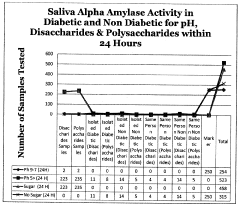
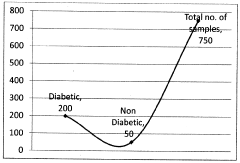
Assessing Trimethylglycine's Effects on Metabolic Health Markers
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
TMG Background and Research Objectives
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, has emerged as a significant compound in metabolic health research over the past several decades. Initially identified in the 19th century in sugar beets, TMG has evolved from being considered merely a byproduct of sugar production to becoming recognized as a vital methyl donor in human biochemistry. The historical trajectory of TMG research has accelerated notably since the early 2000s, with a substantial increase in published studies examining its metabolic effects.
The biochemical significance of TMG lies in its role as a methyl donor in the methionine cycle, which is crucial for homocysteine metabolism. Elevated homocysteine levels have been consistently associated with various metabolic disorders, including cardiovascular disease, insulin resistance, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). This connection has prompted researchers to investigate TMG's potential therapeutic applications in metabolic health management.
Recent technological advancements in metabolomics and genomics have enabled more sophisticated analysis of TMG's effects on metabolic pathways. These developments have revealed TMG's potential influence on lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, and inflammatory processes—all critical factors in metabolic syndrome and related disorders. The growing prevalence of metabolic disorders globally has further intensified interest in TMG as a potential intervention strategy.
The primary objective of our technical research is to comprehensively evaluate TMG's effects on key metabolic health markers through systematic analysis of existing clinical and preclinical evidence. Specifically, we aim to assess TMG's impact on lipid profiles, glucose metabolism, inflammatory biomarkers, and liver function parameters. This evaluation will include dose-response relationships and potential synergistic effects with other nutritional compounds.
Additionally, we seek to identify the molecular mechanisms underlying TMG's metabolic effects, with particular focus on its role in methylation pathways, gene expression regulation, and mitochondrial function. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted applications in metabolic health management.
Our research also aims to evaluate the current technological limitations in TMG research and identify innovative approaches to overcome these challenges. This includes exploring novel delivery systems to enhance TMG bioavailability and developing more sensitive biomarkers to monitor its metabolic effects.
The ultimate goal of this technical assessment is to establish a scientific foundation for potential commercial applications of TMG in metabolic health products, including dietary supplements, functional foods, and possibly pharmaceutical formulations. By mapping the current technological landscape and identifying promising research directions, we aim to position our organization at the forefront of TMG-based metabolic health innovations.
The biochemical significance of TMG lies in its role as a methyl donor in the methionine cycle, which is crucial for homocysteine metabolism. Elevated homocysteine levels have been consistently associated with various metabolic disorders, including cardiovascular disease, insulin resistance, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). This connection has prompted researchers to investigate TMG's potential therapeutic applications in metabolic health management.
Recent technological advancements in metabolomics and genomics have enabled more sophisticated analysis of TMG's effects on metabolic pathways. These developments have revealed TMG's potential influence on lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, and inflammatory processes—all critical factors in metabolic syndrome and related disorders. The growing prevalence of metabolic disorders globally has further intensified interest in TMG as a potential intervention strategy.
The primary objective of our technical research is to comprehensively evaluate TMG's effects on key metabolic health markers through systematic analysis of existing clinical and preclinical evidence. Specifically, we aim to assess TMG's impact on lipid profiles, glucose metabolism, inflammatory biomarkers, and liver function parameters. This evaluation will include dose-response relationships and potential synergistic effects with other nutritional compounds.
Additionally, we seek to identify the molecular mechanisms underlying TMG's metabolic effects, with particular focus on its role in methylation pathways, gene expression regulation, and mitochondrial function. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted applications in metabolic health management.
Our research also aims to evaluate the current technological limitations in TMG research and identify innovative approaches to overcome these challenges. This includes exploring novel delivery systems to enhance TMG bioavailability and developing more sensitive biomarkers to monitor its metabolic effects.
