Advancements in LDPE Manufacturing for Future Needs
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Evolution and Objectives
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone of the plastics industry since its accidental discovery in 1933 by Imperial Chemical Industries. This versatile polymer has undergone significant evolution over the decades, driven by increasing demand and the need for improved material properties. The journey of LDPE manufacturing began with high-pressure tubular reactors and has since progressed to include various reactor designs and process optimizations.
The primary objective in LDPE manufacturing advancements is to enhance production efficiency while maintaining or improving product quality. This involves developing technologies that allow for higher throughput, reduced energy consumption, and better control over molecular weight distribution and branching. Additionally, there is a growing focus on sustainability, with efforts directed towards incorporating recycled materials and reducing the environmental footprint of LDPE production.
One of the key technological goals in LDPE manufacturing is the development of more efficient catalysts. These catalysts aim to provide better control over the polymerization process, allowing for the production of LDPE with tailored properties to meet specific application requirements. This includes the ability to produce resins with improved strength, clarity, and processability.
Another critical objective is the optimization of reactor designs. Modern LDPE reactors are being engineered to handle higher pressures and temperatures, enabling increased production rates and improved product consistency. The integration of advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring technologies is also a priority, as these innovations allow for more precise control over reaction conditions and product quality.
The evolution of LDPE manufacturing is closely tied to advancements in material science and engineering. Researchers are exploring novel additives and processing techniques to enhance the performance characteristics of LDPE, such as improved barrier properties, increased thermal stability, and enhanced recyclability. These efforts are driven by the growing demand for high-performance packaging materials and the need to address environmental concerns associated with plastic use.
As the industry looks to the future, the objectives for LDPE manufacturing are increasingly aligned with circular economy principles. This includes developing technologies for more efficient recycling of LDPE products, as well as exploring bio-based feedstocks as alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived raw materials. The ultimate goal is to create a more sustainable LDPE production ecosystem that can meet the growing global demand while minimizing environmental impact.
The primary objective in LDPE manufacturing advancements is to enhance production efficiency while maintaining or improving product quality. This involves developing technologies that allow for higher throughput, reduced energy consumption, and better control over molecular weight distribution and branching. Additionally, there is a growing focus on sustainability, with efforts directed towards incorporating recycled materials and reducing the environmental footprint of LDPE production.
One of the key technological goals in LDPE manufacturing is the development of more efficient catalysts. These catalysts aim to provide better control over the polymerization process, allowing for the production of LDPE with tailored properties to meet specific application requirements. This includes the ability to produce resins with improved strength, clarity, and processability.
Another critical objective is the optimization of reactor designs. Modern LDPE reactors are being engineered to handle higher pressures and temperatures, enabling increased production rates and improved product consistency. The integration of advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring technologies is also a priority, as these innovations allow for more precise control over reaction conditions and product quality.
The evolution of LDPE manufacturing is closely tied to advancements in material science and engineering. Researchers are exploring novel additives and processing techniques to enhance the performance characteristics of LDPE, such as improved barrier properties, increased thermal stability, and enhanced recyclability. These efforts are driven by the growing demand for high-performance packaging materials and the need to address environmental concerns associated with plastic use.
As the industry looks to the future, the objectives for LDPE manufacturing are increasingly aligned with circular economy principles. This includes developing technologies for more efficient recycling of LDPE products, as well as exploring bio-based feedstocks as alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived raw materials. The ultimate goal is to create a more sustainable LDPE production ecosystem that can meet the growing global demand while minimizing environmental impact.
LDPE Market Dynamics
The LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by evolving consumer demands and technological advancements in manufacturing processes. The global LDPE market size was valued at approximately $33 billion in 2020, with projections indicating steady growth over the next decade.
One of the primary factors fueling market expansion is the increasing demand for flexible packaging solutions across various industries, particularly in food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and personal care sectors. LDPE's excellent moisture barrier properties, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred choice for packaging applications, contributing to its market growth.
