Future Outlook: PEMF Therapy in Integrated Health Systems
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Therapy Evolution
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for bone healing, PEMF therapy has expanded its applications across various medical fields. The therapy's evolution can be traced through several key stages, each marked by technological advancements and broadening clinical applications.
In the 1950s and 1960s, researchers began exploring the effects of electromagnetic fields on biological systems. This foundational period laid the groundwork for understanding how electromagnetic fields could influence cellular processes and tissue repair. The 1970s saw the first FDA-approved PEMF device for bone healing, marking a significant milestone in the therapy's clinical acceptance.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed an expansion of PEMF applications beyond orthopedics. Researchers began investigating its potential in pain management, wound healing, and neurological disorders. This period also saw improvements in device design, making PEMF therapy more accessible for clinical and home use.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era for PEMF therapy. Advancements in electronics and materials science led to the development of more sophisticated and targeted PEMF devices. These innovations allowed for better control over field strength, frequency, and waveform, enabling more precise and effective treatments.
In recent years, PEMF therapy has gained traction in integrative medicine approaches. Its non-invasive nature and potential for addressing chronic conditions have made it an attractive option for patients seeking alternative or complementary treatments. The therapy has shown promise in areas such as depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders, expanding its reach into mental health applications.
The integration of PEMF therapy into wearable technology represents the latest evolution in this field. Smart devices capable of delivering personalized PEMF treatments are emerging, allowing for continuous, low-intensity therapy in everyday settings. This development aligns with the growing trend of personalized medicine and patient-centric care.
Looking ahead, the future of PEMF therapy in integrated health systems appears promising. Ongoing research is exploring its potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases, enhancing cognitive function, and supporting overall wellness. As our understanding of the therapy's mechanisms deepens, we can expect to see more targeted and efficient PEMF applications across various medical specialties.
In the 1950s and 1960s, researchers began exploring the effects of electromagnetic fields on biological systems. This foundational period laid the groundwork for understanding how electromagnetic fields could influence cellular processes and tissue repair. The 1970s saw the first FDA-approved PEMF device for bone healing, marking a significant milestone in the therapy's clinical acceptance.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed an expansion of PEMF applications beyond orthopedics. Researchers began investigating its potential in pain management, wound healing, and neurological disorders. This period also saw improvements in device design, making PEMF therapy more accessible for clinical and home use.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era for PEMF therapy. Advancements in electronics and materials science led to the development of more sophisticated and targeted PEMF devices. These innovations allowed for better control over field strength, frequency, and waveform, enabling more precise and effective treatments.
In recent years, PEMF therapy has gained traction in integrative medicine approaches. Its non-invasive nature and potential for addressing chronic conditions have made it an attractive option for patients seeking alternative or complementary treatments. The therapy has shown promise in areas such as depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders, expanding its reach into mental health applications.
The integration of PEMF therapy into wearable technology represents the latest evolution in this field. Smart devices capable of delivering personalized PEMF treatments are emerging, allowing for continuous, low-intensity therapy in everyday settings. This development aligns with the growing trend of personalized medicine and patient-centric care.
Looking ahead, the future of PEMF therapy in integrated health systems appears promising. Ongoing research is exploring its potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases, enhancing cognitive function, and supporting overall wellness. As our understanding of the therapy's mechanisms deepens, we can expect to see more targeted and efficient PEMF applications across various medical specialties.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy in integrated health systems is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of its potential benefits and a shift towards non-invasive treatment options. As healthcare providers and patients seek alternative therapies for chronic conditions and pain management, PEMF therapy has emerged as a promising solution.
The global PEMF therapy devices market is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 10% through 2028. This growth is attributed to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, musculoskeletal disorders, and sports-related injuries, which are key target areas for PEMF therapy applications.
