Deep Learning Models for Predictive Maintenance of Solenoid Valves
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DL for Solenoid Valve PM: Background and Objectives
Predictive maintenance of solenoid valves using deep learning models represents a significant advancement in industrial automation and process control. This technology has evolved from traditional time-based or reactive maintenance approaches to a more sophisticated, data-driven methodology. The development of deep learning models for this purpose stems from the increasing availability of sensor data and the need for more accurate and efficient maintenance strategies in various industries.
The historical context of this technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when condition-based maintenance began gaining traction. However, it was not until the mid-2010s that deep learning techniques started to be applied to predictive maintenance tasks. This shift was driven by the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and the exponential growth in computational power, enabling the processing of large volumes of sensor data in real-time.
Solenoid valves, being critical components in many industrial systems, have become a focal point for predictive maintenance efforts. These electromechanical devices are prone to various failure modes, including coil burnout, mechanical wear, and contamination. Traditional maintenance approaches often led to unnecessary downtime or unexpected failures, highlighting the need for more precise prediction methods.
The primary objective of applying deep learning models to solenoid valve predictive maintenance is to accurately forecast potential failures before they occur. This involves developing algorithms capable of analyzing complex patterns in sensor data to detect subtle changes that may indicate impending issues. By achieving this, industries aim to optimize maintenance schedules, reduce unplanned downtime, and extend the operational life of solenoid valves.
Another crucial goal is to enhance the overall reliability and efficiency of systems that rely on solenoid valves. Deep learning models offer the potential to not only predict failures but also to provide insights into the root causes of these failures. This knowledge can be invaluable for improving valve design and operational practices.
Furthermore, the technology aims to integrate seamlessly with existing industrial control systems and IoT platforms. This integration is essential for real-time monitoring and decision-making, allowing for immediate response to potential issues and more effective resource allocation in maintenance activities.
As the field progresses, researchers and industry professionals are working towards developing more robust and adaptable deep learning models. These models should be capable of handling diverse operating conditions and valve types, as well as accommodating the dynamic nature of industrial environments. The ultimate vision is to create a self-learning system that continuously improves its predictive accuracy over time, adapting to new failure modes and changing operational parameters.
The historical context of this technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when condition-based maintenance began gaining traction. However, it was not until the mid-2010s that deep learning techniques started to be applied to predictive maintenance tasks. This shift was driven by the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and the exponential growth in computational power, enabling the processing of large volumes of sensor data in real-time.
Solenoid valves, being critical components in many industrial systems, have become a focal point for predictive maintenance efforts. These electromechanical devices are prone to various failure modes, including coil burnout, mechanical wear, and contamination. Traditional maintenance approaches often led to unnecessary downtime or unexpected failures, highlighting the need for more precise prediction methods.
The primary objective of applying deep learning models to solenoid valve predictive maintenance is to accurately forecast potential failures before they occur. This involves developing algorithms capable of analyzing complex patterns in sensor data to detect subtle changes that may indicate impending issues. By achieving this, industries aim to optimize maintenance schedules, reduce unplanned downtime, and extend the operational life of solenoid valves.
Another crucial goal is to enhance the overall reliability and efficiency of systems that rely on solenoid valves. Deep learning models offer the potential to not only predict failures but also to provide insights into the root causes of these failures. This knowledge can be invaluable for improving valve design and operational practices.
Furthermore, the technology aims to integrate seamlessly with existing industrial control systems and IoT platforms. This integration is essential for real-time monitoring and decision-making, allowing for immediate response to potential issues and more effective resource allocation in maintenance activities.
As the field progresses, researchers and industry professionals are working towards developing more robust and adaptable deep learning models. These models should be capable of handling diverse operating conditions and valve types, as well as accommodating the dynamic nature of industrial environments. The ultimate vision is to create a self-learning system that continuously improves its predictive accuracy over time, adapting to new failure modes and changing operational parameters.
Market Demand Analysis for Predictive Maintenance
The market demand for predictive maintenance solutions in the solenoid valve industry has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. This surge is primarily driven by the increasing need for operational efficiency, cost reduction, and minimization of unplanned downtime in various industrial sectors.
