Rice Bran Oil By-products Valorization: Defatted Meal and Bran Extract Applications
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Rice Bran Oil By-products Background and Objectives
Rice bran oil, a by-product of rice milling, has gained significant attention in recent decades due to its nutritional properties and health benefits. The extraction process of rice bran oil generates substantial amounts of defatted rice bran and other by-products that have traditionally been underutilized or discarded as waste. This represents both an environmental challenge and a missed economic opportunity in the rice processing value chain.
The evolution of rice bran oil technology dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the 1980s and 1990s when improved extraction methods were developed. Initially, these by-products were primarily used as animal feed or fertilizer, representing low-value applications. However, research has progressively revealed the rich composition of these materials, containing valuable bioactive compounds including proteins, antioxidants, phytosterols, gamma-oryzanol, and dietary fiber.
The global rice production exceeds 500 million tons annually, with approximately 40 million tons of rice bran generated as a by-product. Only a small fraction of this bran is currently processed for oil extraction, leaving enormous potential for value addition. The technological trajectory has been moving from simple extraction processes toward more sophisticated fractionation and biorefinery approaches that can isolate multiple valuable components.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate the potential valorization pathways for rice bran oil by-products, specifically focusing on defatted meal and bran extract applications. This includes identifying novel processing technologies, characterizing bioactive compounds, and exploring high-value applications in food, nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Secondary objectives include assessing the economic feasibility of implementing these valorization strategies at industrial scale, evaluating the environmental benefits through life cycle assessment, and identifying potential regulatory hurdles for novel applications. The research also aims to map the technological readiness levels of different valorization approaches to guide strategic R&D investments.
The ultimate goal is to transform what is currently considered a low-value by-product stream into a source of high-value ingredients and materials, thereby enhancing the sustainability and profitability of rice processing operations. This aligns with broader industry trends toward circular economy principles and zero-waste manufacturing, as well as increasing consumer demand for natural, plant-based ingredients with demonstrated health benefits.
The evolution of rice bran oil technology dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the 1980s and 1990s when improved extraction methods were developed. Initially, these by-products were primarily used as animal feed or fertilizer, representing low-value applications. However, research has progressively revealed the rich composition of these materials, containing valuable bioactive compounds including proteins, antioxidants, phytosterols, gamma-oryzanol, and dietary fiber.
The global rice production exceeds 500 million tons annually, with approximately 40 million tons of rice bran generated as a by-product. Only a small fraction of this bran is currently processed for oil extraction, leaving enormous potential for value addition. The technological trajectory has been moving from simple extraction processes toward more sophisticated fractionation and biorefinery approaches that can isolate multiple valuable components.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate the potential valorization pathways for rice bran oil by-products, specifically focusing on defatted meal and bran extract applications. This includes identifying novel processing technologies, characterizing bioactive compounds, and exploring high-value applications in food, nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Secondary objectives include assessing the economic feasibility of implementing these valorization strategies at industrial scale, evaluating the environmental benefits through life cycle assessment, and identifying potential regulatory hurdles for novel applications. The research also aims to map the technological readiness levels of different valorization approaches to guide strategic R&D investments.
The ultimate goal is to transform what is currently considered a low-value by-product stream into a source of high-value ingredients and materials, thereby enhancing the sustainability and profitability of rice processing operations. This aligns with broader industry trends toward circular economy principles and zero-waste manufacturing, as well as increasing consumer demand for natural, plant-based ingredients with demonstrated health benefits.
Market Analysis for Valorized Rice Bran Products
The global market for valorized rice bran products has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health benefits and the food industry's shift towards sustainable ingredients. The rice bran oil by-products market, specifically defatted meal and bran extracts, is projected to reach $2.3 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2022.
The food and beverage sector represents the largest application segment, accounting for approximately 45% of the total market share. Defatted rice bran meal is increasingly being incorporated into bakery products, breakfast cereals, and plant-based protein formulations due to its high protein content (15-20%) and favorable amino acid profile. Market research indicates that consumer demand for clean-label, plant-based protein ingredients has created a premium segment for rice bran derivatives.
