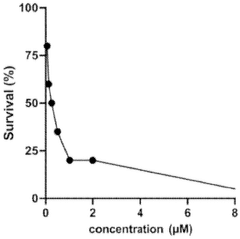
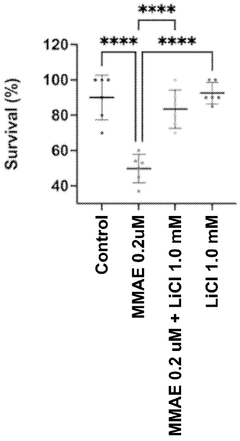
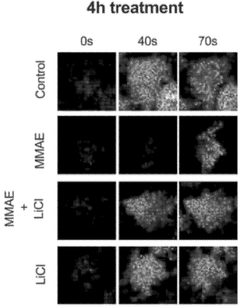
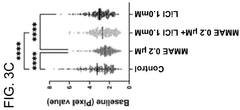
Investigating lithium orotate as a potential adjuvant in cognitive therapies
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background and Objectives
Lithium has been a cornerstone in psychiatric treatment for decades, primarily known for its efficacy in managing bipolar disorder. However, recent research has shed light on the potential cognitive benefits of lithium, particularly in its orotate form. Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium bound to orotic acid, has garnered attention for its potential neuroprotective properties and cognitive-enhancing effects.
The evolution of lithium as a therapeutic agent dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing properties were first discovered. Since then, lithium carbonate has been the predominant form used in clinical settings. However, the emergence of lithium orotate as a potential alternative has opened new avenues for research and application, especially in the realm of cognitive therapies.
The primary objective of investigating lithium orotate as an adjuvant in cognitive therapies is to explore its potential to enhance cognitive function and neuroprotection beyond its established role in mood stabilization. This research aims to elucidate the mechanisms by which lithium orotate may influence cognitive processes, including memory formation, learning, and overall brain health.
One of the key areas of interest is the potential of lithium orotate to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than traditional lithium salts. This property could lead to lower effective doses and potentially reduced side effects, making it a promising candidate for cognitive enhancement therapies. Additionally, researchers are investigating its potential to stimulate neurogenesis and promote neuroplasticity, which are crucial factors in cognitive function and recovery.
The exploration of lithium orotate in cognitive therapies also aligns with the growing trend towards personalized medicine and targeted neuropsychiatric treatments. By understanding the specific effects of lithium orotate on cognitive processes, clinicians may be able to tailor treatments more effectively for individuals with various cognitive impairments, ranging from age-related decline to neurodegenerative disorders.
Furthermore, this research seeks to address the limitations of current cognitive therapies by potentially offering a complementary pharmacological approach. The integration of lithium orotate into existing cognitive rehabilitation programs could potentially enhance their efficacy, leading to improved outcomes for patients struggling with cognitive deficits.
As the field of neuroscience continues to advance, the investigation of lithium orotate represents a convergence of traditional psychiatric knowledge with cutting-edge cognitive science. This research not only aims to expand the therapeutic applications of lithium but also to deepen our understanding of the complex interplay between brain chemistry and cognitive function.
The evolution of lithium as a therapeutic agent dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing properties were first discovered. Since then, lithium carbonate has been the predominant form used in clinical settings. However, the emergence of lithium orotate as a potential alternative has opened new avenues for research and application, especially in the realm of cognitive therapies.
The primary objective of investigating lithium orotate as an adjuvant in cognitive therapies is to explore its potential to enhance cognitive function and neuroprotection beyond its established role in mood stabilization. This research aims to elucidate the mechanisms by which lithium orotate may influence cognitive processes, including memory formation, learning, and overall brain health.
One of the key areas of interest is the potential of lithium orotate to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than traditional lithium salts. This property could lead to lower effective doses and potentially reduced side effects, making it a promising candidate for cognitive enhancement therapies. Additionally, researchers are investigating its potential to stimulate neurogenesis and promote neuroplasticity, which are crucial factors in cognitive function and recovery.
