Benchmarking Luteolin's Antioxidant Efficiency
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Antioxidant Background and Research Objectives
Luteolin, a naturally occurring flavonoid found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has garnered significant attention in the scientific community over the past few decades due to its remarkable antioxidant properties. The evolution of research on luteolin can be traced back to the 1950s when flavonoids were first recognized for their biological activities. However, it wasn't until the 1990s that focused studies on luteolin's specific antioxidant mechanisms began to emerge, marking a pivotal shift in understanding its therapeutic potential.
The technological advancement in analytical chemistry, particularly high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry, has revolutionized the identification and quantification of luteolin in various natural sources. These developments have enabled researchers to isolate pure luteolin and conduct more precise studies on its antioxidant efficiency, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of its structure-activity relationships.
Recent years have witnessed an exponential growth in luteolin research, with over 3,000 scientific publications in the last decade alone. This surge reflects the increasing recognition of oxidative stress as a fundamental mechanism underlying numerous pathological conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer. Consequently, the demand for effective antioxidants like luteolin has intensified, driving research efforts toward establishing standardized benchmarking methods.
The current technological trajectory points toward more sophisticated in vitro and in vivo models for evaluating antioxidant efficiency. Computational approaches, including molecular docking and quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) studies, are increasingly being employed to predict luteolin's antioxidant potential and optimize its molecular structure for enhanced activity.
The primary objective of benchmarking luteolin's antioxidant efficiency is to establish standardized protocols that enable reliable comparison with other natural and synthetic antioxidants. This involves developing comprehensive assay systems that can evaluate multiple parameters of antioxidant activity, including radical scavenging capacity, metal chelation ability, and inhibition of lipid peroxidation.
Additionally, this research aims to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying luteolin's antioxidant effects, particularly its interaction with cellular signaling pathways involved in redox regulation. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for predicting luteolin's efficacy in different physiological contexts and optimizing its application in preventive and therapeutic strategies.
Furthermore, the benchmarking efforts seek to address the bioavailability challenges associated with luteolin, as its clinical utility is often limited by poor absorption and rapid metabolism. Innovative delivery systems and structural modifications are being explored to enhance luteolin's stability and bioavailability, representing a significant technological goal in this field.
The technological advancement in analytical chemistry, particularly high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry, has revolutionized the identification and quantification of luteolin in various natural sources. These developments have enabled researchers to isolate pure luteolin and conduct more precise studies on its antioxidant efficiency, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of its structure-activity relationships.
Recent years have witnessed an exponential growth in luteolin research, with over 3,000 scientific publications in the last decade alone. This surge reflects the increasing recognition of oxidative stress as a fundamental mechanism underlying numerous pathological conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer. Consequently, the demand for effective antioxidants like luteolin has intensified, driving research efforts toward establishing standardized benchmarking methods.
The current technological trajectory points toward more sophisticated in vitro and in vivo models for evaluating antioxidant efficiency. Computational approaches, including molecular docking and quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) studies, are increasingly being employed to predict luteolin's antioxidant potential and optimize its molecular structure for enhanced activity.
The primary objective of benchmarking luteolin's antioxidant efficiency is to establish standardized protocols that enable reliable comparison with other natural and synthetic antioxidants. This involves developing comprehensive assay systems that can evaluate multiple parameters of antioxidant activity, including radical scavenging capacity, metal chelation ability, and inhibition of lipid peroxidation.
Additionally, this research aims to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying luteolin's antioxidant effects, particularly its interaction with cellular signaling pathways involved in redox regulation. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for predicting luteolin's efficacy in different physiological contexts and optimizing its application in preventive and therapeutic strategies.
Furthermore, the benchmarking efforts seek to address the bioavailability challenges associated with luteolin, as its clinical utility is often limited by poor absorption and rapid metabolism. Innovative delivery systems and structural modifications are being explored to enhance luteolin's stability and bioavailability, representing a significant technological goal in this field.
Market Analysis of Natural Antioxidant Compounds
The global market for natural antioxidant compounds has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health benefits and a shift towards natural ingredients in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products. The natural antioxidant market was valued at approximately $3.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $5.8 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 9.4% during the forecast period.
