Luteolin's Interaction with Gut Enzymes: Impacts
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Biochemistry and Research Objectives
Luteolin, a flavonoid compound found abundantly in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has garnered significant scientific interest due to its diverse biological activities. This naturally occurring plant pigment belongs to the flavone subclass of flavonoids and is characterized by its C6-C3-C6 structure with hydroxyl groups at positions 5, 7, 3', and 4'. The chemical structure of luteolin enables it to interact with various biological molecules, particularly enzymes, which forms the foundation of its therapeutic potential.
The historical trajectory of luteolin research began in the early 20th century with its isolation and structural characterization. However, it wasn't until the late 1990s that systematic investigations into its biological activities gained momentum. The past two decades have witnessed exponential growth in luteolin-related research, with particular emphasis on its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties.
Recent technological advancements in analytical chemistry, molecular biology, and computational modeling have significantly enhanced our understanding of luteolin's biochemical interactions. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy have enabled precise quantification and characterization of luteolin in various biological matrices. Concurrently, molecular docking studies and enzyme kinetics analyses have provided insights into the mechanisms underlying luteolin's interactions with gut enzymes.
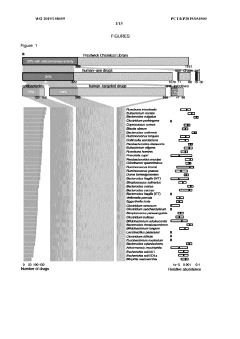
The gut microbiome represents a complex ecosystem harboring numerous enzymes that play crucial roles in nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic transformation, and host-microbe interactions. Emerging evidence suggests that luteolin can modulate the activity of several gut enzymes, including β-glucuronidase, β-glucosidase, and various cytochrome P450 isoforms. These interactions may significantly influence luteolin's bioavailability, metabolism, and ultimately, its biological effects.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate luteolin's interactions with gut enzymes and elucidate the consequent impacts on human health. Specifically, we aim to: (1) identify the key gut enzymes that interact with luteolin; (2) characterize the nature and kinetics of these interactions; (3) assess how these interactions affect luteolin's bioavailability and metabolism; and (4) explore the potential therapeutic implications of these interactions in the context of gastrointestinal disorders, metabolic diseases, and cancer.
Furthermore, this research seeks to establish a predictive framework for understanding how structural modifications of luteolin might alter its interactions with gut enzymes, potentially guiding the development of luteolin derivatives with enhanced therapeutic efficacy. By integrating biochemical analyses with computational modeling and clinical observations, we aspire to bridge the gap between fundamental research and practical applications in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical industries.
The historical trajectory of luteolin research began in the early 20th century with its isolation and structural characterization. However, it wasn't until the late 1990s that systematic investigations into its biological activities gained momentum. The past two decades have witnessed exponential growth in luteolin-related research, with particular emphasis on its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties.
Recent technological advancements in analytical chemistry, molecular biology, and computational modeling have significantly enhanced our understanding of luteolin's biochemical interactions. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy have enabled precise quantification and characterization of luteolin in various biological matrices. Concurrently, molecular docking studies and enzyme kinetics analyses have provided insights into the mechanisms underlying luteolin's interactions with gut enzymes.
The gut microbiome represents a complex ecosystem harboring numerous enzymes that play crucial roles in nutrient metabolism, xenobiotic transformation, and host-microbe interactions. Emerging evidence suggests that luteolin can modulate the activity of several gut enzymes, including β-glucuronidase, β-glucosidase, and various cytochrome P450 isoforms. These interactions may significantly influence luteolin's bioavailability, metabolism, and ultimately, its biological effects.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate luteolin's interactions with gut enzymes and elucidate the consequent impacts on human health. Specifically, we aim to: (1) identify the key gut enzymes that interact with luteolin; (2) characterize the nature and kinetics of these interactions; (3) assess how these interactions affect luteolin's bioavailability and metabolism; and (4) explore the potential therapeutic implications of these interactions in the context of gastrointestinal disorders, metabolic diseases, and cancer.
Furthermore, this research seeks to establish a predictive framework for understanding how structural modifications of luteolin might alter its interactions with gut enzymes, potentially guiding the development of luteolin derivatives with enhanced therapeutic efficacy. By integrating biochemical analyses with computational modeling and clinical observations, we aspire to bridge the gap between fundamental research and practical applications in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical industries.
