Leveraging LDPE for Better Packaging Solutions
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Packaging Evolution
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone in packaging solutions since its introduction in the 1930s. The evolution of LDPE packaging has been marked by continuous improvements in material properties, manufacturing processes, and application techniques. Initially used primarily for film applications, LDPE quickly gained popularity due to its flexibility, transparency, and moisture resistance.
In the 1950s and 1960s, advancements in extrusion technology led to the widespread adoption of LDPE in various packaging formats, including bags, wraps, and containers. This period saw the development of more sophisticated blow molding and injection molding techniques, expanding the range of LDPE packaging products.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a focus on enhancing LDPE's barrier properties. Researchers and manufacturers worked on improving the material's resistance to oxygen and moisture transmission, making it more suitable for food packaging applications. This era also saw the introduction of multilayer LDPE films, combining the benefits of LDPE with other materials to create packaging with superior performance characteristics.
Environmental concerns in the 1990s and 2000s drove innovations in LDPE packaging. The industry responded by developing thinner films that maintained strength while using less material, reducing overall plastic consumption. Recycling initiatives for LDPE packaging also gained momentum during this period, with improved collection and processing methods.
Recent years have seen a surge in sustainable LDPE packaging solutions. Bio-based LDPE, derived from renewable resources like sugarcane, has emerged as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based LDPE. Additionally, advancements in additive technologies have led to the development of oxo-biodegradable LDPE, designed to decompose more rapidly in the environment.
The digital printing revolution has also impacted LDPE packaging evolution. High-quality printing techniques now allow for intricate designs and vibrant colors on LDPE surfaces, enhancing brand visibility and product appeal. This has opened up new possibilities for customization and small-batch production in LDPE packaging.
Smart packaging concepts have begun to incorporate LDPE as well. The integration of RFID tags, QR codes, and other tracking technologies into LDPE packaging has improved supply chain management and consumer engagement. Some innovative applications even explore the use of LDPE films with embedded sensors to monitor product freshness or package integrity.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDPE packaging is likely to continue focusing on sustainability, functionality, and integration with digital technologies. Research into improving the recyclability of LDPE, enhancing its barrier properties, and developing novel applications promises to keep this versatile material at the forefront of packaging solutions for years to come.
In the 1950s and 1960s, advancements in extrusion technology led to the widespread adoption of LDPE in various packaging formats, including bags, wraps, and containers. This period saw the development of more sophisticated blow molding and injection molding techniques, expanding the range of LDPE packaging products.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a focus on enhancing LDPE's barrier properties. Researchers and manufacturers worked on improving the material's resistance to oxygen and moisture transmission, making it more suitable for food packaging applications. This era also saw the introduction of multilayer LDPE films, combining the benefits of LDPE with other materials to create packaging with superior performance characteristics.
Environmental concerns in the 1990s and 2000s drove innovations in LDPE packaging. The industry responded by developing thinner films that maintained strength while using less material, reducing overall plastic consumption. Recycling initiatives for LDPE packaging also gained momentum during this period, with improved collection and processing methods.
Recent years have seen a surge in sustainable LDPE packaging solutions. Bio-based LDPE, derived from renewable resources like sugarcane, has emerged as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based LDPE. Additionally, advancements in additive technologies have led to the development of oxo-biodegradable LDPE, designed to decompose more rapidly in the environment.
The digital printing revolution has also impacted LDPE packaging evolution. High-quality printing techniques now allow for intricate designs and vibrant colors on LDPE surfaces, enhancing brand visibility and product appeal. This has opened up new possibilities for customization and small-batch production in LDPE packaging.
Smart packaging concepts have begun to incorporate LDPE as well. The integration of RFID tags, QR codes, and other tracking technologies into LDPE packaging has improved supply chain management and consumer engagement. Some innovative applications even explore the use of LDPE films with embedded sensors to monitor product freshness or package integrity.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDPE packaging is likely to continue focusing on sustainability, functionality, and integration with digital technologies. Research into improving the recyclability of LDPE, enhancing its barrier properties, and developing novel applications promises to keep this versatile material at the forefront of packaging solutions for years to come.