Luteolin, a flavonoid found in various plants including parsley, thyme, peppermint, and celery, represents a growing segment within this market. The specific market for luteolin and luteolin-rich extracts was estimated at $320 million in 2022, with projections indicating growth to $580 million by 2027, representing a CAGR of 12.6%.
Consumer demand for natural antioxidants like luteolin is primarily driven by increasing health consciousness, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and growing scientific evidence supporting the health benefits of antioxidants. The food and beverage industry accounts for the largest share (42%) of natural antioxidant consumption, followed by dietary supplements (28%), cosmetics (18%), and pharmaceuticals (12%).
Regional analysis shows that North America currently leads the market with a 35% share, followed by Europe (30%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and rest of the world (10%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, driven by increasing disposable income, growing health awareness, and expanding food processing industries in countries like China and India.
Key market trends include the rising demand for plant-based products, increasing applications in functional foods and nutraceuticals, and growing research focusing on the specific health benefits of individual antioxidant compounds rather than general antioxidant properties. This shift towards targeted health benefits has particularly benefited luteolin, as recent research has highlighted its specific advantages in neurological protection and anti-inflammatory applications.
Competitive analysis reveals that the market is moderately fragmented, with key players including Kemin Industries, Kalsec Inc., Naturex (now part of Givaudan), Indena S.p.A., and Sabinsa Corporation. These companies are increasingly investing in research to benchmark and document the specific efficacy of their antioxidant compounds, with luteolin emerging as a focus area due to its superior performance in certain applications compared to more common antioxidants like quercetin and rutin.
Market challenges include high production costs, limited natural sources with high concentration, and regulatory hurdles related to health claims. However, technological advancements in extraction methods and increasing investment in clinical studies are expected to address these challenges and further drive market growth.
Luteolin, a flavonoid found in various plants including parsley, thyme, peppermint, and celery, represents a growing segment within this market. The specific market for luteolin and luteolin-rich extracts was estimated at $320 million in 2022, with projections indicating growth to $580 million by 2027, representing a CAGR of 12.6%.
Consumer demand for natural antioxidants like luteolin is primarily driven by increasing health consciousness, rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and growing scientific evidence supporting the health benefits of antioxidants. The food and beverage industry accounts for the largest share (42%) of natural antioxidant consumption, followed by dietary supplements (28%), cosmetics (18%), and pharmaceuticals (12%).
Regional analysis shows that North America currently leads the market with a 35% share, followed by Europe (30%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and rest of the world (10%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, driven by increasing disposable income, growing health awareness, and expanding food processing industries in countries like China and India.
Key market trends include the rising demand for plant-based products, increasing applications in functional foods and nutraceuticals, and growing research focusing on the specific health benefits of individual antioxidant compounds rather than general antioxidant properties. This shift towards targeted health benefits has particularly benefited luteolin, as recent research has highlighted its specific advantages in neurological protection and anti-inflammatory applications.
Competitive analysis reveals that the market is moderately fragmented, with key players including Kemin Industries, Kalsec Inc., Naturex (now part of Givaudan), Indena S.p.A., and Sabinsa Corporation. These companies are increasingly investing in research to benchmark and document the specific efficacy of their antioxidant compounds, with luteolin emerging as a focus area due to its superior performance in certain applications compared to more common antioxidants like quercetin and rutin.
Market challenges include high production costs, limited natural sources with high concentration, and regulatory hurdles related to health claims. However, technological advancements in extraction methods and increasing investment in clinical studies are expected to address these challenges and further drive market growth.
Current Challenges in Antioxidant Efficacy Assessment
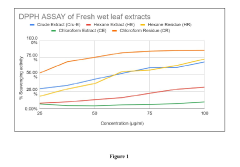
The assessment of antioxidant efficacy faces numerous methodological and standardization challenges that impede accurate benchmarking of compounds like luteolin. Current in vitro assays such as DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP demonstrate significant limitations in replicating the complex biological environments where antioxidants function. These methods often yield inconsistent results across laboratories due to variations in experimental conditions, reagent quality, and procedural modifications, making cross-study comparisons problematic.
