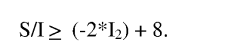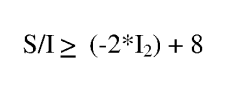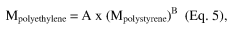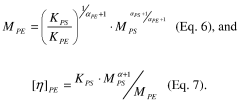How to Boost LDPE's Performance with Modern Techniques?
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Evolution and Objectives
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone in the plastics industry since its accidental discovery by ICI chemists in 1933. This versatile polymer, characterized by its high ductility, low density, and excellent chemical resistance, has found widespread applications in packaging, construction, and consumer goods. The evolution of LDPE technology has been driven by the continuous pursuit of enhanced performance and sustainability.
In the early stages of LDPE development, the focus was primarily on improving the production process and expanding its applications. The original high-pressure process, while effective, was energy-intensive and limited in terms of polymer properties. As the demand for LDPE grew, researchers began exploring ways to optimize the polymerization process and tailor the material properties to meet specific industry needs.
The 1970s and 1980s saw significant advancements in catalyst technology, leading to the development of more efficient production methods. These innovations allowed for better control over molecular weight distribution and branching, resulting in LDPE grades with improved mechanical properties and processability. Concurrently, the introduction of copolymers and blends expanded the range of achievable properties, further broadening LDPE's application scope.
In recent decades, the objectives for LDPE evolution have shifted towards addressing environmental concerns and meeting increasingly stringent regulatory requirements. The industry has been focusing on developing more sustainable production methods, reducing energy consumption, and improving the recyclability of LDPE products. Additionally, there has been a growing emphasis on enhancing LDPE's barrier properties and mechanical strength to compete with other packaging materials and reduce material usage.
The current technological landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for LDPE performance enhancement. Modern techniques such as nanotechnology, surface modification, and advanced polymer blending offer promising avenues for boosting LDPE's capabilities. The integration of these techniques aims to overcome traditional limitations in areas such as gas permeability, thermal stability, and mechanical strength.
Looking ahead, the objectives for LDPE evolution are multifaceted. There is a pressing need to develop LDPE grades with improved recyclability and biodegradability without compromising performance. Enhancing LDPE's barrier properties to extend product shelf life and reduce food waste is another key goal. Furthermore, the industry is exploring ways to incorporate renewable feedstocks into LDPE production, aligning with the global push towards a circular economy.
In conclusion, the evolution of LDPE technology reflects a journey of continuous innovation driven by market demands and environmental considerations. The current objectives focus on leveraging modern techniques to boost LDPE's performance while addressing sustainability challenges, setting the stage for the next generation of high-performance, eco-friendly polyethylene materials.
In the early stages of LDPE development, the focus was primarily on improving the production process and expanding its applications. The original high-pressure process, while effective, was energy-intensive and limited in terms of polymer properties. As the demand for LDPE grew, researchers began exploring ways to optimize the polymerization process and tailor the material properties to meet specific industry needs.
The 1970s and 1980s saw significant advancements in catalyst technology, leading to the development of more efficient production methods. These innovations allowed for better control over molecular weight distribution and branching, resulting in LDPE grades with improved mechanical properties and processability. Concurrently, the introduction of copolymers and blends expanded the range of achievable properties, further broadening LDPE's application scope.
In recent decades, the objectives for LDPE evolution have shifted towards addressing environmental concerns and meeting increasingly stringent regulatory requirements. The industry has been focusing on developing more sustainable production methods, reducing energy consumption, and improving the recyclability of LDPE products. Additionally, there has been a growing emphasis on enhancing LDPE's barrier properties and mechanical strength to compete with other packaging materials and reduce material usage.
The current technological landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for LDPE performance enhancement. Modern techniques such as nanotechnology, surface modification, and advanced polymer blending offer promising avenues for boosting LDPE's capabilities. The integration of these techniques aims to overcome traditional limitations in areas such as gas permeability, thermal stability, and mechanical strength.
Looking ahead, the objectives for LDPE evolution are multifaceted. There is a pressing need to develop LDPE grades with improved recyclability and biodegradability without compromising performance. Enhancing LDPE's barrier properties to extend product shelf life and reduce food waste is another key goal. Furthermore, the industry is exploring ways to incorporate renewable feedstocks into LDPE production, aligning with the global push towards a circular economy.
