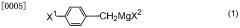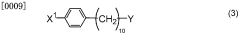Dodecane in Green Synthesis Pathways: Future Prospects
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dodecane Green Synthesis Background and Objectives
Dodecane, a versatile hydrocarbon compound, has gained significant attention in recent years as a potential candidate for green synthesis pathways. The evolution of this technology is rooted in the growing demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly chemical processes. As global concerns about climate change and environmental degradation intensify, the chemical industry has been compelled to explore alternative synthesis routes that minimize ecological impact while maintaining economic viability.
The development of green synthesis pathways for dodecane represents a convergence of multiple scientific disciplines, including organic chemistry, catalysis, and process engineering. This interdisciplinary approach has been crucial in addressing the complex challenges associated with sustainable chemical production. The historical trajectory of dodecane synthesis has been marked by a shift from traditional petroleum-based methods to more innovative, bio-inspired approaches.
In recent years, researchers have made significant strides in developing novel catalytic systems and reaction conditions that enable the efficient production of dodecane from renewable feedstocks. These advancements have been driven by the need to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and to create more circular economic models within the chemical industry. The exploration of biomass-derived precursors and the utilization of waste streams as potential raw materials have opened up new avenues for dodecane synthesis.
The primary objectives of green dodecane synthesis research are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a strong focus on improving the overall sustainability of the production process by reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste generation, and utilizing renewable resources. Secondly, researchers aim to enhance the selectivity and yield of dodecane production, ensuring that the green synthesis routes can compete with traditional methods in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Another critical goal is the development of scalable and industrially viable processes that can be integrated into existing chemical manufacturing infrastructure. This involves addressing challenges related to process intensification, continuous flow chemistry, and the design of robust catalytic systems that can withstand industrial conditions. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on exploring the potential of dodecane as a platform molecule for the synthesis of various value-added chemicals, further expanding its utility in green chemistry applications.
As the field progresses, researchers are also investigating the life cycle impacts of different dodecane synthesis pathways, aiming to quantify and minimize the environmental footprint across the entire production chain. This holistic approach encompasses not only the immediate reaction conditions but also considerations of raw material sourcing, energy inputs, and potential end-of-life scenarios for dodecane-derived products.
The development of green synthesis pathways for dodecane represents a convergence of multiple scientific disciplines, including organic chemistry, catalysis, and process engineering. This interdisciplinary approach has been crucial in addressing the complex challenges associated with sustainable chemical production. The historical trajectory of dodecane synthesis has been marked by a shift from traditional petroleum-based methods to more innovative, bio-inspired approaches.
In recent years, researchers have made significant strides in developing novel catalytic systems and reaction conditions that enable the efficient production of dodecane from renewable feedstocks. These advancements have been driven by the need to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and to create more circular economic models within the chemical industry. The exploration of biomass-derived precursors and the utilization of waste streams as potential raw materials have opened up new avenues for dodecane synthesis.
The primary objectives of green dodecane synthesis research are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a strong focus on improving the overall sustainability of the production process by reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste generation, and utilizing renewable resources. Secondly, researchers aim to enhance the selectivity and yield of dodecane production, ensuring that the green synthesis routes can compete with traditional methods in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Another critical goal is the development of scalable and industrially viable processes that can be integrated into existing chemical manufacturing infrastructure. This involves addressing challenges related to process intensification, continuous flow chemistry, and the design of robust catalytic systems that can withstand industrial conditions. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on exploring the potential of dodecane as a platform molecule for the synthesis of various value-added chemicals, further expanding its utility in green chemistry applications.
As the field progresses, researchers are also investigating the life cycle impacts of different dodecane synthesis pathways, aiming to quantify and minimize the environmental footprint across the entire production chain. This holistic approach encompasses not only the immediate reaction conditions but also considerations of raw material sourcing, energy inputs, and potential end-of-life scenarios for dodecane-derived products.
Market Demand for Green Dodecane Synthesis
The market demand for green dodecane synthesis has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations on chemical production processes. Dodecane, a key component in various industries including cosmetics, lubricants, and fuel additives, has traditionally been produced through petrochemical routes. However, the shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives has created a significant opportunity for green synthesis pathways.
