Zeolite Film Applications in Anti-reflective Coatings
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Zeolite Film Tech Evolution
The evolution of zeolite film technology in anti-reflective coatings has been marked by significant advancements over the past few decades. Initially, zeolite films were primarily used in industrial applications such as gas separation and catalysis. However, their unique properties, including high porosity and tunable refractive indices, soon attracted attention for optical applications.
In the early 1990s, researchers began exploring the potential of zeolite films for anti-reflective coatings. The first attempts focused on synthesizing thin zeolite layers on glass substrates using hydrothermal methods. These early films showed promise in reducing reflectance but suffered from poor adhesion and uniformity.
A major breakthrough came in the late 1990s with the development of in-situ crystallization techniques. This method allowed for better control over film thickness and improved adhesion to the substrate. Concurrently, advances in zeolite synthesis led to the creation of new framework types with tailored pore sizes and structures, expanding the range of achievable refractive indices.
The early 2000s saw the introduction of secondary growth methods, which significantly enhanced film quality and reduced defects. This period also marked the beginning of efforts to incorporate zeolite films into multi-layer anti-reflective coating systems, leveraging their unique optical properties in combination with traditional materials.
By the mid-2000s, researchers had developed techniques to control the orientation of zeolite crystals within the film, further optimizing their anti-reflective properties. This was followed by the exploration of hierarchical zeolite structures, combining micropores and mesopores to achieve even lower refractive indices.
The last decade has witnessed a surge in the development of hybrid zeolite-polymer films. These composites offer improved mechanical properties and easier processing while maintaining the excellent optical characteristics of zeolites. Additionally, recent advancements in nanotechnology have enabled the creation of ultra-thin zeolite films with precisely controlled thicknesses down to a few nanometers.
Current research focuses on enhancing the durability and environmental stability of zeolite films for practical applications. Efforts are also underway to scale up production methods for industrial use, with particular emphasis on large-area coatings for solar panels and architectural glass.
Looking ahead, the integration of zeolite films with smart materials for switchable anti-reflective coatings represents an exciting frontier. Furthermore, the development of bio-inspired zeolite structures mimicking natural anti-reflective surfaces holds promise for achieving unprecedented levels of performance in optical applications.
In the early 1990s, researchers began exploring the potential of zeolite films for anti-reflective coatings. The first attempts focused on synthesizing thin zeolite layers on glass substrates using hydrothermal methods. These early films showed promise in reducing reflectance but suffered from poor adhesion and uniformity.
A major breakthrough came in the late 1990s with the development of in-situ crystallization techniques. This method allowed for better control over film thickness and improved adhesion to the substrate. Concurrently, advances in zeolite synthesis led to the creation of new framework types with tailored pore sizes and structures, expanding the range of achievable refractive indices.
The early 2000s saw the introduction of secondary growth methods, which significantly enhanced film quality and reduced defects. This period also marked the beginning of efforts to incorporate zeolite films into multi-layer anti-reflective coating systems, leveraging their unique optical properties in combination with traditional materials.
By the mid-2000s, researchers had developed techniques to control the orientation of zeolite crystals within the film, further optimizing their anti-reflective properties. This was followed by the exploration of hierarchical zeolite structures, combining micropores and mesopores to achieve even lower refractive indices.
The last decade has witnessed a surge in the development of hybrid zeolite-polymer films. These composites offer improved mechanical properties and easier processing while maintaining the excellent optical characteristics of zeolites. Additionally, recent advancements in nanotechnology have enabled the creation of ultra-thin zeolite films with precisely controlled thicknesses down to a few nanometers.
Current research focuses on enhancing the durability and environmental stability of zeolite films for practical applications. Efforts are also underway to scale up production methods for industrial use, with particular emphasis on large-area coatings for solar panels and architectural glass.
Looking ahead, the integration of zeolite films with smart materials for switchable anti-reflective coatings represents an exciting frontier. Furthermore, the development of bio-inspired zeolite structures mimicking natural anti-reflective surfaces holds promise for achieving unprecedented levels of performance in optical applications.
Anti-reflective Market Analysis
The anti-reflective coating market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industries. This market segment is closely tied to the development and application of advanced materials, including zeolite films, which have shown promising potential in enhancing the performance of anti-reflective coatings.
