Examining the Benefits of LDPE over Other Plastics
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Evolution and Objectives
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has undergone significant evolution since its accidental discovery in 1933 by Imperial Chemical Industries. This versatile plastic material has become an integral part of modern life, finding applications in various industries due to its unique properties and cost-effectiveness.
The development of LDPE began with the high-pressure polymerization process, which allowed for the production of this flexible and durable material. Over the years, advancements in catalysis and polymerization techniques have led to improved LDPE grades with enhanced properties, such as better clarity, strength, and processability.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the introduction of Ziegler-Natta catalysts revolutionized polyethylene production, enabling the synthesis of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE). This innovation expanded the range of available polyethylene products and their applications, further solidifying LDPE's position in the plastics industry.
The 1970s and 1980s saw a focus on improving LDPE's environmental impact, with the development of more efficient production processes and the introduction of recycling initiatives. This period also marked the beginning of research into biodegradable additives and composting technologies for LDPE, addressing growing concerns about plastic waste.
Recent technological advancements have aimed at enhancing LDPE's performance characteristics, such as improved barrier properties for packaging applications and increased resistance to environmental stress cracking. The development of metallocene catalysts in the 1990s allowed for more precise control over polymer structure, leading to LDPE grades with tailored properties for specific applications.
The primary objective in examining the benefits of LDPE over other plastics is to highlight its unique combination of properties that make it suitable for a wide range of applications. These include its flexibility, transparency, and ease of processing, which are particularly valuable in packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods industries.
Another key goal is to assess LDPE's environmental impact compared to alternative plastics. This involves evaluating its recyclability, energy consumption during production, and potential for biodegradation or composting. The analysis aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of LDPE's lifecycle and its position in the context of sustainable materials.
Furthermore, the examination seeks to identify potential areas for innovation and improvement in LDPE technology. This includes exploring new applications, developing more sustainable production methods, and investigating ways to enhance LDPE's properties to meet evolving industry demands and environmental standards.
The development of LDPE began with the high-pressure polymerization process, which allowed for the production of this flexible and durable material. Over the years, advancements in catalysis and polymerization techniques have led to improved LDPE grades with enhanced properties, such as better clarity, strength, and processability.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the introduction of Ziegler-Natta catalysts revolutionized polyethylene production, enabling the synthesis of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE). This innovation expanded the range of available polyethylene products and their applications, further solidifying LDPE's position in the plastics industry.
The 1970s and 1980s saw a focus on improving LDPE's environmental impact, with the development of more efficient production processes and the introduction of recycling initiatives. This period also marked the beginning of research into biodegradable additives and composting technologies for LDPE, addressing growing concerns about plastic waste.
Recent technological advancements have aimed at enhancing LDPE's performance characteristics, such as improved barrier properties for packaging applications and increased resistance to environmental stress cracking. The development of metallocene catalysts in the 1990s allowed for more precise control over polymer structure, leading to LDPE grades with tailored properties for specific applications.
The primary objective in examining the benefits of LDPE over other plastics is to highlight its unique combination of properties that make it suitable for a wide range of applications. These include its flexibility, transparency, and ease of processing, which are particularly valuable in packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods industries.
Another key goal is to assess LDPE's environmental impact compared to alternative plastics. This involves evaluating its recyclability, energy consumption during production, and potential for biodegradation or composting. The analysis aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of LDPE's lifecycle and its position in the context of sustainable materials.
Furthermore, the examination seeks to identify potential areas for innovation and improvement in LDPE technology. This includes exploring new applications, developing more sustainable production methods, and investigating ways to enhance LDPE's properties to meet evolving industry demands and environmental standards.
Market Demand Analysis for LDPE
The global market for Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. The packaging sector remains the primary consumer of LDPE, accounting for a significant portion of the total demand. This is largely due to LDPE's excellent moisture barrier properties, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for food packaging, shrink wraps, and plastic bags.