Solenoid valves are critical components in many industrial processes, including manufacturing, oil and gas, chemical processing, and automotive industries. The failure of these valves can lead to substantial production losses, safety hazards, and increased maintenance costs. As a result, there is a growing demand for advanced predictive maintenance solutions that can accurately forecast potential valve failures before they occur.
The global predictive maintenance market is expected to expand rapidly, with some estimates projecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 25% in the coming years. This growth is particularly pronounced in the industrial equipment segment, where solenoid valves play a crucial role. The adoption of Industry 4.0 principles and the increasing integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies in industrial processes are further fueling this demand.
Deep learning models for predictive maintenance of solenoid valves offer several advantages over traditional maintenance approaches. These models can analyze complex patterns in sensor data, historical maintenance records, and operational parameters to predict potential failures with high accuracy. This capability allows companies to move from reactive or scheduled maintenance to a more proactive and cost-effective predictive maintenance strategy.
The market demand is also driven by the potential for significant cost savings. Predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by up to 30% and eliminate up to 70% of breakdowns, according to some industry reports. For industries where downtime can cost thousands of dollars per hour, the value proposition of deep learning-based predictive maintenance is compelling.
Furthermore, there is an increasing regulatory pressure in many industries to improve safety and reliability. Predictive maintenance of critical components like solenoid valves helps companies comply with these regulations while also enhancing their operational efficiency.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth in demand for predictive maintenance solutions, driven by rapid industrialization and the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies in countries like China and India. North America and Europe, with their established industrial bases, continue to be significant markets for these technologies.
In conclusion, the market demand for deep learning models in predictive maintenance of solenoid valves is robust and growing. This demand is driven by the need for operational efficiency, cost reduction, regulatory compliance, and the broader trend of digital transformation in industrial sectors. As the technology continues to mature and demonstrate its value, we can expect to see accelerated adoption across various industries in the coming years.
Solenoid valves are critical components in many industrial processes, including manufacturing, oil and gas, chemical processing, and automotive industries. The failure of these valves can lead to substantial production losses, safety hazards, and increased maintenance costs. As a result, there is a growing demand for advanced predictive maintenance solutions that can accurately forecast potential valve failures before they occur.
The global predictive maintenance market is expected to expand rapidly, with some estimates projecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 25% in the coming years. This growth is particularly pronounced in the industrial equipment segment, where solenoid valves play a crucial role. The adoption of Industry 4.0 principles and the increasing integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies in industrial processes are further fueling this demand.
Deep learning models for predictive maintenance of solenoid valves offer several advantages over traditional maintenance approaches. These models can analyze complex patterns in sensor data, historical maintenance records, and operational parameters to predict potential failures with high accuracy. This capability allows companies to move from reactive or scheduled maintenance to a more proactive and cost-effective predictive maintenance strategy.
The market demand is also driven by the potential for significant cost savings. Predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by up to 30% and eliminate up to 70% of breakdowns, according to some industry reports. For industries where downtime can cost thousands of dollars per hour, the value proposition of deep learning-based predictive maintenance is compelling.
Furthermore, there is an increasing regulatory pressure in many industries to improve safety and reliability. Predictive maintenance of critical components like solenoid valves helps companies comply with these regulations while also enhancing their operational efficiency.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth in demand for predictive maintenance solutions, driven by rapid industrialization and the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies in countries like China and India. North America and Europe, with their established industrial bases, continue to be significant markets for these technologies.
In conclusion, the market demand for deep learning models in predictive maintenance of solenoid valves is robust and growing. This demand is driven by the need for operational efficiency, cost reduction, regulatory compliance, and the broader trend of digital transformation in industrial sectors. As the technology continues to mature and demonstrate its value, we can expect to see accelerated adoption across various industries in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Solenoid Valve Maintenance
The maintenance of solenoid valves presents several significant challenges in the current industrial landscape. One of the primary issues is the difficulty in accurately predicting valve failures before they occur. Traditional maintenance approaches often rely on fixed schedules or reactive measures, which can lead to unnecessary downtime or catastrophic failures.
