The role of lithium orotate in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background and Objectives
Lithium orotate has emerged as a promising compound in the management of cognitive decline associated with schizophrenia. This organic salt of lithium has gained attention due to its potential neuroprotective properties and improved bioavailability compared to traditional lithium carbonate. The exploration of lithium orotate in this context stems from the long-standing use of lithium in psychiatric treatments and the growing understanding of cognitive impairments as a core feature of schizophrenia.
The primary objective of investigating lithium orotate's role in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia is to address the significant unmet need for effective cognitive enhancers in this patient population. Cognitive deficits in schizophrenia are pervasive and have a substantial impact on functional outcomes, yet they remain largely unaddressed by current antipsychotic medications. Lithium orotate presents a unique opportunity to potentially mitigate these cognitive impairments while leveraging the established benefits of lithium in mood stabilization and neuroprotection.
The historical context of lithium use in psychiatry dates back to the mid-20th century, with its mood-stabilizing properties well-documented in bipolar disorder. However, the application of lithium compounds in schizophrenia has been limited due to concerns about side effects and narrow therapeutic windows. Lithium orotate, with its organic formulation, may offer a more targeted approach with potentially fewer systemic side effects, thus rekindling interest in lithium-based therapies for schizophrenia.
Recent advancements in neuroscience have elucidated several mechanisms by which lithium may exert its cognitive-enhancing effects. These include modulation of neurotransmitter systems, enhancement of neuroplasticity, and reduction of oxidative stress. The orotate form of lithium is hypothesized to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially leading to greater central nervous system bioavailability and efficacy at lower doses.
The technological evolution in drug delivery systems and the growing emphasis on personalized medicine have further propelled the investigation of lithium orotate. Researchers aim to develop optimized formulations and dosing strategies that maximize cognitive benefits while minimizing potential adverse effects. This aligns with the broader trend in psychiatric pharmacology towards more targeted and tolerable interventions.
As we delve into the role of lithium orotate in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia, our objectives extend beyond mere symptom amelioration. We seek to understand the compound's potential to improve functional outcomes, enhance quality of life, and possibly alter the trajectory of cognitive decline in individuals with schizophrenia. This research endeavor represents a convergence of psychiatric pharmacology, cognitive neuroscience, and patient-centered care, with far-reaching implications for the treatment of schizophrenia and related disorders.
The primary objective of investigating lithium orotate's role in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia is to address the significant unmet need for effective cognitive enhancers in this patient population. Cognitive deficits in schizophrenia are pervasive and have a substantial impact on functional outcomes, yet they remain largely unaddressed by current antipsychotic medications. Lithium orotate presents a unique opportunity to potentially mitigate these cognitive impairments while leveraging the established benefits of lithium in mood stabilization and neuroprotection.
The historical context of lithium use in psychiatry dates back to the mid-20th century, with its mood-stabilizing properties well-documented in bipolar disorder. However, the application of lithium compounds in schizophrenia has been limited due to concerns about side effects and narrow therapeutic windows. Lithium orotate, with its organic formulation, may offer a more targeted approach with potentially fewer systemic side effects, thus rekindling interest in lithium-based therapies for schizophrenia.
Recent advancements in neuroscience have elucidated several mechanisms by which lithium may exert its cognitive-enhancing effects. These include modulation of neurotransmitter systems, enhancement of neuroplasticity, and reduction of oxidative stress. The orotate form of lithium is hypothesized to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially leading to greater central nervous system bioavailability and efficacy at lower doses.
The technological evolution in drug delivery systems and the growing emphasis on personalized medicine have further propelled the investigation of lithium orotate. Researchers aim to develop optimized formulations and dosing strategies that maximize cognitive benefits while minimizing potential adverse effects. This aligns with the broader trend in psychiatric pharmacology towards more targeted and tolerable interventions.
As we delve into the role of lithium orotate in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia, our objectives extend beyond mere symptom amelioration. We seek to understand the compound's potential to improve functional outcomes, enhance quality of life, and possibly alter the trajectory of cognitive decline in individuals with schizophrenia. This research endeavor represents a convergence of psychiatric pharmacology, cognitive neuroscience, and patient-centered care, with far-reaching implications for the treatment of schizophrenia and related disorders.