The global anti-reflective coating market is primarily fueled by the expanding electronics and solar energy sectors. In the electronics industry, anti-reflective coatings are essential for improving display quality in smartphones, tablets, and other devices with screens. The growing consumer electronics market, particularly in emerging economies, has contributed to the increased demand for these coatings.
In the solar energy sector, anti-reflective coatings play a crucial role in improving the efficiency of photovoltaic cells by reducing light reflection and maximizing light absorption. As the world shifts towards renewable energy sources, the demand for solar panels continues to rise, subsequently driving the market for anti-reflective coatings.
The automotive industry is another significant contributor to the anti-reflective coating market. These coatings are used on vehicle displays, mirrors, and windows to enhance visibility and reduce glare, improving both safety and aesthetics. With the increasing integration of advanced display technologies in modern vehicles, the demand for high-quality anti-reflective coatings is expected to grow further.
The healthcare sector also presents opportunities for anti-reflective coatings, particularly in medical imaging equipment and eyewear. In ophthalmology, anti-reflective coatings on eyeglasses and contact lenses improve visual clarity and reduce eye strain, driving demand in this segment.
Zeolite films, as a novel material for anti-reflective coatings, offer several advantages over traditional coating materials. Their unique porous structure allows for precise control of refractive index, making them highly effective in reducing reflections across a wide range of wavelengths. Additionally, zeolite films exhibit excellent durability and resistance to environmental factors, addressing some of the limitations of conventional anti-reflective coatings.
The market for zeolite-based anti-reflective coatings is still in its early stages but shows promising growth potential. As research and development efforts continue to improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of zeolite films, their adoption in various applications is expected to increase. This trend aligns with the overall market demand for more efficient and durable anti-reflective coating solutions.
The global anti-reflective coating market is primarily fueled by the expanding electronics and solar energy sectors. In the electronics industry, anti-reflective coatings are essential for improving display quality in smartphones, tablets, and other devices with screens. The growing consumer electronics market, particularly in emerging economies, has contributed to the increased demand for these coatings.
In the solar energy sector, anti-reflective coatings play a crucial role in improving the efficiency of photovoltaic cells by reducing light reflection and maximizing light absorption. As the world shifts towards renewable energy sources, the demand for solar panels continues to rise, subsequently driving the market for anti-reflective coatings.
The automotive industry is another significant contributor to the anti-reflective coating market. These coatings are used on vehicle displays, mirrors, and windows to enhance visibility and reduce glare, improving both safety and aesthetics. With the increasing integration of advanced display technologies in modern vehicles, the demand for high-quality anti-reflective coatings is expected to grow further.
The healthcare sector also presents opportunities for anti-reflective coatings, particularly in medical imaging equipment and eyewear. In ophthalmology, anti-reflective coatings on eyeglasses and contact lenses improve visual clarity and reduce eye strain, driving demand in this segment.
Zeolite films, as a novel material for anti-reflective coatings, offer several advantages over traditional coating materials. Their unique porous structure allows for precise control of refractive index, making them highly effective in reducing reflections across a wide range of wavelengths. Additionally, zeolite films exhibit excellent durability and resistance to environmental factors, addressing some of the limitations of conventional anti-reflective coatings.
The market for zeolite-based anti-reflective coatings is still in its early stages but shows promising growth potential. As research and development efforts continue to improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of zeolite films, their adoption in various applications is expected to increase. This trend aligns with the overall market demand for more efficient and durable anti-reflective coating solutions.
Zeolite Film Challenges
Despite the promising applications of zeolite films in anti-reflective coatings, several significant challenges hinder their widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary obstacles is the difficulty in achieving uniform and defect-free zeolite film deposition over large surface areas. The intricate porous structure of zeolites makes it challenging to create continuous, homogeneous films without cracks or pinholes, which can compromise the anti-reflective properties and overall coating integrity.
Another major challenge lies in controlling the thickness and porosity of zeolite films with high precision. The anti-reflective performance of these coatings is highly dependent on these parameters, and even slight variations can lead to significant changes in optical properties. Achieving the desired thickness and porosity consistently across different substrates and environmental conditions remains a complex task for researchers and manufacturers.
