Future Pathways for LDPE in Green Solutions
JUN 30, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Evolution and Objectives
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone of the plastics industry since its accidental discovery in 1933 by Imperial Chemical Industries. Over the decades, LDPE has evolved from a wartime necessity to a ubiquitous material in everyday products. Its journey reflects the broader narrative of plastic development, intertwined with technological advancements and changing societal needs.
The evolution of LDPE has been marked by continuous improvements in production processes and material properties. Initially produced through high-pressure polymerization, LDPE manufacturing has seen significant enhancements in efficiency and quality control. The introduction of metallocene catalysts in the 1990s allowed for more precise control over polymer structure, leading to LDPE variants with tailored characteristics.
As environmental concerns have grown, the trajectory of LDPE development has shifted towards sustainability. The industry has been exploring ways to reduce the carbon footprint of LDPE production, improve its recyclability, and develop bio-based alternatives. This shift aligns with the global push towards circular economy principles and the reduction of plastic waste.
The current objectives for LDPE in green solutions are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a drive to increase the recyclability of LDPE products, addressing the end-of-life challenges that have plagued plastic materials. This involves not only improving collection and sorting technologies but also enhancing the properties of recycled LDPE to match virgin material quality.
Another key objective is the development of bio-based LDPE, which could significantly reduce the reliance on fossil fuels. Research is ongoing to create LDPE from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, aiming to maintain the material's desirable properties while decreasing its environmental impact.
Furthermore, there is a focus on improving the biodegradability of LDPE or creating hybrid materials that combine the benefits of LDPE with more environmentally friendly alternatives. This includes research into additives that can accelerate the breakdown of LDPE in natural environments without compromising its performance during use.
The industry is also exploring innovative applications for LDPE in green technologies. This includes its use in lightweight materials for electric vehicles, energy-efficient packaging solutions, and as a component in renewable energy systems such as solar panels and wind turbines.
As we look to the future, the evolution of LDPE in green solutions will likely involve a combination of technological innovation, policy changes, and shifts in consumer behavior. The ultimate goal is to transform LDPE from a symbol of environmental concern into a material that contributes positively to sustainability efforts, balancing its undeniable utility with the pressing need for ecological responsibility.
The evolution of LDPE has been marked by continuous improvements in production processes and material properties. Initially produced through high-pressure polymerization, LDPE manufacturing has seen significant enhancements in efficiency and quality control. The introduction of metallocene catalysts in the 1990s allowed for more precise control over polymer structure, leading to LDPE variants with tailored characteristics.
As environmental concerns have grown, the trajectory of LDPE development has shifted towards sustainability. The industry has been exploring ways to reduce the carbon footprint of LDPE production, improve its recyclability, and develop bio-based alternatives. This shift aligns with the global push towards circular economy principles and the reduction of plastic waste.
The current objectives for LDPE in green solutions are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a drive to increase the recyclability of LDPE products, addressing the end-of-life challenges that have plagued plastic materials. This involves not only improving collection and sorting technologies but also enhancing the properties of recycled LDPE to match virgin material quality.
Another key objective is the development of bio-based LDPE, which could significantly reduce the reliance on fossil fuels. Research is ongoing to create LDPE from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, aiming to maintain the material's desirable properties while decreasing its environmental impact.
Furthermore, there is a focus on improving the biodegradability of LDPE or creating hybrid materials that combine the benefits of LDPE with more environmentally friendly alternatives. This includes research into additives that can accelerate the breakdown of LDPE in natural environments without compromising its performance during use.
The industry is also exploring innovative applications for LDPE in green technologies. This includes its use in lightweight materials for electric vehicles, energy-efficient packaging solutions, and as a component in renewable energy systems such as solar panels and wind turbines.
As we look to the future, the evolution of LDPE in green solutions will likely involve a combination of technological innovation, policy changes, and shifts in consumer behavior. The ultimate goal is to transform LDPE from a symbol of environmental concern into a material that contributes positively to sustainability efforts, balancing its undeniable utility with the pressing need for ecological responsibility.