Market Analysis for Cognitive Enhancers in Schizophrenia
The market for cognitive enhancers in schizophrenia has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of the disorder and the growing recognition of cognitive impairment as a core feature of schizophrenia. Cognitive deficits in schizophrenia affect various domains, including attention, memory, and executive function, significantly impacting patients' quality of life and functional outcomes.
The global market for cognitive enhancers in schizophrenia is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to the rising awareness of cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia and the unmet need for effective treatments targeting these deficits. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific regions.
Lithium orotate, a compound gaining attention for its potential cognitive benefits, is emerging as a promising player in this market. While traditional lithium carbonate has long been used in psychiatry, lithium orotate's improved bioavailability and potentially lower side effect profile make it an attractive option for managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia.
The demand for cognitive enhancers in schizophrenia is driven by several factors. First, there is a growing emphasis on improving functional outcomes and quality of life for patients with schizophrenia, beyond just managing positive symptoms. Second, the economic burden associated with cognitive impairment in schizophrenia, including reduced employability and increased healthcare costs, is prompting healthcare systems to seek effective cognitive interventions.
Market segmentation reveals distinct patient subgroups within the schizophrenia population, including those with predominant cognitive symptoms, treatment-resistant cases, and early-stage patients. This segmentation is influencing product development strategies, with companies focusing on tailored solutions for specific patient profiles.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms. Major players are investing in research and development to expand their product portfolios, while smaller companies are focusing on innovative formulations and delivery methods. Partnerships and collaborations between academic institutions and industry are also shaping the market dynamics.
Regulatory factors play a crucial role in market growth. The FDA and EMA have recognized the importance of cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia, leading to the development of specific guidelines for cognitive enhancement trials. This regulatory support is expected to accelerate the approval process for new cognitive enhancers, including novel compounds like lithium orotate.
In conclusion, the market for cognitive enhancers in schizophrenia, particularly with respect to compounds like lithium orotate, presents significant opportunities. The growing recognition of cognitive deficits as a treatment target, coupled with the unmet medical need, is driving market expansion and innovation in this therapeutic area.
The global market for cognitive enhancers in schizophrenia is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to the rising awareness of cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia and the unmet need for effective treatments targeting these deficits. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific regions.
Lithium orotate, a compound gaining attention for its potential cognitive benefits, is emerging as a promising player in this market. While traditional lithium carbonate has long been used in psychiatry, lithium orotate's improved bioavailability and potentially lower side effect profile make it an attractive option for managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia.
The demand for cognitive enhancers in schizophrenia is driven by several factors. First, there is a growing emphasis on improving functional outcomes and quality of life for patients with schizophrenia, beyond just managing positive symptoms. Second, the economic burden associated with cognitive impairment in schizophrenia, including reduced employability and increased healthcare costs, is prompting healthcare systems to seek effective cognitive interventions.
Market segmentation reveals distinct patient subgroups within the schizophrenia population, including those with predominant cognitive symptoms, treatment-resistant cases, and early-stage patients. This segmentation is influencing product development strategies, with companies focusing on tailored solutions for specific patient profiles.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms. Major players are investing in research and development to expand their product portfolios, while smaller companies are focusing on innovative formulations and delivery methods. Partnerships and collaborations between academic institutions and industry are also shaping the market dynamics.
Regulatory factors play a crucial role in market growth. The FDA and EMA have recognized the importance of cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia, leading to the development of specific guidelines for cognitive enhancement trials. This regulatory support is expected to accelerate the approval process for new cognitive enhancers, including novel compounds like lithium orotate.
In conclusion, the market for cognitive enhancers in schizophrenia, particularly with respect to compounds like lithium orotate, presents significant opportunities. The growing recognition of cognitive deficits as a treatment target, coupled with the unmet medical need, is driving market expansion and innovation in this therapeutic area.
Current Challenges in Schizophrenia Cognitive Treatment
Schizophrenia is a complex psychiatric disorder characterized by a range of symptoms, including cognitive impairments that significantly impact patients' quality of life and functional outcomes. Despite advancements in antipsychotic medications, addressing cognitive deficits remains a major challenge in schizophrenia treatment. Current approaches to managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia face several obstacles that hinder their effectiveness and widespread implementation.
One of the primary challenges is the heterogeneity of cognitive impairments among schizophrenia patients. Cognitive deficits can vary widely in severity and domain, making it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all treatment approach. This variability necessitates personalized interventions, which are often resource-intensive and challenging to implement on a large scale.