In recent years, there has been a notable increase in LDPE demand from the construction industry. LDPE is widely used in geomembranes, insulation materials, and vapor barriers, contributing to its growing market share in this sector. The automotive industry has also shown increased interest in LDPE, particularly for interior components and wire insulation, due to its lightweight nature and durability.
The agricultural sector presents another area of growth for LDPE, with its use in greenhouse films, mulch films, and irrigation systems. As global food production needs continue to rise, the demand for LDPE in agriculture is expected to follow suit. Additionally, the healthcare industry has been adopting LDPE for medical packaging and disposable medical devices, further diversifying its market applications.
Despite the growing environmental concerns surrounding plastic usage, LDPE continues to maintain its market position due to its recyclability and ongoing efforts to improve its eco-friendly characteristics. Many manufacturers are investing in research and development to enhance LDPE's recyclability and incorporate bio-based materials, aligning with the increasing consumer demand for sustainable products.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the LDPE market, with China and India being the major consumers. The rapid industrialization and urbanization in these countries are driving the demand for LDPE across various end-use industries. North America and Europe also maintain significant market shares, with a focus on high-quality, specialized LDPE products for advanced applications.
The LDPE market faces competition from other plastic types, particularly High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE). However, LDPE's unique properties, such as its high clarity and ease of processing, continue to make it the preferred choice for certain applications. The ongoing development of metallocene LDPE, which offers improved strength and optical properties, is expected to further boost market demand in the coming years.
In conclusion, the market demand for LDPE remains robust, with diverse applications across multiple industries driving its growth. While environmental concerns pose challenges, ongoing innovations in recyclability and sustainability are likely to sustain LDPE's market position in the foreseeable future.
In recent years, there has been a notable increase in LDPE demand from the construction industry. LDPE is widely used in geomembranes, insulation materials, and vapor barriers, contributing to its growing market share in this sector. The automotive industry has also shown increased interest in LDPE, particularly for interior components and wire insulation, due to its lightweight nature and durability.
The agricultural sector presents another area of growth for LDPE, with its use in greenhouse films, mulch films, and irrigation systems. As global food production needs continue to rise, the demand for LDPE in agriculture is expected to follow suit. Additionally, the healthcare industry has been adopting LDPE for medical packaging and disposable medical devices, further diversifying its market applications.
Despite the growing environmental concerns surrounding plastic usage, LDPE continues to maintain its market position due to its recyclability and ongoing efforts to improve its eco-friendly characteristics. Many manufacturers are investing in research and development to enhance LDPE's recyclability and incorporate bio-based materials, aligning with the increasing consumer demand for sustainable products.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the LDPE market, with China and India being the major consumers. The rapid industrialization and urbanization in these countries are driving the demand for LDPE across various end-use industries. North America and Europe also maintain significant market shares, with a focus on high-quality, specialized LDPE products for advanced applications.
The LDPE market faces competition from other plastic types, particularly High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE). However, LDPE's unique properties, such as its high clarity and ease of processing, continue to make it the preferred choice for certain applications. The ongoing development of metallocene LDPE, which offers improved strength and optical properties, is expected to further boost market demand in the coming years.
In conclusion, the market demand for LDPE remains robust, with diverse applications across multiple industries driving its growth. While environmental concerns pose challenges, ongoing innovations in recyclability and sustainability are likely to sustain LDPE's market position in the foreseeable future.
LDPE vs Other Plastics: Current Status and Challenges
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has emerged as a prominent plastic material in various industries, offering unique advantages over other plastics. However, it also faces several challenges in its current applications and future development. The global LDPE market has shown steady growth, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.5% from 2015 to 2020, indicating its increasing importance in the plastics industry.
One of the primary advantages of LDPE is its excellent flexibility and toughness, making it ideal for applications such as packaging films, bags, and containers. Its low melting point and ease of processing contribute to its widespread use in the packaging industry. LDPE also demonstrates good chemical resistance and moisture barrier properties, further enhancing its appeal in various sectors.
Despite these benefits, LDPE faces competition from other plastic materials, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE). HDPE offers higher strength and stiffness, while LLDPE provides improved tear and puncture resistance. This competition has led to ongoing research and development efforts to enhance LDPE's properties and expand its applications.