Green LDPE Market Analysis
The global market for green Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations on plastic waste. As consumers and businesses alike seek more sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics, the demand for eco-friendly LDPE solutions has surged across various industries.
In the packaging sector, which accounts for a substantial portion of LDPE consumption, there is a notable shift towards green LDPE products. This trend is particularly evident in the food and beverage industry, where companies are adopting biodegradable and recyclable LDPE packaging to meet consumer preferences and comply with environmental standards. The agricultural sector is also embracing green LDPE for mulch films and greenhouse covers, recognizing the benefits of reduced environmental impact and improved soil health.
The construction industry represents another key market for green LDPE, with applications in insulation materials, vapor barriers, and protective films. As sustainable building practices gain traction globally, the demand for eco-friendly construction materials, including green LDPE, is expected to rise substantially in the coming years.
Geographically, Europe leads the green LDPE market, owing to its stringent environmental regulations and high consumer awareness. North America follows closely, with rapid adoption in the packaging and construction sectors. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is emerging as a lucrative market for green LDPE, driven by growing environmental consciousness and government initiatives to reduce plastic waste.
Market analysis indicates that the green LDPE segment is outpacing the growth of conventional LDPE, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) significantly higher than the overall plastics market. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of circular economy principles and the push for sustainable materials across industries.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of green LDPE. The higher production costs compared to traditional LDPE and the need for specialized recycling infrastructure are potential barriers to market expansion. Additionally, the performance characteristics of some green LDPE products may not yet match those of conventional LDPE in certain applications, necessitating further research and development.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for the green LDPE market remains highly positive. Technological advancements in bio-based and recycled LDPE production are expected to drive down costs and improve performance, making green LDPE more competitive with traditional alternatives. As global efforts to combat plastic pollution intensify, the green LDPE market is poised for sustained growth, offering significant opportunities for innovation and market expansion in the coming decades.
In the packaging sector, which accounts for a substantial portion of LDPE consumption, there is a notable shift towards green LDPE products. This trend is particularly evident in the food and beverage industry, where companies are adopting biodegradable and recyclable LDPE packaging to meet consumer preferences and comply with environmental standards. The agricultural sector is also embracing green LDPE for mulch films and greenhouse covers, recognizing the benefits of reduced environmental impact and improved soil health.
The construction industry represents another key market for green LDPE, with applications in insulation materials, vapor barriers, and protective films. As sustainable building practices gain traction globally, the demand for eco-friendly construction materials, including green LDPE, is expected to rise substantially in the coming years.
Geographically, Europe leads the green LDPE market, owing to its stringent environmental regulations and high consumer awareness. North America follows closely, with rapid adoption in the packaging and construction sectors. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is emerging as a lucrative market for green LDPE, driven by growing environmental consciousness and government initiatives to reduce plastic waste.
Market analysis indicates that the green LDPE segment is outpacing the growth of conventional LDPE, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) significantly higher than the overall plastics market. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of circular economy principles and the push for sustainable materials across industries.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of green LDPE. The higher production costs compared to traditional LDPE and the need for specialized recycling infrastructure are potential barriers to market expansion. Additionally, the performance characteristics of some green LDPE products may not yet match those of conventional LDPE in certain applications, necessitating further research and development.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for the green LDPE market remains highly positive. Technological advancements in bio-based and recycled LDPE production are expected to drive down costs and improve performance, making green LDPE more competitive with traditional alternatives. As global efforts to combat plastic pollution intensify, the green LDPE market is poised for sustained growth, offering significant opportunities for innovation and market expansion in the coming decades.
LDPE Eco-Challenges
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone of the plastics industry for decades, but its environmental impact has become a significant concern in recent years. The primary eco-challenges associated with LDPE stem from its persistence in the environment, its contribution to plastic pollution, and the carbon footprint of its production process.
One of the most pressing issues is the longevity of LDPE in natural ecosystems. With a degradation time that can span hundreds of years, LDPE products contribute significantly to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills, oceans, and terrestrial environments. This persistence leads to the formation of microplastics, which have been found to infiltrate food chains and potentially impact human health.