Nutraceutical and dietary supplement applications constitute the fastest-growing segment, with a growth rate of 8.2% annually. Rice bran extracts rich in bioactive compounds such as γ-oryzanol, tocotrienols, and phytosterols are being formulated into supplements targeting cholesterol management, antioxidant support, and immune health. The global nutraceutical market's expansion has created substantial opportunities for specialized rice bran extracts with clinically validated health benefits.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the market with 42% share, followed by North America (28%) and Europe (21%). Japan and South Korea lead in high-value applications, particularly in functional foods and cosmeceuticals. The North American market shows strong growth in organic and non-GMO certified rice bran products, with premium pricing structures reflecting consumer willingness to pay for sustainable, health-promoting ingredients.
The animal feed sector represents another significant market segment, valued at $380 million in 2022. Defatted rice bran meal serves as a cost-effective protein source in poultry, aquaculture, and livestock feed formulations. The increasing restrictions on antibiotic growth promoters have created new opportunities for rice bran derivatives as natural feed additives with prebiotic properties.
Emerging applications in cosmetics and personal care products are creating new value streams, with rice bran extracts being incorporated into anti-aging formulations, skin brightening products, and natural exfoliants. This segment is growing at 7.5% annually, driven by consumer preference for natural, plant-derived cosmetic ingredients.
Market challenges include price volatility due to fluctuating rice production, quality standardization issues, and competition from alternative plant-based ingredients. However, technological advancements in extraction methods and increasing vertical integration among processors are gradually addressing these challenges, improving market stability and product consistency.
The food and beverage sector represents the largest application segment, accounting for approximately 45% of the total market share. Defatted rice bran meal is increasingly being incorporated into bakery products, breakfast cereals, and plant-based protein formulations due to its high protein content (15-20%) and favorable amino acid profile. Market research indicates that consumer demand for clean-label, plant-based protein ingredients has created a premium segment for rice bran derivatives.
Nutraceutical and dietary supplement applications constitute the fastest-growing segment, with a growth rate of 8.2% annually. Rice bran extracts rich in bioactive compounds such as γ-oryzanol, tocotrienols, and phytosterols are being formulated into supplements targeting cholesterol management, antioxidant support, and immune health. The global nutraceutical market's expansion has created substantial opportunities for specialized rice bran extracts with clinically validated health benefits.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the market with 42% share, followed by North America (28%) and Europe (21%). Japan and South Korea lead in high-value applications, particularly in functional foods and cosmeceuticals. The North American market shows strong growth in organic and non-GMO certified rice bran products, with premium pricing structures reflecting consumer willingness to pay for sustainable, health-promoting ingredients.
The animal feed sector represents another significant market segment, valued at $380 million in 2022. Defatted rice bran meal serves as a cost-effective protein source in poultry, aquaculture, and livestock feed formulations. The increasing restrictions on antibiotic growth promoters have created new opportunities for rice bran derivatives as natural feed additives with prebiotic properties.
Emerging applications in cosmetics and personal care products are creating new value streams, with rice bran extracts being incorporated into anti-aging formulations, skin brightening products, and natural exfoliants. This segment is growing at 7.5% annually, driven by consumer preference for natural, plant-derived cosmetic ingredients.
Market challenges include price volatility due to fluctuating rice production, quality standardization issues, and competition from alternative plant-based ingredients. However, technological advancements in extraction methods and increasing vertical integration among processors are gradually addressing these challenges, improving market stability and product consistency.
Technical Challenges in Rice Bran Valorization
Despite significant advancements in rice bran valorization, several technical challenges persist that hinder the full utilization of rice bran by-products. The primary obstacle remains the rapid deterioration of rice bran quality due to lipase activity, which causes rancidity within hours of milling. This enzymatic degradation significantly reduces the nutritional value and functional properties of rice bran components, necessitating immediate stabilization through thermal treatments, microwave processing, or chemical methods.