The ultimate goal of this technical assessment is to establish a scientific foundation for potential commercial applications of TMG in metabolic health products, including dietary supplements, functional foods, and possibly pharmaceutical formulations. By mapping the current technological landscape and identifying promising research directions, we aim to position our organization at the forefront of TMG-based metabolic health innovations.
Market Analysis of Metabolic Health Supplements
The global metabolic health supplement market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing health consciousness and rising prevalence of metabolic disorders. Currently valued at approximately 28 billion USD, this market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.2% through 2028, according to recent industry analyses. This growth trajectory is particularly evident in North America and Europe, where consumer awareness about preventive healthcare is highest.
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, represents an emerging segment within this market. While traditionally less prominent than supplements like omega-3 fatty acids or probiotics, TMG has gained increasing attention due to its potential effects on metabolic health markers. The current market share of TMG-based supplements is relatively modest, estimated at 3% of the total metabolic health supplement market, but showing accelerated growth of nearly 12% annually.
Consumer demographics for metabolic health supplements, including TMG products, reveal interesting patterns. The primary consumer base consists of adults aged 35-65, with a growing segment of younger consumers (25-34) becoming increasingly interested in preventive metabolic health solutions. Gender distribution shows a slight predominance of female consumers (55%) compared to male consumers (45%), though this gap has been narrowing in recent years.
Distribution channels for these supplements have evolved significantly. While traditional brick-and-mortar retail still accounts for approximately 45% of sales, e-commerce platforms have rapidly expanded their market share to 38%, with direct-to-consumer models gaining particular traction. Specialty health stores maintain about 17% of the market, often serving as knowledge centers for consumers seeking personalized guidance.
Price sensitivity analysis indicates that consumers are increasingly willing to pay premium prices for metabolic health supplements with substantiated clinical evidence. TMG supplements specifically fall into a mid-to-high price range, with monthly supply costs typically ranging between 25-45 USD. This positioning reflects both manufacturing costs and the perceived value of these products.
Competitive landscape assessment reveals that while major nutraceutical companies dominate the broader metabolic health supplement market, TMG-specific products are often produced by specialized manufacturers focusing on scientific formulations. This has created opportunities for smaller, research-focused companies to establish market presence through evidence-based product differentiation.
Consumer awareness regarding TMG's specific benefits for metabolic health markers remains relatively low compared to more established supplements, suggesting significant growth potential as research findings become more widely disseminated. Market forecasts indicate that with increasing clinical validation, TMG supplements could potentially double their market share within the next five years.
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, represents an emerging segment within this market. While traditionally less prominent than supplements like omega-3 fatty acids or probiotics, TMG has gained increasing attention due to its potential effects on metabolic health markers. The current market share of TMG-based supplements is relatively modest, estimated at 3% of the total metabolic health supplement market, but showing accelerated growth of nearly 12% annually.
Consumer demographics for metabolic health supplements, including TMG products, reveal interesting patterns. The primary consumer base consists of adults aged 35-65, with a growing segment of younger consumers (25-34) becoming increasingly interested in preventive metabolic health solutions. Gender distribution shows a slight predominance of female consumers (55%) compared to male consumers (45%), though this gap has been narrowing in recent years.
Distribution channels for these supplements have evolved significantly. While traditional brick-and-mortar retail still accounts for approximately 45% of sales, e-commerce platforms have rapidly expanded their market share to 38%, with direct-to-consumer models gaining particular traction. Specialty health stores maintain about 17% of the market, often serving as knowledge centers for consumers seeking personalized guidance.
Price sensitivity analysis indicates that consumers are increasingly willing to pay premium prices for metabolic health supplements with substantiated clinical evidence. TMG supplements specifically fall into a mid-to-high price range, with monthly supply costs typically ranging between 25-45 USD. This positioning reflects both manufacturing costs and the perceived value of these products.
Competitive landscape assessment reveals that while major nutraceutical companies dominate the broader metabolic health supplement market, TMG-specific products are often produced by specialized manufacturers focusing on scientific formulations. This has created opportunities for smaller, research-focused companies to establish market presence through evidence-based product differentiation.