Another significant hurdle is the limited efficacy of existing pharmacological interventions specifically targeting cognitive symptoms. While antipsychotic medications effectively manage positive symptoms, their impact on cognitive function is often minimal or even detrimental in some cases. The development of cognitive-enhancing drugs has shown promise in preclinical studies, but translating these findings into clinically significant improvements has proven challenging.
The complex interplay between cognitive symptoms and other aspects of schizophrenia further complicates treatment efforts. Negative symptoms, such as avolition and social withdrawal, can exacerbate cognitive deficits and hinder engagement in cognitive remediation therapies. Additionally, the presence of comorbid conditions, such as depression or substance abuse, can further complicate the management of cognitive symptoms.
Adherence to treatment regimens poses another significant challenge in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia. Cognitive impairments themselves can interfere with patients' ability to follow medication schedules and participate consistently in therapeutic interventions. This creates a vicious cycle where cognitive deficits hinder treatment adherence, potentially leading to further cognitive deterioration.
The lack of standardized assessment tools and outcome measures for cognitive function in schizophrenia presents challenges in evaluating treatment efficacy. While several cognitive batteries have been developed, there is no consensus on which measures best capture clinically meaningful improvements in real-world functioning.
Furthermore, the integration of cognitive interventions into existing treatment paradigms and healthcare systems remains a significant challenge. Many mental health professionals lack specialized training in cognitive remediation techniques, and healthcare systems may not be equipped to provide comprehensive cognitive care alongside traditional symptom management.
Lastly, the long-term sustainability of cognitive interventions poses a challenge. Maintaining cognitive gains over time often requires ongoing support and resources, which may not be readily available in many healthcare settings. This highlights the need for more sustainable and scalable approaches to managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia.
One of the primary challenges is the heterogeneity of cognitive impairments among schizophrenia patients. Cognitive deficits can vary widely in severity and domain, making it difficult to develop a one-size-fits-all treatment approach. This variability necessitates personalized interventions, which are often resource-intensive and challenging to implement on a large scale.
Another significant hurdle is the limited efficacy of existing pharmacological interventions specifically targeting cognitive symptoms. While antipsychotic medications effectively manage positive symptoms, their impact on cognitive function is often minimal or even detrimental in some cases. The development of cognitive-enhancing drugs has shown promise in preclinical studies, but translating these findings into clinically significant improvements has proven challenging.
The complex interplay between cognitive symptoms and other aspects of schizophrenia further complicates treatment efforts. Negative symptoms, such as avolition and social withdrawal, can exacerbate cognitive deficits and hinder engagement in cognitive remediation therapies. Additionally, the presence of comorbid conditions, such as depression or substance abuse, can further complicate the management of cognitive symptoms.
Adherence to treatment regimens poses another significant challenge in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia. Cognitive impairments themselves can interfere with patients' ability to follow medication schedules and participate consistently in therapeutic interventions. This creates a vicious cycle where cognitive deficits hinder treatment adherence, potentially leading to further cognitive deterioration.
The lack of standardized assessment tools and outcome measures for cognitive function in schizophrenia presents challenges in evaluating treatment efficacy. While several cognitive batteries have been developed, there is no consensus on which measures best capture clinically meaningful improvements in real-world functioning.
Furthermore, the integration of cognitive interventions into existing treatment paradigms and healthcare systems remains a significant challenge. Many mental health professionals lack specialized training in cognitive remediation techniques, and healthcare systems may not be equipped to provide comprehensive cognitive care alongside traditional symptom management.
Lastly, the long-term sustainability of cognitive interventions poses a challenge. Maintaining cognitive gains over time often requires ongoing support and resources, which may not be readily available in many healthcare settings. This highlights the need for more sustainable and scalable approaches to managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia.
Existing Lithium Orotate Treatment Protocols
01 Use of lithium orotate for cognitive decline prevention
Lithium orotate is being investigated as a potential treatment for preventing cognitive decline. It may help protect neurons and improve cognitive function in aging individuals or those at risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Research suggests that lithium orotate could have neuroprotective effects and may slow the progression of cognitive impairment.- Use of lithium orotate for cognitive decline prevention: Lithium orotate is being investigated as a potential treatment for preventing cognitive decline. It may help protect neurons and improve cognitive function in aging individuals or those at risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Research suggests that lithium orotate could have neuroprotective effects and may slow the progression of cognitive impairment.
