Biodegradable Plastics for Eco-Friendly & Circular Packaging
Biodegradable Plastics Evolution and Objectives
Biodegradable plastics have emerged as a pivotal component in the quest for eco-friendly and circular packaging solutions. The evolution of biodegradable plastics can be traced back to early innovations in the polymer industry aimed at reducing the environmental impact of traditional plastics. These biodegradable materials are designed to break down naturally by microorganisms into benign compounds, contrasting sharply with conventional plastics that can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, leading to severe ecological and health issues.
Over the past decades, the development of biodegradable plastics has seen significant advancements. Initially, efforts focused on producing bioplastics from agricultural waste and renewable resources, such as starches, cellulose, and other plant-derived materials. The goal was to minimize dependency on petrochemical sources and enhance the biodegradability of the products. Scientists and researchers have continually worked to improve the mechanical properties, durability, and degradation rates of these materials, making them increasingly viable for diverse packaging applications.
One major trend in the evolution of biodegradable plastics is the shift towards incorporating additives that can accelerate the degradation process without compromising product integrity. Vendors and developers are exploring innovative ways to use enzymatic processes and microbial action to catalyze the breakdown of polymers under various environmental conditions. This has included the use of biopolymers that are engineered to degrade effectively in both aerobic and anaerobic environments, expanding their applicability across different waste management systems, including composting and landfill scenarios.
The objectives of developing biodegradable plastics for packaging are multifaceted. Primarily, they aim to reduce plastic pollution and its damaging impact on marine and terrestrial ecosystems. By creating packaging materials that biologically disintegrate, stakeholders hope to mitigate the long-term environmental harm caused by plastic waste accumulation. Additionally, these innovations seek to lessen the carbon footprint associated with plastic production and disposal, thereby contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Another important objective is to promote circular economy practices. Biodegradable plastics can be part of larger sustainable practices that emphasize resource efficiency and waste reduction. The focus is on creating a closed-loop system where packaging materials are cycled back into production and consumption processes without adverse environmental impact, thus maintaining the value and function of the products over time.
In conclusion, biodegradable plastics have evolved from initial experimental materials to integral components of sustainable packaging strategies. The technological advancements in this field reflect a broader commitment to environmental conservation and resource efficiency, aligning with global sustainable development goals. By achieving the outlined objectives, biodegradable plastics are set to revolutionize packaging practices, offering a crucial step towards a more sustainable future.
Eco-Friendly Packaging Market Analysis
The eco-friendly packaging market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness and stringent regulations on plastic waste. This market segment encompasses a wide range of sustainable packaging solutions, including biodegradable plastics, recyclable materials, and compostable alternatives.
The global eco-friendly packaging market was valued at approximately $245 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $380 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising demand for sustainable packaging solutions across various industries, including food and beverage, personal care, and healthcare.
Consumer preferences have shifted towards environmentally responsible products, with a growing number of consumers willing to pay a premium for eco-friendly packaging. A survey conducted in 2022 revealed that 74% of consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable packaging options, highlighting the market's potential for further expansion.
The food and beverage industry remains the largest end-user segment for eco-friendly packaging, accounting for over 40% of the market share. This is due to the increasing adoption of biodegradable and compostable materials for food packaging, driven by consumer demand and regulatory pressures to reduce single-use plastics.
Geographically, Europe leads the eco-friendly packaging market, followed by North America and Asia-Pacific. Europe's dominance is attributed to stringent environmental regulations and high consumer awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental concerns in countries like China and India.
Key market trends include the development of innovative biodegradable materials, such as PLA (polylactic acid) and PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates), which offer improved performance and biodegradability compared to traditional plastics. Additionally, there is a growing focus on circular economy principles, with companies investing in closed-loop recycling systems and packaging designs that facilitate easy recycling.
Challenges in the eco-friendly packaging market include higher production costs compared to conventional packaging materials, limited availability of raw materials, and the need for improved waste management infrastructure to support proper disposal and recycling of biodegradable plastics.
Current Biodegradable Plastics Challenges
Despite significant advancements in biodegradable plastics technology, several challenges persist in their widespread adoption for eco-friendly and circular packaging. One of the primary obstacles is the higher production cost compared to conventional plastics. The complex manufacturing processes and specialized materials required for biodegradable plastics result in increased expenses, making them less economically viable for many businesses.
Another major challenge is the limited performance capabilities of current biodegradable plastics. Many biodegradable alternatives struggle to match the durability, flexibility, and barrier properties of traditional plastics. This limitation restricts their use in certain packaging applications, particularly those requiring long shelf life or protection against moisture and oxygen.
The inconsistent degradation rates of biodegradable plastics pose a significant hurdle. Depending on environmental conditions, these materials may degrade too quickly, compromising product integrity, or too slowly, failing to provide the intended environmental benefits. This variability makes it difficult to predict and control the lifecycle of biodegradable packaging in different disposal scenarios.