The construction industry has also emerged as a significant consumer of LDPE, utilizing the material for applications such as geomembranes, pipes, and insulation. The growing emphasis on sustainable building practices and energy efficiency has further boosted LDPE demand in this sector.
In terms of regional dynamics, Asia-Pacific dominates the LDPE market, accounting for the largest share of global production and consumption. This is primarily attributed to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the presence of key manufacturing hubs in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow as significant markets, driven by technological advancements and stringent regulations promoting sustainable packaging solutions.
The automotive industry represents another key growth area for LDPE, with increasing use in vehicle components to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency. As electric vehicles gain traction, LDPE's role in battery components and lightweight structural elements is expected to expand further.
However, the LDPE market faces challenges from growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures regarding plastic waste. This has led to increased focus on recycling and the development of bio-based alternatives. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve LDPE's recyclability and explore more sustainable production methods.
The competitive landscape of the LDPE market is characterized by the presence of several major players, including ExxonMobil, SABIC, Dow Chemical, and LyondellBasell. These companies are actively engaged in capacity expansions, technological innovations, and strategic partnerships to maintain their market positions and address evolving customer needs.
Looking ahead, the LDPE market is poised for continued growth, driven by innovations in manufacturing processes that enhance product quality and sustainability. The development of advanced catalysts and process technologies is expected to improve LDPE's performance characteristics, opening up new application areas and market opportunities.
One of the primary factors fueling market expansion is the increasing demand for flexible packaging solutions across various industries, particularly in food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and personal care sectors. LDPE's excellent moisture barrier properties, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred choice for packaging applications, contributing to its market growth.
The construction industry has also emerged as a significant consumer of LDPE, utilizing the material for applications such as geomembranes, pipes, and insulation. The growing emphasis on sustainable building practices and energy efficiency has further boosted LDPE demand in this sector.
In terms of regional dynamics, Asia-Pacific dominates the LDPE market, accounting for the largest share of global production and consumption. This is primarily attributed to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the presence of key manufacturing hubs in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow as significant markets, driven by technological advancements and stringent regulations promoting sustainable packaging solutions.
The automotive industry represents another key growth area for LDPE, with increasing use in vehicle components to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency. As electric vehicles gain traction, LDPE's role in battery components and lightweight structural elements is expected to expand further.
However, the LDPE market faces challenges from growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures regarding plastic waste. This has led to increased focus on recycling and the development of bio-based alternatives. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve LDPE's recyclability and explore more sustainable production methods.
The competitive landscape of the LDPE market is characterized by the presence of several major players, including ExxonMobil, SABIC, Dow Chemical, and LyondellBasell. These companies are actively engaged in capacity expansions, technological innovations, and strategic partnerships to maintain their market positions and address evolving customer needs.
Looking ahead, the LDPE market is poised for continued growth, driven by innovations in manufacturing processes that enhance product quality and sustainability. The development of advanced catalysts and process technologies is expected to improve LDPE's performance characteristics, opening up new application areas and market opportunities.
LDPE Tech Challenges
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) manufacturing faces several significant challenges as the industry strives to meet future needs. One of the primary issues is energy efficiency. The traditional high-pressure process used for LDPE production is energy-intensive, consuming substantial amounts of electricity and fossil fuels. This not only increases production costs but also contributes to environmental concerns, particularly in terms of carbon emissions.
Another major challenge lies in product quality and consistency. As applications for LDPE become more sophisticated, there is an increasing demand for higher-quality polymers with specific properties. Achieving precise control over molecular weight distribution, branching, and other structural characteristics remains a complex task, especially at industrial scales.
Raw material sourcing presents an ongoing challenge for LDPE manufacturers. The industry's heavy reliance on fossil fuel-derived ethylene raises sustainability concerns and exposes producers to price volatility in the oil and gas markets. There is a growing need to explore alternative feedstocks, such as bio-based or recycled materials, to enhance sustainability and reduce dependency on non-renewable resources.
Process safety is another critical concern in LDPE manufacturing. The high-pressure conditions required for polymerization pose significant risks, necessitating robust safety measures and continuous improvement in process control systems. Balancing safety requirements with production efficiency remains a persistent challenge for manufacturers.