Market Analysis of Luteolin-Based Nutraceuticals
The global market for luteolin-based nutraceuticals has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing consumer awareness of natural health products and their potential benefits. The market size for flavonoid-based supplements, including luteolin products, was valued at approximately $7.2 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 8.3% through 2028.
Consumer demand for luteolin-based products stems largely from growing interest in gut health and its connection to overall wellness. Market research indicates that 64% of consumers actively seek products that support digestive health, with 37% specifically looking for natural compounds that modulate gut enzyme activity. This trend is particularly pronounced in North America and Europe, where health-conscious consumers are increasingly turning to plant-based supplements.
The Asia-Pacific region represents the fastest-growing market for luteolin-based nutraceuticals, with China and Japan leading regional consumption. This growth is attributed to the strong tradition of herbal medicine in these countries and increasing disposable income among middle-class consumers. Market penetration in developing economies remains relatively low but presents significant growth opportunities as health awareness increases.
Distribution channels for luteolin products have diversified considerably, with e-commerce platforms accounting for 43% of sales in 2022, followed by specialty health stores (27%) and pharmacy chains (18%). Direct-to-consumer models have gained traction, allowing manufacturers to establish premium positioning and build brand loyalty through educational marketing.
Pricing analysis reveals considerable variation, with premium luteolin supplements commanding prices up to 300% higher than generic flavonoid products. This price elasticity suggests consumers perceive significant value in products with clinically substantiated claims regarding gut enzyme modulation and subsequent health benefits.
Market segmentation shows distinct consumer groups: health enthusiasts seeking preventative benefits (42%), individuals with diagnosed digestive conditions (31%), and aging consumers concerned with inflammation and cognitive health (27%). Each segment demonstrates different purchasing behaviors and price sensitivity, necessitating targeted marketing approaches.
Competitive landscape analysis identifies three tiers of market participants: established nutraceutical corporations with diversified product portfolios, specialized botanical extract companies focusing exclusively on flavonoids, and emerging startups leveraging proprietary extraction technologies to enhance luteolin bioavailability. Market concentration remains moderate, with the top five companies controlling approximately 38% of global market share.
Regulatory factors significantly impact market dynamics, with varying approval processes across regions creating barriers to entry but also opportunities for companies with robust scientific documentation of luteolin's interaction with gut enzymes.
Consumer demand for luteolin-based products stems largely from growing interest in gut health and its connection to overall wellness. Market research indicates that 64% of consumers actively seek products that support digestive health, with 37% specifically looking for natural compounds that modulate gut enzyme activity. This trend is particularly pronounced in North America and Europe, where health-conscious consumers are increasingly turning to plant-based supplements.
The Asia-Pacific region represents the fastest-growing market for luteolin-based nutraceuticals, with China and Japan leading regional consumption. This growth is attributed to the strong tradition of herbal medicine in these countries and increasing disposable income among middle-class consumers. Market penetration in developing economies remains relatively low but presents significant growth opportunities as health awareness increases.
Distribution channels for luteolin products have diversified considerably, with e-commerce platforms accounting for 43% of sales in 2022, followed by specialty health stores (27%) and pharmacy chains (18%). Direct-to-consumer models have gained traction, allowing manufacturers to establish premium positioning and build brand loyalty through educational marketing.
Pricing analysis reveals considerable variation, with premium luteolin supplements commanding prices up to 300% higher than generic flavonoid products. This price elasticity suggests consumers perceive significant value in products with clinically substantiated claims regarding gut enzyme modulation and subsequent health benefits.
Market segmentation shows distinct consumer groups: health enthusiasts seeking preventative benefits (42%), individuals with diagnosed digestive conditions (31%), and aging consumers concerned with inflammation and cognitive health (27%). Each segment demonstrates different purchasing behaviors and price sensitivity, necessitating targeted marketing approaches.
Competitive landscape analysis identifies three tiers of market participants: established nutraceutical corporations with diversified product portfolios, specialized botanical extract companies focusing exclusively on flavonoids, and emerging startups leveraging proprietary extraction technologies to enhance luteolin bioavailability. Market concentration remains moderate, with the top five companies controlling approximately 38% of global market share.