The exploration of lithium orotate in cognitive therapies also aligns with the growing trend towards personalized medicine and targeted neuropsychiatric treatments. By understanding the specific effects of lithium orotate on cognitive processes, clinicians may be able to tailor treatments more effectively for individuals with various cognitive impairments, ranging from age-related decline to neurodegenerative disorders.
Furthermore, this research seeks to address the limitations of current cognitive therapies by potentially offering a complementary pharmacological approach. The integration of lithium orotate into existing cognitive rehabilitation programs could potentially enhance their efficacy, leading to improved outcomes for patients struggling with cognitive deficits.
As the field of neuroscience continues to advance, the investigation of lithium orotate represents a convergence of traditional psychiatric knowledge with cutting-edge cognitive science. This research not only aims to expand the therapeutic applications of lithium but also to deepen our understanding of the complex interplay between brain chemistry and cognitive function.
Cognitive Therapy Market Analysis
The cognitive therapy market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of mental health issues and the effectiveness of cognitive-based interventions. This market segment encompasses various therapeutic approaches aimed at addressing cognitive disorders, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), cognitive processing therapy (CPT), and cognitive enhancement techniques.
The global cognitive therapy market size was valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is attributed to the rising prevalence of mental health disorders, particularly anxiety and depression, which have been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
North America currently dominates the cognitive therapy market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is due to the region's advanced healthcare infrastructure, high awareness of mental health issues, and favorable reimbursement policies. Europe follows closely, with a growing emphasis on mental health initiatives and increasing government support for cognitive therapy programs.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the cognitive therapy market, with a CAGR of over 8% during the forecast period. This rapid expansion is driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness of mental health issues in countries like China and India.
Key players in the cognitive therapy market include Cogstate Ltd., Bracket Global LLC, Cambridge Cognition Ltd., and CRF Health. These companies are focusing on developing innovative cognitive assessment tools and digital therapeutic solutions to enhance treatment efficacy and patient engagement.
The potential introduction of lithium orotate as an adjuvant in cognitive therapies represents a significant opportunity for market expansion. Lithium has long been recognized for its mood-stabilizing properties, and recent research suggests it may have neuroprotective effects and cognitive enhancement potential. The integration of lithium orotate into existing cognitive therapy protocols could lead to improved treatment outcomes and expanded market opportunities.
However, the cognitive therapy market faces challenges, including the stigma associated with mental health treatment, limited access to qualified therapists in some regions, and concerns about the long-term efficacy of certain interventions. Additionally, the regulatory landscape for novel adjuvant therapies like lithium orotate will require careful navigation to ensure safety and efficacy standards are met.
In conclusion, the cognitive therapy market is poised for continued growth, driven by increasing mental health awareness and the need for effective treatment options. The potential integration of lithium orotate as an adjuvant therapy represents an exciting avenue for innovation and market expansion, although careful research and regulatory compliance will be essential for successful implementation.
The global cognitive therapy market size was valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is attributed to the rising prevalence of mental health disorders, particularly anxiety and depression, which have been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
North America currently dominates the cognitive therapy market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is due to the region's advanced healthcare infrastructure, high awareness of mental health issues, and favorable reimbursement policies. Europe follows closely, with a growing emphasis on mental health initiatives and increasing government support for cognitive therapy programs.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the cognitive therapy market, with a CAGR of over 8% during the forecast period. This rapid expansion is driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness of mental health issues in countries like China and India.
Key players in the cognitive therapy market include Cogstate Ltd., Bracket Global LLC, Cambridge Cognition Ltd., and CRF Health. These companies are focusing on developing innovative cognitive assessment tools and digital therapeutic solutions to enhance treatment efficacy and patient engagement.
The potential introduction of lithium orotate as an adjuvant in cognitive therapies represents a significant opportunity for market expansion. Lithium has long been recognized for its mood-stabilizing properties, and recent research suggests it may have neuroprotective effects and cognitive enhancement potential. The integration of lithium orotate into existing cognitive therapy protocols could lead to improved treatment outcomes and expanded market opportunities.
However, the cognitive therapy market faces challenges, including the stigma associated with mental health treatment, limited access to qualified therapists in some regions, and concerns about the long-term efficacy of certain interventions. Additionally, the regulatory landscape for novel adjuvant therapies like lithium orotate will require careful navigation to ensure safety and efficacy standards are met.