In the context of integrated health systems, PEMF therapy is gaining traction due to its potential to complement traditional medical treatments. Healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the value of incorporating PEMF therapy into comprehensive treatment plans, particularly for conditions such as osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic pain syndromes.
The aging population in many developed countries is a significant driver of market demand for PEMF therapy. As the elderly population grows, there is an increased need for non-pharmacological interventions to manage age-related health issues, including bone and joint problems. PEMF therapy's potential to improve bone density and reduce inflammation makes it an attractive option for this demographic.
Another factor contributing to market growth is the increasing adoption of PEMF therapy in sports medicine and rehabilitation. Professional athletes and sports teams are incorporating PEMF devices into their recovery and injury prevention protocols, which is raising awareness and driving demand in the broader consumer market.
The home healthcare segment is also showing promising growth potential for PEMF therapy devices. As patients seek convenient and cost-effective treatment options, portable PEMF devices for home use are becoming increasingly popular. This trend is expected to continue, especially in light of the recent global health crisis, which has accelerated the adoption of home-based medical technologies.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges remain in terms of regulatory approval and insurance coverage for PEMF therapy. As more clinical evidence accumulates and regulatory bodies recognize the efficacy of PEMF treatments, these barriers are expected to diminish, further driving market growth and integration into mainstream healthcare systems.
In conclusion, the market demand for PEMF therapy in integrated health systems is robust and poised for continued expansion. The convergence of factors such as an aging population, increasing chronic disease prevalence, and a shift towards non-invasive treatments is creating a favorable environment for PEMF therapy adoption. As research advances and clinical evidence strengthens, PEMF therapy is likely to become an increasingly integral component of holistic healthcare approaches in the coming years.
The global PEMF therapy devices market is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 10% through 2028. This growth is attributed to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, musculoskeletal disorders, and sports-related injuries, which are key target areas for PEMF therapy applications.
In the context of integrated health systems, PEMF therapy is gaining traction due to its potential to complement traditional medical treatments. Healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the value of incorporating PEMF therapy into comprehensive treatment plans, particularly for conditions such as osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic pain syndromes.
The aging population in many developed countries is a significant driver of market demand for PEMF therapy. As the elderly population grows, there is an increased need for non-pharmacological interventions to manage age-related health issues, including bone and joint problems. PEMF therapy's potential to improve bone density and reduce inflammation makes it an attractive option for this demographic.
Another factor contributing to market growth is the increasing adoption of PEMF therapy in sports medicine and rehabilitation. Professional athletes and sports teams are incorporating PEMF devices into their recovery and injury prevention protocols, which is raising awareness and driving demand in the broader consumer market.
The home healthcare segment is also showing promising growth potential for PEMF therapy devices. As patients seek convenient and cost-effective treatment options, portable PEMF devices for home use are becoming increasingly popular. This trend is expected to continue, especially in light of the recent global health crisis, which has accelerated the adoption of home-based medical technologies.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges remain in terms of regulatory approval and insurance coverage for PEMF therapy. As more clinical evidence accumulates and regulatory bodies recognize the efficacy of PEMF treatments, these barriers are expected to diminish, further driving market growth and integration into mainstream healthcare systems.
In conclusion, the market demand for PEMF therapy in integrated health systems is robust and poised for continued expansion. The convergence of factors such as an aging population, increasing chronic disease prevalence, and a shift towards non-invasive treatments is creating a favorable environment for PEMF therapy adoption. As research advances and clinical evidence strengthens, PEMF therapy is likely to become an increasingly integral component of holistic healthcare approaches in the coming years.
Current PEMF Challenges
Despite the growing popularity and potential of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy, several challenges hinder its widespread integration into mainstream healthcare systems. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardization in PEMF devices and treatment protocols. The wide variety of devices available in the market, each with different frequencies, intensities, and waveforms, makes it difficult for healthcare providers to determine the most effective treatment parameters for specific conditions.
