Gel Electrophoresis in Veterinary Diagnostics: Top Uses
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Gel Electrophoresis in Veterinary Diagnostics: Overview and Objectives
Gel electrophoresis has emerged as a cornerstone technique in veterinary diagnostics, revolutionizing the field with its ability to separate and analyze biological molecules. This method, which utilizes an electric field to separate molecules based on their size and charge, has become indispensable in various aspects of animal health care and research.
The evolution of gel electrophoresis in veterinary science can be traced back to its initial applications in human medicine and biochemistry. As the technique matured, veterinary researchers recognized its potential for diagnosing and monitoring animal diseases. Over the years, advancements in gel materials, buffer systems, and detection methods have significantly enhanced the sensitivity and specificity of this technique in veterinary applications.
In the current veterinary landscape, gel electrophoresis serves multiple critical functions. It is extensively used for protein analysis, enabling the detection of abnormal protein patterns associated with various diseases in animals. This application is particularly valuable in diagnosing conditions such as multiple myeloma and other protein-related disorders in companion animals.
DNA analysis through gel electrophoresis has become a staple in veterinary genetics and forensics. It allows for the identification of genetic markers associated with hereditary diseases, breed identification, and parentage verification. This has profound implications for animal breeding programs and the management of genetic disorders in livestock and companion animals.
Another significant application is in the field of infectious disease diagnostics. Gel electrophoresis techniques, particularly when combined with PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), enable the rapid and accurate identification of pathogens. This is crucial for the timely diagnosis and treatment of bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections in animals.
The technique also plays a vital role in vaccine development and efficacy testing for veterinary use. By analyzing the immune response through antibody profiling, researchers can assess the effectiveness of vaccines and monitor the immune status of animals.
Looking ahead, the objectives for gel electrophoresis in veterinary diagnostics are multifaceted. There is a push towards developing more rapid and field-deployable electrophoresis systems, which would allow for on-site diagnostics in remote or resource-limited settings. This could significantly improve the speed and accessibility of veterinary care, especially in large animal practice and wildlife conservation efforts.
Another key objective is to enhance the integration of gel electrophoresis with other diagnostic technologies. The combination of electrophoresis with mass spectrometry, for instance, promises to provide even more detailed molecular insights, potentially leading to earlier and more accurate disease detection.
The evolution of gel electrophoresis in veterinary science can be traced back to its initial applications in human medicine and biochemistry. As the technique matured, veterinary researchers recognized its potential for diagnosing and monitoring animal diseases. Over the years, advancements in gel materials, buffer systems, and detection methods have significantly enhanced the sensitivity and specificity of this technique in veterinary applications.
In the current veterinary landscape, gel electrophoresis serves multiple critical functions. It is extensively used for protein analysis, enabling the detection of abnormal protein patterns associated with various diseases in animals. This application is particularly valuable in diagnosing conditions such as multiple myeloma and other protein-related disorders in companion animals.
DNA analysis through gel electrophoresis has become a staple in veterinary genetics and forensics. It allows for the identification of genetic markers associated with hereditary diseases, breed identification, and parentage verification. This has profound implications for animal breeding programs and the management of genetic disorders in livestock and companion animals.
Another significant application is in the field of infectious disease diagnostics. Gel electrophoresis techniques, particularly when combined with PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), enable the rapid and accurate identification of pathogens. This is crucial for the timely diagnosis and treatment of bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections in animals.
The technique also plays a vital role in vaccine development and efficacy testing for veterinary use. By analyzing the immune response through antibody profiling, researchers can assess the effectiveness of vaccines and monitor the immune status of animals.
Looking ahead, the objectives for gel electrophoresis in veterinary diagnostics are multifaceted. There is a push towards developing more rapid and field-deployable electrophoresis systems, which would allow for on-site diagnostics in remote or resource-limited settings. This could significantly improve the speed and accessibility of veterinary care, especially in large animal practice and wildlife conservation efforts.