A significant challenge for LDPE is its environmental impact. Like many plastics, LDPE is derived from non-renewable fossil fuels and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. This has led to increased scrutiny and regulatory pressure on single-use plastic products, many of which are made from LDPE. The industry is responding by investing in recycling technologies and exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional LDPE.
Another challenge lies in the volatility of raw material prices, particularly ethylene, which is the primary feedstock for LDPE production. Fluctuations in oil and natural gas prices can significantly impact LDPE production costs, affecting its competitiveness against other materials.
The geographical distribution of LDPE production and consumption shows interesting patterns. Asia-Pacific leads in both production and consumption, driven by rapid industrialization and population growth. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets focusing on high-value applications and sustainability initiatives.
Technological advancements in LDPE production, such as improved catalysts and process optimizations, are ongoing to address these challenges. These innovations aim to enhance LDPE's properties, reduce production costs, and minimize environmental impact. Additionally, research into blending LDPE with other materials to create composite products with superior characteristics is gaining traction.
In conclusion, while LDPE continues to be a versatile and widely used plastic, it faces a complex landscape of opportunities and challenges. Balancing its beneficial properties with environmental concerns and market competition will be crucial for its future development and sustained relevance in the plastics industry.
One of the primary advantages of LDPE is its excellent flexibility and toughness, making it ideal for applications such as packaging films, bags, and containers. Its low melting point and ease of processing contribute to its widespread use in the packaging industry. LDPE also demonstrates good chemical resistance and moisture barrier properties, further enhancing its appeal in various sectors.
Despite these benefits, LDPE faces competition from other plastic materials, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE). HDPE offers higher strength and stiffness, while LLDPE provides improved tear and puncture resistance. This competition has led to ongoing research and development efforts to enhance LDPE's properties and expand its applications.
A significant challenge for LDPE is its environmental impact. Like many plastics, LDPE is derived from non-renewable fossil fuels and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. This has led to increased scrutiny and regulatory pressure on single-use plastic products, many of which are made from LDPE. The industry is responding by investing in recycling technologies and exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional LDPE.
Another challenge lies in the volatility of raw material prices, particularly ethylene, which is the primary feedstock for LDPE production. Fluctuations in oil and natural gas prices can significantly impact LDPE production costs, affecting its competitiveness against other materials.
The geographical distribution of LDPE production and consumption shows interesting patterns. Asia-Pacific leads in both production and consumption, driven by rapid industrialization and population growth. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets focusing on high-value applications and sustainability initiatives.
Technological advancements in LDPE production, such as improved catalysts and process optimizations, are ongoing to address these challenges. These innovations aim to enhance LDPE's properties, reduce production costs, and minimize environmental impact. Additionally, research into blending LDPE with other materials to create composite products with superior characteristics is gaining traction.
In conclusion, while LDPE continues to be a versatile and widely used plastic, it faces a complex landscape of opportunities and challenges. Balancing its beneficial properties with environmental concerns and market competition will be crucial for its future development and sustained relevance in the plastics industry.
Current LDPE Manufacturing Processes
01 Improved flexibility and impact resistance
LDPE offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and shock absorption. Its molecular structure allows for better elongation and toughness compared to other polyethylene types, enhancing its performance in various products.- Improved flexibility and impact resistance: LDPE offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and shock absorption. Its molecular structure allows for better elongation and toughness compared to other polyethylene types, enhancing its performance in various products.
- Enhanced chemical resistance and barrier properties: LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance and barrier properties, making it ideal for packaging applications. It provides effective protection against moisture, gases, and certain chemicals, extending the shelf life of products and maintaining their quality.
- Ease of processing and manufacturing: LDPE is known for its ease of processing and manufacturing, allowing for efficient production of various products. It can be easily molded, extruded, or blown into different shapes and forms, making it versatile for diverse applications in industries such as packaging, construction, and consumer goods.