The complexity of solenoid valve systems, with their intricate mechanical and electrical components, makes it challenging to identify early signs of degradation. Factors such as wear, corrosion, and environmental conditions can affect valve performance in subtle ways that are not easily detectable through conventional monitoring methods.
Another major challenge is the lack of real-time data on valve health and performance. Many industrial settings still rely on periodic inspections, which may miss intermittent issues or gradual deterioration. This gap in continuous monitoring capabilities limits the ability to implement proactive maintenance strategies effectively.
The variability in operating conditions across different industries and applications further complicates maintenance efforts. Solenoid valves used in harsh environments, such as chemical processing plants or offshore oil rigs, face different stressors compared to those in more controlled settings. This diversity makes it difficult to develop universally applicable maintenance protocols.
Data interpretation and analysis pose additional challenges. Even when sensor data is available, extracting meaningful insights and translating them into actionable maintenance decisions requires sophisticated analytical tools and expertise. Many organizations struggle with the sheer volume of data generated by modern industrial systems.
The integration of predictive maintenance technologies with existing infrastructure is another hurdle. Legacy systems may not be compatible with advanced sensors or data analytics platforms, necessitating significant upgrades or retrofitting. This can be both costly and disruptive to ongoing operations.
Skill shortages in predictive maintenance and data analytics further exacerbate these challenges. As maintenance strategies become more technology-driven, there is a growing need for personnel with expertise in both mechanical systems and data science – a combination that is often in short supply.
Lastly, the cost-benefit analysis of implementing advanced maintenance techniques can be complex. While predictive maintenance promises long-term savings and improved reliability, the initial investment in technology and training can be substantial. Organizations must carefully weigh these factors against the potential benefits, especially in industries with tight profit margins.
The complexity of solenoid valve systems, with their intricate mechanical and electrical components, makes it challenging to identify early signs of degradation. Factors such as wear, corrosion, and environmental conditions can affect valve performance in subtle ways that are not easily detectable through conventional monitoring methods.
Another major challenge is the lack of real-time data on valve health and performance. Many industrial settings still rely on periodic inspections, which may miss intermittent issues or gradual deterioration. This gap in continuous monitoring capabilities limits the ability to implement proactive maintenance strategies effectively.
The variability in operating conditions across different industries and applications further complicates maintenance efforts. Solenoid valves used in harsh environments, such as chemical processing plants or offshore oil rigs, face different stressors compared to those in more controlled settings. This diversity makes it difficult to develop universally applicable maintenance protocols.
Data interpretation and analysis pose additional challenges. Even when sensor data is available, extracting meaningful insights and translating them into actionable maintenance decisions requires sophisticated analytical tools and expertise. Many organizations struggle with the sheer volume of data generated by modern industrial systems.
The integration of predictive maintenance technologies with existing infrastructure is another hurdle. Legacy systems may not be compatible with advanced sensors or data analytics platforms, necessitating significant upgrades or retrofitting. This can be both costly and disruptive to ongoing operations.
Skill shortages in predictive maintenance and data analytics further exacerbate these challenges. As maintenance strategies become more technology-driven, there is a growing need for personnel with expertise in both mechanical systems and data science – a combination that is often in short supply.
Lastly, the cost-benefit analysis of implementing advanced maintenance techniques can be complex. While predictive maintenance promises long-term savings and improved reliability, the initial investment in technology and training can be substantial. Organizations must carefully weigh these factors against the potential benefits, especially in industries with tight profit margins.
Existing DL Solutions for Valve Maintenance
01 Deep learning models for equipment health monitoring
Deep learning models are employed to analyze sensor data from industrial equipment to predict potential failures and assess overall health. These models can process large volumes of data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate impending maintenance needs, enabling proactive maintenance strategies.- Deep learning models for equipment health monitoring: Deep learning models are utilized to monitor the health status of equipment in real-time. These models analyze sensor data to detect anomalies, predict potential failures, and assess the overall condition of machinery. This approach enables proactive maintenance scheduling and reduces unexpected downtime.
- Predictive maintenance using machine learning algorithms: Machine learning algorithms are employed to predict maintenance needs based on historical data and current operating conditions. These algorithms can identify patterns and trends that indicate impending equipment failures, allowing for timely interventions and optimized maintenance schedules.
