Biodegradable Plastics in Food Processing: Safer for Environment
Biodegradable Plastics in Food Processing: Background and Objectives
Biodegradable plastics have emerged as a promising solution to address the growing environmental concerns associated with conventional plastic waste in the food processing industry. The development of these materials represents a significant shift in packaging technology, aiming to reduce the long-term environmental impact of food packaging while maintaining food safety and quality standards.
The evolution of biodegradable plastics in food processing can be traced back to the late 20th century when awareness of plastic pollution began to rise. Initially, the focus was on creating materials that could break down more quickly than traditional plastics. However, early attempts often resulted in products that either degraded too slowly or compromised food preservation capabilities.
As environmental concerns intensified, research efforts expanded to explore a wider range of biodegradable materials derived from renewable resources. This led to the development of various bioplastics, including those made from polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), and starch-based compounds. These materials offered the potential to decompose naturally in the environment without leaving harmful residues.
The primary objective of research in this field is to create biodegradable plastics that can effectively replace conventional plastics in food processing applications while meeting stringent food safety regulations. This involves developing materials that provide adequate barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and microorganisms to ensure food preservation and extend shelf life.
Another crucial goal is to improve the mechanical properties of biodegradable plastics to match the performance of traditional plastics in various food processing and packaging scenarios. This includes enhancing tensile strength, flexibility, and heat resistance to withstand the rigors of food processing, transportation, and storage.
Researchers are also focusing on optimizing the biodegradation process of these materials. The aim is to ensure that they break down completely within a reasonable timeframe under various environmental conditions, including industrial composting facilities and natural settings, without producing harmful byproducts.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant challenge in the widespread adoption of biodegradable plastics in food processing. Therefore, an important objective is to develop economically viable production methods that can compete with conventional plastic manufacturing processes. This involves improving production efficiency, exploring new raw material sources, and scaling up manufacturing capabilities.
As the field progresses, there is an increasing emphasis on creating circular economy solutions. This involves designing biodegradable plastics that not only decompose safely but also contribute to nutrient cycles or can be efficiently recycled into new materials, further reducing their environmental footprint.
Market Demand Analysis for Eco-friendly Food Packaging
The demand for eco-friendly food packaging has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness and consumer preferences for sustainable products. This trend is particularly evident in the food processing industry, where traditional plastic packaging has long been a major contributor to environmental pollution.
Market research indicates that the global biodegradable packaging market is expanding rapidly, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 17% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is fueled by stringent government regulations on single-use plastics, rising consumer consciousness about environmental issues, and the food industry's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint.
Consumer surveys reveal that a growing number of shoppers are willing to pay a premium for products packaged in environmentally friendly materials. This shift in consumer behavior is prompting food manufacturers and retailers to adopt biodegradable packaging solutions to meet market demands and enhance brand image.
The food processing sector, in particular, has shown a strong interest in biodegradable plastics due to their potential to address food safety concerns while minimizing environmental impact. These materials offer benefits such as extended shelf life for perishable goods, reduced risk of chemical leaching, and improved end-of-life disposal options.
Key market segments driving the demand for eco-friendly food packaging include fresh produce, dairy products, bakery items, and ready-to-eat meals. Each of these segments presents unique challenges and opportunities for biodegradable plastic applications, ranging from moisture resistance requirements to temperature stability needs.
Industry analysts predict that the adoption of biodegradable plastics in food processing will continue to accelerate as technological advancements improve material performance and cost-effectiveness. This trend is expected to reshape the competitive landscape of the packaging industry, with companies investing heavily in research and development to gain a competitive edge.
The market demand for eco-friendly food packaging is also influenced by regional factors. Developed economies in North America and Europe are currently leading the adoption of biodegradable plastics, while emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing rapid growth potential as environmental regulations tighten and consumer awareness increases.
As the food processing industry seeks safer and more sustainable packaging solutions, the market for biodegradable plastics is poised for substantial expansion. This growth presents significant opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and market differentiation across the entire food value chain.
Current State and Challenges in Biodegradable Plastics Technology
The current state of biodegradable plastics technology in food processing is marked by significant advancements, yet it faces several challenges. Globally, there is a growing adoption of biodegradable plastics in food packaging and processing, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. These materials are designed to decompose naturally, reducing the long-term environmental impact associated with traditional plastics.
One of the primary technological achievements in this field is the development of PLA (Polylactic Acid), a biodegradable polymer derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. PLA has gained traction in food packaging applications due to its biodegradability and compatibility with food contact. However, its widespread adoption is hindered by higher production costs compared to conventional plastics and limitations in heat resistance and barrier properties.
Another significant development is the creation of PHAs (Polyhydroxyalkanoates), which are produced by microorganisms and offer excellent biodegradability. PHAs show promise in various food packaging applications but face challenges in scaling up production and reducing costs.