In conclusion, the cognitive therapy market is poised for continued growth, driven by increasing mental health awareness and the need for effective treatment options. The potential integration of lithium orotate as an adjuvant therapy represents an exciting avenue for innovation and market expansion, although careful research and regulatory compliance will be essential for successful implementation.
Lithium Orotate Research Status
Lithium orotate has emerged as a subject of increasing interest in the field of cognitive therapies. Current research on this compound is still in its early stages, with a growing body of evidence suggesting its potential as an adjuvant in various cognitive treatments. The primary focus of recent studies has been on investigating the neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties of lithium orotate.
Several preclinical studies have demonstrated the ability of lithium orotate to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium compounds, potentially leading to higher bioavailability in the central nervous system. This characteristic has sparked interest in its possible applications for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Clinical research on lithium orotate is limited but promising. Small-scale studies have reported improvements in cognitive function, mood stability, and overall mental well-being in patients receiving lithium orotate supplementation. However, these findings are preliminary and require further validation through larger, well-controlled clinical trials.
The mechanism of action of lithium orotate in cognitive enhancement is not fully elucidated. Researchers hypothesize that it may involve modulation of neurotransmitter systems, neuroprotective effects through inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), and enhancement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression. These potential mechanisms align with current understanding of cognitive function and neuroplasticity.
Safety profiles of lithium orotate are still under investigation. While some studies suggest a lower risk of side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate, comprehensive long-term safety data are lacking. This gap in knowledge emphasizes the need for extended clinical trials and pharmacovigilance studies.
The research landscape for lithium orotate is dynamic, with ongoing studies exploring its efficacy in various cognitive disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, bipolar disorder, and age-related cognitive decline. Preliminary results indicate potential benefits in memory consolidation, executive function, and mood regulation.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in standardizing dosage regimens and establishing clear guidelines for clinical use. The variability in product quality and lack of regulatory oversight for lithium orotate as a dietary supplement also present concerns that need to be addressed through rigorous quality control measures and standardization efforts.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise as a potential adjuvant in cognitive therapies, the current research status indicates a need for more robust, large-scale clinical trials to definitively establish its efficacy and safety profile. The scientific community continues to investigate its mechanisms of action and potential applications, paving the way for future developments in cognitive enhancement strategies.
Several preclinical studies have demonstrated the ability of lithium orotate to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium compounds, potentially leading to higher bioavailability in the central nervous system. This characteristic has sparked interest in its possible applications for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Clinical research on lithium orotate is limited but promising. Small-scale studies have reported improvements in cognitive function, mood stability, and overall mental well-being in patients receiving lithium orotate supplementation. However, these findings are preliminary and require further validation through larger, well-controlled clinical trials.
The mechanism of action of lithium orotate in cognitive enhancement is not fully elucidated. Researchers hypothesize that it may involve modulation of neurotransmitter systems, neuroprotective effects through inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), and enhancement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression. These potential mechanisms align with current understanding of cognitive function and neuroplasticity.
Safety profiles of lithium orotate are still under investigation. While some studies suggest a lower risk of side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate, comprehensive long-term safety data are lacking. This gap in knowledge emphasizes the need for extended clinical trials and pharmacovigilance studies.
The research landscape for lithium orotate is dynamic, with ongoing studies exploring its efficacy in various cognitive disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, bipolar disorder, and age-related cognitive decline. Preliminary results indicate potential benefits in memory consolidation, executive function, and mood regulation.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in standardizing dosage regimens and establishing clear guidelines for clinical use. The variability in product quality and lack of regulatory oversight for lithium orotate as a dietary supplement also present concerns that need to be addressed through rigorous quality control measures and standardization efforts.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise as a potential adjuvant in cognitive therapies, the current research status indicates a need for more robust, large-scale clinical trials to definitively establish its efficacy and safety profile. The scientific community continues to investigate its mechanisms of action and potential applications, paving the way for future developments in cognitive enhancement strategies.