In conclusion, the evolution of LDPE technology reflects a journey of continuous innovation driven by market demands and environmental considerations. The current objectives focus on leveraging modern techniques to boost LDPE's performance while addressing sustainability challenges, setting the stage for the next generation of high-performance, eco-friendly polyethylene materials.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for enhanced Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) performance has been steadily growing across various industries. LDPE, known for its flexibility, toughness, and chemical resistance, is widely used in packaging, construction, and consumer goods. However, as industries evolve and sustainability concerns rise, there is an increasing need for LDPE with improved properties.
In the packaging sector, which accounts for a significant portion of LDPE consumption, there is a strong demand for materials with enhanced barrier properties. This is driven by the need to extend shelf life, reduce food waste, and improve product protection. Manufacturers are seeking LDPE formulations that offer better oxygen and moisture barriers without compromising recyclability or increasing costs significantly.
The construction industry is another major consumer of LDPE, particularly in applications such as geomembranes, pipes, and insulation. Here, the demand is for LDPE with improved mechanical strength, UV resistance, and long-term durability. As infrastructure projects grow globally, especially in developing countries, the need for high-performance LDPE in construction is expected to rise.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures are also shaping market demand. There is a growing interest in LDPE that is more easily recyclable or incorporates recycled content without sacrificing performance. This trend is particularly strong in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as the European Union and parts of North America.
The automotive industry presents another avenue for enhanced LDPE demand. As vehicle manufacturers strive to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency, there is a need for lightweight yet durable materials. LDPE with improved impact resistance and thermal stability could find increased applications in automotive interiors and under-the-hood components.
In the medical and healthcare sectors, there is a rising demand for LDPE with enhanced purity and biocompatibility. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, highlighting the need for high-performance materials in medical packaging and devices.
The agriculture sector is also showing increased interest in LDPE with improved properties. Greenhouse films and agricultural covers made from LDPE with better UV stability and mechanical strength are in demand to enhance crop yields and reduce material replacement frequency.
Market analysts project that the global LDPE market will continue to grow, with a particular emphasis on high-performance variants. Regions such as Asia-Pacific, led by China and India, are expected to be major growth drivers due to rapid industrialization and urbanization. North America and Europe are likely to focus on innovative, sustainable LDPE solutions to meet stringent environmental standards.
In the packaging sector, which accounts for a significant portion of LDPE consumption, there is a strong demand for materials with enhanced barrier properties. This is driven by the need to extend shelf life, reduce food waste, and improve product protection. Manufacturers are seeking LDPE formulations that offer better oxygen and moisture barriers without compromising recyclability or increasing costs significantly.
The construction industry is another major consumer of LDPE, particularly in applications such as geomembranes, pipes, and insulation. Here, the demand is for LDPE with improved mechanical strength, UV resistance, and long-term durability. As infrastructure projects grow globally, especially in developing countries, the need for high-performance LDPE in construction is expected to rise.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures are also shaping market demand. There is a growing interest in LDPE that is more easily recyclable or incorporates recycled content without sacrificing performance. This trend is particularly strong in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as the European Union and parts of North America.
The automotive industry presents another avenue for enhanced LDPE demand. As vehicle manufacturers strive to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency, there is a need for lightweight yet durable materials. LDPE with improved impact resistance and thermal stability could find increased applications in automotive interiors and under-the-hood components.
In the medical and healthcare sectors, there is a rising demand for LDPE with enhanced purity and biocompatibility. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, highlighting the need for high-performance materials in medical packaging and devices.
The agriculture sector is also showing increased interest in LDPE with improved properties. Greenhouse films and agricultural covers made from LDPE with better UV stability and mechanical strength are in demand to enhance crop yields and reduce material replacement frequency.
Market analysts project that the global LDPE market will continue to grow, with a particular emphasis on high-performance variants. Regions such as Asia-Pacific, led by China and India, are expected to be major growth drivers due to rapid industrialization and urbanization. North America and Europe are likely to focus on innovative, sustainable LDPE solutions to meet stringent environmental standards.
