid, wired devices that limited maneuverability and often caused discomfort for patients. The integration of wireless technology into laryngoscopes has marked a pivotal shift in their design and functionality. This transition began in the early 2000s with the introduction of video laryngoscopes, which incorporated small cameras at the blade tip to provide a clear view of the larynx on an external monitor.
The primary objective of wireless laryngoscopy is to overcome the limitations of conventional devices by eliminating cables and enhancing portability. This advancement aims to improve the success rate of first-attempt intubations, reduce the risk of trauma to the patient's airway, and minimize the time required for the procedure, which is crucial in emergency situations.
Wireless laryngoscopes utilize various technologies to transmit video feeds, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and proprietary wireless protocols. These systems typically consist of a handle with a detachable blade, an integrated camera and light source, and a separate display unit. The wireless connectivity allows for greater flexibility in positioning the display, enabling multiple healthcare providers to view the procedure simultaneously.
As the technology continues to evolve, the objectives for wireless laryngoscopy extend beyond mere cable elimination. Current goals include the integration of augmented reality (AR) features to provide real-time guidance during intubation, the development of AI-assisted intubation systems to help identify optimal insertion paths, and the creation of more compact and energy-efficient devices for extended use in various healthcare settings.
The future trajectory of wireless laryngoscopy technology is focused on further miniaturization, improved battery life, and enhanced image quality. There is also a push towards developing disposable wireless blades to reduce the risk of cross-contamination and streamline sterilization processes. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of 5G connectivity to enable remote assistance during difficult intubations, allowing specialists to guide procedures from a distance.
In conclusion, the evolution of wireless laryngoscopy technology has significantly transformed laryngoscope operations, with clear objectives to enhance patient care, improve procedural outcomes, and advance the capabilities of healthcare providers in managing airway interventions.
Market Analysis for Wireless Laryngoscopes
The wireless laryngoscope market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for minimally invasive medical procedures. This market segment is part of the broader medical devices industry, which is projected to reach $612.7 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2020 to 2025.
Wireless laryngoscopes offer several advantages over traditional wired devices, including improved maneuverability, reduced risk of cross-contamination, and enhanced patient comfort. These benefits have led to increased adoption in hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers, and emergency medical services.
The market for wireless laryngoscopes is segmented by product type, end-user, and geography. Product types include video laryngoscopes and optical laryngoscopes, with video laryngoscopes gaining popularity due to their superior visualization capabilities. End-users primarily consist of hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers, and emergency medical services.
Geographically, North America dominates the wireless laryngoscope market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds a significant market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high adoption rate of new medical technologies.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of chronic respiratory diseases, increasing geriatric population, and growing demand for minimally invasive diagnostic procedures. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, as wireless laryngoscopes reduce the risk of virus transmission during intubation procedures.
However, the market faces challenges such as high initial costs, limited reimbursement policies in some regions, and the need for specialized training for healthcare professionals. These factors may hinder market growth in developing economies and smaller healthcare facilities.
The competitive landscape of the wireless laryngoscope market is characterized by the presence of both established medical device manufacturers and innovative start-ups. Key players in the market include Medtronic, Karl Storz, Verathon, Ambu, and Teleflex Incorporated.
Looking ahead, the wireless laryngoscope market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by ongoing technological innovations, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of the benefits of wireless medical devices. Emerging trends such as the integration of artificial intelligence and augmented reality in laryngoscopy procedures are likely to shape the future of this market.
Wireless laryngoscopes offer several advantages over traditional wired devices, including improved maneuverability, reduced risk of cross-contamination, and enhanced patient comfort. These benefits have led to increased adoption in hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers, and emergency medical services.
The market for wireless laryngoscopes is segmented by product type, end-user, and geography. Product types include video laryngoscopes and optical laryngoscopes, with video laryngoscopes gaining popularity due to their superior visualization capabilities. End-users primarily consist of hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers, and emergency medical services.
Geographically, North America dominates the wireless laryngoscope market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds a significant market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high adoption rate of new medical technologies.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of chronic respiratory diseases, increasing geriatric population, and growing demand for minimally invasive diagnostic procedures. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, as wireless laryngoscopes reduce the risk of virus transmission during intubation procedures.
