Potential mood-stabilizing effects of low-dose lithium orotate in preclinical models
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background and Research Objectives
Lithium has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder for decades, with its mood-stabilizing properties well-established in clinical practice. However, the traditional use of lithium carbonate has been associated with various side effects and the need for regular blood monitoring. In recent years, there has been growing interest in alternative forms of lithium, particularly lithium orotate, which may offer similar therapeutic benefits with potentially fewer adverse effects.
The exploration of low-dose lithium orotate represents a promising avenue in the field of mood disorders research. This compound combines lithium with orotic acid, potentially enhancing its bioavailability and allowing for lower dosages to achieve therapeutic effects. The rationale behind this approach is to harness the neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties of lithium while minimizing the risk of toxicity associated with higher doses.
The primary objective of this research is to investigate the potential mood-stabilizing effects of low-dose lithium orotate in preclinical models. This aim encompasses several key aspects of inquiry. First, it seeks to establish the efficacy of lithium orotate in modulating mood-related behaviors in animal models of bipolar disorder and depression. Second, it aims to elucidate the neurobiological mechanisms underlying these effects, focusing on lithium's impact on neurotransmitter systems, neuroplasticity, and cellular signaling pathways.
Furthermore, this research endeavors to compare the efficacy and safety profile of lithium orotate with traditional lithium carbonate formulations. By examining the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of low-dose lithium orotate, researchers hope to determine whether this form of lithium can achieve therapeutic effects at lower plasma concentrations, potentially reducing the risk of side effects and the need for intensive monitoring.
Another crucial objective is to investigate the long-term effects of low-dose lithium orotate on brain health and cognitive function. This includes assessing its potential neuroprotective properties and its impact on cognitive domains often affected in mood disorders, such as memory and executive function.
The research also aims to explore the potential of lithium orotate as a preventive intervention for individuals at high risk of developing bipolar disorder or as an adjunctive treatment in combination with other mood stabilizers. This approach could potentially expand the therapeutic applications of lithium and improve outcomes for patients with mood disorders.
By focusing on preclinical models, this research lays the groundwork for future translational studies and clinical trials. The insights gained from these animal studies will be crucial in designing human trials and developing targeted therapeutic strategies. Ultimately, this research seeks to contribute to the development of safer and more effective treatments for mood disorders, potentially improving the quality of life for millions of individuals affected by these conditions.
The exploration of low-dose lithium orotate represents a promising avenue in the field of mood disorders research. This compound combines lithium with orotic acid, potentially enhancing its bioavailability and allowing for lower dosages to achieve therapeutic effects. The rationale behind this approach is to harness the neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties of lithium while minimizing the risk of toxicity associated with higher doses.
The primary objective of this research is to investigate the potential mood-stabilizing effects of low-dose lithium orotate in preclinical models. This aim encompasses several key aspects of inquiry. First, it seeks to establish the efficacy of lithium orotate in modulating mood-related behaviors in animal models of bipolar disorder and depression. Second, it aims to elucidate the neurobiological mechanisms underlying these effects, focusing on lithium's impact on neurotransmitter systems, neuroplasticity, and cellular signaling pathways.
Furthermore, this research endeavors to compare the efficacy and safety profile of lithium orotate with traditional lithium carbonate formulations. By examining the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of low-dose lithium orotate, researchers hope to determine whether this form of lithium can achieve therapeutic effects at lower plasma concentrations, potentially reducing the risk of side effects and the need for intensive monitoring.
Another crucial objective is to investigate the long-term effects of low-dose lithium orotate on brain health and cognitive function. This includes assessing its potential neuroprotective properties and its impact on cognitive domains often affected in mood disorders, such as memory and executive function.
The research also aims to explore the potential of lithium orotate as a preventive intervention for individuals at high risk of developing bipolar disorder or as an adjunctive treatment in combination with other mood stabilizers. This approach could potentially expand the therapeutic applications of lithium and improve outcomes for patients with mood disorders.
By focusing on preclinical models, this research lays the groundwork for future translational studies and clinical trials. The insights gained from these animal studies will be crucial in designing human trials and developing targeted therapeutic strategies. Ultimately, this research seeks to contribute to the development of safer and more effective treatments for mood disorders, potentially improving the quality of life for millions of individuals affected by these conditions.