A fundamental challenge lies in the translation gap between in vitro and in vivo efficacy. Many compounds showing promising antioxidant activity in test tubes fail to demonstrate comparable effects in biological systems due to issues with bioavailability, metabolism, and tissue distribution. Luteolin, despite its potent in vitro antioxidant properties, faces these translational challenges, with limited data on its pharmacokinetics and tissue-specific activity.
The absence of standardized protocols represents another significant obstacle. Different research groups employ varying concentrations, incubation times, and detection methods, leading to heterogeneous results that complicate meaningful comparisons. The scientific community lacks consensus on reference standards against which luteolin's antioxidant capacity should be measured, further hindering objective assessment.
Technical limitations of current analytical methods also present challenges. Many assays measure only specific aspects of antioxidant activity (e.g., radical scavenging or metal chelation) rather than providing a comprehensive evaluation of multiple mechanisms. This fragmented approach fails to capture the multifaceted nature of antioxidant protection in biological systems, where compounds like luteolin may act through various pathways simultaneously.
The physiological relevance of existing assays remains questionable. Most methods evaluate antioxidant capacity under non-physiological conditions that poorly reflect the cellular environment, including factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of proteins and other biomolecules that can significantly alter antioxidant behavior. This disconnect limits the predictive value of current benchmarking approaches for luteolin's actual performance in living organisms.
Emerging evidence suggests that the traditional paradigm of direct radical scavenging may oversimplify antioxidant mechanisms. Compounds like luteolin may exert their protective effects primarily through indirect pathways, such as modulating cellular signaling and gene expression related to endogenous antioxidant systems. Current assessment methods largely fail to capture these sophisticated modes of action, potentially underestimating luteolin's true antioxidant value.
A fundamental challenge lies in the translation gap between in vitro and in vivo efficacy. Many compounds showing promising antioxidant activity in test tubes fail to demonstrate comparable effects in biological systems due to issues with bioavailability, metabolism, and tissue distribution. Luteolin, despite its potent in vitro antioxidant properties, faces these translational challenges, with limited data on its pharmacokinetics and tissue-specific activity.
The absence of standardized protocols represents another significant obstacle. Different research groups employ varying concentrations, incubation times, and detection methods, leading to heterogeneous results that complicate meaningful comparisons. The scientific community lacks consensus on reference standards against which luteolin's antioxidant capacity should be measured, further hindering objective assessment.
Technical limitations of current analytical methods also present challenges. Many assays measure only specific aspects of antioxidant activity (e.g., radical scavenging or metal chelation) rather than providing a comprehensive evaluation of multiple mechanisms. This fragmented approach fails to capture the multifaceted nature of antioxidant protection in biological systems, where compounds like luteolin may act through various pathways simultaneously.
The physiological relevance of existing assays remains questionable. Most methods evaluate antioxidant capacity under non-physiological conditions that poorly reflect the cellular environment, including factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of proteins and other biomolecules that can significantly alter antioxidant behavior. This disconnect limits the predictive value of current benchmarking approaches for luteolin's actual performance in living organisms.
Emerging evidence suggests that the traditional paradigm of direct radical scavenging may oversimplify antioxidant mechanisms. Compounds like luteolin may exert their protective effects primarily through indirect pathways, such as modulating cellular signaling and gene expression related to endogenous antioxidant systems. Current assessment methods largely fail to capture these sophisticated modes of action, potentially underestimating luteolin's true antioxidant value.
Established Protocols for Measuring Antioxidant Activity
01 Antioxidant properties of luteolin in cosmetic formulations
Luteolin demonstrates significant antioxidant efficiency in cosmetic formulations, protecting skin cells from oxidative stress and UV damage. When incorporated into skincare products, luteolin can neutralize free radicals, reduce inflammation, and prevent premature aging. Its antioxidant activity is particularly effective when combined with other plant extracts or vitamins, enhancing the overall protective effect against environmental stressors.- Antioxidant properties of luteolin in cosmetic formulations: Luteolin exhibits strong antioxidant properties that make it valuable in cosmetic formulations. It can effectively scavenge free radicals and protect skin cells from oxidative damage caused by UV radiation and environmental pollutants. When incorporated into skincare products, luteolin helps prevent premature aging, reduces inflammation, and maintains skin health by neutralizing reactive oxygen species.