Extraction efficiency presents another major challenge, particularly for bioactive compounds like γ-oryzanol, phytosterols, and phenolics. Current extraction methodologies often employ organic solvents that raise environmental and safety concerns, while yielding inconsistent recovery rates. Green extraction technologies such as supercritical fluid extraction and enzyme-assisted extraction show promise but face scalability issues and high operational costs when implemented at industrial scale.
The heterogeneous composition of rice bran creates significant variability in by-product quality across different rice varieties, growing conditions, and processing methods. This inconsistency complicates standardization efforts and makes it difficult to develop universal valorization protocols. Researchers must contend with batch-to-batch variations that affect both extraction yields and final product characteristics.
Purification and fractionation of rice bran components represent additional technical hurdles. Separating high-value compounds from complex matrices requires sophisticated techniques like chromatography and membrane filtration, which are often cost-prohibitive at commercial scale. The presence of anti-nutritional factors such as phytic acid and trypsin inhibitors further complicates utilization of defatted rice bran in food applications.
Formulation challenges emerge when incorporating rice bran derivatives into food systems. Issues with sensory properties—particularly the characteristic grainy texture and slightly bitter taste—limit consumer acceptance. Additionally, stability concerns during processing and storage affect shelf-life and functional performance of rice bran ingredients in final products.
Regulatory hurdles and safety assessments present non-technical but equally important challenges. Novel food ingredients derived from rice bran require extensive toxicological studies and regulatory approvals, which can delay commercialization efforts. The lack of standardized analytical methods for characterizing rice bran bioactives further complicates compliance with regulatory requirements.
Scaling production from laboratory to industrial level remains perhaps the most significant barrier to widespread commercialization. Many promising valorization technologies demonstrate excellent results at bench scale but encounter engineering challenges during scale-up, including heat transfer limitations, mixing inefficiencies, and increased processing times that compromise product quality.
Extraction efficiency presents another major challenge, particularly for bioactive compounds like γ-oryzanol, phytosterols, and phenolics. Current extraction methodologies often employ organic solvents that raise environmental and safety concerns, while yielding inconsistent recovery rates. Green extraction technologies such as supercritical fluid extraction and enzyme-assisted extraction show promise but face scalability issues and high operational costs when implemented at industrial scale.
The heterogeneous composition of rice bran creates significant variability in by-product quality across different rice varieties, growing conditions, and processing methods. This inconsistency complicates standardization efforts and makes it difficult to develop universal valorization protocols. Researchers must contend with batch-to-batch variations that affect both extraction yields and final product characteristics.
Purification and fractionation of rice bran components represent additional technical hurdles. Separating high-value compounds from complex matrices requires sophisticated techniques like chromatography and membrane filtration, which are often cost-prohibitive at commercial scale. The presence of anti-nutritional factors such as phytic acid and trypsin inhibitors further complicates utilization of defatted rice bran in food applications.
Formulation challenges emerge when incorporating rice bran derivatives into food systems. Issues with sensory properties—particularly the characteristic grainy texture and slightly bitter taste—limit consumer acceptance. Additionally, stability concerns during processing and storage affect shelf-life and functional performance of rice bran ingredients in final products.
Regulatory hurdles and safety assessments present non-technical but equally important challenges. Novel food ingredients derived from rice bran require extensive toxicological studies and regulatory approvals, which can delay commercialization efforts. The lack of standardized analytical methods for characterizing rice bran bioactives further complicates compliance with regulatory requirements.
Scaling production from laboratory to industrial level remains perhaps the most significant barrier to widespread commercialization. Many promising valorization technologies demonstrate excellent results at bench scale but encounter engineering challenges during scale-up, including heat transfer limitations, mixing inefficiencies, and increased processing times that compromise product quality.