The stability and durability of zeolite films in various operating conditions pose additional challenges. Anti-reflective coatings are often exposed to harsh environments, including high temperatures, humidity, and mechanical stress. Ensuring that zeolite films maintain their structural integrity and optical properties over extended periods under these conditions is crucial for their practical application but remains a significant hurdle.
Furthermore, the adhesion of zeolite films to different substrate materials presents another challenge. Poor adhesion can lead to delamination or flaking of the coating, severely impacting its performance and longevity. Developing robust bonding techniques that work across a range of substrate materials while preserving the zeolite film's anti-reflective properties is an ongoing area of research.
The scalability of zeolite film production for industrial applications is also a considerable challenge. Current synthesis methods often involve time-consuming and complex processes that are difficult to scale up without compromising film quality. Developing cost-effective, large-scale production techniques that maintain the desired film characteristics is essential for the commercial viability of zeolite-based anti-reflective coatings.
Lastly, the environmental impact and sustainability of zeolite film production and application processes need to be addressed. As industries move towards more eco-friendly practices, finding green synthesis methods and ensuring the recyclability or safe disposal of zeolite-based coatings at the end of their lifecycle presents additional challenges that researchers must overcome.
Another major challenge lies in controlling the thickness and porosity of zeolite films with high precision. The anti-reflective performance of these coatings is highly dependent on these parameters, and even slight variations can lead to significant changes in optical properties. Achieving the desired thickness and porosity consistently across different substrates and environmental conditions remains a complex task for researchers and manufacturers.
The stability and durability of zeolite films in various operating conditions pose additional challenges. Anti-reflective coatings are often exposed to harsh environments, including high temperatures, humidity, and mechanical stress. Ensuring that zeolite films maintain their structural integrity and optical properties over extended periods under these conditions is crucial for their practical application but remains a significant hurdle.
Furthermore, the adhesion of zeolite films to different substrate materials presents another challenge. Poor adhesion can lead to delamination or flaking of the coating, severely impacting its performance and longevity. Developing robust bonding techniques that work across a range of substrate materials while preserving the zeolite film's anti-reflective properties is an ongoing area of research.
The scalability of zeolite film production for industrial applications is also a considerable challenge. Current synthesis methods often involve time-consuming and complex processes that are difficult to scale up without compromising film quality. Developing cost-effective, large-scale production techniques that maintain the desired film characteristics is essential for the commercial viability of zeolite-based anti-reflective coatings.
Lastly, the environmental impact and sustainability of zeolite film production and application processes need to be addressed. As industries move towards more eco-friendly practices, finding green synthesis methods and ensuring the recyclability or safe disposal of zeolite-based coatings at the end of their lifecycle presents additional challenges that researchers must overcome.
Current Zeolite Solutions
01 Zeolite-based anti-reflective coatings
Zeolite films can be used to create anti-reflective coatings on various surfaces. These coatings utilize the porous structure of zeolites to reduce light reflection and improve optical performance. The zeolite films can be applied to glass, lenses, and other optical components to enhance light transmission and reduce glare.- Zeolite-based anti-reflective coatings: Zeolite films can be used to create anti-reflective coatings on various surfaces. These coatings utilize the porous structure of zeolites to reduce light reflection and improve optical performance. The zeolite films can be applied to glass, lenses, and other optical components to enhance their anti-reflective properties.
- Fabrication methods for zeolite anti-reflective films: Various techniques are employed to fabricate zeolite-based anti-reflective films. These methods may include sol-gel processes, hydrothermal synthesis, and vapor deposition. The fabrication process can be optimized to control the film thickness, porosity, and zeolite crystal size, which are crucial factors in determining the anti-reflective properties of the coating.
- Zeolite film composition and structure: The composition and structure of zeolite films play a crucial role in their anti-reflective properties. Different types of zeolites, such as ZSM-5, silicalite, and beta zeolite, can be used to create films with varying pore sizes and structures. The film's refractive index can be tuned by adjusting the zeolite composition and incorporating additional materials to enhance its anti-reflective performance.