Scalability and flexibility in production are becoming increasingly important as market demands fluctuate. LDPE producers must adapt to changing customer requirements and market trends, which often necessitates the ability to quickly adjust production parameters or switch between different grades of LDPE. This flexibility can be challenging to achieve in large-scale, continuous production environments.
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals pose additional challenges for the LDPE industry. Reducing waste, minimizing emissions, and improving overall environmental performance are crucial objectives that require ongoing innovation in process technology and product design.
Lastly, the development of new catalysts and initiators represents both a challenge and an opportunity for LDPE manufacturing. While advances in catalyst technology could potentially address many of the aforementioned challenges, the research and development process is complex, time-consuming, and resource-intensive. Balancing the need for innovation with the practical constraints of industrial-scale production remains a significant hurdle for the industry.
Another major challenge lies in product quality and consistency. As applications for LDPE become more sophisticated, there is an increasing demand for higher-quality polymers with specific properties. Achieving precise control over molecular weight distribution, branching, and other structural characteristics remains a complex task, especially at industrial scales.
Raw material sourcing presents an ongoing challenge for LDPE manufacturers. The industry's heavy reliance on fossil fuel-derived ethylene raises sustainability concerns and exposes producers to price volatility in the oil and gas markets. There is a growing need to explore alternative feedstocks, such as bio-based or recycled materials, to enhance sustainability and reduce dependency on non-renewable resources.
Process safety is another critical concern in LDPE manufacturing. The high-pressure conditions required for polymerization pose significant risks, necessitating robust safety measures and continuous improvement in process control systems. Balancing safety requirements with production efficiency remains a persistent challenge for manufacturers.
Scalability and flexibility in production are becoming increasingly important as market demands fluctuate. LDPE producers must adapt to changing customer requirements and market trends, which often necessitates the ability to quickly adjust production parameters or switch between different grades of LDPE. This flexibility can be challenging to achieve in large-scale, continuous production environments.
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals pose additional challenges for the LDPE industry. Reducing waste, minimizing emissions, and improving overall environmental performance are crucial objectives that require ongoing innovation in process technology and product design.
Lastly, the development of new catalysts and initiators represents both a challenge and an opportunity for LDPE manufacturing. While advances in catalyst technology could potentially address many of the aforementioned challenges, the research and development process is complex, time-consuming, and resource-intensive. Balancing the need for innovation with the practical constraints of industrial-scale production remains a significant hurdle for the industry.
Current LDPE Processes
01 Improved catalyst systems for LDPE production
Advanced catalyst systems have been developed to enhance the efficiency and control of LDPE polymerization. These catalysts offer better activity, selectivity, and stability, resulting in improved product quality and reduced energy consumption during manufacturing.- Improved catalyst systems for LDPE production: Advanced catalyst systems have been developed to enhance the efficiency and control of LDPE polymerization. These catalysts offer better activity, selectivity, and stability, resulting in improved product quality and reduced energy consumption during manufacturing.
- Novel reactor designs for LDPE synthesis: Innovative reactor designs have been introduced to optimize LDPE production processes. These include advanced tubular reactors, improved autoclave systems, and novel configurations that enhance heat transfer, mixing, and pressure control, leading to better product consistency and increased throughput.
- Process control and automation advancements: Implementation of advanced process control systems and automation technologies in LDPE manufacturing has led to improved product quality, reduced variability, and increased operational efficiency. These advancements include real-time monitoring, predictive modeling, and adaptive control strategies.
- Sustainable and eco-friendly LDPE production methods: Development of sustainable LDPE manufacturing processes that focus on reducing environmental impact. These include the use of renewable feedstocks, energy-efficient technologies, and improved recycling methods to create more environmentally friendly LDPE products.
- Enhanced LDPE properties through additives and blending: Advancements in the use of additives and blending techniques to improve LDPE properties. These innovations allow for the production of LDPE with enhanced mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties, expanding its applications in various industries.