- Cost-effectiveness and recyclability: LDPE offers a cost-effective solution for many applications due to its relatively low production costs and wide availability. Additionally, it is recyclable, contributing to sustainability efforts and reducing environmental impact when properly managed in waste streams.
- Electrical insulation properties: LDPE possesses excellent electrical insulation properties, making it suitable for use in various electrical and electronic applications. Its low dielectric constant and high resistivity contribute to its effectiveness as an insulating material in cables, wires, and other electrical components.
02 Enhanced chemical resistance and barrier properties
LDPE exhibits good chemical resistance and barrier properties, making it ideal for packaging applications. It provides effective protection against moisture, gases, and certain chemicals, extending the shelf life of products and maintaining their quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ease of processing and manufacturing
LDPE is known for its ease of processing and manufacturing, allowing for efficient production of various products. It can be easily molded, extruded, or blown into different shapes and forms, making it versatile for a wide range of applications in industries such as packaging, construction, and consumer goods.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cost-effectiveness and recyclability
LDPE is a cost-effective material that offers good performance at a relatively low price point. Additionally, it is recyclable, contributing to sustainability efforts and reducing environmental impact. Its recyclability makes it an attractive option for manufacturers and consumers alike.Expand Specific Solutions05 Versatility in applications
LDPE's unique properties make it suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries. It is commonly used in packaging films, bags, containers, toys, wire and cable insulation, and agricultural products. Its versatility allows for innovation in product design and development.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in LDPE Industry
The competitive landscape for examining the benefits of LDPE over other plastics is characterized by a mature industry with established players and ongoing innovation. The global LDPE market is substantial, valued at over $33 billion in 2020, with steady growth projected. Technologically, LDPE production is well-established, but companies are continually refining processes and exploring new applications. Key players like Dow Global Technologies, ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, and SABIC Global Technologies are at the forefront of LDPE research and development, focusing on enhancing properties, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Emerging trends include bio-based LDPE and recycling technologies, with companies like Braskem SA leading in sustainable alternatives. The competitive landscape is dynamic, with both large petrochemical corporations and specialized firms contributing to advancements in LDPE technology and applications.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed advanced LDPE resins with enhanced properties for various applications. Their AGILITY™ LDPE resins offer improved processability and mechanical properties. These resins are produced using high-pressure tubular reactor technology, allowing for precise control of molecular weight distribution and long-chain branching[1]. This results in LDPE with superior optical properties, enhanced sealability, and improved tear resistance. Dow's LDPE innovations also include the development of sustainable solutions, such as bio-based LDPE made from renewable feedstocks, reducing the carbon footprint by up to 75% compared to fossil-based alternatives[2].
Strengths: Superior optical properties, enhanced sealability, improved tear resistance, and sustainable options. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to standard LDPE, potential limitations in high-temperature applications.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed a range of LDPE resins under their Exceed™ XP performance polymers line. These resins are designed to offer exceptional toughness, high flex-crack resistance, and superior processability. ExxonMobil's LDPE technology focuses on creating resins with a balanced set of properties, including high melt strength and excellent optical characteristics. Their patented process allows for the production of LDPE with controlled long-chain branching, resulting in improved film strength and enhanced bubble stability during extrusion[3]. ExxonMobil's LDPE resins also demonstrate superior heat sealing properties, with seal initiation temperatures as low as 85°C, enabling faster packaging line speeds[4].
Strengths: Exceptional toughness, high flex-crack resistance, superior processability, and low seal initiation temperatures. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to commodity LDPE grades, may require specialized equipment for optimal processing.
