Investigating Glycerol's Influence on Nutritional Quality of Food
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glycerol in Food: Background and Objectives
Glycerol, also known as glycerin or glycerine, has been a subject of increasing interest in the food industry due to its unique properties and potential applications. This compound, a simple polyol with three hydroxyl groups, has been used in various food products for decades, primarily as a humectant, sweetener, and texture modifier. However, recent research has shed light on its potential influence on the nutritional quality of food, prompting a deeper investigation into its role in food science and nutrition.
The evolution of glycerol's use in food can be traced back to its discovery in the late 18th century. Initially recognized for its sweet taste and hygroscopic nature, glycerol found its way into food products as a preservative and moisture-retaining agent. As food technology advanced, the applications of glycerol expanded, and it became a common ingredient in a wide range of processed foods, from baked goods to beverages.
In recent years, the focus on glycerol has shifted from its functional properties to its potential nutritional impact. This shift is driven by several factors, including the growing consumer demand for healthier food options, the rise of functional foods, and the increasing scrutiny of food additives. The food industry is now faced with the challenge of understanding how glycerol interacts with other food components and how it affects the overall nutritional profile of food products.
The primary objective of investigating glycerol's influence on the nutritional quality of food is to gain a comprehensive understanding of its effects on various aspects of food composition and human nutrition. This includes examining how glycerol impacts macronutrient absorption, energy metabolism, and the bioavailability of micronutrients. Additionally, researchers aim to explore potential synergistic or antagonistic effects between glycerol and other food components, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Another critical aspect of this investigation is to assess the safety and efficacy of glycerol as a food ingredient, particularly in light of its increased use in functional foods and dietary supplements. This involves evaluating the optimal concentrations of glycerol in different food matrices and determining any potential adverse effects associated with its consumption.
Furthermore, the research aims to explore the potential of glycerol as a functional ingredient that could enhance the nutritional value of food products. This includes investigating its role in improving texture, extending shelf life, and potentially serving as a prebiotic or energy substrate for beneficial gut bacteria.
As the food industry continues to evolve, with a growing emphasis on clean label products and natural ingredients, understanding glycerol's influence on nutritional quality becomes increasingly important. This research has the potential to inform product development strategies, regulatory decisions, and dietary recommendations, ultimately contributing to the advancement of food science and nutrition.
The evolution of glycerol's use in food can be traced back to its discovery in the late 18th century. Initially recognized for its sweet taste and hygroscopic nature, glycerol found its way into food products as a preservative and moisture-retaining agent. As food technology advanced, the applications of glycerol expanded, and it became a common ingredient in a wide range of processed foods, from baked goods to beverages.
In recent years, the focus on glycerol has shifted from its functional properties to its potential nutritional impact. This shift is driven by several factors, including the growing consumer demand for healthier food options, the rise of functional foods, and the increasing scrutiny of food additives. The food industry is now faced with the challenge of understanding how glycerol interacts with other food components and how it affects the overall nutritional profile of food products.
The primary objective of investigating glycerol's influence on the nutritional quality of food is to gain a comprehensive understanding of its effects on various aspects of food composition and human nutrition. This includes examining how glycerol impacts macronutrient absorption, energy metabolism, and the bioavailability of micronutrients. Additionally, researchers aim to explore potential synergistic or antagonistic effects between glycerol and other food components, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Another critical aspect of this investigation is to assess the safety and efficacy of glycerol as a food ingredient, particularly in light of its increased use in functional foods and dietary supplements. This involves evaluating the optimal concentrations of glycerol in different food matrices and determining any potential adverse effects associated with its consumption.
Furthermore, the research aims to explore the potential of glycerol as a functional ingredient that could enhance the nutritional value of food products. This includes investigating its role in improving texture, extending shelf life, and potentially serving as a prebiotic or energy substrate for beneficial gut bacteria.
As the food industry continues to evolve, with a growing emphasis on clean label products and natural ingredients, understanding glycerol's influence on nutritional quality becomes increasingly important. This research has the potential to inform product development strategies, regulatory decisions, and dietary recommendations, ultimately contributing to the advancement of food science and nutrition.