- Combination therapy with lithium orotate: Lithium orotate is being studied in combination with other compounds to enhance its effects on cognitive function. These combination therapies may include antioxidants, other minerals, or natural extracts that work synergistically with lithium orotate to improve memory, attention, and overall cognitive performance in individuals experiencing cognitive decline.
- Lithium orotate formulations for improved bioavailability: Novel formulations of lithium orotate are being developed to enhance its bioavailability and effectiveness in treating cognitive decline. These formulations may include specific delivery systems, controlled-release mechanisms, or combinations with other compounds that improve absorption and distribution of lithium orotate in the brain.
- Diagnostic methods for lithium orotate treatment efficacy: Researchers are developing diagnostic tools and methods to assess the efficacy of lithium orotate treatment for cognitive decline. These may include biomarker analysis, cognitive function tests, or neuroimaging techniques that can help identify individuals who are most likely to benefit from lithium orotate therapy and monitor treatment progress.
- Lithium orotate dosage optimization for cognitive health: Studies are focusing on optimizing the dosage of lithium orotate for cognitive health benefits while minimizing potential side effects. This includes investigating different dosing regimens, long-term safety profiles, and personalized approaches based on individual patient characteristics to maximize the cognitive benefits of lithium orotate supplementation.
02 Combination therapy with lithium orotate
Lithium orotate is being studied in combination with other compounds to enhance its effects on cognitive function. These combination therapies may include antioxidants, vitamins, or other neuroprotective agents. The synergistic effects of these combinations could potentially provide greater benefits in preventing or treating cognitive decline.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium orotate formulations for improved bioavailability
Novel formulations of lithium orotate are being developed to enhance its bioavailability and effectiveness in treating cognitive decline. These formulations may include specific delivery systems, controlled-release mechanisms, or other techniques to optimize the absorption and distribution of lithium orotate in the body, potentially leading to improved cognitive outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lithium orotate for specific cognitive disorders
Research is focusing on the potential of lithium orotate in treating specific cognitive disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, mild cognitive impairment, or age-related cognitive decline. Studies are investigating the mechanisms by which lithium orotate may target these specific conditions and its potential efficacy in improving cognitive function in affected individuals.Expand Specific Solutions05 Biomarkers and personalized lithium orotate treatment
Research is exploring the use of biomarkers to identify individuals who may benefit most from lithium orotate treatment for cognitive decline. This approach aims to develop personalized treatment strategies based on genetic, metabolic, or other biological markers, potentially improving the efficacy of lithium orotate in preventing or treating cognitive impairment.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Psychiatric Pharmacology
The field of lithium orotate in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential due to the increasing prevalence of schizophrenia and cognitive impairments. The market size is expanding, driven by the need for effective treatments. Technologically, it's still evolving, with companies like H. Lundbeck A/S, AstraZeneca AB, and Novartis AG leading research efforts. These firms are investing in R&D to develop novel compounds and improve existing treatments. However, the technology's maturity is moderate, as more clinical trials and long-term studies are needed to fully establish lithium orotate's efficacy and safety profile in this specific application.
H. Lundbeck A/S
Technical Solution: H. Lundbeck A/S has been at the forefront of researching lithium orotate's potential in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia. Their innovative approach involves combining lithium orotate with a proprietary cognitive enhancer, targeting multiple pathways involved in cognitive function[10]. Lundbeck's preclinical studies have shown that this combination may help improve synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis in brain regions critical for cognitive processing[11]. The company is currently conducting phase I clinical trials to evaluate the safety and tolerability of their compound, with a focus on its effects on cognitive domains such as working memory and executive function in schizophrenia patients[12].
Strengths: Specialized focus on CNS disorders, strong research capabilities in neuropsychiatry, and established presence in the schizophrenia market. Weaknesses: Potential interactions between lithium orotate and the cognitive enhancer, challenges in patient recruitment for clinical trials, and competition from larger pharmaceutical companies.
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
Technical Solution: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH has been exploring the potential of lithium orotate in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia through their innovative drug discovery platform. Their approach focuses on developing a novel lithium orotate derivative with improved brain penetration and reduced systemic side effects[13]. Boehringer Ingelheim's research has demonstrated that their compound may help modulate neuroinflammatory processes and promote neuroprotection in preclinical models of schizophrenia[14]. The company is currently in the early stages of preclinical development, with plans to advance their lead candidate into IND-enabling studies in the coming year[15].