Market Demand Analysis
The global packaging industry has witnessed a significant shift towards sustainable and efficient solutions, with Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) emerging as a key player in this transformation. Market demand for LDPE in packaging applications has been steadily increasing, driven by its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and potential for improved environmental performance.
Consumer awareness and regulatory pressures have created a strong demand for eco-friendly packaging options. LDPE, being recyclable and potentially incorporating recycled content, aligns well with these market trends. The food and beverage sector, in particular, has shown a growing interest in LDPE packaging due to its excellent moisture barrier properties and suitability for flexible packaging formats.
E-commerce expansion has further fueled the demand for LDPE packaging solutions. The material's lightweight nature and durability make it ideal for shipping and protective packaging, addressing the need for cost-effective and damage-resistant packaging in the booming online retail sector.
The healthcare and pharmaceutical industries have also contributed to the rising demand for LDPE packaging. The material's chemical resistance and ability to maintain product integrity have made it a preferred choice for medical device packaging and pharmaceutical blister packs.
Market analysis indicates that the LDPE packaging market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of several percentage points over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of flexible packaging across various industries and the material's ability to meet stringent sustainability requirements.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the fastest-growing market for LDPE packaging, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and changing consumer lifestyles. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on innovative LDPE formulations that enhance recyclability and reduce environmental impact.
The automotive industry has also shown increased interest in LDPE packaging solutions, particularly for the protection of sensitive components during transportation and storage. This trend is expected to continue as the automotive supply chain becomes more global and complex.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges remain. The packaging industry faces pressure to reduce plastic waste, which has led to increased scrutiny of all plastic materials, including LDPE. This has created opportunities for innovation in LDPE formulations and recycling technologies to address environmental concerns and meet evolving market demands.
In conclusion, the market demand for LDPE in packaging solutions is robust and multifaceted, spanning various industries and geographical regions. The material's versatility, coupled with ongoing innovations to enhance its sustainability profile, positions LDPE as a critical component in the future of packaging solutions.
Consumer awareness and regulatory pressures have created a strong demand for eco-friendly packaging options. LDPE, being recyclable and potentially incorporating recycled content, aligns well with these market trends. The food and beverage sector, in particular, has shown a growing interest in LDPE packaging due to its excellent moisture barrier properties and suitability for flexible packaging formats.
E-commerce expansion has further fueled the demand for LDPE packaging solutions. The material's lightweight nature and durability make it ideal for shipping and protective packaging, addressing the need for cost-effective and damage-resistant packaging in the booming online retail sector.
The healthcare and pharmaceutical industries have also contributed to the rising demand for LDPE packaging. The material's chemical resistance and ability to maintain product integrity have made it a preferred choice for medical device packaging and pharmaceutical blister packs.
Market analysis indicates that the LDPE packaging market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of several percentage points over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of flexible packaging across various industries and the material's ability to meet stringent sustainability requirements.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the fastest-growing market for LDPE packaging, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and changing consumer lifestyles. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on innovative LDPE formulations that enhance recyclability and reduce environmental impact.
The automotive industry has also shown increased interest in LDPE packaging solutions, particularly for the protection of sensitive components during transportation and storage. This trend is expected to continue as the automotive supply chain becomes more global and complex.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges remain. The packaging industry faces pressure to reduce plastic waste, which has led to increased scrutiny of all plastic materials, including LDPE. This has created opportunities for innovation in LDPE formulations and recycling technologies to address environmental concerns and meet evolving market demands.
In conclusion, the market demand for LDPE in packaging solutions is robust and multifaceted, spanning various industries and geographical regions. The material's versatility, coupled with ongoing innovations to enhance its sustainability profile, positions LDPE as a critical component in the future of packaging solutions.
LDPE Technical Challenges
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone in the packaging industry for decades, valued for its flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. However, as the demand for more sustainable and high-performance packaging solutions grows, LDPE faces several technical challenges that need to be addressed to maintain its relevance in the market.