Market Analysis of Glycerol-Enhanced Foods
The market for glycerol-enhanced foods has shown significant growth potential in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health and wellness. Glycerol, also known as glycerin, is a versatile compound that has found applications in various food products due to its unique properties and potential nutritional benefits.
The global glycerol market size was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.2% during the forecast period. The food and beverage industry accounts for a substantial portion of this market, with glycerol being used as a humectant, sweetener, and texture modifier in a wide range of products.
In the food sector, glycerol-enhanced products are gaining traction across multiple categories. The bakery and confectionery segment has seen a particularly strong uptake, with glycerol being used to improve moisture retention and extend shelf life in products such as cakes, cookies, and candies. The dairy industry has also embraced glycerol as an ingredient in low-fat yogurts and ice creams, where it helps maintain texture and mouthfeel while reducing overall fat content.
The beverage industry represents another significant market for glycerol-enhanced products. Sports drinks and functional beverages are incorporating glycerol to improve hydration and potentially enhance athletic performance. This trend aligns with the growing demand for natural and clean-label ingredients in the sports nutrition market.
Consumer demand for healthier food options is a key driver of the glycerol-enhanced food market. As awareness of the potential health benefits of glycerol grows, including its low glycemic index and potential to aid in blood sugar management, consumers are increasingly seeking out products that incorporate this ingredient. This trend is particularly evident in the diabetic food market, where glycerol is being used as a sugar substitute in various products.
The market for glycerol-enhanced foods is not without challenges, however. Regulatory considerations vary by region, with some countries imposing limits on glycerol usage in food products. Additionally, consumer perception of glycerol as an artificial or chemical ingredient may pose a barrier to adoption in certain segments of the natural and organic food market.
Looking ahead, the glycerol-enhanced food market is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Emerging applications in functional foods and nutraceuticals present new opportunities for market expansion. As research into the nutritional benefits of glycerol progresses, it is likely to open up additional avenues for product development and market growth in the food and beverage industry.
The global glycerol market size was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.2% during the forecast period. The food and beverage industry accounts for a substantial portion of this market, with glycerol being used as a humectant, sweetener, and texture modifier in a wide range of products.
In the food sector, glycerol-enhanced products are gaining traction across multiple categories. The bakery and confectionery segment has seen a particularly strong uptake, with glycerol being used to improve moisture retention and extend shelf life in products such as cakes, cookies, and candies. The dairy industry has also embraced glycerol as an ingredient in low-fat yogurts and ice creams, where it helps maintain texture and mouthfeel while reducing overall fat content.
The beverage industry represents another significant market for glycerol-enhanced products. Sports drinks and functional beverages are incorporating glycerol to improve hydration and potentially enhance athletic performance. This trend aligns with the growing demand for natural and clean-label ingredients in the sports nutrition market.
Consumer demand for healthier food options is a key driver of the glycerol-enhanced food market. As awareness of the potential health benefits of glycerol grows, including its low glycemic index and potential to aid in blood sugar management, consumers are increasingly seeking out products that incorporate this ingredient. This trend is particularly evident in the diabetic food market, where glycerol is being used as a sugar substitute in various products.
The market for glycerol-enhanced foods is not without challenges, however. Regulatory considerations vary by region, with some countries imposing limits on glycerol usage in food products. Additionally, consumer perception of glycerol as an artificial or chemical ingredient may pose a barrier to adoption in certain segments of the natural and organic food market.
Looking ahead, the glycerol-enhanced food market is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Emerging applications in functional foods and nutraceuticals present new opportunities for market expansion. As research into the nutritional benefits of glycerol progresses, it is likely to open up additional avenues for product development and market growth in the food and beverage industry.
Current Challenges in Glycerol Application
Despite the potential benefits of glycerol in food applications, several challenges hinder its widespread adoption and optimal utilization. One of the primary concerns is the impact of glycerol on food texture and sensory properties. When used in high concentrations, glycerol can impart an undesirable sweetness and alter the mouthfeel of food products, potentially affecting consumer acceptance. This necessitates careful formulation and dosage control to maintain the desired organoleptic qualities.
Another significant challenge lies in the stability of glycerol-containing food products during processing and storage. Glycerol's hygroscopic nature can lead to moisture absorption, potentially compromising the shelf life and quality of certain food items. This is particularly problematic in low-moisture foods, where water activity control is crucial for microbial stability and texture preservation.