- Integration of IoT sensors with deep learning for predictive maintenance: Internet of Things (IoT) sensors are integrated with deep learning models to collect and analyze real-time data from equipment. This combination enables more accurate predictions of maintenance requirements and enhances the overall efficiency of predictive maintenance systems.
- Fault diagnosis and classification using neural networks: Neural networks are utilized to diagnose and classify equipment faults based on sensor data and operational parameters. These models can identify specific types of failures and their root causes, enabling targeted maintenance interventions and reducing diagnostic time.
- Optimization of maintenance schedules using deep reinforcement learning: Deep reinforcement learning techniques are applied to optimize maintenance schedules based on equipment condition, operational constraints, and cost considerations. This approach helps in balancing maintenance costs with equipment reliability and performance, leading to more efficient resource allocation.
02 Predictive maintenance using neural networks
Neural networks are utilized to forecast equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules. These models learn from historical data to predict when maintenance is required, reducing downtime and improving overall equipment efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of IoT and deep learning for real-time monitoring
The combination of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and deep learning models enables real-time monitoring of equipment performance. This integration allows for continuous data collection and analysis, providing immediate insights into machine health and facilitating timely maintenance interventions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Transfer learning techniques for predictive maintenance
Transfer learning approaches are applied to adapt pre-trained deep learning models to specific maintenance tasks. This technique allows for efficient model development even with limited domain-specific data, improving the accuracy and generalization of predictive maintenance systems across different types of equipment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Explainable AI for interpretable maintenance predictions
Explainable AI techniques are incorporated into deep learning models for predictive maintenance to provide interpretable results. This approach helps maintenance teams understand the reasoning behind predictions, enabling more informed decision-making and increasing trust in the AI-driven maintenance recommendations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Industrial IoT and Predictive Analytics
The competitive landscape for deep learning models in predictive maintenance of solenoid valves is in an early growth stage, with increasing market size and evolving technological maturity. The market is driven by the growing demand for predictive maintenance solutions in various industries, including manufacturing, oil and gas, and automotive. Companies like Hitachi, Robert Bosch, and ExxonMobil are leveraging their expertise in industrial automation and data analytics to develop advanced deep learning models. Academic institutions such as Beihang University and Nanyang Technological University are contributing to research and development in this field. As the technology matures, we can expect increased competition and innovation from both established players and emerging startups.
Hitachi Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hitachi has developed an advanced deep learning model for predictive maintenance of solenoid valves. Their approach utilizes a combination of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks to analyze time-series data from valve sensors[1]. The model is trained on historical operational data, including pressure, temperature, and flow rate measurements, to detect anomalies and predict potential failures. Hitachi's system incorporates real-time data processing and edge computing capabilities, allowing for on-site analysis and rapid response to emerging issues[3]. The company has also implemented transfer learning techniques to improve model performance across different valve types and operating conditions[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive data analysis, real-time processing, and adaptability to various valve types. Weaknesses: May require significant historical data for accurate predictions and could be computationally intensive for complex systems.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has implemented a deep learning-based predictive maintenance solution for solenoid valves in industrial settings. Their approach uses a hybrid model combining recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and autoencoders to capture both temporal dependencies and feature extraction from sensor data[2]. The system integrates with Bosch's IoT platform, allowing for seamless data collection and analysis across multiple valve installations. Bosch's model incorporates unsupervised learning techniques for anomaly detection, enabling it to identify novel failure modes without prior labeling[4]. Additionally, they have developed a federated learning framework to enhance model performance while maintaining data privacy across different industrial sites[6].
Strengths: Integration with IoT ecosystem, privacy-preserving learning, and ability to detect novel failure modes. Weaknesses: May require significant computational resources and could face challenges in highly diverse industrial environments.