LDPE Challenges
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone in the plastics industry for decades, valued for its flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. However, as modern applications demand increasingly sophisticated material properties, LDPE faces several significant challenges that limit its performance and potential for expansion into new markets.
One of the primary challenges confronting LDPE is its relatively low mechanical strength compared to other polyethylene grades. This limitation restricts its use in applications requiring high tensile strength or impact resistance, such as heavy-duty packaging or automotive components. The inherent molecular structure of LDPE, characterized by long chains with numerous short branches, contributes to its flexibility but also results in lower crystallinity and reduced mechanical properties.
Another critical challenge is LDPE's limited heat resistance. The material's low melting point and softening temperature restrict its use in high-temperature environments or applications involving hot-fill processes. This thermal sensitivity not only narrows the range of potential applications but also poses challenges in processing and manufacturing, where precise temperature control is crucial to maintain product quality and consistency.
LDPE also faces environmental concerns, particularly regarding its recyclability and biodegradability. While LDPE is technically recyclable, the presence of additives and contaminants often complicates the recycling process, leading to downcycling rather than true circular recycling. Moreover, like most conventional plastics, LDPE's persistence in the environment has raised sustainability concerns, prompting the need for more eco-friendly alternatives or improved end-of-life solutions.
The material's barrier properties present another area of challenge. LDPE exhibits moderate permeability to gases and moisture, which can be problematic in packaging applications requiring high barrier performance. This limitation often necessitates the use of multi-layer structures or barrier coatings, increasing complexity and cost in product design and manufacturing.
Furthermore, LDPE faces competition from newer polyethylene grades and alternative materials that offer superior performance in specific applications. Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) and metallocene-catalyzed polyethylenes, for instance, provide improved mechanical properties and processability, challenging LDPE's market position in certain sectors.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches to enhance LDPE's performance without compromising its desirable characteristics or significantly increasing production costs. Modern techniques in polymer science, nanotechnology, and materials engineering offer promising avenues for overcoming these limitations and expanding LDPE's capabilities to meet evolving market demands.
One of the primary challenges confronting LDPE is its relatively low mechanical strength compared to other polyethylene grades. This limitation restricts its use in applications requiring high tensile strength or impact resistance, such as heavy-duty packaging or automotive components. The inherent molecular structure of LDPE, characterized by long chains with numerous short branches, contributes to its flexibility but also results in lower crystallinity and reduced mechanical properties.
Another critical challenge is LDPE's limited heat resistance. The material's low melting point and softening temperature restrict its use in high-temperature environments or applications involving hot-fill processes. This thermal sensitivity not only narrows the range of potential applications but also poses challenges in processing and manufacturing, where precise temperature control is crucial to maintain product quality and consistency.
LDPE also faces environmental concerns, particularly regarding its recyclability and biodegradability. While LDPE is technically recyclable, the presence of additives and contaminants often complicates the recycling process, leading to downcycling rather than true circular recycling. Moreover, like most conventional plastics, LDPE's persistence in the environment has raised sustainability concerns, prompting the need for more eco-friendly alternatives or improved end-of-life solutions.
The material's barrier properties present another area of challenge. LDPE exhibits moderate permeability to gases and moisture, which can be problematic in packaging applications requiring high barrier performance. This limitation often necessitates the use of multi-layer structures or barrier coatings, increasing complexity and cost in product design and manufacturing.
Furthermore, LDPE faces competition from newer polyethylene grades and alternative materials that offer superior performance in specific applications. Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) and metallocene-catalyzed polyethylenes, for instance, provide improved mechanical properties and processability, challenging LDPE's market position in certain sectors.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches to enhance LDPE's performance without compromising its desirable characteristics or significantly increasing production costs. Modern techniques in polymer science, nanotechnology, and materials engineering offer promising avenues for overcoming these limitations and expanding LDPE's capabilities to meet evolving market demands.
Current LDPE Solutions
01 Improved mechanical properties of LDPE
Various methods are employed to enhance the mechanical properties of LDPE, including the incorporation of additives, blending with other polymers, and optimizing processing conditions. These improvements can result in increased tensile strength, impact resistance, and overall durability of LDPE products.- Improved mechanical properties of LDPE: Various methods are employed to enhance the mechanical properties of LDPE, including tensile strength, impact resistance, and elongation at break. These improvements are achieved through the incorporation of additives, blending with other polymers, or modifying the polymerization process. The enhanced mechanical properties expand the range of applications for LDPE in packaging, construction, and automotive industries.