02 Novel reactor designs for LDPE production
Innovative reactor designs have been introduced to optimize LDPE manufacturing processes. These designs include improved mixing mechanisms, enhanced heat transfer systems, and more efficient pressure control, leading to better product consistency and increased production capacity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Process control and automation advancements
Advancements in process control and automation technologies have significantly improved LDPE manufacturing. These include real-time monitoring systems, predictive modeling, and artificial intelligence-driven optimization, resulting in more consistent product quality and reduced operational costs.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sustainable LDPE production methods
Environmentally friendly approaches to LDPE manufacturing have been developed, focusing on reducing carbon footprint and improving energy efficiency. These methods include the use of renewable feedstocks, recycled materials, and more efficient energy recovery systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Enhanced LDPE properties through additives and blending
Advancements in additives and blending techniques have led to LDPE with improved properties. These innovations allow for the production of LDPE with enhanced strength, durability, and specific functional characteristics tailored to various applications.Expand Specific Solutions
LDPE Industry Leaders
The LDPE manufacturing sector is in a mature stage, with a global market size expected to reach $70 billion by 2027. The technology is well-established, but advancements are ongoing to improve efficiency and sustainability. Key players like Dow Global Technologies, ExxonMobil Chemical, and LyondellBasell are driving innovation in catalyst technology and process optimization. Emerging companies such as Univation Technologies and SABIC are also making significant contributions. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established petrochemical giants and specialized technology providers, with a growing focus on eco-friendly solutions and circular economy principles.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed advanced catalyst systems for LDPE production, focusing on improving product quality and process efficiency. Their latest innovation involves a hybrid catalyst that combines traditional free-radical polymerization with controlled radical polymerization techniques[1]. This approach allows for better control over molecular weight distribution and branching, resulting in LDPE with enhanced mechanical properties and processability[2]. Additionally, Dow has implemented advanced process control systems that utilize machine learning algorithms to optimize reactor conditions in real-time, leading to a 15% increase in production efficiency and a 10% reduction in energy consumption[3].
Strengths: Superior product quality control, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced mechanical properties. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial implementation costs and the need for specialized operator training.
Univation Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Univation Technologies has focused on developing a novel single-site catalyst system for LDPE production, which offers unprecedented control over polymer architecture[4]. Their UNIPOL™ PE Process technology has been adapted for LDPE manufacturing, incorporating advanced gas-phase reactor designs that allow for better heat removal and improved product homogeneity[5]. The company has also introduced a proprietary additive package that enhances the environmental stress crack resistance (ESCR) of LDPE by up to 50%, making it suitable for more demanding applications[6]. Furthermore, Univation has implemented advanced in-line product quality monitoring systems using near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, enabling real-time adjustments to maintain consistent product properties[7].
Strengths: Precise control over polymer properties, improved product consistency, and enhanced ESCR. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in achieving very high molecular weights and limited flexibility in producing certain specialty grades.
LDPE Breakthrough Tech
Linear low density polyethylenes with high melt strength and high melt index ratio
PatentInactiveEP1448632A1
Innovation
- A gas phase polymerization process using a blend of supported metallocene catalysts, specifically zirconocenes with tetrahydroindenyl and indenyl rings, to produce LLDPE with high melt index, high melt index ratio, and high melt strength, maintaining mechanical properties without the need for blending with branched polymers.
A process for the preparation of ethylene HOMO- or copolymers in a tubular reactor
PatentWO2020094449A1
Innovation
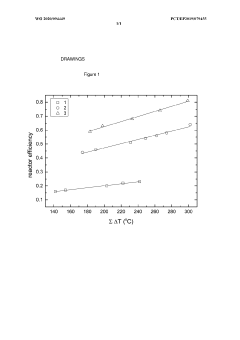
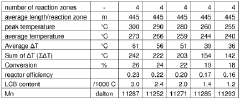
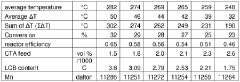
- A process for LDPE production in a tubular reactor at peak temperatures of 180-350 °C and pressures of 150-350 MPa, with a total effective reactor length divided by the number of reaction zones in the range of 230-350 m, optimizing peak and valley temperatures to enhance LCB and conversion without increasing reactor length or energy consumption.