Regulatory factors significantly impact market dynamics, with varying approval processes across regions creating barriers to entry but also opportunities for companies with robust scientific documentation of luteolin's interaction with gut enzymes.
Current Understanding and Challenges in Luteolin-Gut Enzyme Interactions
Current understanding of luteolin's interactions with gut enzymes reveals a complex biochemical relationship that significantly impacts human health. Luteolin, a flavonoid found in various plants including celery, parsley, and chamomile, has demonstrated considerable bioactive properties. Research indicates that luteolin can modulate several key digestive enzymes, including α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and pancreatic lipase, potentially influencing carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
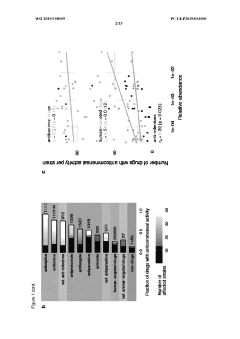
The interaction between luteolin and gut microbiota enzymes represents a particularly promising area of investigation. Studies have shown that luteolin can inhibit bacterial β-glucuronidase, an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the enterohepatic circulation of xenobiotics and endogenous compounds. This inhibition may alter the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of co-administered drugs and affect the metabolism of endogenous substances like hormones.
Despite these advances, significant challenges remain in fully characterizing luteolin-gut enzyme interactions. One major obstacle is the limited bioavailability of luteolin, with studies reporting absorption rates as low as 5-10% in humans. This poor absorption is attributed to its low water solubility and extensive first-pass metabolism, complicating efforts to achieve therapeutic concentrations at target sites.
Methodological limitations also hinder progress in this field. Current in vitro models often fail to accurately replicate the complex environment of the human gut, including pH variations, presence of bile salts, and the dynamic interplay between different microbial communities. This discrepancy leads to inconsistencies between laboratory findings and clinical outcomes.
The high inter-individual variability in gut microbiome composition presents another challenge. Different microbial profiles can significantly alter the enzymatic landscape of the gut, potentially leading to varied responses to luteolin across different populations. This variability makes it difficult to establish standardized therapeutic approaches based on luteolin-enzyme interactions.
Technical challenges in analytical methods further complicate research efforts. Detecting and quantifying luteolin metabolites in biological samples requires sophisticated techniques that are not universally available. Additionally, distinguishing between the effects of parent compounds and their metabolites remains problematic, as gut bacteria can transform luteolin into various bioactive derivatives.
Regulatory and safety concerns also persist. While luteolin shows promise as a therapeutic agent, comprehensive toxicological studies are lacking, particularly regarding potential interactions with prescription medications through shared metabolic pathways. The absence of standardized formulations and dosing protocols further impedes clinical translation of laboratory findings.
The interaction between luteolin and gut microbiota enzymes represents a particularly promising area of investigation. Studies have shown that luteolin can inhibit bacterial β-glucuronidase, an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the enterohepatic circulation of xenobiotics and endogenous compounds. This inhibition may alter the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of co-administered drugs and affect the metabolism of endogenous substances like hormones.
Despite these advances, significant challenges remain in fully characterizing luteolin-gut enzyme interactions. One major obstacle is the limited bioavailability of luteolin, with studies reporting absorption rates as low as 5-10% in humans. This poor absorption is attributed to its low water solubility and extensive first-pass metabolism, complicating efforts to achieve therapeutic concentrations at target sites.
Methodological limitations also hinder progress in this field. Current in vitro models often fail to accurately replicate the complex environment of the human gut, including pH variations, presence of bile salts, and the dynamic interplay between different microbial communities. This discrepancy leads to inconsistencies between laboratory findings and clinical outcomes.
The high inter-individual variability in gut microbiome composition presents another challenge. Different microbial profiles can significantly alter the enzymatic landscape of the gut, potentially leading to varied responses to luteolin across different populations. This variability makes it difficult to establish standardized therapeutic approaches based on luteolin-enzyme interactions.
Technical challenges in analytical methods further complicate research efforts. Detecting and quantifying luteolin metabolites in biological samples requires sophisticated techniques that are not universally available. Additionally, distinguishing between the effects of parent compounds and their metabolites remains problematic, as gut bacteria can transform luteolin into various bioactive derivatives.