Another significant challenge is the limited body of high-quality clinical evidence supporting PEMF therapy's efficacy for various health conditions. While numerous studies have shown promising results, many are small-scale or lack rigorous methodological designs. This paucity of large-scale, randomized controlled trials makes it challenging for PEMF therapy to gain widespread acceptance within the medical community and secure regulatory approvals for specific indications.
The complexity of PEMF technology and its underlying mechanisms of action also presents a barrier to integration. Many healthcare professionals lack a comprehensive understanding of how PEMF therapy works at the cellular and molecular levels, which can lead to skepticism or reluctance to incorporate it into their practice. This knowledge gap extends to patients as well, who may struggle to grasp the concept of electromagnetic fields for healing, potentially affecting treatment adherence and outcomes.
Regulatory hurdles pose another significant challenge for PEMF therapy integration. The classification and approval processes for PEMF devices vary across different countries and regions, creating a complex landscape for manufacturers and healthcare providers to navigate. In some jurisdictions, PEMF devices may be classified as medical devices requiring extensive clinical trials and regulatory approvals, while in others, they may be considered wellness products with less stringent requirements.
Cost and accessibility issues also impede the widespread adoption of PEMF therapy. High-quality PEMF devices can be expensive, limiting their availability in resource-constrained healthcare settings. Additionally, insurance coverage for PEMF treatments is often limited or non-existent, placing the financial burden on patients and potentially restricting access to those who could benefit from the therapy.
Lastly, the integration of PEMF therapy into existing healthcare workflows and treatment paradigms presents logistical challenges. Healthcare systems are often resistant to change, and incorporating a new modality like PEMF therapy requires adjustments to clinical protocols, staff training, and resource allocation. Overcoming these operational hurdles requires a concerted effort from healthcare administrators, clinicians, and technology providers to develop seamless integration strategies that maximize the potential benefits of PEMF therapy while minimizing disruption to existing care pathways.
Another significant challenge is the limited body of high-quality clinical evidence supporting PEMF therapy's efficacy for various health conditions. While numerous studies have shown promising results, many are small-scale or lack rigorous methodological designs. This paucity of large-scale, randomized controlled trials makes it challenging for PEMF therapy to gain widespread acceptance within the medical community and secure regulatory approvals for specific indications.
The complexity of PEMF technology and its underlying mechanisms of action also presents a barrier to integration. Many healthcare professionals lack a comprehensive understanding of how PEMF therapy works at the cellular and molecular levels, which can lead to skepticism or reluctance to incorporate it into their practice. This knowledge gap extends to patients as well, who may struggle to grasp the concept of electromagnetic fields for healing, potentially affecting treatment adherence and outcomes.
Regulatory hurdles pose another significant challenge for PEMF therapy integration. The classification and approval processes for PEMF devices vary across different countries and regions, creating a complex landscape for manufacturers and healthcare providers to navigate. In some jurisdictions, PEMF devices may be classified as medical devices requiring extensive clinical trials and regulatory approvals, while in others, they may be considered wellness products with less stringent requirements.
Cost and accessibility issues also impede the widespread adoption of PEMF therapy. High-quality PEMF devices can be expensive, limiting their availability in resource-constrained healthcare settings. Additionally, insurance coverage for PEMF treatments is often limited or non-existent, placing the financial burden on patients and potentially restricting access to those who could benefit from the therapy.
Lastly, the integration of PEMF therapy into existing healthcare workflows and treatment paradigms presents logistical challenges. Healthcare systems are often resistant to change, and incorporating a new modality like PEMF therapy requires adjustments to clinical protocols, staff training, and resource allocation. Overcoming these operational hurdles requires a concerted effort from healthcare administrators, clinicians, and technology providers to develop seamless integration strategies that maximize the potential benefits of PEMF therapy while minimizing disruption to existing care pathways.