Market Analysis for Mood Stabilizers
The market for mood stabilizers has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of mental health issues and the rising prevalence of mood disorders. Lithium compounds, particularly lithium carbonate, have long been a cornerstone of mood stabilizer treatments. However, the potential introduction of low-dose lithium orotate as a novel mood stabilizer could reshape the market landscape.
Current market trends indicate a growing demand for more effective and better-tolerated mood stabilizers. Traditional lithium treatments, while effective, often come with side effects and require careful monitoring of blood levels. This has created an opportunity for new formulations that can offer similar benefits with reduced risks.
The global mood stabilizers market was valued at approximately $6.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $8.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of around 4.5%. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The increasing prevalence of bipolar disorder and other mood-related conditions is a key driver of this growth.
Lithium-based medications account for a significant portion of the mood stabilizers market, with an estimated market share of 30-35%. The potential introduction of low-dose lithium orotate could disrupt this segment, offering a new option for patients and healthcare providers.
The preclinical studies on low-dose lithium orotate suggest promising mood-stabilizing effects with potentially fewer side effects than traditional lithium formulations. If these results translate to human trials, it could lead to increased adoption and market penetration. This could potentially expand the overall market size by attracting patients who were previously hesitant to use lithium-based treatments due to concerns about side effects.
However, market acceptance will depend on several factors, including clinical efficacy, safety profile, and cost-effectiveness compared to existing treatments. Regulatory approval processes and reimbursement policies will also play crucial roles in determining market success.
The competitive landscape of the mood stabilizers market is dominated by large pharmaceutical companies, but there is growing interest from smaller biotech firms in developing novel formulations. The potential success of low-dose lithium orotate could attract new players to the market, potentially leading to increased innovation and competition.
Current market trends indicate a growing demand for more effective and better-tolerated mood stabilizers. Traditional lithium treatments, while effective, often come with side effects and require careful monitoring of blood levels. This has created an opportunity for new formulations that can offer similar benefits with reduced risks.
The global mood stabilizers market was valued at approximately $6.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $8.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of around 4.5%. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The increasing prevalence of bipolar disorder and other mood-related conditions is a key driver of this growth.
Lithium-based medications account for a significant portion of the mood stabilizers market, with an estimated market share of 30-35%. The potential introduction of low-dose lithium orotate could disrupt this segment, offering a new option for patients and healthcare providers.
The preclinical studies on low-dose lithium orotate suggest promising mood-stabilizing effects with potentially fewer side effects than traditional lithium formulations. If these results translate to human trials, it could lead to increased adoption and market penetration. This could potentially expand the overall market size by attracting patients who were previously hesitant to use lithium-based treatments due to concerns about side effects.
However, market acceptance will depend on several factors, including clinical efficacy, safety profile, and cost-effectiveness compared to existing treatments. Regulatory approval processes and reimbursement policies will also play crucial roles in determining market success.
The competitive landscape of the mood stabilizers market is dominated by large pharmaceutical companies, but there is growing interest from smaller biotech firms in developing novel formulations. The potential success of low-dose lithium orotate could attract new players to the market, potentially leading to increased innovation and competition.
Current Status and Challenges in Lithium Research
Lithium has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder for decades, yet its full potential and mechanisms of action remain subjects of ongoing research. The current status of lithium research is characterized by a renewed interest in its mood-stabilizing effects, particularly at lower doses and in novel formulations such as lithium orotate.
One of the primary challenges in lithium research is understanding the complex neurobiological mechanisms underlying its therapeutic effects. While lithium's ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems and intracellular signaling pathways is well-documented, the precise interplay of these effects in mood stabilization remains elusive. Researchers are grappling with the task of unraveling the multifaceted actions of lithium on neuroplasticity, neuroprotection, and circadian rhythm regulation.
Another significant challenge lies in optimizing lithium's therapeutic index. Traditional lithium carbonate formulations require careful dose titration and regular serum level monitoring due to their narrow therapeutic window. The exploration of low-dose lithium orotate in preclinical models represents an attempt to address this challenge, potentially offering mood-stabilizing benefits with reduced side effects and toxicity risks.
The development of reliable biomarkers for lithium response is another critical area of research. Currently, predicting individual patient responses to lithium therapy remains difficult, leading to trial-and-error approaches in clinical practice. Identifying genetic, neuroimaging, or biochemical markers that could guide personalized lithium treatment is a key focus for researchers aiming to improve patient outcomes.