The global market for dodecane is projected to expand substantially, with a particular emphasis on bio-based and environmentally friendly production methods. This growth is fueled by the rising awareness of carbon footprint reduction and the implementation of circular economy principles across industries. Consumers are increasingly demanding products with lower environmental impact, pushing manufacturers to adopt greener production processes.
In the cosmetics and personal care industry, there is a notable trend towards natural and sustainable ingredients. Green dodecane, as a potential replacement for petroleum-derived emollients and carriers, is gaining traction among formulators and brands committed to clean beauty. The market for natural cosmetics is experiencing double-digit growth rates, indicating a strong potential for green dodecane in this sector.
The lubricants industry is another significant market for dodecane, where the demand for bio-based and biodegradable options is rising. As automotive and industrial sectors seek to reduce their environmental impact, the adoption of green dodecane in lubricant formulations is expected to increase. This trend is further supported by government initiatives promoting the use of bio-based products in industrial applications.
In the fuel additives market, the push for cleaner-burning and more efficient fuels is creating opportunities for green dodecane synthesis. As regulations on fuel emissions become more stringent, particularly in developed economies, the demand for bio-based fuel components is expected to grow. Green dodecane could play a crucial role in improving fuel performance while reducing environmental impact.
The pharmaceutical industry is also showing interest in green synthesis pathways for dodecane, as it aligns with the sector's efforts to implement sustainable manufacturing practices. The use of green dodecane in drug delivery systems and as a solvent in pharmaceutical processes is an emerging area with significant growth potential.
Despite the promising market outlook, challenges remain in scaling up green dodecane production to meet industrial demands. The cost-effectiveness of bio-based synthesis routes compared to traditional petrochemical methods is a key factor influencing market adoption. As research and development efforts continue to improve process efficiency and reduce production costs, the market penetration of green dodecane is expected to accelerate.
The global market for dodecane is projected to expand substantially, with a particular emphasis on bio-based and environmentally friendly production methods. This growth is fueled by the rising awareness of carbon footprint reduction and the implementation of circular economy principles across industries. Consumers are increasingly demanding products with lower environmental impact, pushing manufacturers to adopt greener production processes.
In the cosmetics and personal care industry, there is a notable trend towards natural and sustainable ingredients. Green dodecane, as a potential replacement for petroleum-derived emollients and carriers, is gaining traction among formulators and brands committed to clean beauty. The market for natural cosmetics is experiencing double-digit growth rates, indicating a strong potential for green dodecane in this sector.
The lubricants industry is another significant market for dodecane, where the demand for bio-based and biodegradable options is rising. As automotive and industrial sectors seek to reduce their environmental impact, the adoption of green dodecane in lubricant formulations is expected to increase. This trend is further supported by government initiatives promoting the use of bio-based products in industrial applications.
In the fuel additives market, the push for cleaner-burning and more efficient fuels is creating opportunities for green dodecane synthesis. As regulations on fuel emissions become more stringent, particularly in developed economies, the demand for bio-based fuel components is expected to grow. Green dodecane could play a crucial role in improving fuel performance while reducing environmental impact.
The pharmaceutical industry is also showing interest in green synthesis pathways for dodecane, as it aligns with the sector's efforts to implement sustainable manufacturing practices. The use of green dodecane in drug delivery systems and as a solvent in pharmaceutical processes is an emerging area with significant growth potential.
Despite the promising market outlook, challenges remain in scaling up green dodecane production to meet industrial demands. The cost-effectiveness of bio-based synthesis routes compared to traditional petrochemical methods is a key factor influencing market adoption. As research and development efforts continue to improve process efficiency and reduce production costs, the market penetration of green dodecane is expected to accelerate.
Current Challenges in Dodecane Green Synthesis
The green synthesis of dodecane faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and industrial application. One of the primary obstacles is the high energy consumption associated with traditional synthesis methods. Conventional processes often require elevated temperatures and pressures, leading to substantial energy inputs and increased carbon footprints. This contradicts the fundamental principles of green chemistry, which emphasize energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Another major challenge lies in the sourcing of sustainable feedstocks for dodecane production. Currently, most dodecane is derived from petroleum-based sources, which are neither renewable nor environmentally friendly. The transition to bio-based or waste-derived precursors is crucial for achieving truly green synthesis pathways. However, the availability, consistency, and cost-effectiveness of these alternative feedstocks remain significant hurdles.