However, the market faces challenges such as high initial costs, limited reimbursement policies in some regions, and the need for specialized training for healthcare professionals. These factors may hinder market growth in developing economies and smaller healthcare facilities.
The competitive landscape of the wireless laryngoscope market is characterized by the presence of both established medical device manufacturers and innovative start-ups. Key players in the market include Medtronic, Karl Storz, Verathon, Ambu, and Teleflex Incorporated.
Looking ahead, the wireless laryngoscope market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by ongoing technological innovations, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of the benefits of wireless medical devices. Emerging trends such as the integration of artificial intelligence and augmented reality in laryngoscopy procedures are likely to shape the future of this market.
Current Wireless Laryngoscope Technologies and Challenges
Wireless technology has significantly transformed laryngoscope operations, offering numerous advantages over traditional wired systems. Currently, the most prevalent wireless laryngoscope technologies utilize Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connectivity to transmit video feed from the laryngoscope to a display device. These systems typically consist of a high-resolution camera mounted on the laryngoscope blade, a wireless transmitter, and a receiver connected to a monitor or mobile device.
One of the primary challenges in wireless laryngoscope technology is ensuring reliable and low-latency video transmission. The critical nature of intubation procedures demands real-time, high-quality imaging with minimal delay. Manufacturers have addressed this by implementing advanced compression algorithms and utilizing higher frequency bands to increase data transfer rates.
Battery life remains a significant concern for wireless laryngoscopes. The power requirements of the camera, LED light source, and wireless transmitter can quickly drain batteries, potentially limiting the device's operational time during extended procedures. To mitigate this, some manufacturers have developed rapid charging systems and hot-swappable battery packs.
Signal interference is another challenge, particularly in healthcare environments with numerous electronic devices. To combat this, modern wireless laryngoscopes employ frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) technology or operate in the less congested 5 GHz band to minimize interference and maintain a stable connection.
Durability and sterilization present unique challenges for wireless laryngoscopes. The integration of electronic components and batteries makes these devices more complex than their wired counterparts. Manufacturers have responded by developing sealed, waterproof designs that can withstand rigorous sterilization processes without compromising the internal electronics.
Interoperability between different wireless laryngoscope systems and hospital equipment is an ongoing challenge. The lack of standardization in wireless protocols and data formats can lead to compatibility issues when integrating these devices into existing hospital systems. Some manufacturers are addressing this by adopting open standards and developing software interfaces that allow for easier integration.
Cost remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption of wireless laryngoscope technology. The advanced components and manufacturing processes required for these devices result in higher prices compared to traditional laryngoscopes. However, as technology advances and production scales up, costs are expected to decrease, making wireless laryngoscopes more accessible to a broader range of healthcare providers.
One of the primary challenges in wireless laryngoscope technology is ensuring reliable and low-latency video transmission. The critical nature of intubation procedures demands real-time, high-quality imaging with minimal delay. Manufacturers have addressed this by implementing advanced compression algorithms and utilizing higher frequency bands to increase data transfer rates.
Battery life remains a significant concern for wireless laryngoscopes. The power requirements of the camera, LED light source, and wireless transmitter can quickly drain batteries, potentially limiting the device's operational time during extended procedures. To mitigate this, some manufacturers have developed rapid charging systems and hot-swappable battery packs.
Signal interference is another challenge, particularly in healthcare environments with numerous electronic devices. To combat this, modern wireless laryngoscopes employ frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) technology or operate in the less congested 5 GHz band to minimize interference and maintain a stable connection.
Durability and sterilization present unique challenges for wireless laryngoscopes. The integration of electronic components and batteries makes these devices more complex than their wired counterparts. Manufacturers have responded by developing sealed, waterproof designs that can withstand rigorous sterilization processes without compromising the internal electronics.
Interoperability between different wireless laryngoscope systems and hospital equipment is an ongoing challenge. The lack of standardization in wireless protocols and data formats can lead to compatibility issues when integrating these devices into existing hospital systems. Some manufacturers are addressing this by adopting open standards and developing software interfaces that allow for easier integration.
Cost remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption of wireless laryngoscope technology. The advanced components and manufacturing processes required for these devices result in higher prices compared to traditional laryngoscopes. However, as technology advances and production scales up, costs are expected to decrease, making wireless laryngoscopes more accessible to a broader range of healthcare providers.