Another key objective is to enhance the integration of gel electrophoresis with other diagnostic technologies. The combination of electrophoresis with mass spectrometry, for instance, promises to provide even more detailed molecular insights, potentially leading to earlier and more accurate disease detection.
Market Demand Analysis for Veterinary Diagnostic Tools
The veterinary diagnostics market has been experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for advanced diagnostic tools in animal healthcare. Gel electrophoresis, a well-established technique in molecular biology, has found numerous applications in veterinary diagnostics, contributing to the expanding market for these tools.
The global veterinary diagnostics market is projected to grow steadily over the coming years, with gel electrophoresis playing a crucial role in this expansion. The technique's versatility in analyzing proteins, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules makes it an indispensable tool for veterinary practitioners and researchers alike.
One of the primary drivers of market demand for gel electrophoresis in veterinary diagnostics is the rising prevalence of zoonotic diseases. As these diseases pose significant risks to both animal and human health, there is an increased need for rapid and accurate diagnostic methods. Gel electrophoresis enables the detection and characterization of pathogens, helping veterinarians identify and monitor disease outbreaks more effectively.
Another factor contributing to the growing demand is the increasing focus on food safety and quality control in the livestock industry. Gel electrophoresis techniques are widely used to detect contaminants, assess meat quality, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. This application is particularly important in the context of global trade and the need for stringent quality assurance measures.
The companion animal sector is also driving market growth for gel electrophoresis-based diagnostic tools. With pet owners becoming more invested in their animals' health and well-being, there is a growing demand for advanced diagnostic techniques to detect genetic disorders, infectious diseases, and other health issues in pets.
Technological advancements in gel electrophoresis systems have further fueled market demand. The development of automated, high-throughput systems has improved efficiency and reduced turnaround times, making the technique more accessible and cost-effective for veterinary clinics and laboratories.
The market for gel electrophoresis in veterinary diagnostics is also benefiting from increased research and development activities in the field of animal health. As new diseases emerge and existing ones evolve, there is a constant need for innovative diagnostic approaches, driving investment in gel electrophoresis technology and related applications.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for veterinary diagnostic tools, including gel electrophoresis. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by increasing awareness of animal health issues and improving veterinary infrastructure.
The global veterinary diagnostics market is projected to grow steadily over the coming years, with gel electrophoresis playing a crucial role in this expansion. The technique's versatility in analyzing proteins, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules makes it an indispensable tool for veterinary practitioners and researchers alike.
One of the primary drivers of market demand for gel electrophoresis in veterinary diagnostics is the rising prevalence of zoonotic diseases. As these diseases pose significant risks to both animal and human health, there is an increased need for rapid and accurate diagnostic methods. Gel electrophoresis enables the detection and characterization of pathogens, helping veterinarians identify and monitor disease outbreaks more effectively.
Another factor contributing to the growing demand is the increasing focus on food safety and quality control in the livestock industry. Gel electrophoresis techniques are widely used to detect contaminants, assess meat quality, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. This application is particularly important in the context of global trade and the need for stringent quality assurance measures.
The companion animal sector is also driving market growth for gel electrophoresis-based diagnostic tools. With pet owners becoming more invested in their animals' health and well-being, there is a growing demand for advanced diagnostic techniques to detect genetic disorders, infectious diseases, and other health issues in pets.
Technological advancements in gel electrophoresis systems have further fueled market demand. The development of automated, high-throughput systems has improved efficiency and reduced turnaround times, making the technique more accessible and cost-effective for veterinary clinics and laboratories.
The market for gel electrophoresis in veterinary diagnostics is also benefiting from increased research and development activities in the field of animal health. As new diseases emerge and existing ones evolve, there is a constant need for innovative diagnostic approaches, driving investment in gel electrophoresis technology and related applications.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for veterinary diagnostic tools, including gel electrophoresis. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by increasing awareness of animal health issues and improving veterinary infrastructure.