The interaction of glycerol with other food components presents additional complexities. Its influence on protein denaturation, starch gelatinization, and lipid oxidation processes is not fully understood, making it challenging to predict and control food quality parameters in complex food systems. This knowledge gap hampers the development of optimized formulations and processing conditions for glycerol-enhanced foods.
From a regulatory perspective, the use of glycerol in food applications faces scrutiny and varying regulations across different regions. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) in many countries, there are still concerns about its potential health effects when consumed in large quantities. This regulatory landscape creates uncertainty for food manufacturers and may limit innovation in glycerol applications.
The sourcing and quality of glycerol also pose challenges. With the increasing demand for bio-based glycerol, ensuring consistent quality and purity from various feedstocks becomes crucial. Impurities in crude glycerol can negatively impact food quality and safety, necessitating additional purification steps that may increase production costs.
Furthermore, the nutritional impact of glycerol in food products remains a subject of debate. While it can potentially serve as an energy source, its effects on overall nutrient absorption and metabolism are not fully elucidated. This lack of comprehensive nutritional data makes it difficult to accurately label and market glycerol-containing foods, potentially limiting consumer acceptance and market penetration.
Lastly, the technological challenges in incorporating glycerol into diverse food matrices persist. Developing effective delivery systems and ensuring uniform distribution of glycerol in complex food structures require innovative approaches. This is particularly challenging in solid and semi-solid foods, where glycerol's liquid nature can lead to phase separation or migration issues during processing and storage.
Another significant challenge lies in the stability of glycerol-containing food products during processing and storage. Glycerol's hygroscopic nature can lead to moisture absorption, potentially compromising the shelf life and quality of certain food items. This is particularly problematic in low-moisture foods, where water activity control is crucial for microbial stability and texture preservation.
The interaction of glycerol with other food components presents additional complexities. Its influence on protein denaturation, starch gelatinization, and lipid oxidation processes is not fully understood, making it challenging to predict and control food quality parameters in complex food systems. This knowledge gap hampers the development of optimized formulations and processing conditions for glycerol-enhanced foods.
From a regulatory perspective, the use of glycerol in food applications faces scrutiny and varying regulations across different regions. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) in many countries, there are still concerns about its potential health effects when consumed in large quantities. This regulatory landscape creates uncertainty for food manufacturers and may limit innovation in glycerol applications.
The sourcing and quality of glycerol also pose challenges. With the increasing demand for bio-based glycerol, ensuring consistent quality and purity from various feedstocks becomes crucial. Impurities in crude glycerol can negatively impact food quality and safety, necessitating additional purification steps that may increase production costs.
Furthermore, the nutritional impact of glycerol in food products remains a subject of debate. While it can potentially serve as an energy source, its effects on overall nutrient absorption and metabolism are not fully elucidated. This lack of comprehensive nutritional data makes it difficult to accurately label and market glycerol-containing foods, potentially limiting consumer acceptance and market penetration.
Lastly, the technological challenges in incorporating glycerol into diverse food matrices persist. Developing effective delivery systems and ensuring uniform distribution of glycerol in complex food structures require innovative approaches. This is particularly challenging in solid and semi-solid foods, where glycerol's liquid nature can lead to phase separation or migration issues during processing and storage.
Existing Glycerol Incorporation Methods
01 Glycerol as a nutritional supplement
Glycerol can be used as a nutritional supplement to enhance the overall nutritional quality of food products. It serves as a source of energy and can improve the texture and moisture retention in various food applications. Glycerol's ability to act as a humectant and its low caloric value make it a valuable ingredient in nutritional formulations.- Glycerol as a nutritional supplement: Glycerol can be used as a nutritional supplement to enhance the overall nutritional quality of food products. It serves as a source of energy and can improve the texture and moisture retention in various food applications. Glycerol's low glycemic index makes it suitable for diabetic-friendly products.
- Glycerol in animal feed: Glycerol can be incorporated into animal feed to improve its nutritional quality. It serves as an energy source and can enhance feed efficiency in livestock. The addition of glycerol to animal diets may also have positive effects on meat quality and animal performance.