- Applications of zeolite anti-reflective films: Zeolite-based anti-reflective films find applications in various fields, including optics, solar cells, and display technologies. These films can be used to improve the efficiency of photovoltaic devices, enhance the performance of optical sensors, and reduce glare in electronic displays. The versatility of zeolite films makes them suitable for a wide range of anti-reflective applications.
- Durability and performance enhancement of zeolite anti-reflective films: Efforts are made to improve the durability and performance of zeolite-based anti-reflective films. This includes developing methods to enhance the mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and long-term stability of the films. Additionally, research focuses on optimizing the film's optical properties, such as broadband anti-reflection and omnidirectional performance, to meet the requirements of various applications.
02 Fabrication methods for zeolite anti-reflective films
Various techniques are employed to fabricate zeolite-based anti-reflective films. These methods may include sol-gel processes, chemical vapor deposition, and spin coating. The fabrication process often involves controlling the thickness and porosity of the zeolite layer to achieve optimal anti-reflective properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Zeolite film composition and structure
The composition and structure of zeolite films play a crucial role in their anti-reflective properties. Specific zeolite types, particle sizes, and pore structures are selected to achieve desired optical characteristics. The films may also incorporate additional materials or undergo surface modifications to enhance their performance and durability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of zeolite anti-reflective films
Zeolite-based anti-reflective films find applications in various fields, including optics, electronics, and solar energy. They are used in optical devices, display screens, solar panels, and architectural glass to improve light transmission, reduce glare, and enhance overall performance. The films can be tailored for specific wavelength ranges and environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Performance optimization and characterization
Researchers focus on optimizing the performance of zeolite anti-reflective films through various techniques. This includes studying the relationship between film properties and anti-reflective performance, developing methods for characterizing film quality, and exploring ways to enhance durability and longevity. Advanced analytical techniques are employed to assess film structure and optical properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Anti-reflective Players
The zeolite film applications in anti-reflective coatings market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for high-performance optical coatings across various industries. The market size is expanding, with potential applications in electronics, solar panels, and automotive sectors. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Industrial Technology Research Institute, DuPont, and First Solar leading research efforts. Established players such as AGC, Nitto Denko, and Saint-Gobain are leveraging their expertise in materials science to develop innovative zeolite-based coatings. Emerging companies like JGC Catalysts & Chemicals and Maxim Integrated are also contributing to the technological maturation of this field, indicating a competitive and dynamic market landscape.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed advanced zeolite film technology for anti-reflective coatings, focusing on enhancing optical performance and durability. Their approach involves synthesizing zeolite nanoparticles with controlled size and porosity, which are then deposited onto substrates using sol-gel techniques[1]. This results in a highly uniform and thin zeolite film with excellent anti-reflective properties. DuPont's process allows for precise control of film thickness and refractive index, enabling customization for specific wavelengths and applications[3]. The company has also incorporated hydrophobic treatments to improve the coating's resistance to environmental factors and extend its lifespan[5].
Strengths: Precise control over film properties, excellent optical performance, and improved durability. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and complexity compared to traditional coatings.
First Solar, Inc.
Technical Solution: First Solar has integrated zeolite film technology into their photovoltaic module production, focusing on enhancing light transmission and energy conversion efficiency. Their approach involves depositing a thin zeolite layer on the glass surface of solar panels using a proprietary deposition technique[2]. This zeolite film acts as an anti-reflective coating, reducing light reflection and increasing the amount of light reaching the photovoltaic cells. First Solar's method also incorporates specific zeolite structures that provide additional benefits such as self-cleaning properties and improved durability under harsh environmental conditions[4]. The company has reported efficiency gains of up to 3% in their solar modules due to this zeolite-based anti-reflective coating[6].
Strengths: Directly applicable to solar industry, improved module efficiency, and added functional properties. Weaknesses: Potentially limited to specific types of solar panels and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Zeolite Film Innovations
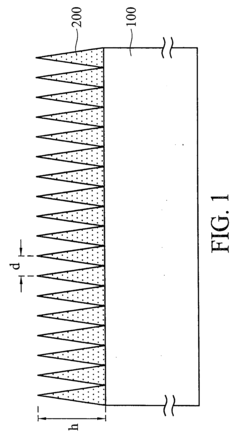
Coating Composition for Low-Refractive Index Anti-Reflection Film
PatentInactiveUS20120167800A1
Innovation
- A composition comprising zeolite nanocrystals and zeolite precursor nanoparticles, where the zeolite nanocrystals are mixed with a zeolite precursor sol prepared from tetraalkoxysilanes in an aqueous solution of tetraalkylammonium hydroxide, allowing for a direct application and conversion to a zeolite anti-reflection film upon heat treatment, enhancing the abrasive resistance and reducing production time.