- Enhanced thermal stability of LDPE: Techniques are developed to improve the thermal stability of LDPE, allowing it to maintain its properties at higher temperatures. This is achieved through the addition of heat stabilizers, antioxidants, or by modifying the polymer structure. Improved thermal stability extends the use of LDPE in applications requiring higher temperature resistance, such as in electrical insulation and automotive components.
- Increased barrier properties of LDPE: Methods are developed to enhance the barrier properties of LDPE against gases, moisture, and other substances. This is achieved through the incorporation of nanoparticles, surface treatments, or by creating multi-layer structures. Improved barrier properties expand the use of LDPE in food packaging, pharmaceutical packaging, and other applications requiring protection against external factors.
- Biodegradability and environmental performance of LDPE: Research focuses on improving the environmental performance of LDPE by enhancing its biodegradability or developing bio-based alternatives. This includes the incorporation of biodegradable additives, blending with biodegradable polymers, or modifying the polymer structure to facilitate degradation. These advancements aim to address environmental concerns associated with plastic waste and promote sustainability in LDPE applications.
- Processing improvements for LDPE: Advancements in processing techniques for LDPE are developed to enhance its performance and efficiency during manufacturing. This includes improvements in extrusion, molding, and film-forming processes, as well as the development of new additives to enhance processability. These improvements lead to better quality LDPE products, reduced production costs, and expanded applications in various industries.
02 Enhanced thermal stability of LDPE
Techniques are developed to improve the thermal stability of LDPE, allowing it to maintain its properties at higher temperatures. This can involve the use of heat stabilizers, antioxidants, or modifications to the polymer structure, resulting in improved performance in high-temperature applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Increased barrier properties of LDPE
Methods are explored to enhance the barrier properties of LDPE against gases, moisture, and other substances. This can include the use of nanocomposites, surface treatments, or multi-layer structures, leading to improved packaging performance and extended shelf life for various products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Improved processability of LDPE
Techniques are developed to enhance the processability of LDPE, including the use of processing aids, optimized extrusion conditions, and modified polymer structures. These improvements can lead to better melt flow properties, reduced energy consumption during processing, and improved product quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Enhanced environmental performance of LDPE
Efforts are made to improve the environmental performance of LDPE, including the development of biodegradable or compostable variants, incorporation of recycled content, and optimization of material usage. These advancements aim to reduce the environmental impact of LDPE products throughout their lifecycle.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for LDPE performance enhancement techniques is in a mature stage, with ongoing innovation driving incremental improvements. The global LDPE market size is substantial, valued at over $33 billion in 2020 and expected to grow steadily. Technologically, the field is well-developed but still evolving. Major players like Dow Global Technologies, Univation Technologies, and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. are at the forefront of innovation, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities. Companies such as LG Chem and SABIC Global Technologies are also making significant contributions, particularly in developing advanced catalysts and process technologies to improve LDPE properties and production efficiency.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed advanced catalyst systems and process technologies to enhance LDPE performance. Their AGILITY™ technology platform enables the production of LDPE with improved mechanical properties and processability. This includes the use of novel metallocene catalysts that allow for precise control over molecular weight distribution and long-chain branching[1]. Additionally, Dow has implemented advanced reactor designs and post-reactor treatment processes to optimize polymer morphology and reduce gel content, resulting in LDPE with enhanced optical properties and film strength[2][3].
Strengths: Precise control over polymer architecture, improved mechanical and optical properties. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs, may require specialized equipment.
Univation Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Univation Technologies has developed the UNIPOL™ PE Process for producing LDPE with enhanced performance characteristics. This technology utilizes advanced single-site catalysts and a unique gas-phase fluidized bed reactor system. The process allows for the production of LDPE with a wide range of densities and melt indices, enabling tailored properties for specific applications[4]. Univation's technology also incorporates in-line blending capabilities, allowing for the creation of custom LDPE formulations with optimized performance attributes such as improved impact strength and environmental stress crack resistance[5].