Core Innovations in DL for Predictive Maintenance
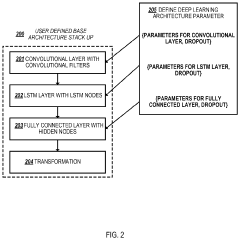
Deep learning architecture for maintenance predictions with multiple modes
PatentActiveUS11099551B2
Innovation
- A single deep learning architecture that supports multiple modes, including failure prediction, RUL estimation, and a unified mode, allowing for consistent predictions by learning parameters through historical data and applying transformation functions to generate maintenance recommendations.
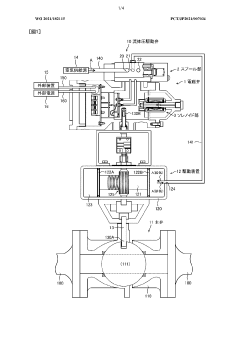
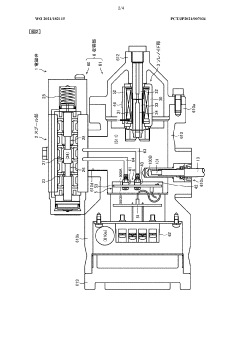
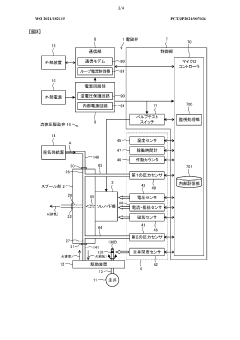
Electromagnetic valve
PatentWO2021182115A1
Innovation
- Integration of sensors within the solenoid valve housing to monitor the status of each part, including a spool section, solenoid section, and control unit, simplifying the device configuration and enabling predictive maintenance.
Industrial Standards and Compliance
In the context of deep learning models for predictive maintenance of solenoid valves, adherence to industrial standards and compliance requirements is crucial. The implementation of such advanced technologies must align with established industry norms to ensure safety, reliability, and interoperability across various industrial sectors.
One of the primary standards relevant to this field is ISO 13849, which focuses on safety-related parts of control systems. This standard is particularly important for solenoid valves used in safety-critical applications. Deep learning models deployed for predictive maintenance must be developed and implemented in a way that does not compromise the safety integrity levels (SIL) defined by this standard.
The IEC 61508 series of standards, which deals with functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-related systems, is another key consideration. These standards provide guidelines for the entire lifecycle of safety-related systems, including the integration of software-based components like deep learning models.
For industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation, compliance with ATEX directives is essential. These directives govern equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres. Any predictive maintenance system for solenoid valves in these environments must be certified to meet ATEX requirements.
The NFPA 70E standard, which addresses electrical safety in the workplace, is also relevant when implementing deep learning models for predictive maintenance. This standard ensures that the integration of such technologies does not introduce new electrical hazards or compromise existing safety measures.
Data privacy and security standards, such as ISO/IEC 27001 and GDPR, must be considered when collecting and processing data for predictive maintenance models. These standards ensure that sensitive industrial data is protected and handled in compliance with international regulations.
Industry-specific standards also play a crucial role. For instance, in the automotive sector, compliance with ISO 26262 for functional safety of road vehicles is essential. In aerospace, adherence to DO-178C for software considerations in airborne systems is mandatory.
Lastly, emerging standards related to artificial intelligence and machine learning, such as IEEE P2801 and ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 42, are becoming increasingly important. These standards aim to establish guidelines for the development and deployment of AI systems, including those used in industrial predictive maintenance.
One of the primary standards relevant to this field is ISO 13849, which focuses on safety-related parts of control systems. This standard is particularly important for solenoid valves used in safety-critical applications. Deep learning models deployed for predictive maintenance must be developed and implemented in a way that does not compromise the safety integrity levels (SIL) defined by this standard.
The IEC 61508 series of standards, which deals with functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-related systems, is another key consideration. These standards provide guidelines for the entire lifecycle of safety-related systems, including the integration of software-based components like deep learning models.
For industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation, compliance with ATEX directives is essential. These directives govern equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres. Any predictive maintenance system for solenoid valves in these environments must be certified to meet ATEX requirements.
The NFPA 70E standard, which addresses electrical safety in the workplace, is also relevant when implementing deep learning models for predictive maintenance. This standard ensures that the integration of such technologies does not introduce new electrical hazards or compromise existing safety measures.