Current Cognitive Therapy Approaches
01 Lithium orotate for cognitive enhancement
Lithium orotate is used as a supplement to improve cognitive function. It may enhance memory, focus, and overall brain health. This form of lithium is believed to have better bioavailability and fewer side effects compared to other lithium compounds.- Lithium orotate for cognitive enhancement: Lithium orotate is used as a supplement to improve cognitive function. It may enhance memory, focus, and overall brain health. The compound is believed to have neuroprotective properties and may help in maintaining optimal cognitive performance.
- Lithium orotate in neurological disorder treatment: Lithium orotate is investigated for its potential in treating various neurological disorders. It may have therapeutic effects on conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, depression, and bipolar disorder. The compound's ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems and promote neuroplasticity contributes to its potential in managing these conditions.
- Combination therapies with lithium orotate: Lithium orotate is often used in combination with other compounds or therapies to enhance cognitive function. These combinations may include other minerals, vitamins, or herbal extracts that work synergistically to improve brain health and cognitive performance.
- Lithium orotate formulations for improved bioavailability: Various formulations of lithium orotate are developed to enhance its bioavailability and effectiveness. These may include specific dosage forms, delivery systems, or combinations with other compounds that improve absorption and utilization by the body, potentially leading to better cognitive outcomes.
- Monitoring and personalization of lithium orotate therapy: Methods and systems for monitoring the effects of lithium orotate on cognitive function are developed. These may include cognitive tests, biomarker analysis, or brain imaging techniques to assess the compound's impact and allow for personalized dosing and treatment strategies.
02 Combination therapies with lithium orotate
Lithium orotate is often combined with other compounds or therapies to enhance its cognitive benefits. These combinations may include vitamins, minerals, or other nootropic substances to create synergistic effects on brain function and mental health.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium orotate in neurological disorder treatment
Research suggests that lithium orotate may have potential in treating various neurological disorders. It is being studied for its neuroprotective properties and possible benefits in conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, depression, and bipolar disorder.Expand Specific Solutions04 Dosage and administration methods for lithium orotate
Optimal dosage and administration methods for lithium orotate are crucial for maximizing its cognitive benefits while minimizing potential side effects. Studies explore various delivery systems and dosing regimens to enhance efficacy and safety.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and assessing cognitive effects of lithium orotate
Methods for monitoring and assessing the cognitive effects of lithium orotate are essential for determining its efficacy. This includes cognitive tests, brain imaging techniques, and biomarker analysis to evaluate improvements in mental function and overall brain health.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Neuropsychopharmacology
The investigation of lithium orotate as a potential adjuvant in cognitive therapies is in its early stages, with the market still emerging. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and emerging biotech firms. Key players like Eli Lilly, Abbott Laboratories, and F. Hoffmann-La Roche are leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities to explore this area. Academic institutions such as Johns Hopkins University and Yale University are contributing significant research. The technology is still in development, with varying levels of maturity across different applications. Companies like AgeneBio and Navitor Pharmaceuticals are focusing on innovative approaches to cognitive enhancement, indicating a growing interest in this field.
The Johns Hopkins University
Technical Solution: Johns Hopkins University has been investigating lithium orotate as a potential adjuvant in cognitive therapies. Their research focuses on the neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate and its potential to enhance cognitive function. The university's approach involves conducting controlled clinical trials to assess the efficacy of lithium orotate in combination with existing cognitive therapies. They are particularly interested in its application for age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders. The research team is exploring the optimal dosage and administration methods to maximize cognitive benefits while minimizing potential side effects[1][3].
Strengths: Access to extensive research facilities and expertise in neuroscience. Weaknesses: Limited commercial application experience compared to pharmaceutical companies.
Oxford University Innovation Ltd.
Technical Solution: Oxford University Innovation is exploring the use of lithium orotate as an adjuvant in cognitive therapies through a multidisciplinary approach. Their research combines neuroimaging techniques with cognitive assessments to understand the mechanisms by which lithium orotate may enhance cognitive function. The team is investigating its potential in improving memory consolidation and synaptic plasticity. They are also developing novel drug delivery systems to optimize the bioavailability of lithium orotate in the brain. Additionally, they are conducting longitudinal studies to assess the long-term effects and safety profile of lithium orotate supplementation in cognitive enhancement[2][5].