Antireflective transparent zeolite hardcoat, method for fabricating the same
PatentActiveUS20080206456A1
Innovation
- A single-layer antireflective transparent zeolite hardcoat is formed using a two-stage thermal condensation process with a mixture of silica source, water, and zeolite structure directing agent, which is then coated on a substrate and heated under low humidity conditions, creating a porous nanostructure with a gradient refractive index that reduces reflectance and provides mechanical strength.
Environmental Impact
The application of zeolite films in anti-reflective coatings has significant environmental implications, both positive and potentially negative. One of the primary environmental benefits is the potential for energy conservation. Anti-reflective coatings enhanced with zeolite films can improve the efficiency of solar panels by reducing light reflection, thereby increasing the amount of light absorbed and converted into electricity. This increased efficiency can lead to a reduction in the overall energy consumption and carbon footprint associated with solar energy production.
Furthermore, the use of zeolite films in anti-reflective coatings can contribute to the longevity of various optical devices and surfaces. By reducing glare and improving visibility, these coatings can extend the lifespan of products such as electronic displays, windows, and optical lenses. This increased durability can result in less frequent replacements, ultimately reducing waste and the environmental impact associated with manufacturing and disposing of these products.
However, the production of zeolite films and their integration into anti-reflective coatings may have some environmental considerations. The synthesis of zeolites often involves the use of chemicals and energy-intensive processes. It is crucial to assess and optimize these production methods to minimize their environmental impact, such as reducing water consumption, managing waste products, and improving energy efficiency in manufacturing.
The disposal and end-of-life management of products containing zeolite-based anti-reflective coatings also require attention. While zeolites themselves are generally considered environmentally friendly due to their inorganic nature, the composite materials used in coatings may pose challenges for recycling or safe disposal. Developing effective recycling methods and establishing proper disposal protocols will be essential to mitigate potential environmental risks.
Another aspect to consider is the potential for zeolite films to contribute to air and water purification. Zeolites are known for their adsorption properties, which could be leveraged in anti-reflective coatings to simultaneously provide optical benefits and environmental remediation capabilities. For instance, coatings on building exteriors could potentially help filter air pollutants or capture harmful particles, contributing to improved air quality in urban environments.
In conclusion, while zeolite film applications in anti-reflective coatings offer promising environmental benefits, particularly in energy conservation and product longevity, it is crucial to address the entire lifecycle of these materials. This includes optimizing production processes, developing sustainable manufacturing practices, and establishing effective recycling and disposal methods to ensure that the overall environmental impact remains positive.
Furthermore, the use of zeolite films in anti-reflective coatings can contribute to the longevity of various optical devices and surfaces. By reducing glare and improving visibility, these coatings can extend the lifespan of products such as electronic displays, windows, and optical lenses. This increased durability can result in less frequent replacements, ultimately reducing waste and the environmental impact associated with manufacturing and disposing of these products.
However, the production of zeolite films and their integration into anti-reflective coatings may have some environmental considerations. The synthesis of zeolites often involves the use of chemicals and energy-intensive processes. It is crucial to assess and optimize these production methods to minimize their environmental impact, such as reducing water consumption, managing waste products, and improving energy efficiency in manufacturing.
The disposal and end-of-life management of products containing zeolite-based anti-reflective coatings also require attention. While zeolites themselves are generally considered environmentally friendly due to their inorganic nature, the composite materials used in coatings may pose challenges for recycling or safe disposal. Developing effective recycling methods and establishing proper disposal protocols will be essential to mitigate potential environmental risks.
Another aspect to consider is the potential for zeolite films to contribute to air and water purification. Zeolites are known for their adsorption properties, which could be leveraged in anti-reflective coatings to simultaneously provide optical benefits and environmental remediation capabilities. For instance, coatings on building exteriors could potentially help filter air pollutants or capture harmful particles, contributing to improved air quality in urban environments.