The production of LDPE is another area of environmental concern. The process relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as a feedstock and energy source, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. The energy-intensive nature of LDPE manufacturing exacerbates its carbon footprint, making it a target for sustainability improvements in industrial processes.
Recycling LDPE presents its own set of challenges. While technically recyclable, the collection and sorting of LDPE products are often economically unfeasible due to contamination and the mixed nature of post-consumer plastic waste. This results in low recycling rates and a significant portion of LDPE ending up in landfills or incineration facilities.
The widespread use of LDPE in single-use applications, such as plastic bags and packaging, has led to increased scrutiny and regulatory pressure. Many jurisdictions have implemented bans or taxes on single-use plastic items, forcing industries to seek alternative materials or redesign their products for reusability.
As global awareness of plastic pollution grows, there is mounting pressure on manufacturers to address the end-of-life issues associated with LDPE products. This includes developing more effective recycling technologies, exploring biodegradable alternatives, and implementing extended producer responsibility schemes to manage plastic waste.
The challenge of reducing the environmental impact of LDPE while maintaining its beneficial properties in various applications requires a multifaceted approach. This involves innovations in material science to create more environmentally friendly alternatives, improvements in recycling technologies and infrastructure, and shifts in consumer behavior and industrial practices towards more sustainable consumption patterns.
One of the most pressing issues is the longevity of LDPE in natural ecosystems. With a degradation time that can span hundreds of years, LDPE products contribute significantly to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills, oceans, and terrestrial environments. This persistence leads to the formation of microplastics, which have been found to infiltrate food chains and potentially impact human health.
The production of LDPE is another area of environmental concern. The process relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as a feedstock and energy source, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. The energy-intensive nature of LDPE manufacturing exacerbates its carbon footprint, making it a target for sustainability improvements in industrial processes.
Recycling LDPE presents its own set of challenges. While technically recyclable, the collection and sorting of LDPE products are often economically unfeasible due to contamination and the mixed nature of post-consumer plastic waste. This results in low recycling rates and a significant portion of LDPE ending up in landfills or incineration facilities.
The widespread use of LDPE in single-use applications, such as plastic bags and packaging, has led to increased scrutiny and regulatory pressure. Many jurisdictions have implemented bans or taxes on single-use plastic items, forcing industries to seek alternative materials or redesign their products for reusability.
As global awareness of plastic pollution grows, there is mounting pressure on manufacturers to address the end-of-life issues associated with LDPE products. This includes developing more effective recycling technologies, exploring biodegradable alternatives, and implementing extended producer responsibility schemes to manage plastic waste.
The challenge of reducing the environmental impact of LDPE while maintaining its beneficial properties in various applications requires a multifaceted approach. This involves innovations in material science to create more environmentally friendly alternatives, improvements in recycling technologies and infrastructure, and shifts in consumer behavior and industrial practices towards more sustainable consumption patterns.
Current Green LDPE Solutions
01 LDPE composition and manufacturing process
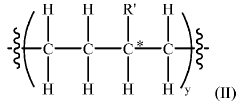
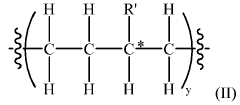
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a versatile polymer with various compositions and manufacturing processes. These processes often involve high-pressure polymerization of ethylene, resulting in a material with unique properties such as flexibility and low density. Different additives and catalysts can be used to modify the characteristics of LDPE for specific applications.- Composition and properties of LDPE: Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a low density and high flexibility. It is characterized by its branched structure, which results in lower crystallinity and density compared to other polyethylene types. LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance, electrical insulation properties, and processability, making it suitable for various applications.
- Manufacturing processes for LDPE: LDPE is typically produced through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene using free-radical initiators. Various manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the production efficiency and control the properties of LDPE. These may include modifications to reactor design, catalyst systems, and process conditions to achieve desired molecular weight distribution and branching characteristics.