Consumer awareness regarding TMG's specific benefits for metabolic health markers remains relatively low compared to more established supplements, suggesting significant growth potential as research findings become more widely disseminated. Market forecasts indicate that with increasing clinical validation, TMG supplements could potentially double their market share within the next five years.
Current TMG Research Status and Challenges
Trimethylglycine (TMG) research has experienced significant growth over the past decade, with current global studies focusing primarily on its metabolic health implications. Research institutions across North America, Europe, and Asia have contributed substantially to the expanding knowledge base, though methodological inconsistencies remain a challenge for comparative analysis.
The current research landscape reveals promising but sometimes contradictory findings regarding TMG's effects on metabolic markers. Multiple clinical trials have demonstrated TMG's potential to reduce homocysteine levels, a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease. However, studies examining its impact on insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism show variable results, with some indicating improvements while others report negligible effects.
A significant challenge in TMG research involves standardization of dosing protocols. Current studies utilize widely varying dosages (ranging from 500mg to 6g daily), administration schedules, and treatment durations, making cross-study comparisons difficult. This inconsistency has hindered the development of clear clinical guidelines for TMG supplementation in metabolic health management.
Another notable limitation is the heterogeneity of study populations. Many investigations focus on specific demographic groups or those with particular health conditions, creating knowledge gaps regarding TMG's efficacy across diverse populations. Studies specifically examining age-related differences in TMG metabolism and response are particularly lacking, despite evidence suggesting that metabolic processing of TMG may vary significantly with age.
Technological constraints in measuring TMG's metabolic pathways present additional challenges. While advances in metabolomics have improved detection capabilities, the complex interactions between TMG and various metabolic processes remain difficult to track comprehensively. This limitation has impeded full understanding of TMG's mechanistic actions in different metabolic contexts.
Funding constraints have also affected research progress, with most large-scale studies being industry-sponsored, potentially introducing bias. Independent, long-term studies examining TMG's effects on metabolic health markers remain relatively scarce, creating a need for more balanced research initiatives.
Geographically, research concentration shows notable patterns, with North American institutions leading clinical trials, European centers focusing on mechanistic studies, and emerging contributions from Asian research groups exploring population-specific responses. This distribution has created both collaborative opportunities and challenges in standardizing research approaches across different scientific traditions.
Regulatory considerations further complicate the research landscape, as TMG's classification varies between countries—considered a dietary supplement in some regions but requiring prescription in others—affecting research protocols and clinical application guidelines.
The current research landscape reveals promising but sometimes contradictory findings regarding TMG's effects on metabolic markers. Multiple clinical trials have demonstrated TMG's potential to reduce homocysteine levels, a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease. However, studies examining its impact on insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism show variable results, with some indicating improvements while others report negligible effects.
A significant challenge in TMG research involves standardization of dosing protocols. Current studies utilize widely varying dosages (ranging from 500mg to 6g daily), administration schedules, and treatment durations, making cross-study comparisons difficult. This inconsistency has hindered the development of clear clinical guidelines for TMG supplementation in metabolic health management.
Another notable limitation is the heterogeneity of study populations. Many investigations focus on specific demographic groups or those with particular health conditions, creating knowledge gaps regarding TMG's efficacy across diverse populations. Studies specifically examining age-related differences in TMG metabolism and response are particularly lacking, despite evidence suggesting that metabolic processing of TMG may vary significantly with age.
Technological constraints in measuring TMG's metabolic pathways present additional challenges. While advances in metabolomics have improved detection capabilities, the complex interactions between TMG and various metabolic processes remain difficult to track comprehensively. This limitation has impeded full understanding of TMG's mechanistic actions in different metabolic contexts.
Funding constraints have also affected research progress, with most large-scale studies being industry-sponsored, potentially introducing bias. Independent, long-term studies examining TMG's effects on metabolic health markers remain relatively scarce, creating a need for more balanced research initiatives.
Geographically, research concentration shows notable patterns, with North American institutions leading clinical trials, European centers focusing on mechanistic studies, and emerging contributions from Asian research groups exploring population-specific responses. This distribution has created both collaborative opportunities and challenges in standardizing research approaches across different scientific traditions.