The catalytic systems employed in dodecane synthesis also present challenges. Many existing catalysts contain precious metals or toxic components, which are expensive, scarce, and potentially harmful to the environment. Developing efficient, selective, and environmentally benign catalysts is essential for advancing green synthesis methods. Additionally, catalyst recovery and reusability are critical factors that need improvement to enhance the overall sustainability of the process.
Reaction selectivity and yield optimization continue to be areas of concern in green dodecane synthesis. Undesired side reactions and byproduct formation not only reduce the efficiency of the process but also complicate downstream separation and purification steps. This leads to increased waste generation and resource consumption, contradicting the principles of atom economy and waste minimization in green chemistry.
The scalability of green synthesis methods for dodecane production poses another significant challenge. Many promising laboratory-scale techniques struggle to maintain their efficiency and environmental benefits when scaled up to industrial levels. Issues such as heat and mass transfer limitations, reactor design complexities, and process control difficulties often emerge during scale-up attempts, hindering the commercial viability of these green technologies.
Lastly, the economic feasibility of green dodecane synthesis remains a critical challenge. The higher costs associated with sustainable feedstocks, novel catalysts, and advanced process technologies often make green synthesis routes less competitive compared to conventional petroleum-based methods. Overcoming this economic barrier requires a combination of technological innovations, policy support, and market incentives to drive the transition towards more sustainable production practices in the chemical industry.
Another major challenge lies in the sourcing of sustainable feedstocks for dodecane production. Currently, most dodecane is derived from petroleum-based sources, which are neither renewable nor environmentally friendly. The transition to bio-based or waste-derived precursors is crucial for achieving truly green synthesis pathways. However, the availability, consistency, and cost-effectiveness of these alternative feedstocks remain significant hurdles.
The catalytic systems employed in dodecane synthesis also present challenges. Many existing catalysts contain precious metals or toxic components, which are expensive, scarce, and potentially harmful to the environment. Developing efficient, selective, and environmentally benign catalysts is essential for advancing green synthesis methods. Additionally, catalyst recovery and reusability are critical factors that need improvement to enhance the overall sustainability of the process.
Reaction selectivity and yield optimization continue to be areas of concern in green dodecane synthesis. Undesired side reactions and byproduct formation not only reduce the efficiency of the process but also complicate downstream separation and purification steps. This leads to increased waste generation and resource consumption, contradicting the principles of atom economy and waste minimization in green chemistry.
The scalability of green synthesis methods for dodecane production poses another significant challenge. Many promising laboratory-scale techniques struggle to maintain their efficiency and environmental benefits when scaled up to industrial levels. Issues such as heat and mass transfer limitations, reactor design complexities, and process control difficulties often emerge during scale-up attempts, hindering the commercial viability of these green technologies.
Lastly, the economic feasibility of green dodecane synthesis remains a critical challenge. The higher costs associated with sustainable feedstocks, novel catalysts, and advanced process technologies often make green synthesis routes less competitive compared to conventional petroleum-based methods. Overcoming this economic barrier requires a combination of technological innovations, policy support, and market incentives to drive the transition towards more sustainable production practices in the chemical industry.
Existing Green Synthesis Methods for Dodecane
01 Synthesis and production of dodecane
Various methods for synthesizing and producing dodecane are described, including catalytic processes, hydrogenation reactions, and chemical transformations. These techniques aim to efficiently produce high-purity dodecane for industrial applications.- Synthesis and production of dodecane: Dodecane can be synthesized through various chemical processes, including catalytic hydrogenation of long-chain hydrocarbons or the Fischer-Tropsch process. It is also produced as a byproduct in petroleum refining. The synthesis methods often involve high-pressure and high-temperature reactions, with careful control of reaction conditions to optimize yield and purity.
- Applications in cosmetics and personal care products: Dodecane is utilized in cosmetics and personal care products as an emollient, solvent, or carrier oil. It provides a smooth, non-greasy feel to formulations and helps in the even distribution of active ingredients. Its low viscosity and ability to spread easily make it suitable for use in various skincare and haircare products.