- Glycerol as a functional ingredient in food products: Glycerol can be used as a functional ingredient in various food products to enhance their nutritional quality. It acts as a humectant, preservative, and sweetener, while also providing texture improvements. Glycerol can be incorporated into low-fat and low-sugar products to maintain desirable sensory properties.
- Glycerol in sports nutrition: Glycerol is utilized in sports nutrition products to improve hydration and endurance performance. It can help maintain fluid balance in the body during intense physical activity. The inclusion of glycerol in sports drinks and supplements may enhance overall nutritional quality for athletes.
- Glycerol production and purification for nutritional applications: Various methods for producing and purifying glycerol are developed to ensure its suitability for nutritional applications. These processes aim to remove impurities and enhance the overall quality of glycerol for use in food and feed products. Improved production techniques can lead to higher-quality glycerol with better nutritional properties.
02 Glycerol in animal feed
Glycerol can be incorporated into animal feed to improve its nutritional quality. It serves as an energy source and can enhance feed efficiency in livestock. The addition of glycerol to animal diets may also have positive effects on growth performance and meat quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Glycerol in functional foods
Glycerol can be used in the formulation of functional foods to enhance their nutritional profile. It can act as a carrier for bioactive compounds, improve texture, and contribute to the overall nutritional value of the product. Glycerol's versatility allows for its incorporation into various functional food applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Glycerol in sports nutrition
Glycerol has applications in sports nutrition due to its potential to improve hydration and endurance. It can be used in sports drinks and supplements to enhance fluid retention and potentially improve athletic performance. The nutritional quality of glycerol in this context relates to its role in maintaining proper hydration levels during physical activity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Glycerol in medical nutrition
Glycerol can be utilized in medical nutrition products to address specific nutritional needs. It may be incorporated into enteral or parenteral nutrition formulations to provide energy and support various physiological functions. The nutritional quality of glycerol in medical applications is related to its ability to be metabolized and its potential benefits in certain clinical conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Glycerol-Based Food Additives
The investigation into glycerol's influence on food nutritional quality is in a developing stage, with the market showing potential for growth. The technology is still maturing, as evidenced by ongoing research from various players. Key companies like Nestlé, Cargill, and Ajinomoto are likely at the forefront, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities. Academic institutions such as South China University of Technology and Huazhong Agricultural University are contributing valuable research. The involvement of diverse players, from food giants to specialized biotechnology firms like Fengyi Biotechnology, indicates a competitive landscape with opportunities for innovation and market expansion in this niche area of food science and nutrition.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Technical Solution: Nestlé has developed a comprehensive approach to investigating glycerol's influence on food nutritional quality. Their research focuses on using glycerol as a humectant and sweetener in various food products. They have conducted extensive studies on the impact of glycerol on moisture retention, texture, and shelf life of processed foods [1]. Nestlé's approach involves using glycerol in combination with other polyols to create low-calorie alternatives to sugar while maintaining product quality. They have also explored the prebiotic potential of glycerol and its effects on gut microbiota [3]. Nestlé has implemented advanced analytical techniques, including high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry, to accurately measure glycerol content and its interactions with other food components [5].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, global market presence, and diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Potential consumer concerns about processed ingredients and artificial sweeteners.
Cargill, Inc.
Technical Solution: Cargill has developed innovative solutions for incorporating glycerol into food products to enhance nutritional quality. Their approach focuses on utilizing glycerol as a functional ingredient in low-fat and low-sugar formulations. Cargill has conducted research on the synergistic effects of glycerol with other ingredients to improve texture and mouthfeel in reduced-calorie foods [2]. They have also explored the use of glycerol in microencapsulation technologies to protect sensitive nutrients and enhance their bioavailability [4]. Cargill's research extends to the application of glycerol in sports nutrition products, leveraging its potential to improve hydration and energy metabolism [6]. Their studies have shown that glycerol can help maintain product stability and extend shelf life in certain food categories.
Strengths: Strong expertise in food ingredients and formulations, global supply chain. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in consumer perception of highly processed ingredients.