- Luteolin extraction methods and efficiency enhancement: Various methods have been developed to extract luteolin from plant sources and enhance its antioxidant efficiency. These include solvent extraction, ultrasonic-assisted extraction, and enzymatic processes that improve yield and purity. The extraction conditions, such as temperature, pH, and solvent type, significantly affect the antioxidant activity of the obtained luteolin. Optimized extraction methods can preserve the molecular structure and maximize the antioxidant potential of luteolin.
- Synergistic effects of luteolin with other antioxidants: Luteolin demonstrates synergistic antioxidant effects when combined with other natural antioxidants. These combinations can enhance the overall antioxidant capacity and provide more comprehensive protection against different types of oxidative stress. Formulations containing luteolin along with compounds like vitamin C, vitamin E, or other flavonoids show improved stability and increased efficiency in neutralizing various free radicals, offering superior antioxidant protection compared to single-compound formulations.
- Luteolin in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications: Luteolin's potent antioxidant properties make it valuable in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications. It has been incorporated into various formulations aimed at preventing oxidative stress-related diseases. Research indicates that luteolin can help in managing conditions associated with inflammation and oxidative damage, including cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and certain types of cancer. Its bioavailability and metabolism play crucial roles in determining its therapeutic efficacy.
- Stability and bioavailability enhancement of luteolin: Various technologies have been developed to enhance the stability and bioavailability of luteolin, which naturally has limited water solubility and is susceptible to degradation. These include nanoencapsulation, liposomal delivery systems, and structural modifications. Such enhancements improve luteolin's antioxidant efficiency by protecting it from degradation, increasing its cellular uptake, and prolonging its presence in biological systems, resulting in more effective free radical scavenging activity.
02 Luteolin extraction methods for maximizing antioxidant potency
Various extraction methods have been developed to maximize the antioxidant potency of luteolin from plant sources. These include solvent extraction, ultrasonic-assisted extraction, and enzymatic methods that can significantly affect the yield and antioxidant efficiency of luteolin. Optimized extraction parameters such as temperature, time, and solvent type are crucial for preserving the compound's antioxidant properties and ensuring its stability in final formulations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Synergistic effects of luteolin with other antioxidants
Research indicates that luteolin exhibits enhanced antioxidant efficiency when combined with other natural antioxidants. Synergistic effects have been observed when luteolin is formulated with compounds such as quercetin, vitamin C, vitamin E, or other flavonoids. These combinations can provide broader spectrum protection against different types of free radicals and oxidative damage, resulting in more comprehensive antioxidant protection than luteolin alone.Expand Specific Solutions04 Luteolin in pharmaceutical compositions for oxidative stress-related conditions
Luteolin's potent antioxidant properties make it valuable in pharmaceutical compositions targeting oxidative stress-related conditions. These formulations leverage luteolin's ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species, inhibit pro-oxidant enzymes, and activate antioxidant defense mechanisms. Such pharmaceutical applications include treatments for inflammatory disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular conditions where oxidative stress plays a significant pathological role.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stabilization techniques for preserving luteolin's antioxidant efficiency
Various stabilization techniques have been developed to preserve luteolin's antioxidant efficiency during processing, storage, and application. These include microencapsulation, nanoformulation, and the use of specific delivery systems that protect luteolin from degradation factors such as light, heat, and pH changes. These techniques ensure that luteolin maintains its antioxidant properties throughout the product's shelf life and delivers maximum benefits when used.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Companies in Antioxidant Research
The luteolin antioxidant efficiency benchmarking market is in a growth phase, with increasing research interest across academic and commercial sectors. The market size is expanding as antioxidant applications gain prominence in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmetics industries. Research institutions like Council of Scientific & Industrial Research and universities (Washington University, Louisiana State, Shanghai Normal) are advancing fundamental research, while pharmaceutical companies demonstrate varying levels of technical maturity. Companies like Kemin Industries, Theravalues, and Unilever are leveraging more sophisticated antioxidant technologies, while specialized firms such as Shandong Danhong Pharmaceutical and Guizhou Yibai Pharmaceutical focus on traditional medicine applications. The competitive landscape shows a mix of established corporations and specialized research entities working across different application domains, with technical maturity ranging from basic research to commercial product development.