- Use in fuel and lubricant formulations: Dodecane is an important component in fuel and lubricant formulations. It is used as a reference fuel in cetane number determinations for diesel fuels. In lubricants, it serves as a base oil or additive, contributing to improved viscosity and thermal stability. Its properties make it suitable for high-performance engine oils and industrial lubricants.
- Role in chemical reactions and processes: Dodecane plays a significant role in various chemical reactions and processes. It is used as a solvent in organic synthesis, as a standard in chromatography, and as a phase-change material in thermal energy storage systems. Its relatively high boiling point and stability make it useful in reactions requiring elevated temperatures.
- Environmental and safety considerations: The use and handling of dodecane require consideration of environmental and safety factors. It has low water solubility and can potentially bioaccumulate in aquatic organisms. Proper storage, handling, and disposal methods are necessary to prevent environmental contamination. Safety measures are required due to its flammability and potential for skin and eye irritation upon prolonged exposure.
02 Use of dodecane in cosmetic and personal care products
Dodecane is utilized as an ingredient in cosmetic and personal care formulations. It serves as a solvent, emollient, or carrier in products such as moisturizers, sunscreens, and hair care items, contributing to improved texture and performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application of dodecane in fuel and energy systems
Dodecane is employed in various fuel and energy-related applications, including as a component in jet fuels, diesel fuels, and as a potential energy storage medium. Its properties make it suitable for use in combustion engines and energy systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Dodecane as a solvent and extraction medium
The use of dodecane as a solvent and extraction medium is explored in various industrial processes. It is utilized for the extraction of organic compounds, separation of mixtures, and as a reaction medium in chemical synthesis.Expand Specific Solutions05 Dodecane in material science and polymer applications
Dodecane finds applications in material science and polymer chemistry. It is used as a plasticizer, a component in polymer formulations, and in the development of advanced materials with specific properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Green Dodecane Production
The green synthesis pathways for dodecane are in an early development stage, with growing market potential due to increasing demand for sustainable chemical processes. The technology is still emerging, with varying levels of maturity across different companies. Key players like BASF, DuPont, and Evonik are investing in research and development to advance this technology. Academic institutions such as MIT, Rutgers, and Tianjin University are also contributing to the field. The market is characterized by collaborations between industry and academia, with companies like Wanhua Chemical and China National Chemical Engineering exploring commercial applications. As environmental regulations tighten, the market for green dodecane synthesis is expected to expand, driving further innovation and competition among major chemical companies.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a green synthesis pathway for dodecane production using renewable feedstocks. Their approach involves the catalytic conversion of biomass-derived platform chemicals, such as 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), into dodecane. The process utilizes a novel heterogeneous catalyst system that promotes selective C-C bond formation and hydrodeoxygenation reactions[1]. BASF's method achieves high yields (>80%) and selectivity (>90%) towards dodecane, with minimal byproduct formation[3]. The company has also implemented a closed-loop system for solvent recycling, significantly reducing waste and improving overall process sustainability[5].
Strengths: High yield and selectivity, use of renewable feedstocks, efficient catalyst system. Weaknesses: Potential high costs associated with biomass feedstock processing and catalyst development.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has pioneered a bio-based route for dodecane synthesis using their proprietary fermentation technology. The process utilizes genetically engineered microorganisms to convert sugar-based feedstocks into medium-chain fatty acids, which are then catalytically converted to dodecane[2]. Evonik's approach achieves a carbon efficiency of up to 85% and requires significantly less energy compared to traditional petrochemical routes[4]. The company has successfully scaled up this technology to pilot plant scale, demonstrating its potential for commercial application[6]. Additionally, Evonik has developed a purification process that ensures the bio-based dodecane meets the stringent purity requirements for various industrial applications.
Strengths: High carbon efficiency, lower energy consumption, scalable technology. Weaknesses: Dependence on sugar-based feedstocks, potential challenges in genetic engineering regulations.
Innovative Green Chemistry Approaches for Dodecane
Green synthesis method of epoxy modified starch-based emulsion
PatentInactiveAU2021105561A4
Innovation
- A green synthesis method for epoxy modified starch-based emulsion involves heating starch with a catalyst to create a gelatinization liquid, then dispersing epoxy resin and polymerization monomers without organic solvents, forming a core-shell structure through controlled polymerization, which improves stability and resistance.