Glycerol's Impact on Nutrient Bioavailability
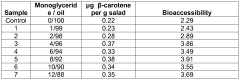
Edible product and use thereof for increasing bioavailability of micronutrients comprised in vegetables or fruit
PatentWO2013060577A1
Innovation
- An edible product containing a glyceride component composed of 76-97% triglycerides, 0-8% diglycerides, and 3-16% monoglycerides, with a weight ratio of diglycerides to monoglycerides less than 1:2, is consumed within 30 minutes of eating vegetables or fruits to increase the absorption of these micronutrients.
Therapeutic bakery product
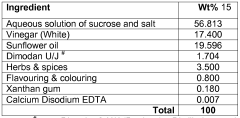
PatentActiveIN202131042282A
Innovation
- Development of gluten-free, low-glycemic index oats-based bakery products incorporating bael leaf powder, jaggery or dates as sweeteners, and a specific combination of ingredients to create cakes, cookies, and muffins that are low in calories and provide nutritional benefits, including protein and roughage, while being easily digestible.
Regulatory Framework for Glycerol in Food
The regulatory framework for glycerol in food is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and quality of food products. Glycerol, also known as glycerin, is widely used in the food industry as a humectant, sweetener, and preservative. Its regulatory status varies across different regions and countries, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of the global regulatory environment.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes glycerol as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food products. The FDA has established specific guidelines for its use, including maximum allowable levels in various food categories. These regulations are outlined in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, which provides detailed information on the permitted uses and limitations of glycerol in food applications.
The European Union (EU) has its own set of regulations governing the use of glycerol in food products. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated the safety of glycerol and established acceptable daily intake (ADI) levels. The EU's food additive regulations, specifically Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008, provide guidelines on the use of glycerol in different food categories, including maximum permitted levels and specific conditions of use.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks for glycerol vary by country. Japan, for instance, classifies glycerol as a food additive and regulates its use through the Food Sanitation Act. China's National Health Commission has established standards for glycerol use in food products, which are outlined in the National Food Safety Standard for Food Additives (GB 2760).
International organizations also play a role in shaping the regulatory landscape for glycerol in food. The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) has evaluated the safety of glycerol and provided recommendations for its use in food products. These recommendations often serve as a reference point for countries developing their own regulatory frameworks.
As research continues to investigate glycerol's influence on the nutritional quality of food, regulatory bodies are likely to update their guidelines to reflect new findings. This dynamic nature of food regulations underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring and compliance efforts by food manufacturers and regulatory professionals.
The regulatory framework for glycerol in food also extends to labeling requirements. Many jurisdictions mandate the declaration of glycerol on food labels, either by its common name or its E-number (E422 in the EU). These labeling regulations aim to provide consumers with transparent information about the ingredients in their food products.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes glycerol as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food products. The FDA has established specific guidelines for its use, including maximum allowable levels in various food categories. These regulations are outlined in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, which provides detailed information on the permitted uses and limitations of glycerol in food applications.
The European Union (EU) has its own set of regulations governing the use of glycerol in food products. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated the safety of glycerol and established acceptable daily intake (ADI) levels. The EU's food additive regulations, specifically Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008, provide guidelines on the use of glycerol in different food categories, including maximum permitted levels and specific conditions of use.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks for glycerol vary by country. Japan, for instance, classifies glycerol as a food additive and regulates its use through the Food Sanitation Act. China's National Health Commission has established standards for glycerol use in food products, which are outlined in the National Food Safety Standard for Food Additives (GB 2760).
International organizations also play a role in shaping the regulatory landscape for glycerol in food. The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) has evaluated the safety of glycerol and provided recommendations for its use in food products. These recommendations often serve as a reference point for countries developing their own regulatory frameworks.
As research continues to investigate glycerol's influence on the nutritional quality of food, regulatory bodies are likely to update their guidelines to reflect new findings. This dynamic nature of food regulations underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring and compliance efforts by food manufacturers and regulatory professionals.
The regulatory framework for glycerol in food also extends to labeling requirements. Many jurisdictions mandate the declaration of glycerol on food labels, either by its common name or its E-number (E422 in the EU). These labeling regulations aim to provide consumers with transparent information about the ingredients in their food products.
Consumer Perception of Glycerol-Enhanced Foods
Consumer perception plays a crucial role in the acceptance and adoption of glycerol-enhanced foods. As glycerol finds increasing applications in food products, understanding how consumers view and respond to these innovations becomes paramount for both manufacturers and marketers.