PEMF Treatment Protocols
01 PEMF devices for therapeutic applications
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices are designed for various therapeutic applications. These devices generate electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and regeneration, potentially alleviating pain and promoting healing in different parts of the body.- PEMF devices for therapeutic applications: Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices are designed for various therapeutic applications. These devices generate electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and improve overall health. They can be used for pain management, tissue healing, and treating various medical conditions.
- PEMF therapy for specific medical conditions: PEMF therapy is utilized to treat specific medical conditions such as osteoarthritis, bone fractures, and neurological disorders. The therapy aims to reduce inflammation, promote tissue regeneration, and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions. Different PEMF protocols and frequencies may be used depending on the targeted condition.
- Wearable PEMF devices: Wearable PEMF devices have been developed to provide convenient and continuous therapy. These devices can be worn on various parts of the body, allowing for targeted treatment while the user goes about their daily activities. Wearable designs include braces, wraps, and garments with integrated PEMF technology.
- PEMF therapy combined with other treatments: PEMF therapy is often combined with other treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic outcomes. This may include combining PEMF with heat therapy, light therapy, or traditional medical treatments. The synergistic effects of these combinations aim to provide more comprehensive and effective treatment options.
- Advanced PEMF control systems and protocols: Innovations in PEMF therapy focus on developing advanced control systems and treatment protocols. These advancements include precise frequency modulation, customizable treatment programs, and smart devices that can adapt to individual patient needs. Such systems aim to optimize the effectiveness of PEMF therapy and improve patient outcomes.
02 PEMF therapy for specific medical conditions
PEMF therapy is utilized to treat specific medical conditions, including but not limited to musculoskeletal disorders, neurological issues, and chronic pain. The therapy aims to improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and enhance the body's natural healing processes through targeted electromagnetic stimulation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advancements in PEMF technology
Recent advancements in PEMF technology focus on improving the efficacy and versatility of treatment devices. These innovations include the development of portable and wearable PEMF devices, integration with other therapies, and the use of smart technology for personalized treatment protocols.Expand Specific Solutions04 PEMF therapy in veterinary and agricultural applications
PEMF therapy is not limited to human applications; it is also being explored and utilized in veterinary medicine and agriculture. The technology is adapted to treat animals and potentially enhance plant growth, showcasing the versatility of PEMF therapy across different fields.Expand Specific Solutions05 Combination of PEMF with other therapeutic modalities
Research and development efforts are focusing on combining PEMF therapy with other therapeutic modalities to enhance overall treatment outcomes. This includes integration with light therapy, heat therapy, and other complementary approaches to create more comprehensive and effective treatment solutions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Industry Players
The PEMF therapy market is in a growth phase, with increasing integration into mainstream healthcare systems. The global market size is projected to expand significantly, driven by rising awareness of non-invasive treatment options. Technological maturity varies, with established players like Regenesis Biomedical and Medtronic offering advanced solutions, while newer entrants such as Galvanize Therapeutics and Humanity Neurotech are innovating in specific applications. Academic institutions like Yale University and the National University of Singapore are contributing to research advancements, potentially accelerating the technology's adoption in integrated health systems. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring medical device manufacturers, specialized PEMF companies, and research institutions, indicating a dynamic and evolving market with substantial growth potential.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical is pioneering advanced PEMF therapy systems for integrated health systems. Their technology utilizes precise electromagnetic pulses to stimulate cellular repair and regeneration. The company's flagship device, the Provant Therapy System, delivers targeted PEMF treatment for post-operative pain and edema reduction. Regenesis is also developing next-generation PEMF devices with smart sensors and AI-driven treatment protocols to optimize therapy for individual patients. Their research focuses on expanding PEMF applications to chronic conditions like osteoarthritis and diabetic neuropathy[1][3].
Strengths: Established track record in PEMF therapy, FDA-cleared devices, ongoing R&D for new applications. Weaknesses: Limited to specific medical indications, potential competition from larger medical device companies.