Current Valorization Methods for Defatted Rice Bran
01 Extraction and utilization of bioactive compounds
Rice bran oil by-products contain valuable bioactive compounds such as oryzanol, tocopherols, tocotrienols, and phytosterols that can be extracted and utilized in various applications. These compounds have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cholesterol-lowering properties. Extraction methods include solvent extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and enzymatic processes to obtain these high-value components from defatted rice bran meal and extracts for use in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and functional foods.- Extraction and utilization of bioactive compounds: Rice bran oil by-products contain valuable bioactive compounds such as oryzanol, tocopherols, tocotrienols, and phenolic compounds that can be extracted and utilized for various applications. These compounds have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and other health-promoting properties. Extraction methods include solvent extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and enzymatic processes to obtain these high-value components from defatted rice bran meal and extracts.
- Production of functional food ingredients: Defatted rice bran and its extracts can be processed into various functional food ingredients. These include protein concentrates, dietary fiber products, and prebiotic formulations. The high protein content, balanced amino acid profile, and rich fiber composition make these by-products valuable for food fortification and development of health-promoting food products. Processing techniques involve fractionation, enzymatic modification, and controlled fermentation to enhance nutritional and functional properties.
- Cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications: Rice bran oil by-products contain compounds beneficial for skin health and can be incorporated into cosmetic and pharmaceutical formulations. The antioxidant properties help in anti-aging products, while peptides and other bioactive compounds contribute to skin moisturization and protection. These by-products can be processed into extracts, powders, or specialized fractions for targeted applications in personal care products and therapeutic formulations.
- Agricultural and environmental applications: Defatted rice bran and its derivatives can be utilized in agricultural applications such as organic fertilizers, soil amendments, and animal feed supplements. The high nutrient content, including proteins, minerals, and fiber, makes these by-products valuable for improving soil health and animal nutrition. Additionally, these materials can be used for environmental remediation, such as in the production of biodegradable materials or as adsorbents for pollutant removal.
- Biofuel and industrial product development: Rice bran oil by-products can be converted into biofuels and various industrial products. The carbohydrate-rich fractions can be fermented to produce bioethanol, while the lignocellulosic components can be processed into biogas or solid biofuels. Other industrial applications include the production of enzymes, organic acids, and biopolymers through microbial fermentation or chemical modification of the by-product components.
02 Production of protein-rich products
Defatted rice bran is a rich source of high-quality protein that can be extracted and utilized in food applications. Various processes have been developed to isolate, concentrate, and modify rice bran proteins to improve their functional properties such as solubility, emulsification, and foaming capacity. These protein products can be incorporated into food formulations as nutritional supplements, meat alternatives, and protein-enriched beverages, adding value to what would otherwise be a low-value by-product.Expand Specific Solutions03 Conversion to functional food ingredients
Rice bran by-products can be processed into various functional food ingredients through enzymatic hydrolysis, fermentation, and other modification techniques. These processes can enhance the bioavailability of nutrients, reduce anti-nutritional factors, and improve sensory properties. The resulting ingredients include dietary fiber products, prebiotics, flavor enhancers, and natural food preservatives that can be used in bakery products, beverages, and health foods, providing both nutritional and technological benefits.Expand Specific Solutions04 Development of nutraceuticals and pharmaceuticals
Rice bran oil by-products contain compounds with significant health-promoting properties that can be developed into nutraceuticals and pharmaceuticals. Research has focused on extracting and formulating these bioactive components for targeted health applications such as cholesterol management, blood glucose control, immune system enhancement, and cancer prevention. These formulations include tablets, capsules, functional beverages, and medical foods that deliver the therapeutic benefits of rice bran components in convenient forms.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial and agricultural applications
Beyond food and pharmaceutical applications, rice bran by-products can be valorized for various industrial and agricultural uses. These include the production of biofuels, organic fertilizers, animal feed supplements, biodegradable packaging materials, and natural pesticides. The high fiber content, mineral composition, and bioactive compounds in rice bran make it suitable for these diverse applications, providing sustainable alternatives to conventional products while reducing waste from rice processing industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Rice By-product Valorization
The rice bran oil by-products valorization market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable food ingredients and value-added applications. The global market size for defatted rice bran and extracts is expanding, particularly in Asia-Pacific regions where rice processing is prevalent. Technologically, the field is advancing from basic extraction to sophisticated bioactive compound isolation and application development. Leading companies like CJ CheilJedang, Tsuno Food Industrial, and General Mills are investing in R&D for functional food applications, while academic institutions such as Jiangnan University and Zhejiang University are pioneering extraction technologies. PRAJ Industries and DSM IP Assets are developing industrial-scale valorization processes, indicating the transition from research to commercial implementation across the food, nutraceutical, and cosmetic sectors.