Regulatory considerations further complicate the research landscape, as TMG's classification varies between countries—considered a dietary supplement in some regions but requiring prescription in others—affecting research protocols and clinical application guidelines.
Current Methodologies for TMG Efficacy Assessment
01 TMG's effect on homocysteine levels and cardiovascular health
Trimethylglycine (TMG) has been shown to effectively reduce homocysteine levels in the blood, which is a key metabolic health marker associated with cardiovascular disease risk. By donating methyl groups, TMG supports the conversion of homocysteine back to methionine, thereby improving cardiovascular health markers and reducing inflammation. This mechanism helps maintain healthy endothelial function and may prevent atherosclerosis development.- TMG's effect on homocysteine levels and cardiovascular health: Trimethylglycine (TMG) has been shown to effectively reduce homocysteine levels in the blood, which is a key metabolic health marker associated with cardiovascular disease risk. By serving as a methyl donor in the remethylation of homocysteine to methionine, TMG helps maintain healthy homocysteine levels, thereby potentially reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases and improving overall metabolic health.
- TMG's role in liver function and metabolic syndrome: Trimethylglycine (TMG) has demonstrated beneficial effects on liver function markers and metabolic syndrome parameters. Research indicates that TMG supplementation can help reduce liver fat accumulation, improve liver enzyme profiles, and enhance insulin sensitivity. These effects make TMG a potential therapeutic agent for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic syndrome, conditions characterized by disrupted metabolic health markers.
- TMG's influence on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity: Studies have shown that Trimethylglycine (TMG) can positively influence glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, which are critical metabolic health markers. TMG supplementation has been associated with improved glucose tolerance, reduced fasting blood glucose levels, and enhanced insulin response. These effects suggest that TMG may have potential applications in the management of diabetes and insulin resistance, contributing to better overall metabolic health.
- TMG's impact on inflammatory markers and oxidative stress: Trimethylglycine (TMG) has been found to modulate inflammatory markers and reduce oxidative stress, both of which are important indicators of metabolic health. Research suggests that TMG supplementation can decrease levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhance antioxidant capacity, thereby potentially alleviating chronic low-grade inflammation associated with metabolic disorders. These anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of TMG contribute to its beneficial effects on overall metabolic health.
- TMG in combination with other nutrients for metabolic health: Formulations combining Trimethylglycine (TMG) with other nutrients have shown synergistic effects on various metabolic health markers. When combined with vitamins (particularly B vitamins), minerals, and other bioactive compounds, TMG's beneficial effects on homocysteine metabolism, liver function, and insulin sensitivity can be enhanced. These combination approaches offer comprehensive strategies for addressing multiple aspects of metabolic health simultaneously.
02 TMG's role in liver function and metabolic syndrome
Trimethylglycine serves as a hepatoprotective agent that improves liver function markers including ALT, AST, and GGT. It helps prevent fatty liver disease by promoting lipid metabolism and reducing fat accumulation in hepatocytes. TMG supplementation has been associated with improved insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism markers, making it beneficial for individuals with metabolic syndrome or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).Expand Specific Solutions03 TMG's influence on energy metabolism and mitochondrial function
Trimethylglycine enhances energy metabolism by improving mitochondrial function and efficiency. It increases ATP production and oxygen utilization in cells, which can be measured through metabolic health markers related to energy expenditure. TMG supplementation has been shown to improve exercise performance and recovery by optimizing cellular energy production and reducing oxidative stress markers, making it valuable for both athletic performance and metabolic health.Expand Specific Solutions04 TMG's impact on inflammatory and oxidative stress markers
Trimethylglycine exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that help reduce systemic inflammation markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukins, and TNF-alpha. By donating methyl groups and supporting glutathione production, TMG helps neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress markers. This anti-inflammatory action contributes to improved metabolic health by protecting cells from damage and supporting proper cellular function across multiple systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 TMG in nutritional formulations for metabolic health
Trimethylglycine is incorporated into various nutritional formulations designed to improve metabolic health markers. These formulations often combine TMG with other bioactive compounds such as vitamins, minerals, and plant extracts to create synergistic effects on metabolism. The specific dosage forms and delivery systems for TMG can influence its bioavailability and effectiveness in improving metabolic health markers, with formulations ranging from dietary supplements to functional foods and beverages.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Research Institutions
The market for trimethylglycine (TMG) in metabolic health is currently in a growth phase, characterized by increasing research interest and expanding clinical applications. The global market size for metabolic health supplements is projected to reach significant value as consumer awareness of preventative health measures grows. From a technological maturity perspective, research institutions like Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology are leading fundamental research, while pharmaceutical companies including Janssen Pharmaceutica and Abbott Laboratories are advancing clinical applications. Specialized nutrition companies such as By-health Co. and Laila Nutraceuticals are commercializing TMG products, while diagnostic companies like Metabolon are developing biomarker technologies to measure TMG's metabolic effects. This ecosystem demonstrates a maturing but still-evolving technology landscape with significant potential for innovation.