Current State and Challenges in Veterinary Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis has become an indispensable tool in veterinary diagnostics, offering rapid and accurate analysis of biological molecules. However, the current state of this technology in veterinary medicine presents both advancements and challenges.
One of the primary strengths of gel electrophoresis in veterinary diagnostics is its versatility. It is widely used for protein analysis, DNA fingerprinting, and disease diagnosis across various animal species. The technique has been refined to provide high-resolution separation of complex biological samples, enabling veterinarians to detect subtle changes in protein or DNA profiles associated with different health conditions.
Recent advancements have led to the development of more sensitive and specific gel electrophoresis methods. For instance, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis has gained traction in veterinary proteomics, allowing for the simultaneous analysis of thousands of proteins. This has significantly enhanced the ability to identify biomarkers for various animal diseases and physiological states.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in the field of veterinary gel electrophoresis. One major issue is the lack of standardization across laboratories. Different protocols and equipment can lead to variations in results, making it difficult to compare findings between institutions or establish universal diagnostic criteria.
Another significant challenge is the interpretation of complex electrophoresis patterns, particularly in less common animal species. While extensive databases and reference patterns exist for common domestic animals, there is a notable gap in knowledge for exotic or wildlife species. This limitation can hinder accurate diagnosis and treatment in these animals.
The time-consuming nature of gel electrophoresis remains a hurdle in emergency veterinary situations. Although improvements have been made in reducing run times, the technique still requires several hours to complete, which can be critical in acute cases requiring rapid diagnosis and intervention.
Cost considerations also pose a challenge, especially for smaller veterinary practices. High-end electrophoresis equipment and specialized reagents can be expensive, limiting the widespread adoption of advanced techniques like capillary electrophoresis or pulsed-field gel electrophoresis in routine veterinary diagnostics.
Environmental concerns related to the use of potentially harmful chemicals in gel preparation and staining have led to a push for more eco-friendly alternatives. While progress has been made in developing safer reagents, balancing performance with environmental sustainability remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
Lastly, the integration of gel electrophoresis results with other diagnostic tools and emerging technologies presents both an opportunity and a challenge. There is a growing need for comprehensive diagnostic platforms that can seamlessly combine electrophoresis data with other molecular and imaging techniques to provide a more holistic view of animal health.
One of the primary strengths of gel electrophoresis in veterinary diagnostics is its versatility. It is widely used for protein analysis, DNA fingerprinting, and disease diagnosis across various animal species. The technique has been refined to provide high-resolution separation of complex biological samples, enabling veterinarians to detect subtle changes in protein or DNA profiles associated with different health conditions.
Recent advancements have led to the development of more sensitive and specific gel electrophoresis methods. For instance, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis has gained traction in veterinary proteomics, allowing for the simultaneous analysis of thousands of proteins. This has significantly enhanced the ability to identify biomarkers for various animal diseases and physiological states.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in the field of veterinary gel electrophoresis. One major issue is the lack of standardization across laboratories. Different protocols and equipment can lead to variations in results, making it difficult to compare findings between institutions or establish universal diagnostic criteria.
Another significant challenge is the interpretation of complex electrophoresis patterns, particularly in less common animal species. While extensive databases and reference patterns exist for common domestic animals, there is a notable gap in knowledge for exotic or wildlife species. This limitation can hinder accurate diagnosis and treatment in these animals.
The time-consuming nature of gel electrophoresis remains a hurdle in emergency veterinary situations. Although improvements have been made in reducing run times, the technique still requires several hours to complete, which can be critical in acute cases requiring rapid diagnosis and intervention.
Cost considerations also pose a challenge, especially for smaller veterinary practices. High-end electrophoresis equipment and specialized reagents can be expensive, limiting the widespread adoption of advanced techniques like capillary electrophoresis or pulsed-field gel electrophoresis in routine veterinary diagnostics.