CJ CheilJedang Corp.
Technical Solution: CJ CheilJedang has developed a biotechnological platform for rice bran valorization called "BYO-Bran" that focuses on protein functionality enhancement and bioactive peptide production. Their approach begins with a specialized fractionation process that separates defatted rice bran into protein-rich, fiber-rich, and phenolic-rich streams. The protein fraction undergoes controlled enzymatic hydrolysis using their proprietary enzyme cocktail to produce bioactive peptides with antihypertensive, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory properties. These peptides are incorporated into their functional food products and dietary supplements. CJ CheilJedang has also developed fermentation technology using selected microbial strains to enhance the bioavailability of rice bran phytochemicals and improve digestibility of the fiber fraction. Their process includes a patented extrusion technology that modifies the physical properties of defatted rice bran, improving its functionality as a food ingredient with enhanced water absorption, oil-binding capacity, and emulsification properties.
Strengths: Advanced biotechnological expertise in enzyme technology and fermentation; established commercial applications in functional foods; integrated approach connecting agricultural side-streams with consumer products. Weaknesses: Relatively high processing costs; technology requires specialized knowledge and equipment; limited application in lower-value markets where cost is a primary consideration.
PRAJ Industries Ltd.
Technical Solution: PRAJ Industries has developed an innovative biorefinery approach for rice bran valorization centered on their "RiceXtract" technology platform. This system employs a combination of supercritical fluid extraction and green solvent technologies to fractionate rice bran components sequentially, maximizing the recovery of valuable compounds. Their process first stabilizes fresh rice bran using a proprietary enzyme inhibition technique that prevents lipase activity, extending shelf life while preserving nutritional integrity. The defatted meal undergoes controlled hydrolysis to release bound phenolics and improve protein digestibility, followed by membrane filtration to concentrate protein fractions with functional properties. PRAJ has also developed a fermentation-based platform that converts rice bran carbohydrates into prebiotics and organic acids. Their integrated biorefinery concept includes energy recovery from residual biomass through anaerobic digestion, creating a closed-loop system that generates biogas for powering the processing facility.
Strengths: Comprehensive biorefinery approach that maximizes value extraction from multiple components; environmentally friendly processing using green technologies; integrated energy recovery system improving overall sustainability. Weaknesses: Complex multi-stage process requiring significant capital investment; higher operational costs compared to conventional single-product extraction; technology adoption barriers in traditional rice processing regions.
Critical Patents in Rice Bran Extract Applications
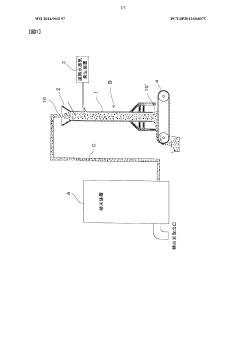
Method for obtaining rice oil and defatted rice bran from fresh rice bran
PatentWO2014003197A1
Innovation
- Immediate contact of fresh rice bran with superheated steam at 200°C to 650°C for 0.5 to 60 seconds to deactivate enzymes, followed by solvent extraction to obtain rice bran oil and defatted rice bran, ensuring enzyme and microbial deactivation, and using a device connected to the rice polishing process for efficient processing.