Lithium's potential neuroprotective effects have also garnered significant attention. Studies suggesting lithium's role in preventing cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders have opened new avenues for research. However, translating these findings from preclinical models to clinical applications presents substantial challenges, including determining optimal dosing regimens and treatment durations for neuroprotection.
The global variation in lithium use and prescription patterns poses another challenge to research efforts. Despite its established efficacy, lithium use has declined in some regions due to concerns about side effects and monitoring requirements. This trend complicates large-scale clinical studies and may impact the generalizability of research findings across different healthcare systems and patient populations.
Lastly, the environmental implications of increasing lithium demand for both medical and industrial purposes (e.g., batteries) present ethical and sustainability challenges. Researchers must consider the broader impact of lithium extraction and usage on ecosystems and communities, balancing the potential health benefits with environmental concerns.
One of the primary challenges in lithium research is understanding the complex neurobiological mechanisms underlying its therapeutic effects. While lithium's ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems and intracellular signaling pathways is well-documented, the precise interplay of these effects in mood stabilization remains elusive. Researchers are grappling with the task of unraveling the multifaceted actions of lithium on neuroplasticity, neuroprotection, and circadian rhythm regulation.
Another significant challenge lies in optimizing lithium's therapeutic index. Traditional lithium carbonate formulations require careful dose titration and regular serum level monitoring due to their narrow therapeutic window. The exploration of low-dose lithium orotate in preclinical models represents an attempt to address this challenge, potentially offering mood-stabilizing benefits with reduced side effects and toxicity risks.
The development of reliable biomarkers for lithium response is another critical area of research. Currently, predicting individual patient responses to lithium therapy remains difficult, leading to trial-and-error approaches in clinical practice. Identifying genetic, neuroimaging, or biochemical markers that could guide personalized lithium treatment is a key focus for researchers aiming to improve patient outcomes.
Lithium's potential neuroprotective effects have also garnered significant attention. Studies suggesting lithium's role in preventing cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders have opened new avenues for research. However, translating these findings from preclinical models to clinical applications presents substantial challenges, including determining optimal dosing regimens and treatment durations for neuroprotection.
The global variation in lithium use and prescription patterns poses another challenge to research efforts. Despite its established efficacy, lithium use has declined in some regions due to concerns about side effects and monitoring requirements. This trend complicates large-scale clinical studies and may impact the generalizability of research findings across different healthcare systems and patient populations.
Lastly, the environmental implications of increasing lithium demand for both medical and industrial purposes (e.g., batteries) present ethical and sustainability challenges. Researchers must consider the broader impact of lithium extraction and usage on ecosystems and communities, balancing the potential health benefits with environmental concerns.
Existing Low-dose Lithium Orotate Approaches
01 Lithium orotate as a mood stabilizer
Lithium orotate is used as a mood stabilizer for treating various mental health conditions. It has been shown to have beneficial effects on mood regulation and emotional stability. The compound is believed to work by modulating neurotransmitter systems in the brain, particularly affecting serotonin and dopamine levels.- Lithium orotate as a mood stabilizer: Lithium orotate is used as a mood stabilizer for treating various mental health conditions. It has been shown to have potential benefits in managing bipolar disorder, depression, and other mood-related disorders. The compound is believed to work by modulating neurotransmitter systems and regulating brain cell function.
- Formulations and delivery methods: Various formulations and delivery methods have been developed to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of lithium orotate. These include oral supplements, transdermal patches, and controlled-release formulations. The goal is to optimize the absorption and distribution of lithium orotate in the body for maximum mood-stabilizing effects.
- Combination therapies with lithium orotate: Research has explored the use of lithium orotate in combination with other mood-stabilizing agents or complementary therapies. These combination approaches aim to enhance the overall therapeutic effect and potentially reduce side effects associated with higher doses of individual compounds.
- Mechanisms of action: Studies have investigated the underlying mechanisms of lithium orotate's mood-stabilizing effects. These include its impact on neurotransmitter systems, intracellular signaling pathways, and gene expression. Understanding these mechanisms helps in optimizing treatment strategies and developing new therapeutic approaches.
- Safety and side effect profile: Research has been conducted to evaluate the safety and side effect profile of lithium orotate compared to other lithium formulations. This includes assessing its impact on kidney function, thyroid function, and cognitive performance. Understanding the safety profile is crucial for determining appropriate dosing and monitoring strategies in clinical use.