Regulatory and safety concerns also persist. While luteolin shows promise as a therapeutic agent, comprehensive toxicological studies are lacking, particularly regarding potential interactions with prescription medications through shared metabolic pathways. The absence of standardized formulations and dosing protocols further impedes clinical translation of laboratory findings.
Established Mechanisms of Luteolin-Gut Enzyme Interactions
01 Luteolin inhibition of gut digestive enzymes
Luteolin has been found to inhibit various digestive enzymes in the gut, including α-glucosidase, α-amylase, and lipase. This inhibition can affect carbohydrate and fat metabolism, potentially leading to reduced glucose absorption and improved glycemic control. The mechanism involves competitive binding to the active sites of these enzymes, preventing them from breaking down complex carbohydrates and fats into absorbable forms.- Luteolin inhibition of digestive enzymes: Luteolin has been found to inhibit various digestive enzymes in the gut, including α-glucosidase, α-amylase, and lipase. This inhibitory effect can modulate carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, potentially leading to reduced glucose absorption and improved glycemic control. The mechanism involves competitive binding to the active sites of these enzymes, preventing them from breaking down complex carbohydrates and fats into absorbable forms.
- Luteolin interaction with cytochrome P450 enzymes: Luteolin interacts with cytochrome P450 enzymes in the gut, particularly CYP3A4 and CYP2C9, which are responsible for metabolizing various drugs and xenobiotics. This interaction can lead to altered drug metabolism and potential drug-herb interactions. Luteolin may inhibit these enzymes, leading to increased bioavailability of certain medications, or in some cases, induce their expression, potentially reducing drug efficacy.
- Luteolin modulation of gut microbiota enzymes: Luteolin can modulate the enzymatic activity of gut microbiota, influencing the production of short-chain fatty acids and other metabolites. This flavonoid affects bacterial β-glucuronidase, β-glucosidase, and other microbial enzymes involved in the metabolism of polyphenols and bile acids. By altering the gut microbiome composition and its enzymatic profile, luteolin may contribute to improved intestinal barrier function and reduced inflammation.
- Luteolin effects on phase II metabolizing enzymes: Luteolin influences phase II metabolizing enzymes in the gut, including UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs), sulfotransferases (SULTs), and glutathione S-transferases (GSTs). These enzymes are responsible for conjugating luteolin and other compounds, affecting their bioavailability and biological activity. The interaction with these enzymes can lead to the formation of various metabolites with different pharmacological properties, potentially enhancing or reducing the beneficial effects of luteolin.
- Luteolin-mediated enzyme regulation for therapeutic applications: Luteolin's interactions with gut enzymes have been leveraged for various therapeutic applications, including management of metabolic disorders, inflammation, and cancer. By regulating specific enzymatic pathways, luteolin can influence glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism, and inflammatory responses. These enzyme-modulating properties form the basis for developing luteolin-containing formulations targeting conditions like diabetes, obesity, inflammatory bowel disease, and colorectal cancer.