In conclusion, while zeolite film applications in anti-reflective coatings offer promising environmental benefits, particularly in energy conservation and product longevity, it is crucial to address the entire lifecycle of these materials. This includes optimizing production processes, developing sustainable manufacturing practices, and establishing effective recycling and disposal methods to ensure that the overall environmental impact remains positive.
Zeolite Film Manufacturing
Zeolite film manufacturing has evolved significantly over the past decades, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance anti-reflective coatings. The process typically involves several key steps, including substrate preparation, zeolite synthesis, film deposition, and post-treatment.
Substrate preparation is crucial for ensuring proper adhesion and uniformity of the zeolite film. This step often includes cleaning, surface activation, and sometimes the application of a primer layer. The choice of substrate material and its surface properties can significantly influence the final film quality and performance.
Zeolite synthesis is a critical phase in the manufacturing process. Various methods have been developed, including hydrothermal synthesis, sol-gel processes, and in-situ crystallization. Each method offers distinct advantages in terms of film thickness control, crystal size distribution, and pore structure. The selection of zeolite type and synthesis conditions is tailored to achieve the desired optical properties for anti-reflective applications.
Film deposition techniques have also advanced considerably. Common methods include dip-coating, spin-coating, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). More recently, advanced techniques such as atomic layer deposition (ALD) have been employed to achieve precise control over film thickness and composition. These methods allow for the creation of uniform, defect-free zeolite films with excellent anti-reflective properties.
Post-treatment processes are often employed to enhance the film's performance and durability. These may include thermal annealing to improve crystallinity, ion exchange to modify the zeolite's optical properties, or surface functionalization to enhance hydrophobicity or other desired characteristics.
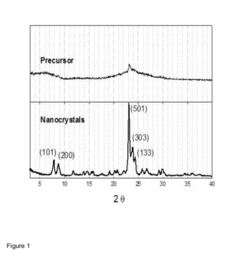
Quality control is an integral part of zeolite film manufacturing. Advanced characterization techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and ellipsometry are routinely used to assess film thickness, crystallinity, and optical properties. These measurements ensure that the manufactured films meet the stringent requirements for anti-reflective coatings.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness remain ongoing challenges in zeolite film manufacturing. While laboratory-scale production has demonstrated excellent results, translating these processes to industrial-scale production requires careful optimization. Efforts are being made to develop continuous manufacturing processes and to reduce the environmental impact of zeolite synthesis through the use of greener solvents and more efficient energy utilization.
Substrate preparation is crucial for ensuring proper adhesion and uniformity of the zeolite film. This step often includes cleaning, surface activation, and sometimes the application of a primer layer. The choice of substrate material and its surface properties can significantly influence the final film quality and performance.
Zeolite synthesis is a critical phase in the manufacturing process. Various methods have been developed, including hydrothermal synthesis, sol-gel processes, and in-situ crystallization. Each method offers distinct advantages in terms of film thickness control, crystal size distribution, and pore structure. The selection of zeolite type and synthesis conditions is tailored to achieve the desired optical properties for anti-reflective applications.
Film deposition techniques have also advanced considerably. Common methods include dip-coating, spin-coating, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). More recently, advanced techniques such as atomic layer deposition (ALD) have been employed to achieve precise control over film thickness and composition. These methods allow for the creation of uniform, defect-free zeolite films with excellent anti-reflective properties.
Post-treatment processes are often employed to enhance the film's performance and durability. These may include thermal annealing to improve crystallinity, ion exchange to modify the zeolite's optical properties, or surface functionalization to enhance hydrophobicity or other desired characteristics.
Quality control is an integral part of zeolite film manufacturing. Advanced characterization techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and ellipsometry are routinely used to assess film thickness, crystallinity, and optical properties. These measurements ensure that the manufactured films meet the stringent requirements for anti-reflective coatings.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness remain ongoing challenges in zeolite film manufacturing. While laboratory-scale production has demonstrated excellent results, translating these processes to industrial-scale production requires careful optimization. Efforts are being made to develop continuous manufacturing processes and to reduce the environmental impact of zeolite synthesis through the use of greener solvents and more efficient energy utilization.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!