- Applications of LDPE in packaging: LDPE is widely used in the packaging industry due to its flexibility, transparency, and moisture resistance. It is commonly employed in the production of plastic bags, food packaging films, and squeeze bottles. Recent innovations focus on improving the barrier properties and recyclability of LDPE packaging materials to meet sustainability requirements.
- LDPE blends and composites: To enhance the performance of LDPE, it is often blended with other polymers or reinforced with various fillers and additives. These blends and composites can exhibit improved mechanical properties, thermal stability, or specific functionalities. Research in this area aims to develop novel LDPE-based materials with tailored characteristics for specialized applications.
- Recycling and sustainability of LDPE: As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on the recycling and sustainable use of LDPE. Efforts are being made to develop more efficient recycling processes, improve the quality of recycled LDPE, and explore biodegradable or bio-based alternatives. This includes research into chemical recycling methods and the incorporation of recycled LDPE into new products.
02 LDPE applications in packaging and films
LDPE is widely used in packaging and film applications due to its excellent flexibility, transparency, and moisture resistance. It is commonly used in the production of plastic bags, food packaging, and agricultural films. The material's properties can be tailored to meet specific requirements for different packaging applications, such as improved barrier properties or enhanced strength.Expand Specific Solutions03 LDPE blends and composites
LDPE can be blended with other polymers or materials to create composites with enhanced properties. These blends and composites can offer improved mechanical strength, thermal stability, or specific functional characteristics. The combination of LDPE with other materials allows for the development of new products with tailored properties for various industries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and sustainability of LDPE
As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on the recycling and sustainability of LDPE products. Various methods and technologies are being developed to improve the recycling efficiency of LDPE materials, reduce waste, and promote circular economy principles. This includes the development of new recycling processes, the use of recycled LDPE in new products, and the design of more easily recyclable LDPE-based materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 LDPE modifications for specific properties
LDPE can be modified through various techniques to enhance specific properties or introduce new functionalities. These modifications can include crosslinking, grafting, or the addition of specific additives. Such modifications can improve properties like heat resistance, chemical resistance, or electrical insulation, expanding the range of applications for LDPE in industries such as automotive, electronics, and construction.Expand Specific Solutions
Key LDPE Industry Players
The competitive landscape for "Future Pathways for LDPE in Green Solutions" is evolving rapidly, reflecting the industry's transition towards sustainability. The market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions. The global LDPE market size is projected to expand significantly, fueled by green initiatives. Technologically, companies like Dow Global Technologies, ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, and SABIC Global Technologies are at the forefront, developing bio-based LDPE and recycling technologies. Braskem SA and Northern Technologies International Corp. are making strides in biodegradable plastics, while established players like Univation Technologies and LyondellBasell (Basell Polyolefine) are adapting their portfolios to include more sustainable options.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed a range of sustainable LDPE solutions for green applications. Their AGILITY™ CE LDPE resins are produced using circular feedstocks, reducing carbon footprint by up to 60% compared to fossil-based alternatives[1]. They've also introduced REVOLOOP™ recycled plastic resins, incorporating up to 70% post-consumer recycled content[2]. Dow's INNATE™ TF Polyethylene Resins for Tenter Frame Biaxial Orientation (TF-BOPE) enable the production of all-polyethylene packaging that's easily recyclable[3]. These innovations demonstrate Dow's commitment to circular economy principles and reducing environmental impact in LDPE production and use.
Strengths: Wide range of sustainable LDPE solutions, significant carbon footprint reduction, high recycled content incorporation. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs compared to traditional LDPE, market acceptance of recycled content materials.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed advanced LDPE technologies focusing on sustainability. Their Exceed™ XP performance polymers offer enhanced toughness and processing stability, allowing for downgauging in packaging applications, thus reducing material use[4]. ExxonMobil's Vistamaxx™ performance polymers enable the creation of recyclable flexible packaging with improved barrier properties[5]. They've also introduced Exxtend™ technology for advanced recycling of plastic waste back into virgin-quality plastics, potentially applicable to LDPE streams[6]. These innovations aim to improve the circularity of LDPE and reduce its environmental footprint while maintaining or enhancing performance.