Medtronic AF Luxembourg SARL
Technical Solution: Medtronic, through its Luxembourg subsidiary, is investing in PEMF technology as part of its broader neurostimulation and pain management portfolio. The company is developing advanced PEMF systems that integrate with their existing neuromodulation platforms. Medtronic's approach combines PEMF with other therapies like spinal cord stimulation for enhanced pain relief. They are also exploring the use of PEMF in combination with their cardiac devices for potential cardiovascular applications. Medtronic's vast resources allow for extensive clinical trials to validate PEMF efficacy in various conditions[2][4].
Strengths: Global reach, substantial R&D budget, diverse medical device portfolio for potential synergies. Weaknesses: PEMF is not their primary focus, may face regulatory challenges in new applications.
PEMF Core Innovations
Treatment of conditions susceptible to pulsed electromagnetic field therapy
PatentActiveUS20170354830A1
Innovation
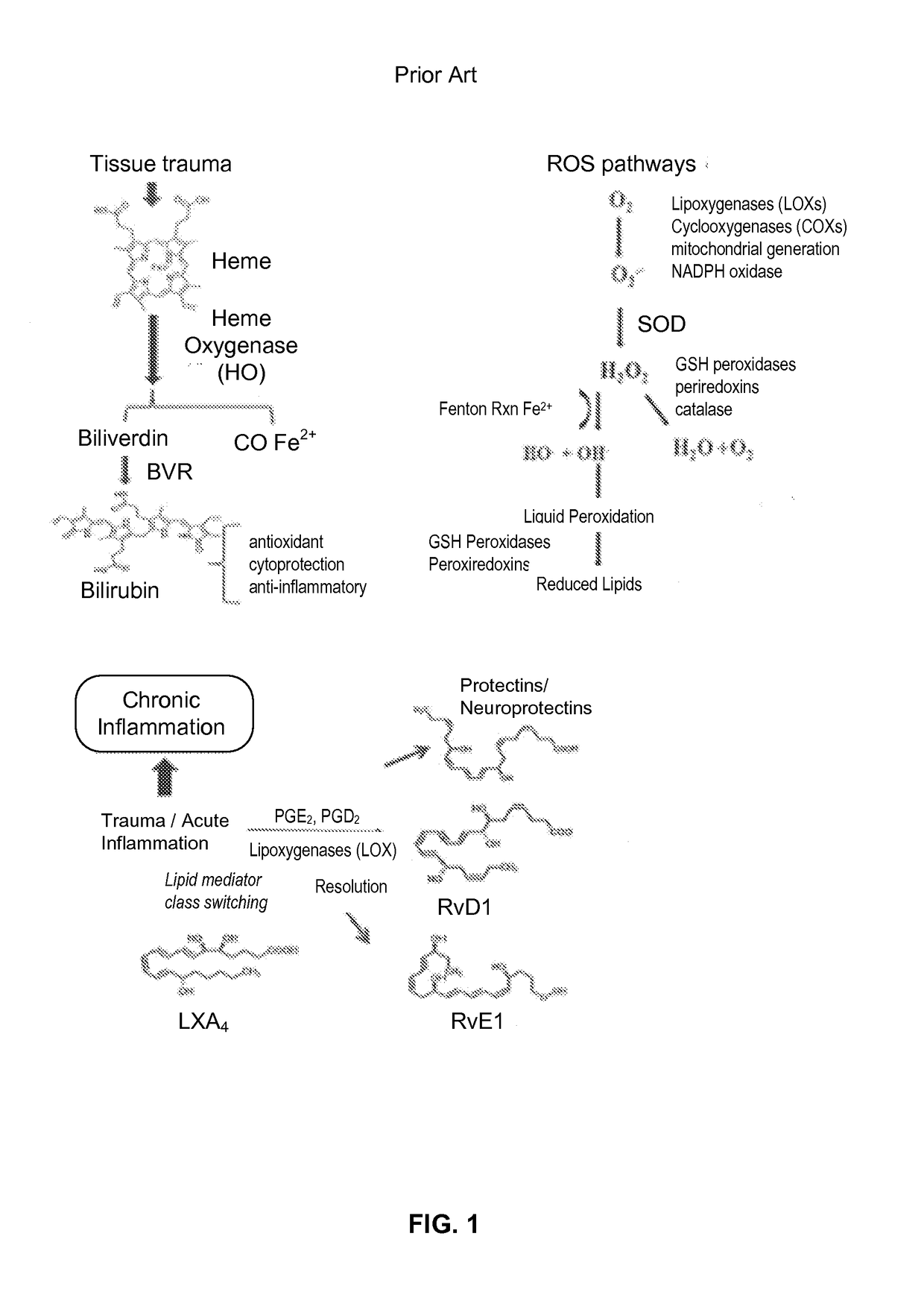
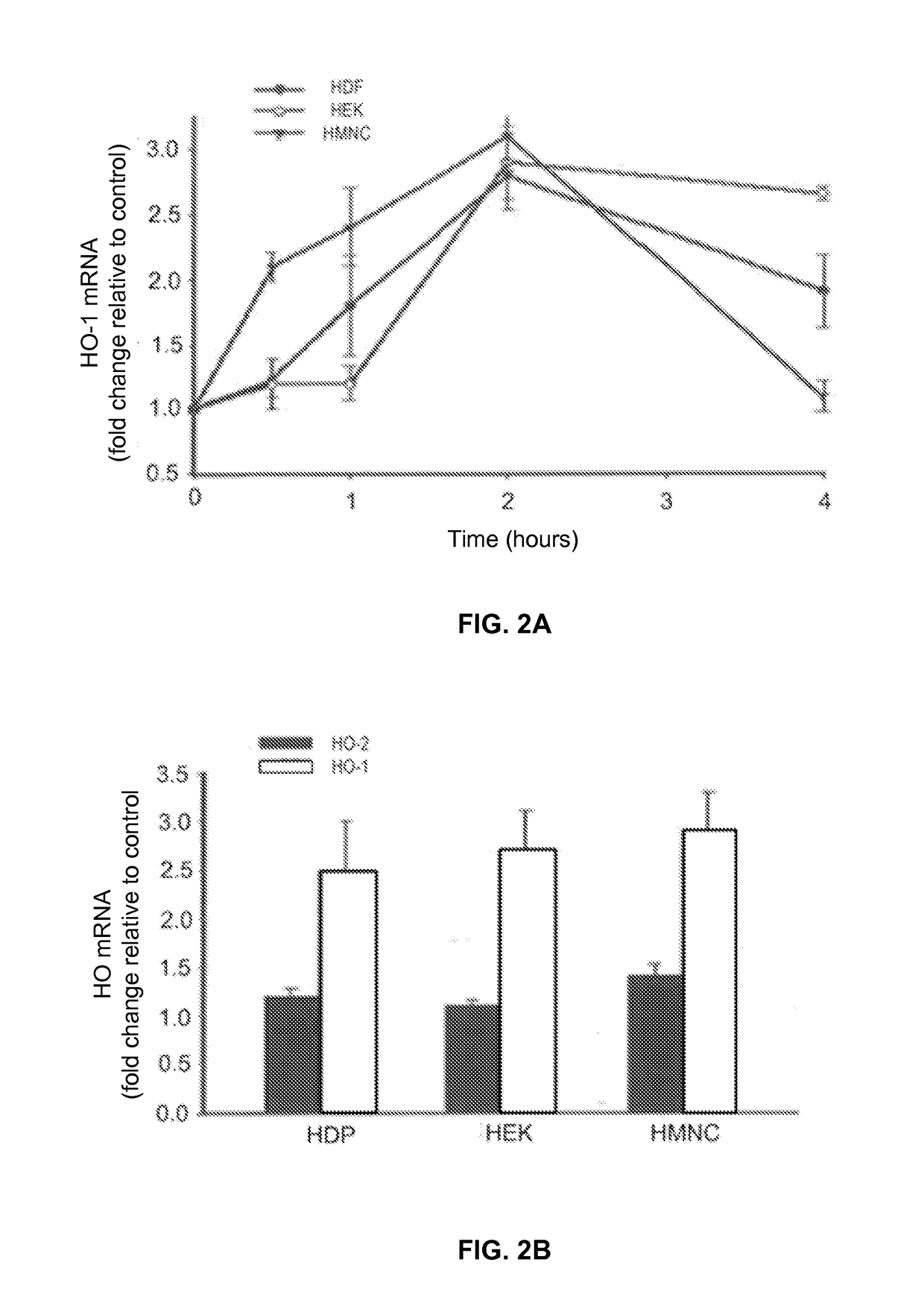
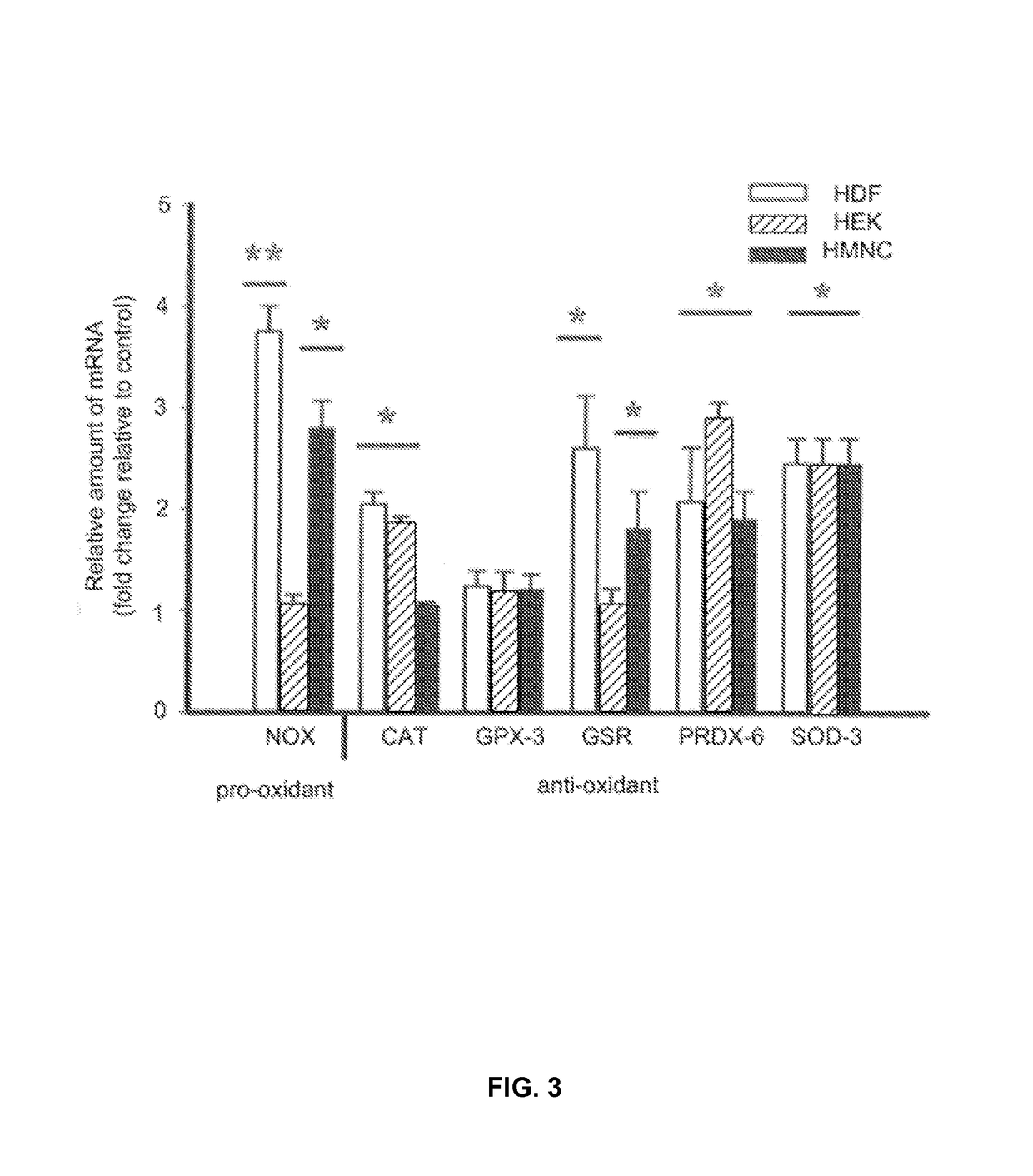
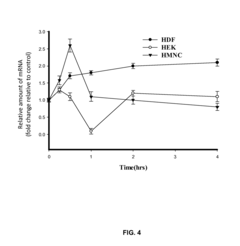
- PEMF therapy is administered to modulate gene expression associated with inflammation pathways, including heme oxygenase, antioxidant enzymes, lipid mediator biosynthesis, and cytokines, using specific parameters such as electric field strength, pulse rate, and duration to produce measurable clinical effects on pain, nerve function, and wound healing.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy Whole Body Wellness Device to increase cells energy, strengthen immune system and promote cell regeneration
PatentInactiveUS20190054308A1
Innovation
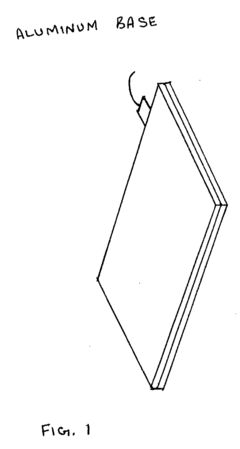
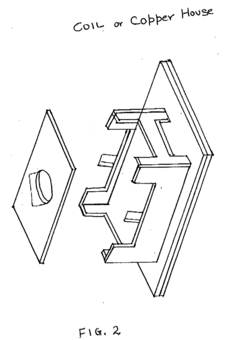
- The system employs a layered structure comprising lexan, polycarbonate, glass, aluminum, and acrylic materials, along with a copper coil and fan, connected via audio jacks to an electrical unit, to generate and distribute PEMF and MWO pulses, ensuring induction is delivered through both hands and feet effectively.