Environmental concerns related to the use of potentially harmful chemicals in gel preparation and staining have led to a push for more eco-friendly alternatives. While progress has been made in developing safer reagents, balancing performance with environmental sustainability remains an ongoing challenge in the field.
Lastly, the integration of gel electrophoresis results with other diagnostic tools and emerging technologies presents both an opportunity and a challenge. There is a growing need for comprehensive diagnostic platforms that can seamlessly combine electrophoresis data with other molecular and imaging techniques to provide a more holistic view of animal health.
Top Applications of Gel Electrophoresis in Veterinary Diagnostics
01 Gel composition and preparation
Various gel compositions and preparation methods are used in gel electrophoresis. These include specific formulations of agarose, polyacrylamide, and other polymers to create gels with desired properties for different separation applications. The composition and preparation of the gel matrix are crucial for achieving optimal resolution and separation of molecules.- Gel composition and preparation: Various gel compositions and preparation methods are used in gel electrophoresis. These include specific formulations of agarose, polyacrylamide, and other polymers to create gels with desired properties for different applications. The composition and preparation of the gel can significantly affect the separation and resolution of molecules during electrophoresis.
- Electrophoresis apparatus design: Innovations in electrophoresis apparatus design focus on improving efficiency, reproducibility, and ease of use. These designs may include features such as integrated cooling systems, adjustable voltage controls, and specialized sample loading mechanisms. Advanced apparatus designs aim to enhance the overall performance and reliability of gel electrophoresis experiments.
- Sample preparation and loading techniques: Effective sample preparation and loading techniques are crucial for successful gel electrophoresis. This includes methods for concentrating and purifying samples, as well as innovative approaches for introducing samples into the gel. Improved loading techniques can enhance the resolution and accuracy of electrophoretic separations.
- Detection and analysis methods: Advanced detection and analysis methods are developed to improve the visualization and quantification of separated molecules in gel electrophoresis. These may include fluorescent labeling techniques, image analysis software, and integration with other analytical tools. Enhanced detection methods allow for more sensitive and accurate analysis of electrophoresis results.
- Specialized electrophoresis techniques: Specialized electrophoresis techniques are developed for specific applications or to overcome limitations of traditional methods. These may include pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, two-dimensional electrophoresis, or capillary electrophoresis. Such techniques expand the capabilities of gel electrophoresis for analyzing complex mixtures or specific types of molecules.
02 Electrophoresis apparatus design
Innovations in electrophoresis apparatus design focus on improving efficiency, reproducibility, and ease of use. These designs may include features such as integrated cooling systems, adjustable voltage controls, and specialized sample loading mechanisms. Advanced apparatus designs aim to enhance separation quality and increase throughput for various analytical applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Detection and imaging techniques
Various detection and imaging techniques are employed to visualize and analyze the separated molecules in gel electrophoresis. These may include fluorescence-based methods, staining protocols, and advanced imaging systems. Improvements in detection sensitivity and resolution enable more accurate analysis of complex biological samples.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sample preparation and loading
Innovations in sample preparation and loading techniques aim to improve the efficiency and accuracy of gel electrophoresis. These may include methods for concentrating samples, removing interfering substances, and ensuring uniform sample application. Advanced loading techniques can enhance the resolution and reproducibility of separations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Specialized electrophoresis applications
Gel electrophoresis techniques are adapted for specialized applications in various fields, including proteomics, genomics, and forensic analysis. These adaptations may involve modifications to gel compositions, running conditions, or detection methods to optimize separation and analysis for specific types of molecules or research questions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Veterinary Diagnostic Equipment Industry
The gel electrophoresis market in veterinary diagnostics is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for accurate and efficient diagnostic tools in animal healthcare. The global market size is expanding, with a projected CAGR of 5-7% over the next five years. Technologically, gel electrophoresis is mature but continues to evolve with innovations in automation and miniaturization. Key players like Bio-Rad Laboratories, Life Technologies, and Beckman Coulter are leading the field, offering advanced systems and reagents. Emerging companies such as BiOptic and Helena Laboratories are also contributing to market competitiveness through specialized products and regional focus.
Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
Technical Solution: Bio-Rad Laboratories has developed advanced gel electrophoresis systems specifically tailored for veterinary diagnostics. Their technology includes high-resolution agarose gels and specialized buffer systems optimized for separating and analyzing animal DNA, proteins, and other biomolecules. The company's automated systems, such as the Bio-Rad NGC Chromatography System, integrate gel electrophoresis with other analytical techniques for comprehensive veterinary sample analysis[1]. Bio-Rad also offers veterinary-specific kits for detecting genetic markers associated with animal diseases and breed characteristics, enhancing the diagnostic capabilities in veterinary medicine[2].
Strengths: Comprehensive range of veterinary-specific products, high-resolution separation capabilities, and integrated analytical systems. Weaknesses: Potentially higher costs compared to basic systems, may require specialized training for optimal use.
Life Technologies Corp.
Technical Solution: Life Technologies Corp. has pioneered advanced gel electrophoresis techniques for veterinary diagnostics, focusing on rapid and accurate DNA analysis. Their Applied Biosystems™ line includes automated capillary electrophoresis systems that allow for high-throughput genetic testing in animals. These systems can detect genetic disorders, identify breed-specific markers, and assist in parentage verification for livestock and companion animals[3]. Life Technologies also offers specialized reagents and kits optimized for veterinary samples, enabling the detection of pathogens and genetic traits with high sensitivity and specificity[4].
Strengths: High-throughput capabilities, advanced automation, and specialized veterinary genetic testing kits. Weaknesses: May be complex for small veterinary practices, potentially high initial investment.
Innovative Gel Electrophoresis Methods for Veterinary Use
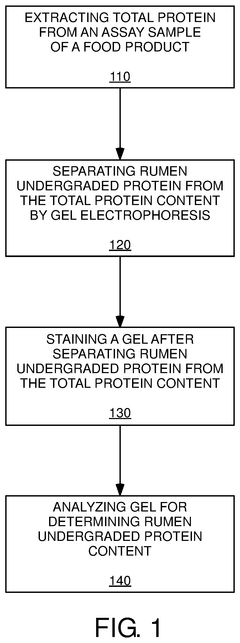
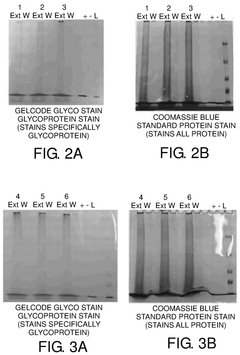
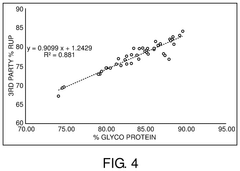
Diagnostic assay for rumen undegraded protein detection
PatentActiveUS12111302B2
Innovation
- A diagnostic assay using gel electrophoresis to separate and quantify rumen undegraded protein by comparing the ratio of glycosylated protein to total protein content, allowing for rapid and cost-effective determination of RUP through a correlation with third-party testing results.
Gelling Electrophoresis Loading Buffer
PatentInactiveUS20070240991A1
Innovation
- A sample buffer comprising a macromolecule, solvent, and solute is used, which remains in a liquid state until converted to a gel upon contact with the electrophoresis device, eliminating mixing with the running buffer and allowing for sharper, more concentrated sample application, especially suitable for multiple tray gel electrophoresis devices.
Regulatory Considerations for Veterinary Diagnostic Tools
Regulatory considerations play a crucial role in the development, validation, and implementation of veterinary diagnostic tools, including gel electrophoresis techniques. These regulations ensure the safety, efficacy, and reliability of diagnostic methods used in veterinary medicine.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of veterinary diagnostic tools through the Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM). The CVM is responsible for evaluating and approving new diagnostic devices and methods for use in animal health. For gel electrophoresis applications in veterinary diagnostics, manufacturers must comply with the FDA's quality system regulations and good manufacturing practices.