One of the primary challenges is improving the barrier properties of LDPE. While it offers good moisture resistance, its gas barrier properties, particularly for oxygen and carbon dioxide, are relatively poor compared to other packaging materials. This limitation restricts its use in applications requiring extended shelf life for sensitive products such as foods and pharmaceuticals. Researchers are exploring various approaches to enhance LDPE's barrier properties, including the incorporation of nanoparticles and the development of multi-layer structures.
Another significant challenge is the need to improve LDPE's mechanical properties without compromising its flexibility. The material's relatively low tensile strength and puncture resistance can limit its use in certain high-stress applications. Efforts are underway to develop LDPE composites and blends that offer enhanced mechanical performance while maintaining the desirable characteristics of traditional LDPE.
The environmental impact of LDPE is a growing concern, particularly in terms of recyclability and biodegradability. While LDPE is technically recyclable, contamination issues and the lack of efficient recycling infrastructure often result in a significant portion of LDPE packaging ending up in landfills or the environment. Developing more easily recyclable LDPE formulations and improving recycling technologies are critical challenges facing the industry.
Heat sealing performance is another area where LDPE faces technical hurdles. While LDPE generally offers good heat sealing properties, there is a constant push for faster sealing speeds and lower sealing temperatures to improve packaging efficiency and reduce energy consumption. This requires fine-tuning of the polymer structure and additives to optimize sealing performance without compromising other properties.
Printability and surface treatment of LDPE films present additional challenges. The low surface energy of LDPE can lead to poor ink adhesion and print quality. Developing surface treatment technologies that provide long-lasting effects and are compatible with high-speed production processes remains an ongoing area of research and development.
Addressing these technical challenges is crucial for leveraging LDPE in better packaging solutions. It requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining polymer science, materials engineering, and process technology to develop innovative solutions that meet the evolving demands of the packaging industry while addressing sustainability concerns.
One of the primary challenges is improving the barrier properties of LDPE. While it offers good moisture resistance, its gas barrier properties, particularly for oxygen and carbon dioxide, are relatively poor compared to other packaging materials. This limitation restricts its use in applications requiring extended shelf life for sensitive products such as foods and pharmaceuticals. Researchers are exploring various approaches to enhance LDPE's barrier properties, including the incorporation of nanoparticles and the development of multi-layer structures.
Another significant challenge is the need to improve LDPE's mechanical properties without compromising its flexibility. The material's relatively low tensile strength and puncture resistance can limit its use in certain high-stress applications. Efforts are underway to develop LDPE composites and blends that offer enhanced mechanical performance while maintaining the desirable characteristics of traditional LDPE.
The environmental impact of LDPE is a growing concern, particularly in terms of recyclability and biodegradability. While LDPE is technically recyclable, contamination issues and the lack of efficient recycling infrastructure often result in a significant portion of LDPE packaging ending up in landfills or the environment. Developing more easily recyclable LDPE formulations and improving recycling technologies are critical challenges facing the industry.
Heat sealing performance is another area where LDPE faces technical hurdles. While LDPE generally offers good heat sealing properties, there is a constant push for faster sealing speeds and lower sealing temperatures to improve packaging efficiency and reduce energy consumption. This requires fine-tuning of the polymer structure and additives to optimize sealing performance without compromising other properties.
Printability and surface treatment of LDPE films present additional challenges. The low surface energy of LDPE can lead to poor ink adhesion and print quality. Developing surface treatment technologies that provide long-lasting effects and are compatible with high-speed production processes remains an ongoing area of research and development.
Addressing these technical challenges is crucial for leveraging LDPE in better packaging solutions. It requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining polymer science, materials engineering, and process technology to develop innovative solutions that meet the evolving demands of the packaging industry while addressing sustainability concerns.
Current LDPE Solutions
01 Composition and properties of LDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a low density and high flexibility. It is characterized by its branched structure, which results in lower crystallinity and density compared to other polyethylene types. LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance, low water absorption, and excellent electrical insulation properties.- Composition and properties of LDPE: Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a low density and high flexibility. It is characterized by its branched structure, which results in lower crystallinity and density compared to other polyethylene types. LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance, low water absorption, and excellent electrical insulation properties.