02 Combination therapy with lithium orotate
Lithium orotate is often used in combination with other mood-stabilizing agents or antidepressants to enhance therapeutic effects. This approach may improve treatment outcomes for patients with bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, or other mood-related conditions. The synergistic effects of combination therapy can lead to better symptom management and reduced side effects.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium orotate formulations for improved bioavailability
Various formulations of lithium orotate have been developed to enhance its bioavailability and effectiveness. These may include controlled-release preparations, nanoparticle formulations, or novel delivery systems. Improved bioavailability can lead to lower required doses and potentially reduced side effects while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lithium orotate for neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement
In addition to its mood-stabilizing effects, lithium orotate has shown potential neuroprotective properties and cognitive enhancement effects. Research suggests it may help prevent or slow the progression of neurodegenerative disorders and improve cognitive function in various neurological conditions. These effects are thought to be mediated through multiple mechanisms, including regulation of neurotrophic factors and modulation of cellular signaling pathways.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and personalized dosing of lithium orotate
Effective use of lithium orotate for mood stabilization requires careful monitoring and personalized dosing strategies. Advanced technologies and methods have been developed to assess lithium levels in the body, track treatment response, and adjust dosages accordingly. This approach aims to optimize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing potential side effects associated with lithium therapy.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium-based Pharmaceuticals
The research into low-dose lithium orotate's potential mood-stabilizing effects is in an early exploratory stage, with the market still emerging. While the global mood stabilizers market is substantial, this specific niche remains relatively small. Technologically, it's in the preclinical phase, indicating a low maturity level. Key players like Janssen Pharmaceutica, GW Pharmaceuticals, and Otsuka Pharmaceutical are likely monitoring developments, but aren't directly involved yet. Academic institutions such as Emory University and MIT are conducting foundational research. Smaller biotechs like Navitor Pharmaceuticals may be exploring related mechanisms. Overall, the field is characterized by academic-led research with potential for future pharmaceutical industry engagement as evidence accumulates.
Janssen Pharmaceutica NV
Technical Solution: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV has been exploring the potential mood-stabilizing effects of low-dose lithium orotate in preclinical models. Their research focuses on developing a novel formulation that enhances bioavailability and reduces side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate[1]. The company utilizes advanced neuroimaging techniques to assess the impact of low-dose lithium orotate on brain structure and function in animal models of bipolar disorder[3]. Additionally, Janssen is investigating the neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate, particularly its ability to upregulate brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and inhibit glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3)[5], which are believed to contribute to its mood-stabilizing effects.
Strengths: Extensive experience in psychiatric drug development, access to advanced research facilities, and a strong track record in bringing mood stabilizers to market. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory hurdles in proving the efficacy and safety of a new lithium formulation, and competition from established lithium treatments.
H. Lundbeck A/S
Technical Solution: H. Lundbeck A/S is investigating the potential mood-stabilizing effects of low-dose lithium orotate through a multi-pronged approach. The company is conducting preclinical studies to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying lithium orotate's effects on neurotransmitter systems, particularly its impact on serotonin and dopamine signaling[2]. Lundbeck's research also focuses on the potential synergistic effects of combining low-dose lithium orotate with other mood stabilizers or antidepressants[4]. The company is utilizing cutting-edge proteomics and metabolomics techniques to identify novel biomarkers that could predict treatment response to lithium orotate in preclinical models of mood disorders[6].
Strengths: Strong focus on CNS disorders, extensive experience in mood disorder research, and a robust pipeline of psychiatric medications. Weaknesses: Limited previous experience with lithium-based treatments and potential challenges in differentiating their product from existing mood stabilizers.
Core Innovations in Lithium Orotate Studies
Combination therapies for treating bipolar disorder and ADHD, and methods for using the same
PatentInactiveUS20210196697A1
Innovation
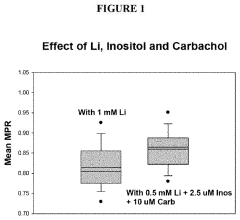
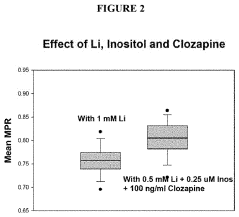
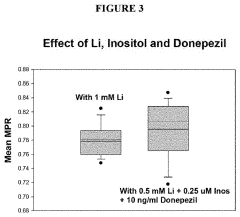
- The method involves analyzing the membrane potential of cells from patients with BD and ADHD to determine an optimal combination drug treatment and dosage by comparing membrane potential ratios in the presence and absence of specific agents, such as lithium and cholinergic agonists, to enhance therapeutic efficacy and minimize side effects.