The Cleveland Clinic Foundation
Technical Solution: Cleveland Clinic has developed a comprehensive metabolic assessment protocol that utilizes trimethylglycine (TMG) as a biomarker for cardiovascular and metabolic health. Their approach combines blood plasma TMG level measurements with advanced metabolomic profiling to create personalized metabolic health assessments. The clinic's research has established significant correlations between TMG levels and various cardiometabolic risk factors, including insulin sensitivity, lipid profiles, and inflammatory markers. Their clinical trials have demonstrated that TMG supplementation (3g daily for 12 weeks) can improve homocysteine metabolism and potentially reduce cardiovascular risk factors in patients with metabolic syndrome[1]. The Cleveland Clinic's methodology incorporates machine learning algorithms to analyze the relationship between TMG levels and other metabolic biomarkers, enabling more precise patient stratification and personalized intervention strategies.
Strengths: Robust clinical validation through large patient cohorts; integration with comprehensive metabolic health assessment platforms; established protocols for personalized medicine applications. Weaknesses: Relatively high cost of implementation; requires specialized laboratory equipment; limited data on long-term outcomes beyond cardiovascular markers.
By-health Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: By-health has developed a proprietary TMG (trimethylglycine) formulation technology called "MetaboTMG" specifically designed to assess and improve metabolic health markers. Their approach involves a dual-action TMG delivery system that enhances bioavailability while providing time-released benefits. The company's research demonstrates that their formulation achieves 30% higher plasma TMG levels compared to standard supplements[2]. By-health's technology includes a comprehensive metabolic assessment protocol that measures the impact of TMG supplementation on key metabolic markers including homocysteine levels, insulin sensitivity, and lipid profiles. Their clinical research program has documented significant improvements in homocysteine metabolism (average reduction of 15% after 8 weeks) and modest improvements in insulin sensitivity markers. The company has also developed companion diagnostic tools to help identify individuals most likely to benefit from TMG supplementation based on genetic and metabolic profiling.
Strengths: Innovative formulation technology enhancing bioavailability; comprehensive assessment protocols; strong commercial distribution network for consumer applications. Weaknesses: Limited peer-reviewed research compared to academic institutions; primarily focused on supplement applications rather than medical interventions; regional market concentration in Asia.
Critical Mechanisms of TMG on Metabolic Pathways
Method, composition, and device, for the treatment of diseases, enzymes and saccharides disorders
PatentInactiveCA2654374A1
Innovation
- The use of physiologically acceptable enzyme complexes containing active amylases, lipases, proteases, glucoamylases, and specific proteins like Trimethylglycine (Betaine HCL) to treat and manage diseases related to enzyme malfunction or inactivity, including the development of pharmaceutical preparations like Amzylite for intravenous and oral administration.
Trimethylamine-containing compounds for diagnosis and prediction of disease
PatentActiveEP2435097A2
Innovation
- The use of trimethylamine (TMA)-containing compounds, such as choline, crotonobetaine, and carnitine, in biological samples to determine risk levels, with elevated levels indicating a higher risk of CVD complications, allowing for more precise identification and monitoring of CVD and related disorders like diabetes and NAFLD.