Strengths: Advanced polymer technologies enabling material reduction and improved recyclability. Weaknesses: May require significant investment in new processing equipment for full benefits realization.
LDPE Eco-Innovation Patents
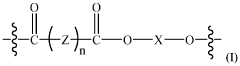
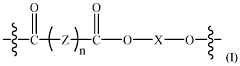
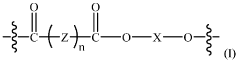
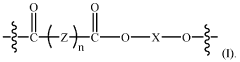
Repeatedly recyclable polymer mimics (RR-pm) of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) polymers
PatentWO2024133401A2
Innovation
- Development of repeatedly recyclable polymer mimics (RR-PM) of LDPE, which are created from a reaction product of difunctional oligomers and linkers obtained through depolymerization of used articles, allowing for repeated recycling with minimal loss of properties and reduced need for virgin materials.
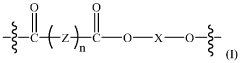
Repeatedly recyclable-polymer mimics (RR-pm) of linear low-density polyethylene
PatentWO2024133403A1
Innovation
- A repeatedly recyclable polymer mimic (RR-PM) of LLDPE is created through a reaction product of difunctional oligomers and linkers obtained from depolymerized articles, allowing for repeated recycling with minimal loss of material quality and reduced need for virgin materials, achieved by liquefying and repolymerizing the RR-PM in a closed-loop process.
LDPE Circular Economy
The circular economy for Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) represents a paradigm shift in how we approach plastic production, consumption, and disposal. This model aims to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency by keeping LDPE materials in use for as long as possible. The LDPE circular economy encompasses several key strategies and innovations that are reshaping the industry.
Recycling technologies play a crucial role in the LDPE circular economy. Advanced mechanical recycling processes have been developed to improve the quality of recycled LDPE, making it suitable for a wider range of applications. Chemical recycling methods, such as pyrolysis and depolymerization, are also gaining traction, allowing LDPE to be broken down into its chemical components for reuse in new plastic production.
Design for recyclability has become a central focus in the LDPE circular economy. Manufacturers are increasingly developing LDPE products that are easier to collect, sort, and recycle. This includes the use of mono-material designs, easily separable components, and clear labeling to facilitate proper disposal and recycling.
Collection and sorting systems are being optimized to improve the recovery rates of LDPE waste. Advanced sorting technologies, including near-infrared spectroscopy and artificial intelligence-driven systems, are enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of LDPE separation from mixed waste streams.
The development of bio-based and biodegradable alternatives to traditional LDPE is another important aspect of the circular economy. These materials aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and address end-of-life concerns, particularly for single-use applications where recycling may not be feasible.
Extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes are being implemented in various regions to encourage manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their LDPE products. These programs incentivize the use of recycled content, design for recyclability, and the establishment of take-back systems.
Collaboration across the value chain is essential for the success of the LDPE circular economy. Partnerships between raw material suppliers, manufacturers, retailers, waste management companies, and recyclers are fostering innovation and creating closed-loop systems for LDPE materials.
As the LDPE circular economy continues to evolve, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving recycling technologies, developing new circular business models, and exploring innovative applications for recycled LDPE. These advancements are crucial for addressing the environmental challenges associated with plastic waste and moving towards a more sustainable future for LDPE production and consumption.
Recycling technologies play a crucial role in the LDPE circular economy. Advanced mechanical recycling processes have been developed to improve the quality of recycled LDPE, making it suitable for a wider range of applications. Chemical recycling methods, such as pyrolysis and depolymerization, are also gaining traction, allowing LDPE to be broken down into its chemical components for reuse in new plastic production.
Design for recyclability has become a central focus in the LDPE circular economy. Manufacturers are increasingly developing LDPE products that are easier to collect, sort, and recycle. This includes the use of mono-material designs, easily separable components, and clear labeling to facilitate proper disposal and recycling.