The lack of standardized testing methods and certification processes for biodegradability claims further complicates the landscape. This absence of uniformity leads to confusion among consumers and businesses, hindering the adoption and proper disposal of biodegradable plastics.
Infrastructure challenges also impede the widespread use of biodegradable plastics. Many existing recycling and waste management systems are not equipped to handle these materials effectively. The mixing of biodegradable plastics with conventional plastics can contaminate recycling streams, reducing the quality and value of recycled materials.
Consumer awareness and behavior present another obstacle. Many consumers lack understanding of proper disposal methods for biodegradable plastics, often mistakenly believing that these materials can be composted in home systems or will degrade quickly in any environment. This misconception can lead to improper disposal and negate the potential environmental benefits.
The sourcing of raw materials for biodegradable plastics raises sustainability concerns. While many biodegradable plastics are derived from renewable resources, the large-scale production of these materials could potentially compete with food crops for agricultural land, leading to ethical and environmental dilemmas.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding biodegradable plastics remains complex and often inconsistent across different regions. The lack of clear, unified regulations and standards creates uncertainty for manufacturers and hinders investment in research and development of improved biodegradable plastic technologies.
Existing Biodegradable Plastic Solutions
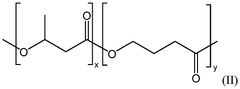
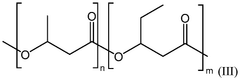
01 Composition of biodegradable plastics
Biodegradable plastics are composed of materials that can break down naturally in the environment. These plastics often include natural polymers or synthetic polymers with biodegradable additives. The composition can be tailored to achieve specific biodegradation rates and properties suitable for various applications.- Composition of biodegradable plastics: Biodegradable plastics are composed of materials that can break down naturally in the environment. These plastics often include natural polymers or synthetic polymers with biodegradable additives. The composition can be tailored to achieve specific biodegradation rates and properties, making them suitable for various applications while reducing environmental impact.
- Biodegradation mechanisms and testing methods: Understanding the mechanisms of biodegradation is crucial for developing effective biodegradable plastics. Various testing methods are employed to assess biodegradability, including composting tests, soil burial tests, and aquatic biodegradation tests. These methods help determine the rate and extent of biodegradation under different environmental conditions.
- Enhancing biodegradability through additives: Additives play a significant role in enhancing the biodegradability of plastics. These additives can include enzymes, microorganisms, or other compounds that accelerate the breakdown of polymer chains. By incorporating these additives, the biodegradation process can be optimized for specific environmental conditions and applications.
- Applications of biodegradable plastics: Biodegradable plastics find applications in various industries, including packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods. These materials are particularly useful in single-use products and packaging, where traditional plastics pose significant environmental challenges. The development of biodegradable plastics for specific applications considers factors such as required lifespan, disposal conditions, and performance characteristics.
- Environmental impact and regulations: The environmental impact of biodegradable plastics is a critical consideration in their development and use. Regulations and standards are being established to ensure that biodegradable plastics meet specific criteria for biodegradability and do not contribute to microplastic pollution. Life cycle assessments are conducted to evaluate the overall environmental impact of these materials compared to traditional plastics.
02 Biodegradation mechanisms and testing methods
Understanding the mechanisms of biodegradation is crucial for developing effective biodegradable plastics. Various testing methods are employed to assess biodegradability, including standardized tests for measuring the rate of decomposition in different environments such as soil, compost, or marine conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Enhancing biodegradability through additives
Additives can be incorporated into plastic formulations to enhance their biodegradability. These additives may include enzymes, microorganisms, or other compounds that accelerate the breakdown of the plastic material when exposed to specific environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of biodegradable plastics
Biodegradable plastics find applications in various industries, including packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods. These materials are designed to provide the functionality of traditional plastics while offering environmental benefits through their ability to decompose naturally.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental impact and regulations
The environmental impact of biodegradable plastics is a subject of ongoing research and debate. Regulations and standards are being developed to ensure that biodegradable plastics meet specific criteria for decomposition and do not contribute to environmental pollution. These regulations aim to promote the responsible use and disposal of biodegradable plastics.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Packaging Industry
The biodegradable plastics market for eco-friendly and circular packaging is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The global market size is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, but still faces challenges in performance and cost-effectiveness. Companies like Novamont SpA, Danimer IPCo LLC, and CJ CheilJedang Corp. are at the forefront, developing innovative solutions. Academic institutions such as Tsinghua University and South China University of Technology are contributing to research advancements. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established players and startups vying for market share, indicating a dynamic and evolving industry.
Danimer IPCo LLC
CJ CheilJedang Corp.