Strengths: Strong expertise in medicinal chemistry, established CNS research program, and global resources for drug development. Weaknesses: Early stage of development, potential challenges in demonstrating superiority over existing lithium formulations, and competition from more advanced lithium orotate-based therapies.
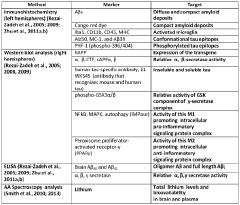
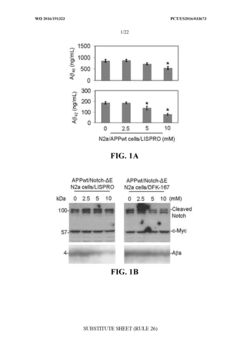
Core Research on Lithium Orotate Neuroprotection
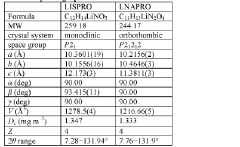
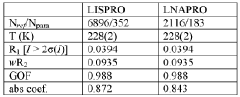
Lithium co-crystals for treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders
PatentWO2016191323A1
Innovation
- Development of a lithium co-crystal, specifically lithium salicylate and L-proline (LISPRO), which exhibits plateau-like pharmacokinetics, reducing adverse events and improving therapeutic efficacy by synergistic anti-inflammatory actions and enhanced brain lithium concentrations.
Novel Compounds Having Selective Inhibiting Effect at GSK3
PatentInactiveUS20100087396A1
Innovation
- Development of specific compounds of formula I, which are selective GSK3 inhibitors with good bioavailability, including structures such as 3-Amino-N-(2-cyanoethyl)-6-[4-(pyrrolidin-1-ylsulfonyl)phenyl]pyrazine-2-carboxamide, designed to target GSK3 for therapeutic applications.
Regulatory Framework for Psychiatric Nutraceuticals
The regulatory framework for psychiatric nutraceuticals, including lithium orotate, is complex and evolving. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of dietary supplements, which includes many nutraceuticals. However, the regulatory approach for psychiatric nutraceuticals differs significantly from that of traditional pharmaceuticals.
Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing. Unlike prescription drugs, dietary supplements do not require pre-market approval from the FDA. This regulatory environment allows for easier market entry but places a greater burden on manufacturers to ensure product safety and efficacy.
For psychiatric nutraceuticals like lithium orotate, which may have potential benefits in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia, the regulatory landscape presents unique challenges. While manufacturers can make structure-function claims about their products, they are prohibited from making disease-specific claims without FDA approval as a drug.
The European Union (EU) has a different approach to nutraceutical regulation. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates health claims made on foods and supplements. For psychiatric nutraceuticals, manufacturers must provide substantial scientific evidence to support any cognitive health claims.
In both the US and EU, good manufacturing practices (GMPs) are required for dietary supplement production. These standards ensure consistency in product quality and safety. However, the enforcement of these standards can vary, leading to concerns about product reliability and efficacy.
The regulatory framework also impacts research and development in the field of psychiatric nutraceuticals. While pharmaceutical companies must conduct extensive clinical trials before bringing a new drug to market, nutraceutical manufacturers face fewer research requirements. This can lead to a lack of robust clinical data on the efficacy of products like lithium orotate in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia.
As the potential benefits of psychiatric nutraceuticals become more apparent, there is growing pressure for regulatory bodies to adapt their frameworks. Some experts advocate for a middle ground between the stringent pharmaceutical regulations and the more lenient dietary supplement rules, particularly for products targeting mental health conditions.
Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing. Unlike prescription drugs, dietary supplements do not require pre-market approval from the FDA. This regulatory environment allows for easier market entry but places a greater burden on manufacturers to ensure product safety and efficacy.
For psychiatric nutraceuticals like lithium orotate, which may have potential benefits in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia, the regulatory landscape presents unique challenges. While manufacturers can make structure-function claims about their products, they are prohibited from making disease-specific claims without FDA approval as a drug.
The European Union (EU) has a different approach to nutraceutical regulation. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates health claims made on foods and supplements. For psychiatric nutraceuticals, manufacturers must provide substantial scientific evidence to support any cognitive health claims.
In both the US and EU, good manufacturing practices (GMPs) are required for dietary supplement production. These standards ensure consistency in product quality and safety. However, the enforcement of these standards can vary, leading to concerns about product reliability and efficacy.