Existing Wireless Solutions for Laryngoscopy
01 Wireless communication and data transmission
Wireless laryngoscopes incorporate wireless communication technology to transmit video and data from the laryngoscope to external devices. This allows for real-time viewing of the laryngeal area on monitors or mobile devices, enhancing visualization and enabling remote consultation.- Wireless communication and data transmission: Wireless laryngoscopes incorporate wireless communication technology to transmit video and data from the laryngoscope to external devices. This allows for real-time viewing of the laryngeal area on monitors or mobile devices, enhancing visualization and enabling remote consultation.
- Power management and battery operation: Wireless laryngoscopes utilize rechargeable batteries or power management systems to ensure continuous operation during procedures. Advanced power-saving features and efficient energy consumption techniques are implemented to extend battery life and improve device reliability.
- Ergonomic design and user interface: The design of wireless laryngoscopes focuses on ergonomics and user-friendly interfaces. This includes features such as adjustable handles, intuitive controls, and lightweight construction to improve operator comfort and ease of use during intubation procedures.
- Image processing and enhancement: Advanced image processing techniques are employed in wireless laryngoscopes to enhance visualization of the airway. This may include features such as image stabilization, contrast adjustment, and digital zoom capabilities to improve the quality and clarity of the video feed.
- Integration with other medical devices: Wireless laryngoscopes are designed to integrate with other medical devices and systems in the operating room or emergency settings. This includes compatibility with patient monitoring systems, anesthesia machines, and electronic health record systems for seamless data sharing and documentation.
02 Power management and battery operation
Wireless laryngoscopes utilize rechargeable batteries or power management systems to ensure continuous operation during procedures. Advanced power-saving features and efficient battery technologies are implemented to extend the device's operational time.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ergonomic design and user interface
The design of wireless laryngoscopes focuses on ergonomics and ease of use. This includes features such as intuitive controls, adjustable handles, and lightweight construction to improve handling and reduce operator fatigue during procedures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Image processing and enhancement
Advanced image processing techniques are employed in wireless laryngoscopes to enhance the quality of captured images and videos. This may include features such as noise reduction, color enhancement, and digital zoom to improve visualization of the laryngeal structures.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration with other medical systems
Wireless laryngoscopes are designed to integrate with existing medical systems and electronic health records. This allows for seamless data transfer, storage of images and videos, and incorporation of patient information into the laryngoscopy procedure.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Wireless Laryngoscope Industry
The wireless laryngoscope market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures and technological advancements. The global market size is expanding, with a projected CAGR of over 10% in the coming years. Technological maturity varies among key players, with companies like Olympus Corp., Ambu A/S, and FUJIFILM Corp. leading in innovation. These firms are developing advanced wireless laryngoscopes with improved imaging capabilities and ergonomic designs. Emerging players such as Zhejiang Youyi Medical Equipment Co Ltd and Chip Ideas Electronics SL are also contributing to market growth by introducing novel features and cost-effective solutions. The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing R&D efforts to enhance product performance and user experience.
Olympus Corp.
Technical Solution: Olympus has developed a wireless video laryngoscope system that integrates advanced imaging technology with wireless connectivity. The system features a high-resolution camera at the tip of the laryngoscope blade, transmitting real-time video to a remote monitor wirelessly. This allows for improved visualization of the airway during intubation procedures. The wireless capability enables greater mobility and flexibility for healthcare providers, reducing cable clutter in critical care environments. Olympus has also incorporated image enhancement algorithms to optimize visibility in challenging conditions, such as low light or presence of secretions[1][3]. The system includes a rechargeable battery with extended operation time, ensuring reliability during prolonged procedures.
Strengths: Superior image quality, wireless mobility, and advanced image processing. Weaknesses: Potential for signal interference in crowded wireless environments and higher initial cost compared to traditional laryngoscopes.
Ambu A/S
Technical Solution: Ambu has pioneered a single-use wireless video laryngoscope that addresses both hygiene concerns and technological advancements. Their system utilizes Bluetooth technology to transmit high-definition video from the laryngoscope to a dedicated display or mobile device. The disposable nature of the device eliminates the need for sterilization between uses, reducing the risk of cross-contamination. Ambu's wireless laryngoscope incorporates a unique ergonomic design that improves handling and maneuverability during intubation. The system also features an integrated LED light source for optimal illumination of the airway. Ambu has developed a companion mobile application that allows for real-time video sharing and recording, facilitating remote consultation and training opportunities[2][5].