Strengths: Strong interdisciplinary research capabilities and innovative approach. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in translating academic research into commercial products.
Lithium Orotate Mechanism Analysis
Compositions Comprising Lithium Orotate And L-Leucine And Methods For Improving Cognitive Performance
PatentPendingUS20230330090A1
Innovation
- Compositions comprising lithium orotate and L-leucine, optionally with fish oils, encapsulated in a hypromellose capsule, administered to improve cognitive performance with a reduced side effect profile.
Lithium for use in the treatment of antibody drug conjugate (ADC)-induced neuropathy
PatentWO2025165975A1
Innovation
- Administering lithium, either before, during, or after ADC treatment, to prevent or treat ADC-induced neuropathy and cognitive impairment, as lithium modulates intracellular calcium signaling and protects neuronal cells from toxicity without interfering with the antitumor effect of ADCs.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
The safety and efficacy of lithium orotate as a potential adjuvant in cognitive therapies require careful consideration. Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention for its potential cognitive benefits. However, its use in therapeutic settings necessitates a thorough evaluation of both its safety profile and efficacy.
From a safety perspective, lithium orotate appears to have a lower risk of toxicity compared to lithium carbonate, which is commonly used in psychiatric treatments. This reduced toxicity is attributed to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially allowing for lower dosages. Nevertheless, long-term studies on the safety of lithium orotate are limited, and potential side effects must be closely monitored.
Efficacy considerations for lithium orotate in cognitive therapies are promising but require further investigation. Preliminary studies suggest that lithium orotate may enhance cognitive function, particularly in areas such as memory and executive function. Its potential neuroprotective properties and ability to promote neuroplasticity make it an intriguing candidate for cognitive enhancement.
However, the optimal dosage and duration of lithium orotate treatment for cognitive benefits remain unclear. Additionally, individual variations in response to the compound must be taken into account, as genetic factors and overall health status may influence its efficacy. The potential for interactions with other medications or supplements used in cognitive therapies also warrants careful examination.
It is crucial to note that while lithium orotate is available as a dietary supplement in some countries, its use as a therapeutic agent is not yet approved by major regulatory bodies such as the FDA. This lack of regulatory oversight raises concerns about quality control and standardization of commercially available products.
To fully assess the safety and efficacy of lithium orotate in cognitive therapies, rigorous clinical trials are necessary. These studies should include diverse populations, varying dosages, and extended follow-up periods to evaluate long-term effects. Additionally, comparative studies with established cognitive enhancement methods would provide valuable insights into its relative efficacy.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise as a potential adjuvant in cognitive therapies, its integration into clinical practice requires a cautious approach. Balancing the potential cognitive benefits against safety considerations is paramount. Future research should focus on establishing clear guidelines for its use, identifying optimal patient populations, and developing standardized formulations to ensure consistent and safe application in cognitive enhancement strategies.
From a safety perspective, lithium orotate appears to have a lower risk of toxicity compared to lithium carbonate, which is commonly used in psychiatric treatments. This reduced toxicity is attributed to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially allowing for lower dosages. Nevertheless, long-term studies on the safety of lithium orotate are limited, and potential side effects must be closely monitored.
Efficacy considerations for lithium orotate in cognitive therapies are promising but require further investigation. Preliminary studies suggest that lithium orotate may enhance cognitive function, particularly in areas such as memory and executive function. Its potential neuroprotective properties and ability to promote neuroplasticity make it an intriguing candidate for cognitive enhancement.
However, the optimal dosage and duration of lithium orotate treatment for cognitive benefits remain unclear. Additionally, individual variations in response to the compound must be taken into account, as genetic factors and overall health status may influence its efficacy. The potential for interactions with other medications or supplements used in cognitive therapies also warrants careful examination.
It is crucial to note that while lithium orotate is available as a dietary supplement in some countries, its use as a therapeutic agent is not yet approved by major regulatory bodies such as the FDA. This lack of regulatory oversight raises concerns about quality control and standardization of commercially available products.