LDPE Properties and Performance Advantages
Polymeric blends and methods of using same
PatentWO2013074287A1
Innovation
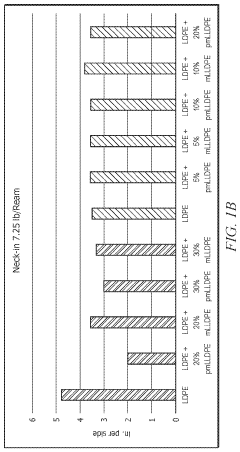
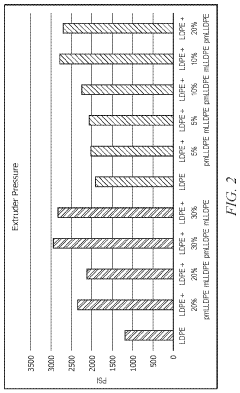
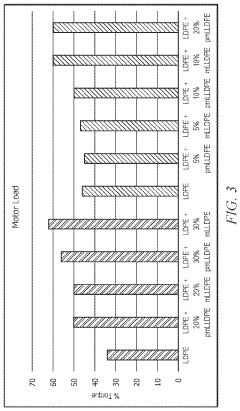
- A composition comprising LDPE and metallocene-catalyzed linear low density polyethylene (mLLDPE) is developed, which when extruded as a molten resin exhibits a neck-in value similar to or slightly increased by less than 10% compared to LDPE alone, and produces 10% less trim waste, with improved miscibility and thermal characteristics.
Extrusion coating with enhanced performance via polymeric blends
PatentActiveUS12018141B2
Innovation
- A composition comprising low density polyethylene (LDPE) and peroxide-treated metallocene-catalyzed linear low density polyethylene (pmLLDPE) is developed, which when blended and extruded, exhibits a reduced neck-in value, improved compatibility, and enhanced processability, allowing for increased useable product width and reduced extrusion pressure.
Environmental Impact of LDPE
The environmental impact of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a critical consideration in assessing its benefits over other plastics. LDPE, widely used in packaging and consumer products, presents both advantages and challenges from an environmental perspective.
One of the primary environmental benefits of LDPE is its recyclability. LDPE can be effectively recycled multiple times without significant degradation of its properties, reducing the need for virgin plastic production. This characteristic contributes to the circular economy model, potentially decreasing the overall environmental footprint of plastic use.
However, the recycling rates for LDPE remain relatively low in many regions, primarily due to challenges in collection and sorting. Improving recycling infrastructure and public awareness could significantly enhance the environmental benefits of LDPE.
LDPE's lightweight nature also contributes to its environmental advantages. In transportation and packaging applications, the use of LDPE can lead to reduced fuel consumption and lower carbon emissions compared to heavier alternative materials. This aspect is particularly relevant in the context of global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The durability of LDPE is a double-edged sword from an environmental standpoint. While its longevity can reduce the need for frequent replacements, potentially lowering overall resource consumption, it also means that LDPE products persist in the environment for extended periods when improperly disposed of.
In marine environments, LDPE poses significant risks. Like other plastics, it can break down into microplastics, which have been found to contaminate marine ecosystems and enter the food chain. This issue highlights the importance of proper waste management and the need for biodegradable alternatives in certain applications.
The production process of LDPE also has environmental implications. While it generally requires less energy to produce compared to some other plastics, it still relies on fossil fuel feedstocks. The extraction and processing of these raw materials contribute to carbon emissions and other environmental impacts associated with the petrochemical industry.
Efforts to improve the environmental profile of LDPE include the development of bio-based alternatives and the incorporation of recycled content. These innovations aim to reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the overall carbon footprint of LDPE products.
In conclusion, while LDPE offers certain environmental advantages, particularly in terms of recyclability and resource efficiency, its impact on the environment remains complex. Addressing the challenges of recycling rates, marine pollution, and fossil fuel dependence is crucial for maximizing the environmental benefits of LDPE over other plastics.
One of the primary environmental benefits of LDPE is its recyclability. LDPE can be effectively recycled multiple times without significant degradation of its properties, reducing the need for virgin plastic production. This characteristic contributes to the circular economy model, potentially decreasing the overall environmental footprint of plastic use.
However, the recycling rates for LDPE remain relatively low in many regions, primarily due to challenges in collection and sorting. Improving recycling infrastructure and public awareness could significantly enhance the environmental benefits of LDPE.