Data privacy and security standards, such as ISO/IEC 27001 and GDPR, must be considered when collecting and processing data for predictive maintenance models. These standards ensure that sensitive industrial data is protected and handled in compliance with international regulations.
Industry-specific standards also play a crucial role. For instance, in the automotive sector, compliance with ISO 26262 for functional safety of road vehicles is essential. In aerospace, adherence to DO-178C for software considerations in airborne systems is mandatory.
Lastly, emerging standards related to artificial intelligence and machine learning, such as IEEE P2801 and ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 42, are becoming increasingly important. These standards aim to establish guidelines for the development and deployment of AI systems, including those used in industrial predictive maintenance.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of DL Implementation
Implementing deep learning models for predictive maintenance of solenoid valves requires a thorough cost-benefit analysis to justify the investment and ensure long-term value for the organization. The initial costs of implementing a deep learning system can be substantial, including hardware expenses for high-performance computing resources, software licensing fees, and the development or acquisition of specialized deep learning algorithms tailored to solenoid valve maintenance.
One of the primary benefits of deep learning implementation is the potential for significant cost savings through reduced downtime and optimized maintenance schedules. By accurately predicting when a solenoid valve is likely to fail, maintenance can be performed proactively, avoiding unexpected breakdowns that can lead to costly production halts. This predictive capability can extend the lifespan of solenoid valves, reducing replacement frequency and associated costs.
The improved accuracy of deep learning models compared to traditional predictive maintenance methods can lead to fewer false positives and negatives. This results in more efficient use of maintenance resources, reducing unnecessary inspections and interventions while ensuring that truly critical issues are not overlooked. Over time, this optimization can lead to substantial savings in labor costs and spare parts inventory management.
However, the implementation of deep learning systems also comes with ongoing costs that must be considered. These include regular model updates and retraining to maintain accuracy, as well as the need for skilled personnel to manage and interpret the system's outputs. Additionally, there may be costs associated with data collection and storage, as deep learning models typically require large amounts of high-quality data to perform effectively.
The return on investment (ROI) for deep learning implementation in solenoid valve maintenance can be calculated by comparing the total cost of ownership (TCO) of the system against the quantifiable benefits it provides. These benefits may include reduced maintenance costs, increased equipment uptime, improved product quality due to more reliable valve operation, and potentially even energy savings from optimized valve performance.
It's important to note that the full benefits of deep learning implementation may not be immediately apparent, as the system's accuracy and effectiveness often improve over time as more data is collected and the models are refined. Therefore, a long-term perspective is crucial when evaluating the cost-benefit ratio of such an implementation.
One of the primary benefits of deep learning implementation is the potential for significant cost savings through reduced downtime and optimized maintenance schedules. By accurately predicting when a solenoid valve is likely to fail, maintenance can be performed proactively, avoiding unexpected breakdowns that can lead to costly production halts. This predictive capability can extend the lifespan of solenoid valves, reducing replacement frequency and associated costs.
The improved accuracy of deep learning models compared to traditional predictive maintenance methods can lead to fewer false positives and negatives. This results in more efficient use of maintenance resources, reducing unnecessary inspections and interventions while ensuring that truly critical issues are not overlooked. Over time, this optimization can lead to substantial savings in labor costs and spare parts inventory management.
However, the implementation of deep learning systems also comes with ongoing costs that must be considered. These include regular model updates and retraining to maintain accuracy, as well as the need for skilled personnel to manage and interpret the system's outputs. Additionally, there may be costs associated with data collection and storage, as deep learning models typically require large amounts of high-quality data to perform effectively.
The return on investment (ROI) for deep learning implementation in solenoid valve maintenance can be calculated by comparing the total cost of ownership (TCO) of the system against the quantifiable benefits it provides. These benefits may include reduced maintenance costs, increased equipment uptime, improved product quality due to more reliable valve operation, and potentially even energy savings from optimized valve performance.
It's important to note that the full benefits of deep learning implementation may not be immediately apparent, as the system's accuracy and effectiveness often improve over time as more data is collected and the models are refined. Therefore, a long-term perspective is crucial when evaluating the cost-benefit ratio of such an implementation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!