Initial consumer reactions to glycerol-enhanced foods are often mixed. Many consumers express curiosity about the potential benefits, particularly in terms of improved texture and moisture retention. However, there is also a notable segment of consumers who harbor concerns about the use of additives in their food, viewing glycerol as an unfamiliar or potentially artificial ingredient.
Studies have shown that consumer education is key to improving perception. When provided with information about glycerol's natural occurrence in foods and its safety profile, consumers tend to become more accepting of its use. This highlights the importance of transparent labeling and effective communication strategies in shaping consumer attitudes.
Taste and texture are primary factors influencing consumer acceptance of glycerol-enhanced foods. Products that successfully incorporate glycerol without compromising flavor or introducing undesirable textural changes are more likely to gain consumer approval. In contrast, products where glycerol's presence is noticeable through an off-taste or unusual mouthfeel face significant barriers to acceptance.
Health-conscious consumers represent a particularly interesting segment in the context of glycerol-enhanced foods. While some view glycerol positively for its potential to reduce sugar content or improve nutrient retention, others are wary of its caloric content and its classification as a type of sugar alcohol. This dichotomy underscores the need for nuanced marketing approaches that address both the benefits and potential concerns associated with glycerol use.
Consumer perception also varies significantly across different food categories. Glycerol's use in bakery products, for instance, is generally well-received due to its moisture-retaining properties that can extend shelf life. However, its application in beverages or dairy products may face more scrutiny, as consumers in these categories often prioritize "natural" or minimally processed options.
Cultural factors play a role in shaping attitudes towards glycerol-enhanced foods. In some markets, there is a growing preference for clean label products, which can pose challenges for the acceptance of foods containing glycerol. Conversely, in markets where functional foods are popular, glycerol's potential health benefits may be viewed more favorably.
As the food industry continues to innovate with glycerol, ongoing consumer research and engagement will be essential. Manufacturers must remain attuned to evolving consumer preferences and concerns, adapting their product development and marketing strategies accordingly to ensure the successful integration of glycerol-enhanced foods into the marketplace.
Initial consumer reactions to glycerol-enhanced foods are often mixed. Many consumers express curiosity about the potential benefits, particularly in terms of improved texture and moisture retention. However, there is also a notable segment of consumers who harbor concerns about the use of additives in their food, viewing glycerol as an unfamiliar or potentially artificial ingredient.
Studies have shown that consumer education is key to improving perception. When provided with information about glycerol's natural occurrence in foods and its safety profile, consumers tend to become more accepting of its use. This highlights the importance of transparent labeling and effective communication strategies in shaping consumer attitudes.
Taste and texture are primary factors influencing consumer acceptance of glycerol-enhanced foods. Products that successfully incorporate glycerol without compromising flavor or introducing undesirable textural changes are more likely to gain consumer approval. In contrast, products where glycerol's presence is noticeable through an off-taste or unusual mouthfeel face significant barriers to acceptance.
Health-conscious consumers represent a particularly interesting segment in the context of glycerol-enhanced foods. While some view glycerol positively for its potential to reduce sugar content or improve nutrient retention, others are wary of its caloric content and its classification as a type of sugar alcohol. This dichotomy underscores the need for nuanced marketing approaches that address both the benefits and potential concerns associated with glycerol use.
Consumer perception also varies significantly across different food categories. Glycerol's use in bakery products, for instance, is generally well-received due to its moisture-retaining properties that can extend shelf life. However, its application in beverages or dairy products may face more scrutiny, as consumers in these categories often prioritize "natural" or minimally processed options.
Cultural factors play a role in shaping attitudes towards glycerol-enhanced foods. In some markets, there is a growing preference for clean label products, which can pose challenges for the acceptance of foods containing glycerol. Conversely, in markets where functional foods are popular, glycerol's potential health benefits may be viewed more favorably.
As the food industry continues to innovate with glycerol, ongoing consumer research and engagement will be essential. Manufacturers must remain attuned to evolving consumer preferences and concerns, adapting their product development and marketing strategies accordingly to ensure the successful integration of glycerol-enhanced foods into the marketplace.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!