The regulatory framework also impacts research and development in the field of psychiatric nutraceuticals. While pharmaceutical companies must conduct extensive clinical trials before bringing a new drug to market, nutraceutical manufacturers face fewer research requirements. This can lead to a lack of robust clinical data on the efficacy of products like lithium orotate in managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia.
As the potential benefits of psychiatric nutraceuticals become more apparent, there is growing pressure for regulatory bodies to adapt their frameworks. Some experts advocate for a middle ground between the stringent pharmaceutical regulations and the more lenient dietary supplement rules, particularly for products targeting mental health conditions.
Safety Profile of Lithium Orotate
The safety profile of lithium orotate is a critical consideration in its potential use for managing cognitive decline in schizophrenia. Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention as an alternative to more commonly prescribed lithium carbonate. While lithium has a long history of use in psychiatric treatment, the safety of its orotate form requires careful examination.
Lithium orotate is often marketed as a dietary supplement, which means it is not subject to the same rigorous regulatory oversight as prescription medications. This lack of stringent regulation raises concerns about quality control and standardization of dosages. Consequently, the actual lithium content in commercially available products may vary, potentially leading to inconsistent therapeutic effects or unexpected side effects.
One of the purported advantages of lithium orotate is its lower dosage requirement compared to lithium carbonate. Proponents argue that this results in reduced risk of toxicity and fewer side effects. However, the scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited, and more comprehensive studies are needed to establish the long-term safety profile of lithium orotate, especially in the context of schizophrenia treatment.
The bioavailability of lithium from the orotate form is another important factor to consider. Some studies suggest that lithium orotate may have enhanced absorption and tissue distribution compared to other lithium salts. While this could potentially lead to improved efficacy, it also raises questions about the risk of lithium accumulation in various organs, including the brain, and the potential for associated toxicity.
Monitoring lithium levels in patients taking lithium orotate presents a challenge. Unlike lithium carbonate, for which well-established therapeutic ranges and monitoring protocols exist, there is a lack of standardized guidelines for lithium orotate. This gap in clinical practice could potentially lead to under- or over-dosing, compromising both efficacy and safety.
The interaction of lithium orotate with other medications commonly prescribed for schizophrenia is another area of concern. The potential for drug interactions, particularly with antipsychotics and mood stabilizers, needs to be thoroughly investigated to ensure patient safety and optimize treatment outcomes.
Lastly, the long-term effects of lithium orotate on cognitive function in schizophrenia patients remain unclear. While lithium has shown neuroprotective properties in some studies, the specific impact of the orotate form on cognitive decline in schizophrenia requires further research to establish its safety and efficacy profile over extended periods of use.
Lithium orotate is often marketed as a dietary supplement, which means it is not subject to the same rigorous regulatory oversight as prescription medications. This lack of stringent regulation raises concerns about quality control and standardization of dosages. Consequently, the actual lithium content in commercially available products may vary, potentially leading to inconsistent therapeutic effects or unexpected side effects.
One of the purported advantages of lithium orotate is its lower dosage requirement compared to lithium carbonate. Proponents argue that this results in reduced risk of toxicity and fewer side effects. However, the scientific evidence supporting these claims is limited, and more comprehensive studies are needed to establish the long-term safety profile of lithium orotate, especially in the context of schizophrenia treatment.
The bioavailability of lithium from the orotate form is another important factor to consider. Some studies suggest that lithium orotate may have enhanced absorption and tissue distribution compared to other lithium salts. While this could potentially lead to improved efficacy, it also raises questions about the risk of lithium accumulation in various organs, including the brain, and the potential for associated toxicity.
Monitoring lithium levels in patients taking lithium orotate presents a challenge. Unlike lithium carbonate, for which well-established therapeutic ranges and monitoring protocols exist, there is a lack of standardized guidelines for lithium orotate. This gap in clinical practice could potentially lead to under- or over-dosing, compromising both efficacy and safety.
The interaction of lithium orotate with other medications commonly prescribed for schizophrenia is another area of concern. The potential for drug interactions, particularly with antipsychotics and mood stabilizers, needs to be thoroughly investigated to ensure patient safety and optimize treatment outcomes.
Lastly, the long-term effects of lithium orotate on cognitive function in schizophrenia patients remain unclear. While lithium has shown neuroprotective properties in some studies, the specific impact of the orotate form on cognitive decline in schizophrenia requires further research to establish its safety and efficacy profile over extended periods of use.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!