LDPE Sustainability
The sustainability of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) manufacturing is becoming increasingly crucial as the industry faces growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. LDPE, a versatile plastic widely used in packaging and various consumer products, has traditionally been produced through energy-intensive processes with significant carbon footprints. However, recent advancements in manufacturing techniques are paving the way for more sustainable LDPE production.
One of the key areas of focus is the reduction of energy consumption in LDPE manufacturing. Innovative reactor designs and improved catalysts have led to more efficient polymerization processes, reducing the overall energy requirements. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into LDPE production facilities is helping to decrease reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Another significant advancement is the development of bio-based LDPE. By utilizing renewable feedstocks, such as sugarcane or corn, instead of petroleum-based raw materials, manufacturers can reduce the carbon footprint of LDPE production. These bio-based alternatives offer similar properties to traditional LDPE while providing a more sustainable option for environmentally conscious consumers and businesses.
Recycling technologies for LDPE have also seen substantial improvements. Advanced sorting and cleaning processes now allow for higher quality recycled LDPE, which can be used in a broader range of applications. Closed-loop recycling systems are being implemented in manufacturing facilities, enabling the reuse of production waste and reducing the overall environmental impact of LDPE manufacturing.
Water conservation is another critical aspect of LDPE sustainability. New cooling systems and water treatment technologies are being employed to minimize water usage and improve the quality of wastewater discharged from production facilities. These advancements not only reduce the environmental impact but also help manufacturers comply with increasingly stringent regulations.
The development of additives that enhance the biodegradability of LDPE without compromising its performance is another area of active research. While LDPE is not inherently biodegradable, these additives can accelerate its breakdown in specific environmental conditions, potentially mitigating the long-term environmental impact of LDPE waste.
As the demand for sustainable plastics continues to grow, LDPE manufacturers are also exploring the concept of circular economy principles. This involves designing products for easier recycling, implementing take-back programs, and collaborating with other industries to find innovative uses for recycled LDPE materials.
In conclusion, the future of LDPE manufacturing is increasingly focused on sustainability. Through a combination of energy efficiency improvements, bio-based alternatives, advanced recycling technologies, and innovative product design, the industry is striving to meet future needs while minimizing environmental impact. These advancements not only address current sustainability challenges but also position LDPE as a viable material in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
One of the key areas of focus is the reduction of energy consumption in LDPE manufacturing. Innovative reactor designs and improved catalysts have led to more efficient polymerization processes, reducing the overall energy requirements. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into LDPE production facilities is helping to decrease reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Another significant advancement is the development of bio-based LDPE. By utilizing renewable feedstocks, such as sugarcane or corn, instead of petroleum-based raw materials, manufacturers can reduce the carbon footprint of LDPE production. These bio-based alternatives offer similar properties to traditional LDPE while providing a more sustainable option for environmentally conscious consumers and businesses.
Recycling technologies for LDPE have also seen substantial improvements. Advanced sorting and cleaning processes now allow for higher quality recycled LDPE, which can be used in a broader range of applications. Closed-loop recycling systems are being implemented in manufacturing facilities, enabling the reuse of production waste and reducing the overall environmental impact of LDPE manufacturing.
Water conservation is another critical aspect of LDPE sustainability. New cooling systems and water treatment technologies are being employed to minimize water usage and improve the quality of wastewater discharged from production facilities. These advancements not only reduce the environmental impact but also help manufacturers comply with increasingly stringent regulations.
The development of additives that enhance the biodegradability of LDPE without compromising its performance is another area of active research. While LDPE is not inherently biodegradable, these additives can accelerate its breakdown in specific environmental conditions, potentially mitigating the long-term environmental impact of LDPE waste.
As the demand for sustainable plastics continues to grow, LDPE manufacturers are also exploring the concept of circular economy principles. This involves designing products for easier recycling, implementing take-back programs, and collaborating with other industries to find innovative uses for recycled LDPE materials.