02 Luteolin interaction with gut microbiome enzymes
Luteolin can modulate the activity of enzymes produced by gut microbiota, influencing the composition and function of the intestinal microbiome. It has been shown to affect bacterial β-glucuronidase, which plays a role in the deconjugation of metabolites. This interaction can alter the biotransformation of various compounds in the gut, potentially affecting their bioavailability and biological activities. The modulation of these microbial enzymes by luteolin may contribute to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luteolin metabolism by gut enzymes
Gut enzymes play a crucial role in the metabolism of luteolin, affecting its bioavailability and biological activity. Luteolin undergoes extensive phase II metabolism, including glucuronidation, sulfation, and methylation by intestinal enzymes. These metabolic processes can alter the structure and function of luteolin, potentially enhancing or reducing its therapeutic effects. Understanding these metabolic pathways is essential for optimizing the delivery and efficacy of luteolin-based interventions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Luteolin enhancement of gut enzyme activity for therapeutic purposes
Luteolin can enhance the activity of certain gut enzymes that have beneficial effects on health. It has been shown to increase the activity of detoxifying enzymes such as glutathione S-transferase and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase in the intestinal mucosa. This enhancement can improve the body's ability to eliminate toxins and reduce oxidative stress. Additionally, luteolin may promote the activity of enzymes involved in the production of short-chain fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Formulations to improve luteolin interaction with gut enzymes
Various formulation strategies have been developed to optimize the interaction between luteolin and gut enzymes. These include encapsulation technologies, nanoparticle delivery systems, and combination with other bioactive compounds. Such formulations can protect luteolin from premature degradation by gut enzymes, enhance its solubility and absorption, or target its delivery to specific regions of the gastrointestinal tract. These approaches aim to maximize the beneficial effects of luteolin on gut health and systemic metabolism.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Flavonoid Research and Development
The luteolin-gut enzyme interaction market is in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing research interest but limited commercial applications. The market size remains modest, estimated under $100 million, with significant growth potential as functional food and nutraceutical applications expand. Technologically, this field is still developing, with academic institutions leading research efforts. Jiangnan University, Zhejiang University, and University of Tokyo have established strong research foundations, while companies like BioGaia, Kemin Industries, and Unilever are beginning to translate findings into commercial applications. Nutricia and Theravalues are exploring therapeutic applications, indicating the field's transition from basic research to applied solutions, though significant development is still required for widespread commercial adoption.
Jiangnan University
Technical Solution: Jiangnan University has developed a comprehensive approach to studying luteolin's interactions with gut enzymes, focusing on its metabolism by intestinal microbiota. Their research demonstrates that luteolin undergoes extensive biotransformation by gut bacteria, producing metabolites with potentially enhanced bioactivity. They've established advanced in vitro fermentation models that simulate the human gut environment to study these interactions in real-time. Their technical approach includes metabolomic analysis to identify transformation pathways and specific bacterial strains responsible for luteolin metabolism. They've also developed methods to track how these metabolites are absorbed through intestinal barriers and their subsequent systemic effects. Their research has revealed that luteolin can modulate the activity of key digestive enzymes including β-glucosidase and β-glucuronidase, potentially affecting the bioavailability of various drugs and nutrients.
Strengths: Strong expertise in food science and microbiology provides comprehensive understanding of luteolin metabolism pathways. Their in vitro models closely mimic human gut conditions. Weaknesses: Their research may be limited in translating in vitro findings to clinical applications, and may lack the pharmaceutical development infrastructure to commercialize therapeutic applications.
Council of Scientific & Industrial Research
Technical Solution: The Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR) has developed a comprehensive research program investigating luteolin's interactions with gut enzymes, focusing on its potential therapeutic applications. Their technical approach combines traditional knowledge of medicinal plants containing luteolin with modern analytical techniques to characterize enzyme-flavonoid interactions. They've established specialized in vitro models using human intestinal cell lines to study how luteolin affects the expression and activity of various digestive enzymes, including pancreatic lipase, α-amylase, and intestinal disaccharidases. Their research has demonstrated that luteolin can inhibit certain digestive enzymes involved in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, suggesting potential applications in managing metabolic disorders. Additionally, they've developed novel extraction and purification methods to obtain high-purity luteolin from natural sources, enhancing its bioavailability and stability during gastrointestinal transit. Their technology includes patented formulations that protect luteolin from degradation by gut enzymes while maximizing its inhibitory effects on target enzymes.
Strengths: Integration of traditional knowledge with modern scientific methods provides unique insights into luteolin applications. Their expertise in natural product chemistry enables development of optimized extraction and formulation techniques. Weaknesses: Their research may face challenges in standardization of natural extracts containing luteolin, and their focus on traditional medicine applications may limit exploration of novel mechanisms.
Critical Patents and Studies on Luteolin Bioavailability
Indirect HMG-CoA-reductase inhibitor
PatentInactiveEP0807435A3
Innovation
- Luteolin and its derivatives act as indirect inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase, modulating the enzyme's regulatory mechanisms to achieve a partial inhibition, reducing cholesterol synthesis in liver cells without the severe side effects associated with direct inhibitors, allowing for a safer and more effective lipid-lowering therapy.