Strengths: Single-use design enhances hygiene, wireless connectivity improves workflow. Weaknesses: Environmental concerns due to disposable components, reliance on compatible display devices.
Core Innovations in Wireless Laryngoscope Technology
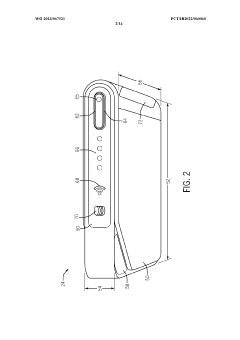
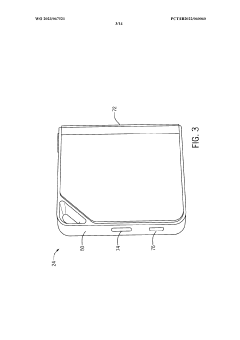
Wireless laryngoscope with internal antenna and one-piece construction adapted for laryngoscopy training
PatentWO2007082294A3
Innovation
- Integrated one-piece construction combining handle and blade portions, creating internal cavities for housing components.
- Internal antenna design, eliminating external protrusions and improving ergonomics.
- Wireless transmission of video images from an internal camera to a remote receiver, facilitating real-time observation and training.
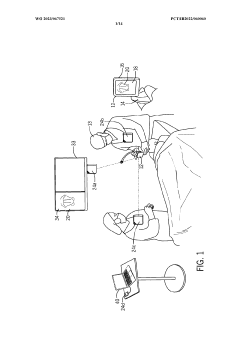
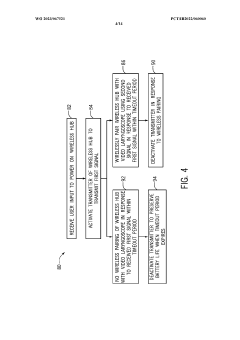
Video laryngoscope wireless HUB systems and methods
PatentWO2023067521A1
Innovation
- A wireless hub system that automatically pairs with video laryngoscopes using infrared signals for secure, line-of-sight pairing, allowing for seamless data transfer and streaming of images to external displays, and acts as a portable storage device for recorded images, enabling easy access and review.
Regulatory Framework for Wireless Medical Devices
The regulatory framework for wireless medical devices plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and reliability of innovative technologies like wireless laryngoscopes. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing medical devices, including those incorporating wireless technology.
The FDA classifies medical devices into three categories based on their risk level and intended use. Wireless laryngoscopes typically fall under Class II, requiring a 510(k) premarket notification submission. This process involves demonstrating that the device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device in terms of safety and effectiveness.
For wireless laryngoscopes, manufacturers must address specific regulatory considerations related to wireless technology. These include electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing to ensure the device does not interfere with other medical equipment or be susceptible to electromagnetic interference. Additionally, cybersecurity measures must be implemented to protect patient data and prevent unauthorized access to the device.
The FDA has issued guidance documents specifically addressing wireless medical devices, such as the "Radio Frequency Wireless Technology in Medical Devices" guidance. This document outlines considerations for wireless coexistence, quality of service, and wireless security that manufacturers must address in their product development and regulatory submissions.
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) have similar requirements for wireless medical devices. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides standards like IEC 60601-1-2 for EMC in medical devices, which are widely recognized and adopted globally.
Manufacturers of wireless laryngoscopes must also comply with radio frequency (RF) regulations set by agencies like the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States. These regulations ensure that the wireless components operate within designated frequency bands and power limits to prevent interference with other wireless devices.
As wireless technology in medical devices continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address new challenges. For instance, the FDA has introduced the Digital Health Software Precertification (Pre-Cert) Program to streamline the review process for software-based medical technologies, which may impact future wireless laryngoscope innovations.
The FDA classifies medical devices into three categories based on their risk level and intended use. Wireless laryngoscopes typically fall under Class II, requiring a 510(k) premarket notification submission. This process involves demonstrating that the device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device in terms of safety and effectiveness.
For wireless laryngoscopes, manufacturers must address specific regulatory considerations related to wireless technology. These include electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing to ensure the device does not interfere with other medical equipment or be susceptible to electromagnetic interference. Additionally, cybersecurity measures must be implemented to protect patient data and prevent unauthorized access to the device.