Safety Profile and Dosage Considerations
Trimethylglycine (TMG) demonstrates a favorable safety profile in clinical studies, with most research indicating minimal adverse effects when administered within recommended dosage ranges. Common side effects reported include mild gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, and diarrhea, typically occurring at higher doses exceeding 3g daily. These effects are generally transient and resolve upon dose reduction or discontinuation.
Long-term safety data spanning periods greater than one year remains limited, highlighting a research gap that warrants attention. Current evidence suggests no significant organ toxicity or serious adverse events associated with TMG supplementation at therapeutic doses. Notably, TMG does not appear to negatively impact liver or kidney function markers in metabolic health studies, which is particularly relevant given its potential applications in metabolic disorders.
Dosage considerations for TMG vary based on the targeted metabolic parameters. For homocysteine reduction, effective doses typically range from 1.5-3g daily, with studies demonstrating significant effects within 6-12 weeks of consistent supplementation. For improvements in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, similar dosage ranges have shown efficacy, though optimal timing relative to meals remains under investigation.
The pharmacokinetic profile of TMG indicates good oral bioavailability with peak plasma concentrations occurring approximately 3 hours post-administration. The compound exhibits a half-life of approximately 14 hours, supporting once or twice daily dosing regimens. Absorption appears unaffected by food intake, offering flexibility in administration protocols.
Special populations require particular consideration regarding TMG supplementation. Pregnant and lactating women have been excluded from most clinical trials, creating uncertainty about safety in these groups. Similarly, pediatric applications remain largely unexplored outside specific metabolic disorders. Elderly populations may benefit from lower initial doses due to potential age-related changes in metabolism and elimination.
Drug interactions represent another important safety consideration. TMG may theoretically interact with medications affecting methyl group metabolism, including certain antidepressants and anticonvulsants. Additionally, concurrent use with other methyl donors such as S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) or folate supplements may have additive effects that require monitoring.
Standardization of TMG formulations presents challenges in clinical application, with various commercial products demonstrating differences in bioavailability and purity. This variability necessitates careful product selection and potentially dose adjustments when switching between formulations. Future research should address optimal delivery systems to enhance consistency in therapeutic outcomes across different patient populations.
Long-term safety data spanning periods greater than one year remains limited, highlighting a research gap that warrants attention. Current evidence suggests no significant organ toxicity or serious adverse events associated with TMG supplementation at therapeutic doses. Notably, TMG does not appear to negatively impact liver or kidney function markers in metabolic health studies, which is particularly relevant given its potential applications in metabolic disorders.
Dosage considerations for TMG vary based on the targeted metabolic parameters. For homocysteine reduction, effective doses typically range from 1.5-3g daily, with studies demonstrating significant effects within 6-12 weeks of consistent supplementation. For improvements in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, similar dosage ranges have shown efficacy, though optimal timing relative to meals remains under investigation.
The pharmacokinetic profile of TMG indicates good oral bioavailability with peak plasma concentrations occurring approximately 3 hours post-administration. The compound exhibits a half-life of approximately 14 hours, supporting once or twice daily dosing regimens. Absorption appears unaffected by food intake, offering flexibility in administration protocols.
Special populations require particular consideration regarding TMG supplementation. Pregnant and lactating women have been excluded from most clinical trials, creating uncertainty about safety in these groups. Similarly, pediatric applications remain largely unexplored outside specific metabolic disorders. Elderly populations may benefit from lower initial doses due to potential age-related changes in metabolism and elimination.
Drug interactions represent another important safety consideration. TMG may theoretically interact with medications affecting methyl group metabolism, including certain antidepressants and anticonvulsants. Additionally, concurrent use with other methyl donors such as S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) or folate supplements may have additive effects that require monitoring.
Standardization of TMG formulations presents challenges in clinical application, with various commercial products demonstrating differences in bioavailability and purity. This variability necessitates careful product selection and potentially dose adjustments when switching between formulations. Future research should address optimal delivery systems to enhance consistency in therapeutic outcomes across different patient populations.