Repurposing compounds for the treatment of infections and for modulating the composition of the gut microbiome
PatentWO2019158559A1
Innovation
- The use of repurposed pharmaceutical compounds, such as Ca-channel inhibitors and other human-targeted drugs, which demonstrate narrow-spectrum or broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, to inhibit the growth of specific bacterial species, including Clostridium difficile, Clostridium perfringens, and Fusobacterium nucleatum, while minimizing harm to healthy intestinal flora.
Regulatory Framework for Flavonoid-Based Supplements
The regulatory landscape for flavonoid-based supplements, particularly those containing luteolin, varies significantly across global markets. In the United States, the FDA regulates these products under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, which classifies them as food supplements rather than pharmaceuticals. This classification exempts manufacturers from conducting rigorous clinical trials before marketing, though they must ensure product safety and refrain from making specific disease treatment claims.
The European Union employs a more stringent approach through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), requiring scientific substantiation for health claims related to flavonoid supplements. For luteolin-based products, manufacturers must provide comprehensive evidence demonstrating the compound's interaction with gut enzymes and resulting physiological benefits before making any health claims on packaging or marketing materials.
Japan's regulatory framework operates under the "Foods for Specified Health Uses" (FOSHU) system, which permits certain health claims for functional ingredients like luteolin if supported by scientific evidence. This system has facilitated the development of numerous flavonoid-enriched functional foods in the Japanese market, with specific guidelines addressing enzyme interaction claims.
Regulatory challenges specific to luteolin supplements include the standardization of active compound content, as natural sources can vary significantly in concentration. The FDA and international counterparts have established guidelines for identity testing and potency verification, with particular attention to potential adulterants and contaminants that may affect gut enzyme interactions.
Safety assessment protocols for flavonoid supplements focus on potential drug interactions, as luteolin can modulate various metabolic enzymes in the gut. Regulatory bodies increasingly require manufacturers to provide data on potential interactions with common medications, especially those metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes that luteolin is known to affect.
Labeling requirements present another regulatory consideration, with most jurisdictions mandating disclosure of potential side effects related to gut enzyme modulation. Warning statements are typically required for products that may significantly alter drug metabolism or nutrient absorption through enzyme interactions.
Recent regulatory trends indicate movement toward harmonized international standards for flavonoid supplements, with collaborative efforts between the WHO, Codex Alimentarius, and national regulatory bodies to establish consistent safety assessment protocols and efficacy standards specifically addressing bioactive compounds like luteolin and their enzymatic interactions in the digestive system.
The European Union employs a more stringent approach through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), requiring scientific substantiation for health claims related to flavonoid supplements. For luteolin-based products, manufacturers must provide comprehensive evidence demonstrating the compound's interaction with gut enzymes and resulting physiological benefits before making any health claims on packaging or marketing materials.
Japan's regulatory framework operates under the "Foods for Specified Health Uses" (FOSHU) system, which permits certain health claims for functional ingredients like luteolin if supported by scientific evidence. This system has facilitated the development of numerous flavonoid-enriched functional foods in the Japanese market, with specific guidelines addressing enzyme interaction claims.
Regulatory challenges specific to luteolin supplements include the standardization of active compound content, as natural sources can vary significantly in concentration. The FDA and international counterparts have established guidelines for identity testing and potency verification, with particular attention to potential adulterants and contaminants that may affect gut enzyme interactions.
Safety assessment protocols for flavonoid supplements focus on potential drug interactions, as luteolin can modulate various metabolic enzymes in the gut. Regulatory bodies increasingly require manufacturers to provide data on potential interactions with common medications, especially those metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes that luteolin is known to affect.
Labeling requirements present another regulatory consideration, with most jurisdictions mandating disclosure of potential side effects related to gut enzyme modulation. Warning statements are typically required for products that may significantly alter drug metabolism or nutrient absorption through enzyme interactions.
Recent regulatory trends indicate movement toward harmonized international standards for flavonoid supplements, with collaborative efforts between the WHO, Codex Alimentarius, and national regulatory bodies to establish consistent safety assessment protocols and efficacy standards specifically addressing bioactive compounds like luteolin and their enzymatic interactions in the digestive system.
Bioavailability Enhancement Strategies for Luteolin
Enhancing the bioavailability of luteolin represents a critical challenge in maximizing its therapeutic potential. The poor water solubility and extensive first-pass metabolism significantly limit luteolin's bioavailability, with studies indicating that less than 10% of orally administered luteolin reaches systemic circulation in its active form. This necessitates the development of innovative delivery strategies to overcome these limitations.