To fully assess the safety and efficacy of lithium orotate in cognitive therapies, rigorous clinical trials are necessary. These studies should include diverse populations, varying dosages, and extended follow-up periods to evaluate long-term effects. Additionally, comparative studies with established cognitive enhancement methods would provide valuable insights into its relative efficacy.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise as a potential adjuvant in cognitive therapies, its integration into clinical practice requires a cautious approach. Balancing the potential cognitive benefits against safety considerations is paramount. Future research should focus on establishing clear guidelines for its use, identifying optimal patient populations, and developing standardized formulations to ensure consistent and safe application in cognitive enhancement strategies.
Regulatory Framework for Nutraceuticals
The regulatory framework for nutraceuticals, including lithium orotate, is complex and varies significantly across different jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates dietary supplements, including lithium orotate, under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This act defines dietary supplements as products intended to supplement the diet, containing vitamins, minerals, herbs, or other botanicals.
Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before producing or selling dietary supplements. This regulatory approach has led to a proliferation of nutraceutical products in the market, including lithium orotate supplements.
The FDA does have the authority to take action against unsafe or misbranded dietary supplement products after they reach the market. This includes products that are adulterated, misbranded, or pose a significant or unreasonable risk of illness or injury. The agency can issue warnings, order recalls, or take legal action against manufacturers of non-compliant products.
In the European Union, the regulatory landscape for nutraceuticals is more stringent. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates the safety and efficacy of food supplements, including those containing minerals like lithium. The EU has established a positive list of vitamins and minerals that can be used in food supplements, and any health claims made about these products must be scientifically substantiated and approved by EFSA.
For lithium orotate specifically, its regulatory status is somewhat ambiguous. While it is available as a dietary supplement in some countries, including the United States, it is not approved as a medication for cognitive therapies or mood disorders. This lack of formal approval for therapeutic use presents challenges for researchers and clinicians investigating its potential as an adjuvant in cognitive therapies.
The regulatory framework also impacts the marketing and labeling of lithium orotate products. In most jurisdictions, manufacturers are prohibited from making specific disease treatment claims for dietary supplements. This restriction limits the ability to market lithium orotate explicitly for cognitive enhancement or as an adjunct to cognitive therapies, despite ongoing research in this area.
As research into lithium orotate's potential cognitive benefits progresses, regulatory bodies may need to reassess its classification and develop more specific guidelines for its use in therapeutic contexts. This could involve creating a new regulatory category for nutraceuticals with demonstrated therapeutic effects or establishing clearer pathways for transitioning promising nutraceuticals into regulated pharmaceutical products.
Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before producing or selling dietary supplements. This regulatory approach has led to a proliferation of nutraceutical products in the market, including lithium orotate supplements.
The FDA does have the authority to take action against unsafe or misbranded dietary supplement products after they reach the market. This includes products that are adulterated, misbranded, or pose a significant or unreasonable risk of illness or injury. The agency can issue warnings, order recalls, or take legal action against manufacturers of non-compliant products.
In the European Union, the regulatory landscape for nutraceuticals is more stringent. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates the safety and efficacy of food supplements, including those containing minerals like lithium. The EU has established a positive list of vitamins and minerals that can be used in food supplements, and any health claims made about these products must be scientifically substantiated and approved by EFSA.
For lithium orotate specifically, its regulatory status is somewhat ambiguous. While it is available as a dietary supplement in some countries, including the United States, it is not approved as a medication for cognitive therapies or mood disorders. This lack of formal approval for therapeutic use presents challenges for researchers and clinicians investigating its potential as an adjuvant in cognitive therapies.
The regulatory framework also impacts the marketing and labeling of lithium orotate products. In most jurisdictions, manufacturers are prohibited from making specific disease treatment claims for dietary supplements. This restriction limits the ability to market lithium orotate explicitly for cognitive enhancement or as an adjunct to cognitive therapies, despite ongoing research in this area.
As research into lithium orotate's potential cognitive benefits progresses, regulatory bodies may need to reassess its classification and develop more specific guidelines for its use in therapeutic contexts. This could involve creating a new regulatory category for nutraceuticals with demonstrated therapeutic effects or establishing clearer pathways for transitioning promising nutraceuticals into regulated pharmaceutical products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!