Despite these advancements, the biodegradable plastics industry confronts several technical hurdles. One major challenge is achieving comparable performance to traditional plastics in terms of durability, barrier properties, and shelf life extension for food products. Many biodegradable plastics struggle to provide the same level of protection against moisture, oxygen, and light, which are crucial for preserving food quality.
The degradation process of these materials also presents challenges. While biodegradability is the key selling point, controlling the rate and conditions of degradation to align with practical waste management systems remains problematic. Some biodegradable plastics require specific industrial composting conditions that are not widely available, limiting their real-world biodegradability.
Furthermore, there is a lack of standardization in testing and certification processes for biodegradable plastics, leading to confusion among consumers and manufacturers. This absence of clear, universally accepted standards hampers the industry's growth and consumer trust.
The food processing industry also faces challenges in integrating biodegradable plastics into existing manufacturing and packaging processes. Many current production lines are optimized for traditional plastics, and switching to biodegradable alternatives often requires significant modifications and investments.
Lastly, the environmental impact of biodegradable plastics throughout their lifecycle remains a subject of debate. While they offer benefits in end-of-life scenarios, the production of some biodegradable plastics can be energy-intensive and may compete with food crops for agricultural resources, raising sustainability concerns.
Existing Biodegradable Plastic Solutions for Food Processing
01 Biodegradable plastic compositions
Development of biodegradable plastic compositions that break down naturally in the environment, reducing long-term pollution. These compositions often include natural polymers or modified synthetic polymers that can be decomposed by microorganisms.- Biodegradable plastic compositions: Development of biodegradable plastic compositions that break down naturally in the environment, reducing long-term pollution. These compositions often include natural polymers or modified synthetic polymers that can be decomposed by microorganisms.
- Environmental safety assessment methods: Methods for evaluating the environmental safety of biodegradable plastics, including toxicity tests, biodegradation rate measurements, and impact assessments on ecosystems. These methods help ensure that biodegradable plastics do not introduce harmful substances into the environment during decomposition.
- Biodegradable plastic applications: Specific applications of biodegradable plastics in various industries, such as packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods. These applications aim to replace conventional plastics with environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain similar performance characteristics.
- Additives for enhancing biodegradability: Development of additives that can be incorporated into plastic formulations to enhance their biodegradability. These additives may include enzymes, pro-oxidants, or other compounds that accelerate the breakdown of plastic materials in natural environments.
- Recycling and end-of-life management: Strategies and technologies for recycling biodegradable plastics and managing their end-of-life disposal. This includes methods for separating biodegradable plastics from other waste streams, composting facilities designed for biodegradable materials, and systems for ensuring proper disposal to maximize environmental benefits.
02 Environmental safety assessment methods
Methods for evaluating the environmental safety of biodegradable plastics, including toxicity tests, biodegradation rate measurements, and impact assessments on ecosystems. These methods help ensure that biodegradable plastics do not introduce harmful substances into the environment during decomposition.Expand Specific Solutions03 Biodegradable plastic applications
Specific applications of biodegradable plastics in various industries, such as packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods. These applications aim to replace conventional plastics with environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain similar performance characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Additives for enhancing biodegradability
Development of additives that can be incorporated into plastic formulations to enhance their biodegradability. These additives may include enzymes, pro-oxidants, or other compounds that accelerate the breakdown of plastic materials in natural environments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recycling and end-of-life management
Strategies and technologies for recycling biodegradable plastics and managing their end-of-life disposal. This includes composting systems, waste sorting methods, and processes for recovering valuable materials from biodegraded plastic waste.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Biodegradable Food Packaging Market
The research on biodegradable plastics in food processing is in a growth phase, with increasing market size due to environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The global biodegradable plastics market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like BASF SE, Kaneka Corp., and Carbiolice SAS leading in innovation. Research institutions such as the Industrial Technology Research Institute and universities like North Carolina State University are contributing to technological advancements. The involvement of major chemical companies like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. indicates the industry's maturity and potential. However, challenges remain in scaling production and improving performance to match traditional plastics, suggesting ongoing opportunities for innovation and market growth.
Chocal Packaging Solutions GmbH
Smartsolve Industries LLC
Core Innovations in Biodegradable Polymer Science
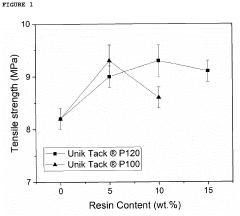
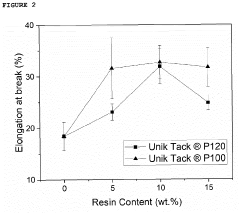
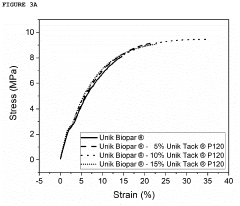
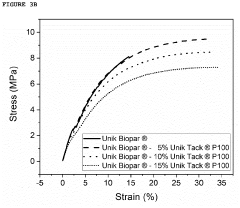
- Incorporating gum rosin ester derivatives with a softening point between 80-120 °C and low acid number into starch-based biodegradable compositions, which act as compatibilizers and plasticizers, enhancing the mechanical and thermal properties and processability of the blends.