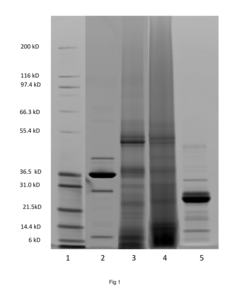
Mild hydrolysis of proteins from rice bran
PatentInactiveUS20150257411A1
Innovation
- A process involving the addition of an endoprotease or metallo-endoprotease enzyme to a rice bran suspension at specific pH and temperature conditions for controlled hydrolysis, followed by separation, to produce a rice bran hydrolysate with a unique molecular weight distribution and improved sensory profile.
Sustainability Impact of Rice Bran Valorization
The valorization of rice bran by-products represents a significant opportunity to enhance sustainability across multiple dimensions of the global food system. By transforming what was once considered waste into valuable resources, the rice processing industry can substantially reduce its environmental footprint while creating economic and social benefits.
From an environmental perspective, rice bran valorization directly addresses the challenge of agricultural waste management. Traditional disposal methods for rice bran, such as landfilling or incineration, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental pollution. The comprehensive utilization of defatted rice bran meal and extracts prevents these negative impacts while reducing the pressure on natural resources through circular economy principles.
The carbon footprint reduction potential is particularly noteworthy. Life cycle assessments indicate that integrated rice bran valorization systems can decrease CO2 emissions by 30-45% compared to conventional processing methods that discard by-products. This reduction stems from both avoided waste disposal emissions and the replacement of resource-intensive ingredients in various applications.
Water conservation represents another critical sustainability benefit. The extraction processes for rice bran bioactive compounds can be designed with water recycling systems, significantly reducing freshwater consumption compared to traditional extraction methods. Some advanced facilities report water usage reductions of up to 60% through closed-loop processing systems.
From an economic sustainability perspective, rice bran valorization creates new revenue streams for rice processors and farmers, particularly in developing regions where rice is a staple crop. The global market for rice bran derivatives is projected to reach $10.8 billion by 2027, representing a substantial opportunity for agricultural communities.
Social sustainability is enhanced through improved nutrition security. Rice bran protein concentrates offer high-quality, plant-based protein alternatives that can address protein deficiencies in vulnerable populations. Additionally, the phenolic compounds and antioxidants extracted from rice bran show promise in addressing various health challenges prevalent in developing countries.
The sustainability benefits extend to land use efficiency as well. By maximizing the value extracted from existing rice cultivation, the pressure to expand agricultural land is reduced. This indirect effect helps preserve natural habitats and biodiversity while still meeting growing global demands for food, feed, and functional ingredients.
From an environmental perspective, rice bran valorization directly addresses the challenge of agricultural waste management. Traditional disposal methods for rice bran, such as landfilling or incineration, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental pollution. The comprehensive utilization of defatted rice bran meal and extracts prevents these negative impacts while reducing the pressure on natural resources through circular economy principles.
The carbon footprint reduction potential is particularly noteworthy. Life cycle assessments indicate that integrated rice bran valorization systems can decrease CO2 emissions by 30-45% compared to conventional processing methods that discard by-products. This reduction stems from both avoided waste disposal emissions and the replacement of resource-intensive ingredients in various applications.
Water conservation represents another critical sustainability benefit. The extraction processes for rice bran bioactive compounds can be designed with water recycling systems, significantly reducing freshwater consumption compared to traditional extraction methods. Some advanced facilities report water usage reductions of up to 60% through closed-loop processing systems.
From an economic sustainability perspective, rice bran valorization creates new revenue streams for rice processors and farmers, particularly in developing regions where rice is a staple crop. The global market for rice bran derivatives is projected to reach $10.8 billion by 2027, representing a substantial opportunity for agricultural communities.
Social sustainability is enhanced through improved nutrition security. Rice bran protein concentrates offer high-quality, plant-based protein alternatives that can address protein deficiencies in vulnerable populations. Additionally, the phenolic compounds and antioxidants extracted from rice bran show promise in addressing various health challenges prevalent in developing countries.