LDPE's lightweight nature also contributes to its environmental advantages. In transportation and packaging applications, the use of LDPE can lead to reduced fuel consumption and lower carbon emissions compared to heavier alternative materials. This aspect is particularly relevant in the context of global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The durability of LDPE is a double-edged sword from an environmental standpoint. While its longevity can reduce the need for frequent replacements, potentially lowering overall resource consumption, it also means that LDPE products persist in the environment for extended periods when improperly disposed of.
In marine environments, LDPE poses significant risks. Like other plastics, it can break down into microplastics, which have been found to contaminate marine ecosystems and enter the food chain. This issue highlights the importance of proper waste management and the need for biodegradable alternatives in certain applications.
The production process of LDPE also has environmental implications. While it generally requires less energy to produce compared to some other plastics, it still relies on fossil fuel feedstocks. The extraction and processing of these raw materials contribute to carbon emissions and other environmental impacts associated with the petrochemical industry.
Efforts to improve the environmental profile of LDPE include the development of bio-based alternatives and the incorporation of recycled content. These innovations aim to reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the overall carbon footprint of LDPE products.
In conclusion, while LDPE offers certain environmental advantages, particularly in terms of recyclability and resource efficiency, its impact on the environment remains complex. Addressing the challenges of recycling rates, marine pollution, and fossil fuel dependence is crucial for maximizing the environmental benefits of LDPE over other plastics.
Regulatory Framework for LDPE Usage
The regulatory framework for LDPE usage is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the production, distribution, and application of this versatile plastic material. At the global level, organizations such as the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the World Health Organization (WHO) provide guidelines and recommendations for plastic use, including LDPE, with a focus on environmental protection and human health.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating LDPE usage, particularly in food contact applications. The FDA has established specific regulations under Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), which outline the permissible uses and limitations of LDPE in food packaging and other consumer products. These regulations ensure that LDPE materials meet safety standards and do not pose risks to human health.
The European Union has implemented a comprehensive regulatory framework for plastics, including LDPE, through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemical substances, including those used in LDPE production, and provide safety information. Additionally, the EU Plastics Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 sets specific requirements for plastic materials intended to come into contact with food.
Many countries have introduced legislation to address plastic waste and promote recycling. For instance, the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive aims to reduce the environmental impact of certain plastic products, including those made from LDPE. This directive has led to increased focus on recyclability and the development of more sustainable LDPE formulations.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. These programs have implications for LDPE producers and users, encouraging the development of more easily recyclable LDPE products and improved waste management systems.
The regulatory landscape also includes industry-specific standards and certifications. For example, the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides standards for LDPE testing and quality control, which are widely recognized and adopted by manufacturers and regulatory bodies worldwide.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, many jurisdictions are implementing or considering plastic bag bans or taxes, which often target LDPE products. These regulations vary widely between countries and even between local municipalities, creating a complex patchwork of requirements for LDPE manufacturers and users to navigate.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating LDPE usage, particularly in food contact applications. The FDA has established specific regulations under Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), which outline the permissible uses and limitations of LDPE in food packaging and other consumer products. These regulations ensure that LDPE materials meet safety standards and do not pose risks to human health.
The European Union has implemented a comprehensive regulatory framework for plastics, including LDPE, through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemical substances, including those used in LDPE production, and provide safety information. Additionally, the EU Plastics Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 sets specific requirements for plastic materials intended to come into contact with food.
Many countries have introduced legislation to address plastic waste and promote recycling. For instance, the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive aims to reduce the environmental impact of certain plastic products, including those made from LDPE. This directive has led to increased focus on recyclability and the development of more sustainable LDPE formulations.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. These programs have implications for LDPE producers and users, encouraging the development of more easily recyclable LDPE products and improved waste management systems.
The regulatory landscape also includes industry-specific standards and certifications. For example, the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides standards for LDPE testing and quality control, which are widely recognized and adopted by manufacturers and regulatory bodies worldwide.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, many jurisdictions are implementing or considering plastic bag bans or taxes, which often target LDPE products. These regulations vary widely between countries and even between local municipalities, creating a complex patchwork of requirements for LDPE manufacturers and users to navigate.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!