- A biodegradable plasticizer comprising bio-molecules and monomers or oligomers of biodegradable polymers, thermal-treated between 50 to 160°C, is used to enhance the tenacity, impact-tolerance, adhesion, and ductility of biodegradable materials, allowing for improved properties such as water-resistance, oil-resistance, and microwave-tolerance, and enabling thermal-compression adhesion between substrates.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Biodegradable Plastics
The environmental impact assessment of biodegradable plastics in food processing is a critical aspect of evaluating their potential as a safer alternative to conventional plastics. These materials offer promising solutions to reduce plastic pollution, but their full lifecycle effects must be carefully examined.
Biodegradable plastics used in food processing can significantly reduce the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and oceans. Unlike traditional plastics that persist for hundreds of years, biodegradable alternatives break down into natural compounds within months or years, depending on environmental conditions. This decomposition process can help mitigate the long-term environmental damage caused by plastic pollution.
However, the environmental benefits of biodegradable plastics are not without complexities. The production of these materials often requires agricultural resources, which can lead to land-use changes and potential competition with food crops. The cultivation of feedstocks for biodegradable plastics may involve the use of pesticides and fertilizers, potentially impacting soil and water quality.
The degradation process of biodegradable plastics in various environments is another crucial consideration. While they break down more readily than conventional plastics, the rate and completeness of degradation can vary significantly depending on factors such as temperature, moisture, and microbial activity. In some cases, incomplete degradation may result in microplastic particles, which can have their own environmental implications.
Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with the production of biodegradable plastics must also be evaluated. Some biodegradable plastics may require more energy-intensive manufacturing processes compared to traditional plastics, potentially offsetting some of their environmental benefits. Life cycle assessments are essential to quantify the overall carbon footprint of these materials.
The end-of-life management of biodegradable plastics presents both opportunities and challenges. While they offer the potential for composting and integration into organic waste streams, proper sorting and processing infrastructure is crucial. Mismanagement or mixing with conventional plastics can compromise recycling efforts and reduce the environmental benefits of biodegradable alternatives.
In the context of food processing, the interaction between biodegradable plastics and food products must be carefully assessed. Potential migration of compounds from the packaging to food items, as well as the impact on food quality and safety, are important considerations in evaluating the overall environmental and health implications of these materials.
Regulatory Framework for Biodegradable Food Packaging
The regulatory framework for biodegradable food packaging is a critical aspect of the broader effort to promote safer environmental practices in the food processing industry. As governments and international organizations increasingly recognize the environmental impact of conventional plastics, they are developing and implementing regulations to encourage the use of biodegradable alternatives.
At the forefront of these regulatory efforts is the European Union, which has introduced comprehensive legislation to address plastic waste and promote sustainable packaging solutions. The EU Directive on Single-Use Plastics, implemented in 2019, sets ambitious targets for reducing plastic waste and encourages the use of biodegradable materials in food packaging. This directive requires member states to ensure that certain single-use plastic products are replaced with more sustainable alternatives, including biodegradable options.
In the United States, the regulatory landscape is more fragmented, with individual states taking the lead in implementing biodegradable packaging regulations. California, for instance, has enacted strict laws governing the labeling and disposal of biodegradable plastics, requiring manufacturers to provide clear evidence of biodegradability before making such claims on their products.
International standards organizations play a crucial role in establishing guidelines for biodegradable food packaging. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several standards, including ISO 17088, which specifies requirements for the labeling of plastics as compostable. These standards provide a framework for manufacturers and regulators to ensure the authenticity of biodegradability claims.
Certification systems have also emerged to support the regulatory framework. Organizations such as the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) in North America and the European Bioplastics Association offer certification programs that verify the biodegradability and compostability of packaging materials. These certifications help manufacturers demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and build consumer trust.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the entire lifecycle of biodegradable food packaging. This includes not only the production and use phases but also the disposal and decomposition processes. Regulations are being developed to ensure that biodegradable plastics can be effectively processed in existing waste management systems, addressing concerns about the potential contamination of recycling streams.
As the field of biodegradable plastics continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to keep pace with technological advancements. There is a growing emphasis on harmonizing regulations across different regions to facilitate international trade and ensure consistent environmental protection standards. This harmonization effort includes aligning definitions, testing methods, and labeling requirements for biodegradable food packaging.