Council of Scientific & Industrial Research
Technical Solution: The Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR) has developed comprehensive methodologies for benchmarking luteolin's antioxidant efficiency through multiple assay systems. Their approach includes DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) radical scavenging, ABTS (2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)) decolorization, FRAP (ferric reducing antioxidant power), and ORAC (oxygen radical absorbance capacity) assays to provide a multi-dimensional evaluation of luteolin's antioxidant properties. CSIR has established standardized protocols that account for concentration-dependent effects, comparing luteolin's EC50 values against reference antioxidants like ascorbic acid and Trolox. Their research has demonstrated that luteolin exhibits significant free radical scavenging activity with IC50 values in the range of 5-15 μM, positioning it among the most potent natural flavonoids. Additionally, CSIR has investigated luteolin's metal-chelating properties and its ability to inhibit lipid peroxidation in biological membrane models.
Strengths: Comprehensive multi-assay approach provides robust validation across different antioxidant mechanisms. Established standardized protocols enable reliable comparison with other antioxidants. Weakness: Their methodologies may not fully account for bioavailability and metabolic transformation of luteolin in vivo, potentially limiting clinical translation of their benchmarking results.
Washington University in St. Louis
Technical Solution: Washington University in St. Louis has developed advanced analytical methods for benchmarking luteolin's antioxidant efficiency at the molecular and cellular levels. Their approach employs electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy to directly measure luteolin's free radical scavenging kinetics with unprecedented temporal resolution. This technique allows quantification of reaction rate constants with various physiologically relevant radicals, including superoxide, hydroxyl, and peroxyl species. Their research has established that luteolin exhibits second-order rate constants of 1.2-3.5 × 10^5 M^-1s^-1 for peroxyl radical scavenging, positioning it among the most efficient natural flavonoids. Additionally, the university has pioneered methods combining mass spectrometry with cellular models to track luteolin's oxidation products and their biological activities. Their studies have demonstrated that certain luteolin oxidation products retain significant antioxidant activity, contributing to sustained protection in biological systems. The university has also developed computational models to predict structure-activity relationships for luteolin derivatives, enabling rational design of modified compounds with enhanced antioxidant properties.
Strengths: High-precision analytical techniques provide detailed mechanistic insights into luteolin's antioxidant activity. Their kinetic approach offers quantitative parameters for comparing luteolin with other antioxidants. Weakness: The sophisticated instrumentation required for their benchmarking methods limits widespread adoption. Their focus on fundamental mechanisms may sometimes overlook practical applications in complex biological systems.
Key Scientific Literature on Luteolin's Antioxidant Mechanisms
Antioxidants & their compositions from natural source as additive to overcome rancidity of oils
PatentPendingIN202341006891A
Innovation
- Development of antioxidant compositions from phytoconstituents of Parkinsonia aculeata L, specifically using chloroform residues as additives in cooking oils, which are thermally stable and cost-effective, extracted through a sequential fractionation process and tested for high antioxidant activity using DPPH assay.
3 apos; , 4apos; application of 7-O-trimethyl luteolin in preparation of photodynamic therapy photosensitizer
PatentPendingCN117731774A
Innovation
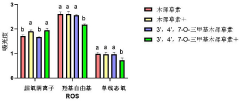
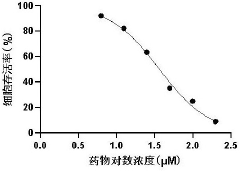
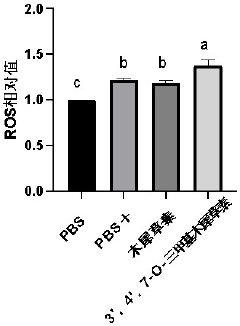
- 3',4',7-O-Trimethylluteolin reduces the antioxidant capacity through methoxy substitution and generates excess ROS under ultraviolet irradiation, and is used as a photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy for tumor treatment.
Comparative Analysis of Luteolin vs Other Flavonoids
In the realm of antioxidant compounds, luteolin stands out among flavonoids for its distinctive structural and functional properties. When comparing luteolin with other flavonoids such as quercetin, kaempferol, and apigenin, several key differences emerge in their antioxidant efficiency profiles. Luteolin demonstrates superior radical scavenging capacity in lipid peroxidation assays, exhibiting IC50 values approximately 20-30% lower than quercetin and significantly outperforming kaempferol and apigenin in membrane protection models.