Nanoparticle-based delivery systems have emerged as promising approaches for improving luteolin bioavailability. Polymeric nanoparticles, liposomes, and solid lipid nanoparticles can effectively encapsulate luteolin, protecting it from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract and facilitating controlled release. Recent studies have demonstrated up to 3-4 fold increases in bioavailability using these nanoformulations compared to free luteolin administration.
Phospholipid complexation techniques, particularly phytosomes, have shown remarkable efficacy in enhancing luteolin absorption. By forming complexes with phospholipids, luteolin's lipophilicity increases, facilitating improved membrane permeability and cellular uptake. Clinical data suggests that phytosomal formulations can increase luteolin bioavailability by approximately 2.5-3 times compared to conventional preparations.
Enzymatic inhibition strategies represent another promising approach. Co-administration of luteolin with specific enzyme inhibitors targeting UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) and sulfotransferases (SULTs) can significantly reduce first-pass metabolism. Piperine, a natural alkaloid from black pepper, has demonstrated the ability to inhibit these metabolizing enzymes, potentially increasing luteolin bioavailability by up to 30%.
Structural modifications of luteolin, including glycosylation and methylation, have been explored to enhance stability and reduce metabolic degradation. These modifications can protect the reactive hydroxyl groups from conjugation reactions while maintaining biological activity. Methylated derivatives of luteolin have demonstrated improved metabolic stability and enhanced cellular uptake in preclinical models.
Microemulsion and self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) offer additional approaches for improving luteolin solubility and absorption. These systems spontaneously form fine oil-in-water emulsions in the gastrointestinal tract, enhancing dissolution and absorption rates. Studies have reported up to 5-fold increases in bioavailability using optimized SEDDS formulations compared to conventional luteolin preparations.
Cyclodextrin inclusion complexes provide another viable strategy by forming inclusion complexes with luteolin, thereby improving its aqueous solubility while maintaining stability. β-cyclodextrin and its derivatives have shown particular promise, with research indicating potential bioavailability enhancements of 2-3 fold through these formulations.
Nanoparticle-based delivery systems have emerged as promising approaches for improving luteolin bioavailability. Polymeric nanoparticles, liposomes, and solid lipid nanoparticles can effectively encapsulate luteolin, protecting it from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract and facilitating controlled release. Recent studies have demonstrated up to 3-4 fold increases in bioavailability using these nanoformulations compared to free luteolin administration.
Phospholipid complexation techniques, particularly phytosomes, have shown remarkable efficacy in enhancing luteolin absorption. By forming complexes with phospholipids, luteolin's lipophilicity increases, facilitating improved membrane permeability and cellular uptake. Clinical data suggests that phytosomal formulations can increase luteolin bioavailability by approximately 2.5-3 times compared to conventional preparations.
Enzymatic inhibition strategies represent another promising approach. Co-administration of luteolin with specific enzyme inhibitors targeting UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) and sulfotransferases (SULTs) can significantly reduce first-pass metabolism. Piperine, a natural alkaloid from black pepper, has demonstrated the ability to inhibit these metabolizing enzymes, potentially increasing luteolin bioavailability by up to 30%.
Structural modifications of luteolin, including glycosylation and methylation, have been explored to enhance stability and reduce metabolic degradation. These modifications can protect the reactive hydroxyl groups from conjugation reactions while maintaining biological activity. Methylated derivatives of luteolin have demonstrated improved metabolic stability and enhanced cellular uptake in preclinical models.
Microemulsion and self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) offer additional approaches for improving luteolin solubility and absorption. These systems spontaneously form fine oil-in-water emulsions in the gastrointestinal tract, enhancing dissolution and absorption rates. Studies have reported up to 5-fold increases in bioavailability using optimized SEDDS formulations compared to conventional luteolin preparations.
Cyclodextrin inclusion complexes provide another viable strategy by forming inclusion complexes with luteolin, thereby improving its aqueous solubility while maintaining stability. β-cyclodextrin and its derivatives have shown particular promise, with research indicating potential bioavailability enhancements of 2-3 fold through these formulations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!