Collection and sorting systems are being optimized to improve the recovery rates of LDPE waste. Advanced sorting technologies, including near-infrared spectroscopy and artificial intelligence-driven systems, are enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of LDPE separation from mixed waste streams.
The development of bio-based and biodegradable alternatives to traditional LDPE is another important aspect of the circular economy. These materials aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and address end-of-life concerns, particularly for single-use applications where recycling may not be feasible.
Extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes are being implemented in various regions to encourage manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their LDPE products. These programs incentivize the use of recycled content, design for recyclability, and the establishment of take-back systems.
Collaboration across the value chain is essential for the success of the LDPE circular economy. Partnerships between raw material suppliers, manufacturers, retailers, waste management companies, and recyclers are fostering innovation and creating closed-loop systems for LDPE materials.
As the LDPE circular economy continues to evolve, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving recycling technologies, developing new circular business models, and exploring innovative applications for recycled LDPE. These advancements are crucial for addressing the environmental challenges associated with plastic waste and moving towards a more sustainable future for LDPE production and consumption.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the future pathways for Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) in green solutions. As global awareness of environmental issues continues to grow, governments and international organizations are implementing increasingly stringent regulations to address plastic pollution and promote sustainable practices.
One of the key regulatory frameworks impacting LDPE is the European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan. This comprehensive strategy aims to reduce plastic waste, increase recycling rates, and promote the use of recycled materials in new products. Under this plan, all plastic packaging in the EU market must be recyclable or reusable by 2030, significantly influencing the production and use of LDPE.
In the United States, several states have implemented plastic bag bans or fees, directly affecting LDPE consumption. California, for instance, has banned single-use plastic bags, encouraging the use of reusable alternatives or recyclable paper bags. These regulations are driving innovation in LDPE alternatives and recycling technologies.
The Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal has also been amended to include plastic waste. This international treaty now regulates the global trade of plastic waste, pushing countries to develop domestic recycling capabilities and reduce plastic waste generation.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes are gaining traction worldwide, holding manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. These regulations incentivize companies to design products with improved recyclability and incorporate more recycled content, directly impacting LDPE production and use.
Many countries are implementing taxes on virgin plastic or setting minimum recycled content requirements for plastic products. For example, the UK has introduced a tax on plastic packaging with less than 30% recycled content, encouraging the use of recycled LDPE in manufacturing processes.
As environmental regulations continue to evolve, the LDPE industry faces both challenges and opportunities. Compliance with these regulations drives innovation in recycling technologies, bio-based alternatives, and circular economy models. Companies investing in sustainable LDPE solutions and recycling infrastructure are likely to gain a competitive advantage in this changing regulatory landscape.
One of the key regulatory frameworks impacting LDPE is the European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan. This comprehensive strategy aims to reduce plastic waste, increase recycling rates, and promote the use of recycled materials in new products. Under this plan, all plastic packaging in the EU market must be recyclable or reusable by 2030, significantly influencing the production and use of LDPE.
In the United States, several states have implemented plastic bag bans or fees, directly affecting LDPE consumption. California, for instance, has banned single-use plastic bags, encouraging the use of reusable alternatives or recyclable paper bags. These regulations are driving innovation in LDPE alternatives and recycling technologies.
The Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal has also been amended to include plastic waste. This international treaty now regulates the global trade of plastic waste, pushing countries to develop domestic recycling capabilities and reduce plastic waste generation.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes are gaining traction worldwide, holding manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. These regulations incentivize companies to design products with improved recyclability and incorporate more recycled content, directly impacting LDPE production and use.
Many countries are implementing taxes on virgin plastic or setting minimum recycled content requirements for plastic products. For example, the UK has introduced a tax on plastic packaging with less than 30% recycled content, encouraging the use of recycled LDPE in manufacturing processes.
As environmental regulations continue to evolve, the LDPE industry faces both challenges and opportunities. Compliance with these regulations drives innovation in recycling technologies, bio-based alternatives, and circular economy models. Companies investing in sustainable LDPE solutions and recycling infrastructure are likely to gain a competitive advantage in this changing regulatory landscape.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!