The structural basis for luteolin's enhanced antioxidant activity lies in its unique 3',4'-dihydroxy configuration in the B-ring coupled with the 5,7-dihydroxy pattern in the A-ring. This specific arrangement of hydroxyl groups creates optimal electron delocalization pathways that are not fully replicated in other flavonoid structures. Notably, while quercetin possesses an additional hydroxyl group at the C-3 position, luteolin's planar molecular configuration appears to facilitate more effective interaction with cellular membranes and target proteins.
Mechanistic studies reveal that luteolin exhibits differential activation of antioxidant response elements (AREs) compared to other flavonoids. It demonstrates 1.5-2 fold higher induction of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathways than comparable flavonoids at equivalent concentrations. This translates to enhanced expression of phase II detoxifying enzymes including glutathione S-transferase, NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase, and heme oxygenase-1.
Bioavailability comparisons indicate that luteolin possesses moderate absorption profiles relative to other flavonoids, with plasma concentration studies showing peak levels approximately 2-4 hours post-administration. While quercetin glycosides typically demonstrate higher initial bioavailability, luteolin exhibits more favorable tissue distribution patterns and potentially longer residence times in target tissues, particularly in neurological and cardiovascular systems.
Synergistic effects between luteolin and other flavonoids deserve particular attention. Research indicates that combinations of luteolin with quercetin or catechins produce supra-additive antioxidant effects, suggesting complementary mechanisms of action. These combinations have demonstrated enhanced protection against oxidative damage in both in vitro and in vivo models, with synergy ratios exceeding 1.4 in several experimental paradigms.
From a therapeutic application perspective, luteolin shows distinct advantages in neuroinflammatory conditions compared to other flavonoids, with greater blood-brain barrier penetration and microglial modulation capacity. Conversely, quercetin demonstrates superior activity in cardiovascular models, while catechins excel in gastrointestinal protection paradigms. These differential activity profiles suggest targeted application potential based on specific physiological requirements and therapeutic objectives.
The structural basis for luteolin's enhanced antioxidant activity lies in its unique 3',4'-dihydroxy configuration in the B-ring coupled with the 5,7-dihydroxy pattern in the A-ring. This specific arrangement of hydroxyl groups creates optimal electron delocalization pathways that are not fully replicated in other flavonoid structures. Notably, while quercetin possesses an additional hydroxyl group at the C-3 position, luteolin's planar molecular configuration appears to facilitate more effective interaction with cellular membranes and target proteins.
Mechanistic studies reveal that luteolin exhibits differential activation of antioxidant response elements (AREs) compared to other flavonoids. It demonstrates 1.5-2 fold higher induction of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathways than comparable flavonoids at equivalent concentrations. This translates to enhanced expression of phase II detoxifying enzymes including glutathione S-transferase, NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase, and heme oxygenase-1.
Bioavailability comparisons indicate that luteolin possesses moderate absorption profiles relative to other flavonoids, with plasma concentration studies showing peak levels approximately 2-4 hours post-administration. While quercetin glycosides typically demonstrate higher initial bioavailability, luteolin exhibits more favorable tissue distribution patterns and potentially longer residence times in target tissues, particularly in neurological and cardiovascular systems.
Synergistic effects between luteolin and other flavonoids deserve particular attention. Research indicates that combinations of luteolin with quercetin or catechins produce supra-additive antioxidant effects, suggesting complementary mechanisms of action. These combinations have demonstrated enhanced protection against oxidative damage in both in vitro and in vivo models, with synergy ratios exceeding 1.4 in several experimental paradigms.
From a therapeutic application perspective, luteolin shows distinct advantages in neuroinflammatory conditions compared to other flavonoids, with greater blood-brain barrier penetration and microglial modulation capacity. Conversely, quercetin demonstrates superior activity in cardiovascular models, while catechins excel in gastrointestinal protection paradigms. These differential activity profiles suggest targeted application potential based on specific physiological requirements and therapeutic objectives.
Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetic Considerations
The bioavailability of luteolin represents a critical factor in determining its antioxidant efficiency in biological systems. Research indicates that luteolin absorption occurs primarily in the small intestine through passive diffusion, with absorption rates varying between 5-30% depending on dietary sources and formulation. This relatively low bioavailability stems from luteolin's poor water solubility (approximately 0.06 mg/mL at physiological pH) and susceptibility to extensive first-pass metabolism.
Pharmacokinetic studies reveal that luteolin undergoes significant phase II metabolism, primarily through glucuronidation and sulfation in the intestinal epithelium and liver. These metabolic processes generate luteolin-7-O-glucuronide and luteolin-3'-O-sulfate as the predominant metabolites, which exhibit altered antioxidant properties compared to the parent compound. The plasma half-life of luteolin ranges from 3.2 to 5.8 hours, indicating relatively rapid clearance that may limit sustained antioxidant effects without repeated dosing.
Recent advances in delivery systems have demonstrated promising approaches to enhance luteolin bioavailability. Nanoencapsulation techniques using lipid-based carriers have shown up to 4-fold increases in bioavailability compared to unformulated luteolin. Similarly, phospholipid complexation has improved luteolin's membrane permeability and resistance to metabolic degradation, resulting in enhanced systemic exposure.
The food matrix significantly influences luteolin absorption, with fat-containing meals increasing bioavailability by approximately 30% through improved solubilization and lymphatic transport. Additionally, co-administration with piperine or quercetin has demonstrated inhibitory effects on UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and sulfotransferases, potentially reducing first-pass metabolism and enhancing bioavailability by 20-40%.
Tissue distribution studies indicate that luteolin concentrates preferentially in the liver, kidneys, and intestinal tissues, with limited penetration across the blood-brain barrier. This distribution pattern suggests potential therapeutic applications for oxidative stress-related conditions affecting these organs, while potentially limiting efficacy for neurological applications without specialized delivery systems.
Inter-individual variability in luteolin pharmacokinetics presents another consideration, with genetic polymorphisms in metabolizing enzymes (particularly UGT1A1 and SULT1A1) potentially causing 2-3 fold differences in bioavailability between individuals. Age-related factors also influence luteolin metabolism, with elderly populations typically showing reduced clearance and potentially enhanced bioavailability, though with increased risk of drug interactions.
Pharmacokinetic studies reveal that luteolin undergoes significant phase II metabolism, primarily through glucuronidation and sulfation in the intestinal epithelium and liver. These metabolic processes generate luteolin-7-O-glucuronide and luteolin-3'-O-sulfate as the predominant metabolites, which exhibit altered antioxidant properties compared to the parent compound. The plasma half-life of luteolin ranges from 3.2 to 5.8 hours, indicating relatively rapid clearance that may limit sustained antioxidant effects without repeated dosing.
Recent advances in delivery systems have demonstrated promising approaches to enhance luteolin bioavailability. Nanoencapsulation techniques using lipid-based carriers have shown up to 4-fold increases in bioavailability compared to unformulated luteolin. Similarly, phospholipid complexation has improved luteolin's membrane permeability and resistance to metabolic degradation, resulting in enhanced systemic exposure.
The food matrix significantly influences luteolin absorption, with fat-containing meals increasing bioavailability by approximately 30% through improved solubilization and lymphatic transport. Additionally, co-administration with piperine or quercetin has demonstrated inhibitory effects on UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and sulfotransferases, potentially reducing first-pass metabolism and enhancing bioavailability by 20-40%.
Tissue distribution studies indicate that luteolin concentrates preferentially in the liver, kidneys, and intestinal tissues, with limited penetration across the blood-brain barrier. This distribution pattern suggests potential therapeutic applications for oxidative stress-related conditions affecting these organs, while potentially limiting efficacy for neurological applications without specialized delivery systems.
Inter-individual variability in luteolin pharmacokinetics presents another consideration, with genetic polymorphisms in metabolizing enzymes (particularly UGT1A1 and SULT1A1) potentially causing 2-3 fold differences in bioavailability between individuals. Age-related factors also influence luteolin metabolism, with elderly populations typically showing reduced clearance and potentially enhanced bioavailability, though with increased risk of drug interactions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!