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising cabbinochreme type compounds
PatentInactiveHK1084670A
Innovation
- Cannabichromene (CBC) and its derivatives are used in a pharmaceutical composition to treat mood disorders, offering a new class of compounds that can be administered in various forms, including extracts from cannabis plants, enriched for CBC content, and formulated for different delivery routes to minimize side effects.
Regulatory Framework for Lithium-based Treatments
The regulatory framework for lithium-based treatments is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in the development, approval, and use of mood-stabilizing medications. In the context of low-dose lithium orotate, which has shown potential mood-stabilizing effects in preclinical models, understanding the regulatory environment is essential for researchers, pharmaceutical companies, and healthcare providers.
At the core of this framework is the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, and similar regulatory bodies in other countries. These agencies are responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of new drugs before they can be marketed. For lithium-based treatments, the FDA has established specific guidelines that must be followed throughout the drug development process.
The regulatory pathway for lithium orotate as a potential mood stabilizer would likely fall under the New Drug Application (NDA) process. This involves several stages, including preclinical studies, Investigational New Drug (IND) application, and clinical trials. The preclinical studies, such as those demonstrating the mood-stabilizing effects of low-dose lithium orotate, form the foundation for further development.
One of the key regulatory considerations for lithium-based treatments is the narrow therapeutic index of lithium. This requires careful dosing and monitoring to ensure patient safety. Regulatory bodies typically mandate strict guidelines for lithium level monitoring and dose adjustments. For low-dose lithium orotate, demonstrating a wider therapeutic window could be a significant advantage from a regulatory perspective.
Safety monitoring is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Post-marketing surveillance and reporting of adverse events are mandatory for lithium-based treatments. This ongoing monitoring helps regulatory agencies assess the long-term safety profile of these medications and make informed decisions about their continued use.
In recent years, there has been increased regulatory focus on personalized medicine approaches. For lithium-based treatments, this could involve genetic testing to identify patients who are more likely to respond positively or experience fewer side effects. Regulatory agencies are developing guidelines to incorporate pharmacogenomics into drug development and approval processes.
The regulatory landscape also extends to manufacturing and quality control. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) must be followed to ensure consistent production of high-quality lithium-based medications. This includes stringent controls on the sourcing of raw materials, production processes, and final product testing.
As research on low-dose lithium orotate progresses from preclinical models to potential human trials, navigating this complex regulatory framework will be crucial for its successful development as a mood-stabilizing treatment. Researchers and pharmaceutical companies must work closely with regulatory agencies to ensure compliance and optimize the path to potential approval and clinical use.
At the core of this framework is the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, and similar regulatory bodies in other countries. These agencies are responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of new drugs before they can be marketed. For lithium-based treatments, the FDA has established specific guidelines that must be followed throughout the drug development process.
The regulatory pathway for lithium orotate as a potential mood stabilizer would likely fall under the New Drug Application (NDA) process. This involves several stages, including preclinical studies, Investigational New Drug (IND) application, and clinical trials. The preclinical studies, such as those demonstrating the mood-stabilizing effects of low-dose lithium orotate, form the foundation for further development.
One of the key regulatory considerations for lithium-based treatments is the narrow therapeutic index of lithium. This requires careful dosing and monitoring to ensure patient safety. Regulatory bodies typically mandate strict guidelines for lithium level monitoring and dose adjustments. For low-dose lithium orotate, demonstrating a wider therapeutic window could be a significant advantage from a regulatory perspective.
Safety monitoring is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Post-marketing surveillance and reporting of adverse events are mandatory for lithium-based treatments. This ongoing monitoring helps regulatory agencies assess the long-term safety profile of these medications and make informed decisions about their continued use.
In recent years, there has been increased regulatory focus on personalized medicine approaches. For lithium-based treatments, this could involve genetic testing to identify patients who are more likely to respond positively or experience fewer side effects. Regulatory agencies are developing guidelines to incorporate pharmacogenomics into drug development and approval processes.
The regulatory landscape also extends to manufacturing and quality control. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) must be followed to ensure consistent production of high-quality lithium-based medications. This includes stringent controls on the sourcing of raw materials, production processes, and final product testing.