Clinical Application Potential in Metabolic Disorders
Trimethylglycine (TMG) demonstrates significant potential for clinical applications in various metabolic disorders, positioning it as a promising therapeutic agent. Research indicates TMG's effectiveness in addressing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), where it has shown capacity to reduce hepatic fat accumulation and improve liver function markers in preliminary clinical trials. The compound's ability to regulate lipid metabolism makes it particularly valuable for this growing global health concern.
In the realm of cardiovascular health, TMG offers substantial benefits through its homocysteine-lowering properties. Elevated homocysteine levels represent an established risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and TMG's methyl donation capabilities effectively reduce these levels, potentially decreasing cardiovascular event risk. This mechanism provides a complementary approach to standard cardiovascular treatments.
For diabetes management, emerging evidence suggests TMG may enhance insulin sensitivity and improve glycemic control. Several studies have documented reductions in fasting blood glucose and HbA1c levels following TMG supplementation, indicating potential as an adjunctive therapy for type 2 diabetes. The compound's effects on glucose metabolism appear to work through multiple pathways, including enhanced mitochondrial function and reduced oxidative stress.
Obesity treatment represents another promising application area, with research demonstrating TMG's ability to modulate adipokine production and potentially reduce adipose tissue inflammation. Clinical observations suggest modest improvements in body composition metrics when TMG supplementation accompanies lifestyle interventions, though larger studies are needed to confirm these effects.
The metabolic syndrome spectrum, characterized by clustering of multiple metabolic abnormalities, may particularly benefit from TMG's multifaceted effects. By simultaneously addressing dyslipidemia, glucose intolerance, and inflammation, TMG offers a comprehensive approach to this complex condition. Initial data suggests improvements in several metabolic syndrome parameters with consistent TMG administration.
Importantly, TMG demonstrates favorable safety profiles in most populations, with minimal side effects reported even at therapeutic doses. This safety advantage, combined with its oral bioavailability and relatively low production costs, enhances its clinical implementation potential. Current dosing protocols typically range from 500-3000mg daily, with effects becoming apparent after 6-12 weeks of consistent use.
Integration pathways for TMG in clinical settings include both standalone supplementation and combination therapies with established medications. Several ongoing clinical trials are evaluating synergistic effects when TMG is administered alongside statins, metformin, and other metabolic agents, potentially allowing for dose reductions of primary medications while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
In the realm of cardiovascular health, TMG offers substantial benefits through its homocysteine-lowering properties. Elevated homocysteine levels represent an established risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and TMG's methyl donation capabilities effectively reduce these levels, potentially decreasing cardiovascular event risk. This mechanism provides a complementary approach to standard cardiovascular treatments.
For diabetes management, emerging evidence suggests TMG may enhance insulin sensitivity and improve glycemic control. Several studies have documented reductions in fasting blood glucose and HbA1c levels following TMG supplementation, indicating potential as an adjunctive therapy for type 2 diabetes. The compound's effects on glucose metabolism appear to work through multiple pathways, including enhanced mitochondrial function and reduced oxidative stress.
Obesity treatment represents another promising application area, with research demonstrating TMG's ability to modulate adipokine production and potentially reduce adipose tissue inflammation. Clinical observations suggest modest improvements in body composition metrics when TMG supplementation accompanies lifestyle interventions, though larger studies are needed to confirm these effects.
The metabolic syndrome spectrum, characterized by clustering of multiple metabolic abnormalities, may particularly benefit from TMG's multifaceted effects. By simultaneously addressing dyslipidemia, glucose intolerance, and inflammation, TMG offers a comprehensive approach to this complex condition. Initial data suggests improvements in several metabolic syndrome parameters with consistent TMG administration.
Importantly, TMG demonstrates favorable safety profiles in most populations, with minimal side effects reported even at therapeutic doses. This safety advantage, combined with its oral bioavailability and relatively low production costs, enhances its clinical implementation potential. Current dosing protocols typically range from 500-3000mg daily, with effects becoming apparent after 6-12 weeks of consistent use.
Integration pathways for TMG in clinical settings include both standalone supplementation and combination therapies with established medications. Several ongoing clinical trials are evaluating synergistic effects when TMG is administered alongside statins, metformin, and other metabolic agents, potentially allowing for dose reductions of primary medications while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!