The sustainability benefits extend to land use efficiency as well. By maximizing the value extracted from existing rice cultivation, the pressure to expand agricultural land is reduced. This indirect effect helps preserve natural habitats and biodiversity while still meeting growing global demands for food, feed, and functional ingredients.
Regulatory Framework for Novel Food Ingredients
The regulatory landscape for novel food ingredients derived from rice bran oil by-products presents a complex framework that varies significantly across global jurisdictions. In the European Union, the Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 governs the introduction of ingredients not significantly consumed before May 15, 1997. Rice bran derivatives seeking novel food status must undergo rigorous safety assessments by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), with particular emphasis on toxicological profiles, allergenicity potential, and nutritional impact.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees novel ingredients through the GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) notification system or food additive petition pathways. Rice bran oil by-products have gained attention under these frameworks, with several components receiving GRAS status in recent years. The FDA particularly scrutinizes health claims associated with bioactive compounds found in defatted rice bran, requiring substantial scientific evidence for validation.
Asian markets, particularly Japan and South Korea, have established specialized regulatory frameworks for functional food ingredients that accommodate rice bran derivatives. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system has approved several rice bran-derived components, recognizing their potential health benefits when supported by clinical evidence. Similarly, China has recently updated its novel food ingredient regulations, creating new opportunities for rice bran by-products in the world's largest food market.
Health claim regulations represent a critical consideration for commercialization strategies. The European Commission maintains stringent requirements for health claims, with only a limited number approved for plant-derived bioactives. Rice bran components seeking health claim approval must demonstrate causality between consumption and claimed effects through human intervention studies, presenting both a challenge and opportunity for market differentiation.
Labeling requirements constitute another regulatory dimension, with transparency regarding allergen potential, processing methods, and source materials being mandatory across most jurisdictions. For rice bran derivatives, clear identification of extraction methods and potential cross-contamination with gluten-containing cereals requires particular attention to ensure compliance.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate increasing harmonization efforts between major markets, potentially streamlining approval processes for novel ingredients. Simultaneously, there is growing regulatory focus on sustainability credentials and environmental impact assessments, creating additional considerations for rice bran valorization strategies that emphasize circular economy principles.
Navigating these regulatory frameworks requires strategic planning and substantial investment in safety studies, but successful compliance opens significant market opportunities for rice bran oil by-products as novel food ingredients with recognized functional benefits.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees novel ingredients through the GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) notification system or food additive petition pathways. Rice bran oil by-products have gained attention under these frameworks, with several components receiving GRAS status in recent years. The FDA particularly scrutinizes health claims associated with bioactive compounds found in defatted rice bran, requiring substantial scientific evidence for validation.
Asian markets, particularly Japan and South Korea, have established specialized regulatory frameworks for functional food ingredients that accommodate rice bran derivatives. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system has approved several rice bran-derived components, recognizing their potential health benefits when supported by clinical evidence. Similarly, China has recently updated its novel food ingredient regulations, creating new opportunities for rice bran by-products in the world's largest food market.
Health claim regulations represent a critical consideration for commercialization strategies. The European Commission maintains stringent requirements for health claims, with only a limited number approved for plant-derived bioactives. Rice bran components seeking health claim approval must demonstrate causality between consumption and claimed effects through human intervention studies, presenting both a challenge and opportunity for market differentiation.
Labeling requirements constitute another regulatory dimension, with transparency regarding allergen potential, processing methods, and source materials being mandatory across most jurisdictions. For rice bran derivatives, clear identification of extraction methods and potential cross-contamination with gluten-containing cereals requires particular attention to ensure compliance.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate increasing harmonization efforts between major markets, potentially streamlining approval processes for novel ingredients. Simultaneously, there is growing regulatory focus on sustainability credentials and environmental impact assessments, creating additional considerations for rice bran valorization strategies that emphasize circular economy principles.
Navigating these regulatory frameworks requires strategic planning and substantial investment in safety studies, but successful compliance opens significant market opportunities for rice bran oil by-products as novel food ingredients with recognized functional benefits.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!