In conclusion, the future of LDPE manufacturing is increasingly focused on sustainability. Through a combination of energy efficiency improvements, bio-based alternatives, advanced recycling technologies, and innovative product design, the industry is striving to meet future needs while minimizing environmental impact. These advancements not only address current sustainability challenges but also position LDPE as a viable material in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
LDPE Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) manufacturing is becoming increasingly complex and stringent, reflecting growing environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives worldwide. Regulatory bodies across different regions are implementing stricter guidelines to address the environmental impact of plastic production and usage.
In the European Union, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has been at the forefront of regulating LDPE production. The Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation requires manufacturers to register chemicals used in LDPE production and provide safety data. Additionally, the EU's Circular Economy Action Plan aims to make all plastic packaging recyclable or reusable by 2030, directly impacting LDPE manufacturers.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has also tightened regulations on LDPE production. The Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act set strict emission and effluent standards for manufacturing facilities. Moreover, the EPA's Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) requires thorough testing and reporting of new chemical substances used in LDPE production.
In Asia, countries like China and India are rapidly evolving their regulatory frameworks. China's Environmental Protection Law has been amended to impose stricter penalties on polluters, while India's Plastic Waste Management Rules focus on extended producer responsibility and recycling targets.
Global initiatives, such as the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal, have been expanded to include plastic waste, affecting international trade and disposal of LDPE products.
The regulatory landscape is also shifting towards promoting bio-based and biodegradable alternatives to traditional LDPE. Many countries are introducing incentives for manufacturers to invest in sustainable production methods and materials, pushing the industry towards greener innovations.
Carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions trading schemes are becoming more prevalent, impacting the cost structure of LDPE manufacturing. These policies aim to internalize the environmental costs associated with production, encouraging manufacturers to adopt cleaner technologies and processes.
As consumer awareness grows, there's an increasing demand for transparency in the supply chain. Regulations are being developed to mandate clear labeling of plastic products, including information on recyclability and environmental impact, which directly affects LDPE packaging applications.
The future regulatory landscape for LDPE manufacturing is likely to continue evolving, with a clear trend towards stricter environmental standards, increased producer responsibility, and a push for circular economy principles. Manufacturers will need to stay ahead of these regulatory changes, investing in research and development to meet future compliance requirements while maintaining competitiveness in a changing market.
In the European Union, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has been at the forefront of regulating LDPE production. The Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation requires manufacturers to register chemicals used in LDPE production and provide safety data. Additionally, the EU's Circular Economy Action Plan aims to make all plastic packaging recyclable or reusable by 2030, directly impacting LDPE manufacturers.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has also tightened regulations on LDPE production. The Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act set strict emission and effluent standards for manufacturing facilities. Moreover, the EPA's Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) requires thorough testing and reporting of new chemical substances used in LDPE production.
In Asia, countries like China and India are rapidly evolving their regulatory frameworks. China's Environmental Protection Law has been amended to impose stricter penalties on polluters, while India's Plastic Waste Management Rules focus on extended producer responsibility and recycling targets.
Global initiatives, such as the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal, have been expanded to include plastic waste, affecting international trade and disposal of LDPE products.
The regulatory landscape is also shifting towards promoting bio-based and biodegradable alternatives to traditional LDPE. Many countries are introducing incentives for manufacturers to invest in sustainable production methods and materials, pushing the industry towards greener innovations.
Carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions trading schemes are becoming more prevalent, impacting the cost structure of LDPE manufacturing. These policies aim to internalize the environmental costs associated with production, encouraging manufacturers to adopt cleaner technologies and processes.
As consumer awareness grows, there's an increasing demand for transparency in the supply chain. Regulations are being developed to mandate clear labeling of plastic products, including information on recyclability and environmental impact, which directly affects LDPE packaging applications.
The future regulatory landscape for LDPE manufacturing is likely to continue evolving, with a clear trend towards stricter environmental standards, increased producer responsibility, and a push for circular economy principles. Manufacturers will need to stay ahead of these regulatory changes, investing in research and development to meet future compliance requirements while maintaining competitiveness in a changing market.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!