The European Union has established the Veterinary Medicinal Products Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2019/6) to govern the approval and use of veterinary diagnostic tools. This regulation aims to harmonize the requirements across EU member states and ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of veterinary products, including diagnostic methods like gel electrophoresis.
Regulatory bodies typically require extensive validation studies to demonstrate the accuracy, precision, and reproducibility of gel electrophoresis techniques for specific veterinary diagnostic applications. These studies often involve comparing the new method to existing gold standard techniques and assessing its performance across different animal species and disease conditions.
Laboratories utilizing gel electrophoresis for veterinary diagnostics must adhere to quality assurance and quality control measures to maintain regulatory compliance. This includes regular calibration of equipment, standardization of protocols, and participation in proficiency testing programs to ensure consistent and reliable results.
Data privacy and security regulations also apply to veterinary diagnostic tools, particularly when patient information is collected and stored electronically. Laboratories must implement appropriate measures to protect sensitive animal health data and comply with relevant data protection laws.
As the field of veterinary diagnostics continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to accommodate new technologies and methodologies. This includes the development of guidelines for the use of advanced molecular techniques, such as next-generation sequencing, which may complement or replace traditional gel electrophoresis methods in certain applications.
International harmonization efforts, such as those led by the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE), aim to establish global standards for veterinary diagnostic tools. These initiatives facilitate the recognition of test results across borders and promote the adoption of best practices in veterinary diagnostics worldwide.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of veterinary diagnostic tools through the Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM). The CVM is responsible for evaluating and approving new diagnostic devices and methods for use in animal health. For gel electrophoresis applications in veterinary diagnostics, manufacturers must comply with the FDA's quality system regulations and good manufacturing practices.
The European Union has established the Veterinary Medicinal Products Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2019/6) to govern the approval and use of veterinary diagnostic tools. This regulation aims to harmonize the requirements across EU member states and ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of veterinary products, including diagnostic methods like gel electrophoresis.
Regulatory bodies typically require extensive validation studies to demonstrate the accuracy, precision, and reproducibility of gel electrophoresis techniques for specific veterinary diagnostic applications. These studies often involve comparing the new method to existing gold standard techniques and assessing its performance across different animal species and disease conditions.
Laboratories utilizing gel electrophoresis for veterinary diagnostics must adhere to quality assurance and quality control measures to maintain regulatory compliance. This includes regular calibration of equipment, standardization of protocols, and participation in proficiency testing programs to ensure consistent and reliable results.
Data privacy and security regulations also apply to veterinary diagnostic tools, particularly when patient information is collected and stored electronically. Laboratories must implement appropriate measures to protect sensitive animal health data and comply with relevant data protection laws.
As the field of veterinary diagnostics continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to accommodate new technologies and methodologies. This includes the development of guidelines for the use of advanced molecular techniques, such as next-generation sequencing, which may complement or replace traditional gel electrophoresis methods in certain applications.
International harmonization efforts, such as those led by the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE), aim to establish global standards for veterinary diagnostic tools. These initiatives facilitate the recognition of test results across borders and promote the adoption of best practices in veterinary diagnostics worldwide.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Gel Electrophoresis in Veterinary Practice
Gel electrophoresis has become an indispensable tool in veterinary diagnostics, offering valuable insights into various animal health conditions. However, the implementation of this technology in veterinary practices requires careful consideration of its cost-effectiveness. This analysis aims to evaluate the financial implications and benefits of incorporating gel electrophoresis into veterinary clinics.
The initial investment for gel electrophoresis equipment can be substantial, ranging from $2,000 to $10,000 for basic setups, with more advanced systems costing upwards of $20,000. Additionally, ongoing expenses include consumables such as gels, buffers, and reagents, which can amount to $500-$1,000 per month for a moderate-sized practice.