- Manufacturing processes for LDPE: LDPE is typically produced through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene using free-radical initiators. Various manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the production efficiency and control the properties of LDPE, including the use of different catalysts, reactor designs, and process conditions.
- Applications of LDPE: LDPE finds widespread use in various industries due to its unique properties. Common applications include packaging materials, such as plastic bags and films, agricultural films, wire and cable insulation, and molded products. Its flexibility and chemical resistance make it suitable for both rigid and flexible packaging solutions.
- Modifications and blends of LDPE: To enhance its properties and expand its applications, LDPE is often modified or blended with other materials. This includes the incorporation of additives, crosslinking agents, or blending with other polymers to improve mechanical strength, thermal stability, or specific functional properties. These modifications allow for tailored solutions in various industries.
- Recycling and sustainability of LDPE: As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on the recycling and sustainability of LDPE products. Research and development efforts are directed towards improving recycling processes, developing biodegradable alternatives, and finding new applications for recycled LDPE materials to reduce environmental impact and promote circular economy principles.
02 Manufacturing processes for LDPE
LDPE is typically produced through high-pressure polymerization of ethylene using free-radical initiators. Various manufacturing techniques have been developed to improve the production efficiency and control the properties of LDPE, including the use of different catalysts, reactor designs, and process conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of LDPE
LDPE finds widespread use in various industries due to its unique properties. Common applications include packaging materials, plastic bags, containers, agricultural films, wire and cable insulation, and disposable medical devices. Its flexibility and chemical resistance make it suitable for a wide range of products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modifications and blends of LDPE
To enhance the performance of LDPE, various modifications and blending techniques have been developed. These include the incorporation of additives, crosslinking, and blending with other polymers to improve specific properties such as strength, barrier properties, or biodegradability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recycling and environmental considerations of LDPE
As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on the recycling and sustainable use of LDPE. Research is being conducted on improving recycling processes, developing biodegradable alternatives, and reducing the environmental impact of LDPE production and disposal.Expand Specific Solutions
Key LDPE Manufacturers
The market for LDPE packaging solutions is in a mature stage, with steady growth driven by increasing demand for flexible and durable packaging across various industries. The global LDPE market size is substantial, valued at billions of dollars annually. Technologically, LDPE production is well-established, but innovation continues in areas like improved barrier properties and sustainability. Key players such as Dow Global Technologies, ExxonMobil Chemical, and SABIC are at the forefront of LDPE technology development, while companies like Tetra Laval and Borealis AG focus on specialized packaging applications. Chinese firms like PetroChina and Sinopec are also significant contributors, reflecting the growing importance of Asian markets in this sector.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed advanced LDPE resins with enhanced properties for packaging applications. Their ELITE™ Enhanced Polyethylene Resins combine the processing ease of LDPE with improved strength and toughness[1]. These resins offer excellent optical properties, seal strength, and hot tack performance, making them ideal for flexible packaging[2]. Dow's AGILITY™ EC series provides high melt strength and bubble stability for extrusion coating applications, enabling faster line speeds and improved coating weights[3]. The company has also introduced INNATE™ Precision Packaging Resins, which offer a balance of stiffness and toughness, allowing for downgauging opportunities in packaging films[4].
Strengths: Wide range of specialized LDPE resins for various packaging needs, strong R&D capabilities, global presence. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs compared to standard LDPE, may require specialized processing equipment for some grades.
Borealis AG
Technical Solution: Borealis has developed Borstar® technology, which allows for the production of bimodal LDPE resins with enhanced properties[8]. Their Anteo™ linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) can be used in combination with LDPE to create high-performance packaging films with excellent sealing properties and good optical characteristics[9]. Borealis has also introduced Borcycle™ M technology, which incorporates recycled polyolefins, including LDPE, into new packaging solutions, supporting circular economy initiatives[10]. Their BorShape™ technology enables the production of LDPE with improved melt strength and processability for extrusion coating and lamination applications[11].
Strengths: Innovative bimodal technology, focus on circular economy solutions, strong presence in European markets. Weaknesses: May have limited market penetration in some regions, potential higher costs for advanced grades.