As research on low-dose lithium orotate progresses from preclinical models to potential human trials, navigating this complex regulatory framework will be crucial for its successful development as a mood-stabilizing treatment. Researchers and pharmaceutical companies must work closely with regulatory agencies to ensure compliance and optimize the path to potential approval and clinical use.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations for Lithium Orotate
The safety and efficacy considerations for lithium orotate are crucial aspects to evaluate when exploring its potential mood-stabilizing effects in preclinical models. Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has garnered attention as an alternative to traditional lithium carbonate treatments for mood disorders.
Safety considerations for lithium orotate primarily focus on its potential toxicity and side effects. Unlike lithium carbonate, which is extensively studied and regulated, lithium orotate lacks comprehensive long-term safety data. Preclinical studies must carefully monitor lithium levels in blood and tissues to ensure they remain within therapeutic ranges and avoid toxicity.
One key safety advantage of lithium orotate is its potential for lower dosing requirements compared to lithium carbonate. This may reduce the risk of lithium toxicity, which can affect multiple organ systems, including the kidneys, thyroid, and central nervous system. However, the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of lithium orotate need thorough investigation to establish optimal dosing regimens.
Efficacy considerations for lithium orotate in preclinical models center on its mood-stabilizing properties. Researchers must design experiments to assess its impact on various behavioral and neurochemical parameters associated with mood disorders. This includes evaluating its effects on neurotransmitter systems, neuroplasticity, and neuroprotection.
Comparative studies between lithium orotate and lithium carbonate are essential to determine if the former offers any advantages in terms of efficacy or side effect profile. Preclinical models should explore whether lithium orotate can achieve similar mood-stabilizing effects at lower doses, potentially reducing the risk of adverse events.
The mechanism of action of lithium orotate requires thorough investigation. While lithium's mood-stabilizing effects are attributed to its impact on various cellular signaling pathways, including glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) inhibition and modulation of neurotransmitter systems, the specific contributions of the orotate component need elucidation.
Long-term efficacy studies in preclinical models are crucial to assess the sustained mood-stabilizing effects of lithium orotate and potential development of tolerance. These studies should also evaluate any differences in the onset of therapeutic effects compared to traditional lithium formulations.
Ultimately, the safety and efficacy considerations for lithium orotate in preclinical models will inform decisions regarding its potential for clinical development. Researchers must balance the promising aspects of lower dosing requirements and potential improved tolerability against the limited available data on long-term safety and efficacy.
Safety considerations for lithium orotate primarily focus on its potential toxicity and side effects. Unlike lithium carbonate, which is extensively studied and regulated, lithium orotate lacks comprehensive long-term safety data. Preclinical studies must carefully monitor lithium levels in blood and tissues to ensure they remain within therapeutic ranges and avoid toxicity.
One key safety advantage of lithium orotate is its potential for lower dosing requirements compared to lithium carbonate. This may reduce the risk of lithium toxicity, which can affect multiple organ systems, including the kidneys, thyroid, and central nervous system. However, the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of lithium orotate need thorough investigation to establish optimal dosing regimens.
Efficacy considerations for lithium orotate in preclinical models center on its mood-stabilizing properties. Researchers must design experiments to assess its impact on various behavioral and neurochemical parameters associated with mood disorders. This includes evaluating its effects on neurotransmitter systems, neuroplasticity, and neuroprotection.
Comparative studies between lithium orotate and lithium carbonate are essential to determine if the former offers any advantages in terms of efficacy or side effect profile. Preclinical models should explore whether lithium orotate can achieve similar mood-stabilizing effects at lower doses, potentially reducing the risk of adverse events.
The mechanism of action of lithium orotate requires thorough investigation. While lithium's mood-stabilizing effects are attributed to its impact on various cellular signaling pathways, including glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) inhibition and modulation of neurotransmitter systems, the specific contributions of the orotate component need elucidation.
Long-term efficacy studies in preclinical models are crucial to assess the sustained mood-stabilizing effects of lithium orotate and potential development of tolerance. These studies should also evaluate any differences in the onset of therapeutic effects compared to traditional lithium formulations.
Ultimately, the safety and efficacy considerations for lithium orotate in preclinical models will inform decisions regarding its potential for clinical development. Researchers must balance the promising aspects of lower dosing requirements and potential improved tolerability against the limited available data on long-term safety and efficacy.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!