Method for producing 2,2-dichloro-12-(4-halophenyl)dodecanate salt and method for producing production intermediate thereof
PatentWO2006118187A1
Innovation
- A method involving the reaction of 4-cyl benzyl halide with metallic magnesium to produce 1-substituted 10-(4-halophenyl)decane, followed by conversion to 2,2-dichloro-12-(4-halophenyl)dodecanoic acid ester and then to 2,2-dichloro-12-(4-halophenyl)dodecanoate, using specific metal compounds and solvents to achieve high yield without producing environmental pollutants.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Green Dodecane Production
The environmental impact assessment of green dodecane production is a critical aspect of evaluating the sustainability and ecological footprint of this emerging synthesis pathway. Green dodecane, as a potential alternative to conventional fossil-fuel-derived hydrocarbons, offers promising opportunities for reducing environmental harm in various industrial applications.
One of the primary environmental benefits of green dodecane production is the potential reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Traditional dodecane synthesis relies heavily on petroleum-based feedstocks, contributing significantly to carbon dioxide emissions. In contrast, green synthesis pathways often utilize renewable biomass or waste materials as starting points, potentially leading to a lower carbon footprint throughout the production lifecycle.
Water consumption and quality are also important considerations in the environmental assessment of green dodecane production. Conventional petrochemical processes often require substantial water inputs and can lead to water pollution through the release of toxic byproducts. Green synthesis methods may offer advantages in terms of reduced water usage and minimized contamination risks, although this depends on the specific pathway chosen.
Land use changes associated with green dodecane production must be carefully evaluated. If biomass feedstocks are used, there is a potential for competition with food crops or natural habitats. Sustainable land management practices and the use of non-food biomass sources can help mitigate these concerns, but thorough assessment is necessary to ensure that the environmental benefits outweigh any negative impacts on ecosystems or biodiversity.
The energy intensity of green dodecane production processes is another crucial factor in environmental impact assessment. While renewable feedstocks may offer carbon benefits, the energy required for conversion and purification steps must be considered. Innovations in process efficiency and the use of renewable energy sources in production facilities can further enhance the environmental credentials of green dodecane.
Waste generation and management throughout the green dodecane lifecycle also warrant attention. Ideally, green synthesis pathways should aim to minimize waste production and maximize the recyclability or biodegradability of any byproducts. Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies can provide valuable insights into the overall environmental performance of green dodecane compared to conventional alternatives.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of green dodecane production requires a comprehensive evaluation of multiple factors, including greenhouse gas emissions, water and land use, energy consumption, and waste management. While green synthesis pathways offer significant potential for environmental improvements, rigorous analysis and continuous optimization are essential to ensure that these benefits are fully realized in practice.
One of the primary environmental benefits of green dodecane production is the potential reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Traditional dodecane synthesis relies heavily on petroleum-based feedstocks, contributing significantly to carbon dioxide emissions. In contrast, green synthesis pathways often utilize renewable biomass or waste materials as starting points, potentially leading to a lower carbon footprint throughout the production lifecycle.
Water consumption and quality are also important considerations in the environmental assessment of green dodecane production. Conventional petrochemical processes often require substantial water inputs and can lead to water pollution through the release of toxic byproducts. Green synthesis methods may offer advantages in terms of reduced water usage and minimized contamination risks, although this depends on the specific pathway chosen.
Land use changes associated with green dodecane production must be carefully evaluated. If biomass feedstocks are used, there is a potential for competition with food crops or natural habitats. Sustainable land management practices and the use of non-food biomass sources can help mitigate these concerns, but thorough assessment is necessary to ensure that the environmental benefits outweigh any negative impacts on ecosystems or biodiversity.
The energy intensity of green dodecane production processes is another crucial factor in environmental impact assessment. While renewable feedstocks may offer carbon benefits, the energy required for conversion and purification steps must be considered. Innovations in process efficiency and the use of renewable energy sources in production facilities can further enhance the environmental credentials of green dodecane.