LDPE Patent Landscape
Laminated packaging material for paper container
PatentWO2000044632A1
Innovation
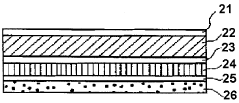
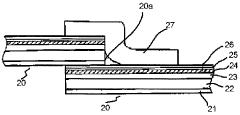
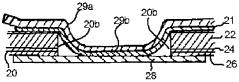
- A packaging material comprising a thermoplastic layer, a paper layer, and a barrier layer, with an innermost thermoplastic layer made of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) having specific molecular weight distribution and melting properties, enhancing sealability and preventing leakage while maintaining quality.
Plastic bottle for hot filling or heat treatment
PatentInactiveEP2025603A1
Innovation
- A packaging system with a higher thermal expansion coefficient than the packaged product, made from materials like low-density polyethylene (LDPE), which expands and contracts with temperature changes, maintaining a positive or zero relative pressure and preventing deformation, and can be manufactured through molding or extrusion blow molding.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) in packaging solutions is a critical consideration in the pursuit of sustainable practices. LDPE, while offering excellent flexibility and durability, presents significant challenges in terms of its ecological footprint throughout its lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with LDPE packaging is its persistence in the environment. As a petroleum-based plastic, LDPE takes hundreds of years to decompose naturally, contributing to long-term pollution in landfills and ecosystems. This longevity leads to accumulation in marine environments, posing threats to wildlife through ingestion and entanglement.
The production of LDPE also raises environmental issues. The manufacturing process relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as raw materials and energy sources, resulting in substantial greenhouse gas emissions. This contributes to climate change and air pollution, with the petrochemical industry being a significant source of carbon dioxide emissions globally.
Recycling LDPE presents both opportunities and challenges. While technically recyclable, the collection and processing of LDPE packaging can be complex due to contamination issues and the need for specialized recycling facilities. The low density of LDPE makes transportation for recycling less efficient, potentially offsetting some environmental benefits.
However, recent advancements in recycling technologies offer promising solutions. Chemical recycling methods, such as pyrolysis, can break down LDPE into its chemical components, allowing for the creation of new plastic products or even fuel. This circular approach could significantly reduce the environmental impact of LDPE packaging.
Efforts to improve the environmental profile of LDPE packaging include the development of bio-based alternatives. These materials, derived from renewable resources like sugarcane or corn, aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease carbon footprints. However, challenges remain in scaling production and ensuring these alternatives do not compete with food crops.
The use of recycled LDPE in packaging is gaining traction as a means to reduce virgin plastic production. This approach not only conserves resources but also helps to close the loop in plastic waste management. Innovations in multi-layer packaging that incorporate recycled LDPE are showing potential in maintaining performance while improving sustainability.
In conclusion, while LDPE offers valuable properties for packaging, its environmental impact necessitates careful consideration and innovative approaches. The industry's focus on improving recycling infrastructure, developing bio-based alternatives, and incorporating recycled content represents crucial steps towards more sustainable packaging solutions.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with LDPE packaging is its persistence in the environment. As a petroleum-based plastic, LDPE takes hundreds of years to decompose naturally, contributing to long-term pollution in landfills and ecosystems. This longevity leads to accumulation in marine environments, posing threats to wildlife through ingestion and entanglement.
The production of LDPE also raises environmental issues. The manufacturing process relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as raw materials and energy sources, resulting in substantial greenhouse gas emissions. This contributes to climate change and air pollution, with the petrochemical industry being a significant source of carbon dioxide emissions globally.
Recycling LDPE presents both opportunities and challenges. While technically recyclable, the collection and processing of LDPE packaging can be complex due to contamination issues and the need for specialized recycling facilities. The low density of LDPE makes transportation for recycling less efficient, potentially offsetting some environmental benefits.
However, recent advancements in recycling technologies offer promising solutions. Chemical recycling methods, such as pyrolysis, can break down LDPE into its chemical components, allowing for the creation of new plastic products or even fuel. This circular approach could significantly reduce the environmental impact of LDPE packaging.