Strengths: Versatile production capabilities, ability to create custom LDPE blends. Weaknesses: May require significant capital investment for implementation.
LDPE Innovation Focus
Novel LDPE enabling high output and good optics when blended with other polymers
PatentActiveEP2440588A1
Innovation
- Development of a new LDPE with specific molecular weight distribution, density, and branching characteristics, allowing for increased output when blended with LLDPE, while maintaining mechanical properties and reducing haze and bubble instability.
Novel LDPE enabling high output and good optics when blended with other polymers
PatentWO2010144784A1
Innovation
- Development of a new LDPE with specific molecular weight distribution, density, and branching characteristics, allowing for increased output when blended with LLDPE, while maintaining mechanical properties and improving optical quality through controlled tubular reactor technology and catalyst systems.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of boosting LDPE's performance through modern techniques is a critical consideration in the pursuit of enhanced material properties. As industries strive to improve the characteristics of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), it is essential to evaluate the ecological implications of these advancements.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with LDPE performance enhancement is the potential increase in energy consumption during production processes. Advanced techniques often require more sophisticated equipment and higher operating temperatures, which can lead to a larger carbon footprint. However, this initial environmental cost may be offset by the improved durability and longevity of the enhanced LDPE products, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements and overall material consumption.
The use of additives and modifiers to boost LDPE performance also raises environmental questions. While these substances can significantly improve the material's properties, their production and eventual disposal may introduce new ecological challenges. It is crucial to assess the biodegradability and toxicity of these additives to ensure they do not pose long-term environmental risks.
On the positive side, enhancing LDPE's performance can contribute to sustainability efforts by enabling the production of thinner, lighter materials with equivalent or superior properties. This reduction in material usage can lead to decreased resource consumption and lower transportation-related emissions throughout the product lifecycle.
Modern techniques for LDPE enhancement often focus on improving recyclability and compatibility with existing recycling streams. By developing LDPE variants that are easier to recycle or that maintain their enhanced properties through multiple recycling cycles, these advancements can support circular economy initiatives and reduce plastic waste.
The potential for bio-based or partially bio-derived LDPE alternatives is another area where performance enhancement intersects with environmental considerations. Techniques that allow for the incorporation of renewable resources into LDPE production without compromising performance could significantly reduce the material's reliance on fossil fuels and overall environmental impact.
As regulations around plastic use and disposal become more stringent, the environmental impact of LDPE performance enhancement techniques will likely face increased scrutiny. Manufacturers and researchers must prioritize eco-friendly approaches that not only improve material properties but also align with sustainability goals and regulatory requirements.
In conclusion, while boosting LDPE's performance through modern techniques presents both environmental challenges and opportunities, the overall impact will depend on the specific methods employed and their implementation. Balancing performance enhancements with ecological considerations is crucial for the sustainable development of improved LDPE materials.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with LDPE performance enhancement is the potential increase in energy consumption during production processes. Advanced techniques often require more sophisticated equipment and higher operating temperatures, which can lead to a larger carbon footprint. However, this initial environmental cost may be offset by the improved durability and longevity of the enhanced LDPE products, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements and overall material consumption.
The use of additives and modifiers to boost LDPE performance also raises environmental questions. While these substances can significantly improve the material's properties, their production and eventual disposal may introduce new ecological challenges. It is crucial to assess the biodegradability and toxicity of these additives to ensure they do not pose long-term environmental risks.
On the positive side, enhancing LDPE's performance can contribute to sustainability efforts by enabling the production of thinner, lighter materials with equivalent or superior properties. This reduction in material usage can lead to decreased resource consumption and lower transportation-related emissions throughout the product lifecycle.
Modern techniques for LDPE enhancement often focus on improving recyclability and compatibility with existing recycling streams. By developing LDPE variants that are easier to recycle or that maintain their enhanced properties through multiple recycling cycles, these advancements can support circular economy initiatives and reduce plastic waste.
The potential for bio-based or partially bio-derived LDPE alternatives is another area where performance enhancement intersects with environmental considerations. Techniques that allow for the incorporation of renewable resources into LDPE production without compromising performance could significantly reduce the material's reliance on fossil fuels and overall environmental impact.