Innovative Biodegradable Polymer Technologies
- A biodegradable plasticizer comprising bio-molecules and monomers or oligomers of biodegradable polymers, thermal-treated between 50 to 160°C, is used to enhance the tenacity, impact-tolerance, adhesion, and ductility of biodegradable materials, allowing for improved properties such as water-resistance, oil-resistance, and microwave-tolerance, and enabling thermal-compression adhesion between substrates.
- Development of biodegradable and compostable bioplastic compositions made from non-petrochemically derived polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) polymers, organic biomass, and flow agents, which are suitable for semi-rigid packaging and can be processed using blow molding and thermoforming techniques.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of biodegradable plastics for eco-friendly and circular packaging is a critical component in evaluating their sustainability and potential to address plastic pollution. Biodegradable plastics offer promising alternatives to conventional plastics, potentially reducing the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and ecosystems.
One of the primary environmental benefits of biodegradable plastics is their ability to decompose naturally, reducing long-term environmental persistence. Unlike traditional plastics that can persist for hundreds of years, biodegradable plastics can break down into harmless substances within months to years, depending on the specific material and environmental conditions. This characteristic significantly reduces the risk of plastic pollution in marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
However, the environmental impact of biodegradable plastics is not uniformly positive. The production of these materials often requires agricultural resources, potentially leading to land-use changes and competition with food crops. Additionally, the energy and water consumption during manufacturing processes must be carefully considered to ensure a net positive environmental impact.
The end-of-life management of biodegradable plastics presents both opportunities and challenges. While they can be composted in industrial facilities, not all regions have the necessary infrastructure to process these materials effectively. Improper disposal or mixing with conventional plastic recycling streams can lead to contamination and reduced recycling efficiency.
Lifecycle assessments (LCAs) of biodegradable plastics reveal varying results depending on the specific material and application. Some biodegradable plastics show lower carbon footprints compared to their petroleum-based counterparts, particularly when considering end-of-life scenarios. However, others may have higher environmental impacts during production, offsetting some of the benefits gained from biodegradability.
The potential for biodegradable plastics to contribute to a circular economy is significant. By designing packaging materials that can be safely returned to the environment or used as feedstock for new products, these materials align with circular economy principles. This approach can help reduce reliance on virgin resources and minimize waste generation.
It is crucial to consider the broader systemic impacts of transitioning to biodegradable plastics. While they offer solutions to certain environmental challenges, they are not a panacea for all plastic-related issues. Effective implementation requires careful consideration of local waste management capabilities, consumer behavior, and potential unintended consequences such as increased littering due to misconceptions about biodegradability.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of biodegradable plastics for eco-friendly and circular packaging reveals a complex picture. While these materials offer significant potential to reduce plastic pollution and support circular economy principles, their overall environmental impact depends on various factors throughout their lifecycle. Continued research and development are necessary to optimize their performance and minimize negative environmental impacts.
Regulatory Framework for Biodegradable Materials
The regulatory framework for biodegradable materials plays a crucial role in shaping the development, production, and use of eco-friendly packaging solutions. As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, governments and international organizations are establishing comprehensive guidelines and standards to ensure the effectiveness and safety of biodegradable plastics.
At the forefront of these regulations is the European Union (EU), which has implemented stringent requirements through its Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive. This directive sets clear targets for the recyclability and biodegradability of packaging materials, encouraging manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices. The EU has also introduced the Single-Use Plastics Directive, which specifically addresses the environmental impact of disposable plastic items and promotes the use of biodegradable alternatives.
In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has established the Green Guides, which provide guidelines for environmental marketing claims, including those related to biodegradability. These guidelines aim to prevent greenwashing and ensure that consumers receive accurate information about the environmental attributes of products.
International standards organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), have developed specific standards for biodegradable plastics. ISO 17088, for instance, outlines the specifications for compostable plastics, providing a framework for testing and certifying biodegradable materials.
Many countries have implemented their own certification systems for biodegradable materials. For example, Germany's DIN CERTCO and Belgium's OK Compost label are widely recognized certifications that validate the biodegradability and compostability of packaging materials. These certifications often require rigorous testing to ensure that materials break down within specified timeframes and under specific environmental conditions.
Regulatory bodies are also addressing the potential environmental impacts of biodegradable plastics. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has published guidelines on the use of biodegradable plastics, emphasizing the importance of proper waste management infrastructure to support their effective decomposition.
As the field of biodegradable plastics continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address new challenges and opportunities. There is a growing focus on lifecycle assessments to evaluate the overall environmental impact of biodegradable materials, considering factors such as production energy, water usage, and end-of-life disposal options.
The regulatory landscape for biodegradable materials is dynamic, with ongoing discussions about standardization, labeling requirements, and disposal methods. As research advances and new materials are developed, it is likely that regulations will continue to evolve to ensure that biodegradable plastics contribute effectively to circular economy goals and environmental protection.