Efforts to improve the environmental profile of LDPE packaging include the development of bio-based alternatives. These materials, derived from renewable resources like sugarcane or corn, aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease carbon footprints. However, challenges remain in scaling production and ensuring these alternatives do not compete with food crops.
The use of recycled LDPE in packaging is gaining traction as a means to reduce virgin plastic production. This approach not only conserves resources but also helps to close the loop in plastic waste management. Innovations in multi-layer packaging that incorporate recycled LDPE are showing potential in maintaining performance while improving sustainability.
In conclusion, while LDPE offers valuable properties for packaging, its environmental impact necessitates careful consideration and innovative approaches. The industry's focus on improving recycling infrastructure, developing bio-based alternatives, and incorporating recycled content represents crucial steps towards more sustainable packaging solutions.
Recycling Technologies
Recycling technologies for Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) have seen significant advancements in recent years, addressing the growing concern for sustainable packaging solutions. Traditional mechanical recycling methods, while effective for certain plastics, have limitations when it comes to LDPE due to its low melting point and tendency to degrade during reprocessing.
Advanced mechanical recycling techniques have been developed to overcome these challenges. These include improved sorting technologies using near-infrared spectroscopy and artificial intelligence, which can more accurately identify and separate LDPE from other plastic types. Additionally, enhanced washing and decontamination processes have been implemented to remove impurities and improve the quality of recycled LDPE.
Chemical recycling has emerged as a promising alternative for LDPE recycling. Pyrolysis, a process that breaks down plastic waste into its chemical components under high temperatures and in the absence of oxygen, has shown particular potential. This method can convert LDPE into valuable hydrocarbons, which can be used as feedstock for new plastic production or as fuel.
Another innovative approach is solvent-based recycling, which dissolves LDPE in specific solvents, allowing for the separation of contaminants and additives. This process can produce high-quality recycled LDPE suitable for food-grade packaging applications, addressing a significant challenge in the recycling industry.
Enzymatic recycling is an emerging technology that uses specially engineered enzymes to break down LDPE into its monomers. While still in the early stages of development, this method shows promise for creating a closed-loop recycling system for LDPE packaging.
The integration of these recycling technologies with smart packaging design is crucial for improving the overall recyclability of LDPE packaging. Design for recycling principles, such as using mono-material structures and easily separable components, can significantly enhance the efficiency of recycling processes.
As the demand for sustainable packaging solutions grows, continued investment in research and development of recycling technologies is essential. Collaboration between packaging manufacturers, recycling companies, and research institutions is driving innovation in this field, with the goal of creating a circular economy for LDPE packaging materials.
Advanced mechanical recycling techniques have been developed to overcome these challenges. These include improved sorting technologies using near-infrared spectroscopy and artificial intelligence, which can more accurately identify and separate LDPE from other plastic types. Additionally, enhanced washing and decontamination processes have been implemented to remove impurities and improve the quality of recycled LDPE.
Chemical recycling has emerged as a promising alternative for LDPE recycling. Pyrolysis, a process that breaks down plastic waste into its chemical components under high temperatures and in the absence of oxygen, has shown particular potential. This method can convert LDPE into valuable hydrocarbons, which can be used as feedstock for new plastic production or as fuel.
Another innovative approach is solvent-based recycling, which dissolves LDPE in specific solvents, allowing for the separation of contaminants and additives. This process can produce high-quality recycled LDPE suitable for food-grade packaging applications, addressing a significant challenge in the recycling industry.
Enzymatic recycling is an emerging technology that uses specially engineered enzymes to break down LDPE into its monomers. While still in the early stages of development, this method shows promise for creating a closed-loop recycling system for LDPE packaging.
The integration of these recycling technologies with smart packaging design is crucial for improving the overall recyclability of LDPE packaging. Design for recycling principles, such as using mono-material structures and easily separable components, can significantly enhance the efficiency of recycling processes.
As the demand for sustainable packaging solutions grows, continued investment in research and development of recycling technologies is essential. Collaboration between packaging manufacturers, recycling companies, and research institutions is driving innovation in this field, with the goal of creating a circular economy for LDPE packaging materials.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!