Despite these costs, the benefits of gel electrophoresis in veterinary diagnostics are significant. The technique allows for rapid and accurate identification of various pathogens, including bacteria and viruses, enabling veterinarians to make timely and informed treatment decisions. This can lead to improved patient outcomes and reduced overall treatment costs.
Furthermore, gel electrophoresis facilitates the detection of genetic disorders in animals, supporting breeding programs and helping to prevent the propagation of hereditary diseases. This capability can enhance the reputation of veterinary practices and attract clients seeking specialized genetic testing services.
The technique also proves valuable in monitoring treatment efficacy, particularly in cases involving protein disorders or certain cancers. By providing a means to track changes in protein profiles over time, gel electrophoresis enables veterinarians to adjust treatment plans more effectively, potentially reducing the duration and cost of long-term therapies.
From a financial perspective, the implementation of gel electrophoresis can lead to increased revenue streams for veterinary practices. The ability to offer advanced diagnostic services may justify higher consultation fees and attract a more diverse client base. Additionally, the improved accuracy in diagnoses can reduce the need for repeated tests or unnecessary treatments, ultimately saving costs for both the practice and pet owners.
However, the cost-benefit ratio may vary depending on the size and specialization of the veterinary practice. Smaller clinics with limited caseloads might find it challenging to justify the initial investment, while larger practices or those specializing in genetic or oncological cases are more likely to see a favorable return on investment.
In conclusion, while the implementation of gel electrophoresis in veterinary practice involves significant upfront and ongoing costs, the potential benefits in terms of improved diagnostic capabilities, treatment outcomes, and revenue generation make it a worthwhile consideration for many veterinary clinics. A careful assessment of the practice's specific needs, patient demographics, and long-term goals is essential in determining the overall cost-effectiveness of this technology.
The initial investment for gel electrophoresis equipment can be substantial, ranging from $2,000 to $10,000 for basic setups, with more advanced systems costing upwards of $20,000. Additionally, ongoing expenses include consumables such as gels, buffers, and reagents, which can amount to $500-$1,000 per month for a moderate-sized practice.
Despite these costs, the benefits of gel electrophoresis in veterinary diagnostics are significant. The technique allows for rapid and accurate identification of various pathogens, including bacteria and viruses, enabling veterinarians to make timely and informed treatment decisions. This can lead to improved patient outcomes and reduced overall treatment costs.
Furthermore, gel electrophoresis facilitates the detection of genetic disorders in animals, supporting breeding programs and helping to prevent the propagation of hereditary diseases. This capability can enhance the reputation of veterinary practices and attract clients seeking specialized genetic testing services.
The technique also proves valuable in monitoring treatment efficacy, particularly in cases involving protein disorders or certain cancers. By providing a means to track changes in protein profiles over time, gel electrophoresis enables veterinarians to adjust treatment plans more effectively, potentially reducing the duration and cost of long-term therapies.
From a financial perspective, the implementation of gel electrophoresis can lead to increased revenue streams for veterinary practices. The ability to offer advanced diagnostic services may justify higher consultation fees and attract a more diverse client base. Additionally, the improved accuracy in diagnoses can reduce the need for repeated tests or unnecessary treatments, ultimately saving costs for both the practice and pet owners.
However, the cost-benefit ratio may vary depending on the size and specialization of the veterinary practice. Smaller clinics with limited caseloads might find it challenging to justify the initial investment, while larger practices or those specializing in genetic or oncological cases are more likely to see a favorable return on investment.
In conclusion, while the implementation of gel electrophoresis in veterinary practice involves significant upfront and ongoing costs, the potential benefits in terms of improved diagnostic capabilities, treatment outcomes, and revenue generation make it a worthwhile consideration for many veterinary clinics. A careful assessment of the practice's specific needs, patient demographics, and long-term goals is essential in determining the overall cost-effectiveness of this technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!