As regulations around plastic use and disposal become more stringent, the environmental impact of LDPE performance enhancement techniques will likely face increased scrutiny. Manufacturers and researchers must prioritize eco-friendly approaches that not only improve material properties but also align with sustainability goals and regulatory requirements.
In conclusion, while boosting LDPE's performance through modern techniques presents both environmental challenges and opportunities, the overall impact will depend on the specific methods employed and their implementation. Balancing performance enhancements with ecological considerations is crucial for the sustainable development of improved LDPE materials.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) and its performance enhancement techniques is complex and evolving. Governments and international organizations have implemented various regulations to ensure the safety, quality, and environmental sustainability of LDPE products. These regulations significantly impact the development and application of modern techniques to boost LDPE's performance.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates LDPE used in food contact applications. The FDA's Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, Part 177, Subpart B, Section 177.1520 specifically addresses olefin polymers, including LDPE. This regulation sets forth the requirements for the composition, properties, and manufacturing processes of LDPE intended for food contact use. Any new techniques or additives used to enhance LDPE's performance must comply with these regulations to ensure food safety.
The European Union has established the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which affects the production and use of LDPE. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals and provide safety information. This regulation impacts the development of new additives or processing techniques for LDPE, as they must be thoroughly evaluated for potential health and environmental risks.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in shaping the development of LDPE performance enhancement techniques. Many countries have implemented plastic waste reduction policies, encouraging the use of recyclable and biodegradable materials. This has led to increased focus on developing LDPE formulations with improved recyclability and biodegradability without compromising performance.
The Global Plastics Treaty, currently under negotiation, aims to address plastic pollution on a global scale. This treaty may introduce new regulations affecting LDPE production, use, and disposal, potentially influencing the direction of performance enhancement research. Manufacturers and researchers must anticipate these future regulatory changes when developing new techniques to boost LDPE's performance.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, impact the manufacturing processes of LDPE. These regulations ensure worker safety during the production and handling of LDPE and its additives, influencing the selection and implementation of performance enhancement techniques.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, many countries are implementing Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs. These programs hold manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. This regulatory approach encourages the development of LDPE formulations that are not only high-performing but also easily recyclable or biodegradable.
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape surrounding LDPE performance enhancement is multifaceted, encompassing food safety, chemical registration, environmental protection, occupational safety, and sustainability. As researchers and manufacturers explore modern techniques to boost LDPE's performance, they must navigate this complex regulatory environment to ensure compliance and market acceptance of their innovations.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates LDPE used in food contact applications. The FDA's Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, Part 177, Subpart B, Section 177.1520 specifically addresses olefin polymers, including LDPE. This regulation sets forth the requirements for the composition, properties, and manufacturing processes of LDPE intended for food contact use. Any new techniques or additives used to enhance LDPE's performance must comply with these regulations to ensure food safety.
The European Union has established the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which affects the production and use of LDPE. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals and provide safety information. This regulation impacts the development of new additives or processing techniques for LDPE, as they must be thoroughly evaluated for potential health and environmental risks.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in shaping the development of LDPE performance enhancement techniques. Many countries have implemented plastic waste reduction policies, encouraging the use of recyclable and biodegradable materials. This has led to increased focus on developing LDPE formulations with improved recyclability and biodegradability without compromising performance.
The Global Plastics Treaty, currently under negotiation, aims to address plastic pollution on a global scale. This treaty may introduce new regulations affecting LDPE production, use, and disposal, potentially influencing the direction of performance enhancement research. Manufacturers and researchers must anticipate these future regulatory changes when developing new techniques to boost LDPE's performance.
Occupational safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, impact the manufacturing processes of LDPE. These regulations ensure worker safety during the production and handling of LDPE and its additives, influencing the selection and implementation of performance enhancement techniques.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, many countries are implementing Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs. These programs hold manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. This regulatory approach encourages the development of LDPE formulations that are not only high-performing but also easily recyclable or biodegradable.
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape surrounding LDPE performance enhancement is multifaceted, encompassing food safety, chemical registration, environmental protection, occupational safety, and sustainability. As researchers and manufacturers explore modern techniques to boost LDPE's performance, they must navigate this complex regulatory environment to ensure compliance and market acceptance of their innovations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!