Waste generation and management throughout the green dodecane lifecycle also warrant attention. Ideally, green synthesis pathways should aim to minimize waste production and maximize the recyclability or biodegradability of any byproducts. Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies can provide valuable insights into the overall environmental performance of green dodecane compared to conventional alternatives.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of green dodecane production requires a comprehensive evaluation of multiple factors, including greenhouse gas emissions, water and land use, energy consumption, and waste management. While green synthesis pathways offer significant potential for environmental improvements, rigorous analysis and continuous optimization are essential to ensure that these benefits are fully realized in practice.
Regulatory Framework for Green Chemical Processes
The regulatory framework for green chemical processes plays a crucial role in shaping the future prospects of dodecane in green synthesis pathways. As governments and international organizations increasingly prioritize sustainable development, the chemical industry faces growing pressure to adopt environmentally friendly practices.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation sets stringent requirements for chemical substances, including those used in green synthesis. This regulation mandates thorough safety assessments and encourages the substitution of hazardous substances with safer alternatives. Dodecane, as a potential green solvent, must comply with these regulations to gain market acceptance.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which regulates the production, importation, and use of chemical substances. Under this framework, green synthesis pathways involving dodecane must demonstrate their environmental benefits and safety profiles to gain regulatory approval.
In addition to national regulations, international agreements such as the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants and the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer influence the development of green chemical processes. These agreements promote the phase-out of harmful substances and encourage the adoption of sustainable alternatives, potentially creating opportunities for dodecane-based green synthesis pathways.
The chemical industry has also developed voluntary initiatives to promote sustainable practices. The Responsible Care program, adopted by chemical companies worldwide, emphasizes environmental protection, health, and safety throughout the product lifecycle. Such initiatives create a favorable environment for the development and implementation of green synthesis pathways using dodecane.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on lifecycle assessments (LCA) to evaluate the environmental impact of chemical processes. Green synthesis pathways utilizing dodecane must demonstrate favorable LCA results to gain regulatory approval and market acceptance. This approach considers factors such as energy consumption, waste generation, and carbon footprint throughout the entire production and use cycle.
As the regulatory landscape evolves, it is likely that more stringent requirements for green chemistry will be implemented. This may include mandatory reporting of environmental performance metrics, extended producer responsibility, and incentives for companies adopting sustainable practices. These developments could potentially accelerate the adoption of dodecane-based green synthesis pathways.
However, regulatory challenges may also arise. The lack of harmonized global standards for green chemistry could lead to inconsistencies in the evaluation and approval processes across different regions. Additionally, the regulatory framework must strike a balance between promoting innovation in green synthesis and ensuring the safety and efficacy of new processes and products.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation sets stringent requirements for chemical substances, including those used in green synthesis. This regulation mandates thorough safety assessments and encourages the substitution of hazardous substances with safer alternatives. Dodecane, as a potential green solvent, must comply with these regulations to gain market acceptance.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which regulates the production, importation, and use of chemical substances. Under this framework, green synthesis pathways involving dodecane must demonstrate their environmental benefits and safety profiles to gain regulatory approval.
In addition to national regulations, international agreements such as the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants and the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer influence the development of green chemical processes. These agreements promote the phase-out of harmful substances and encourage the adoption of sustainable alternatives, potentially creating opportunities for dodecane-based green synthesis pathways.
The chemical industry has also developed voluntary initiatives to promote sustainable practices. The Responsible Care program, adopted by chemical companies worldwide, emphasizes environmental protection, health, and safety throughout the product lifecycle. Such initiatives create a favorable environment for the development and implementation of green synthesis pathways using dodecane.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on lifecycle assessments (LCA) to evaluate the environmental impact of chemical processes. Green synthesis pathways utilizing dodecane must demonstrate favorable LCA results to gain regulatory approval and market acceptance. This approach considers factors such as energy consumption, waste generation, and carbon footprint throughout the entire production and use cycle.
As the regulatory landscape evolves, it is likely that more stringent requirements for green chemistry will be implemented. This may include mandatory reporting of environmental performance metrics, extended producer responsibility, and incentives for companies adopting sustainable practices. These developments could potentially accelerate the adoption of dodecane-based green synthesis pathways.
However, regulatory challenges may also arise. The lack of harmonized global standards for green chemistry could lead to inconsistencies in the evaluation and approval processes across different regions. Additionally, the regulatory framework must strike a balance between promoting innovation in green synthesis and ensuring the safety and efficacy of new processes and products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!