The FDA has issued guidance documents specifically addressing wireless medical devices, such as the "Radio Frequency Wireless Technology in Medical Devices" guidance. This document outlines considerations for wireless coexistence, quality of service, and wireless security that manufacturers must address in their product development and regulatory submissions.
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) have similar requirements for wireless medical devices. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides standards like IEC 60601-1-2 for EMC in medical devices, which are widely recognized and adopted globally.
Manufacturers of wireless laryngoscopes must also comply with radio frequency (RF) regulations set by agencies like the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States. These regulations ensure that the wireless components operate within designated frequency bands and power limits to prevent interference with other wireless devices.
As wireless technology in medical devices continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address new challenges. For instance, the FDA has introduced the Digital Health Software Precertification (Pre-Cert) Program to streamline the review process for software-based medical technologies, which may impact future wireless laryngoscope innovations.
Integration with Telemedicine Platforms
The integration of wireless laryngoscopes with telemedicine platforms represents a significant advancement in remote healthcare delivery. This convergence enables real-time collaboration between on-site medical personnel and remote specialists, enhancing the quality of care in critical situations.
Wireless laryngoscopes equipped with high-definition cameras and secure data transmission capabilities can seamlessly connect to telemedicine platforms. This integration allows for live streaming of laryngoscopy procedures, enabling remote experts to guide and assist in complex intubations or airway assessments.
The incorporation of wireless laryngoscopes into telemedicine systems extends the reach of specialized medical expertise to remote or underserved areas. In emergency situations or resource-limited settings, this technology can provide crucial support to frontline healthcare workers, potentially improving patient outcomes and reducing the need for patient transfers.
Telemedicine platforms integrated with wireless laryngoscopes often feature advanced functionalities such as real-time annotation, multi-party video conferencing, and secure data storage. These features facilitate effective communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals, enabling them to make informed decisions based on shared visual information.
The integration also supports asynchronous consultations, where recorded laryngoscopy videos can be securely transmitted and reviewed by specialists at a later time. This capability is particularly valuable for follow-up assessments, training purposes, and quality assurance reviews.
As telemedicine continues to evolve, the integration of wireless laryngoscopes is likely to expand to include artificial intelligence-driven analysis tools. These may assist in identifying abnormalities, suggesting treatment options, or providing real-time guidance during procedures, further enhancing the capabilities of remote healthcare delivery.
However, the successful integration of wireless laryngoscopes with telemedicine platforms faces challenges such as ensuring consistent connectivity, maintaining data security, and addressing regulatory compliance across different jurisdictions. Overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for widespread adoption and optimal utilization of this transformative technology in healthcare settings.
Wireless laryngoscopes equipped with high-definition cameras and secure data transmission capabilities can seamlessly connect to telemedicine platforms. This integration allows for live streaming of laryngoscopy procedures, enabling remote experts to guide and assist in complex intubations or airway assessments.
The incorporation of wireless laryngoscopes into telemedicine systems extends the reach of specialized medical expertise to remote or underserved areas. In emergency situations or resource-limited settings, this technology can provide crucial support to frontline healthcare workers, potentially improving patient outcomes and reducing the need for patient transfers.
Telemedicine platforms integrated with wireless laryngoscopes often feature advanced functionalities such as real-time annotation, multi-party video conferencing, and secure data storage. These features facilitate effective communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals, enabling them to make informed decisions based on shared visual information.
The integration also supports asynchronous consultations, where recorded laryngoscopy videos can be securely transmitted and reviewed by specialists at a later time. This capability is particularly valuable for follow-up assessments, training purposes, and quality assurance reviews.
As telemedicine continues to evolve, the integration of wireless laryngoscopes is likely to expand to include artificial intelligence-driven analysis tools. These may assist in identifying abnormalities, suggesting treatment options, or providing real-time guidance during procedures, further enhancing the capabilities of remote healthcare delivery.
However, the successful integration of wireless laryngoscopes with telemedicine platforms faces challenges such as ensuring consistent connectivity, maintaining data security, and addressing regulatory compliance across different jurisdictions. Overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for widespread adoption and optimal utilization of this transformative technology in healthcare settings.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!