PEMF Integration Strategies
The integration of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy into existing health systems requires a multifaceted approach that addresses technological, clinical, and operational aspects. A key strategy involves the development of standardized PEMF protocols for various medical conditions, ensuring consistency in treatment delivery across different healthcare settings. This standardization will facilitate the incorporation of PEMF therapy into clinical guidelines and treatment pathways.
Collaboration between PEMF device manufacturers and healthcare providers is crucial for seamless integration. This partnership should focus on designing user-friendly interfaces and intuitive control systems that allow medical professionals to easily incorporate PEMF therapy into their practice. Additionally, the development of compact, portable PEMF devices will enable their use in various healthcare environments, from hospitals to outpatient clinics and home care settings.
Education and training programs for healthcare professionals are essential components of successful PEMF integration. These programs should cover the principles of PEMF therapy, its applications, and proper device operation. By enhancing the knowledge and skills of medical staff, healthcare organizations can ensure the effective and safe implementation of PEMF treatments.
The integration of PEMF therapy with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems is another critical strategy. This integration will allow for seamless documentation of PEMF treatments, tracking of patient outcomes, and facilitation of data-driven decision-making in patient care. Furthermore, the development of AI-powered PEMF treatment planning tools can assist healthcare providers in optimizing treatment parameters based on individual patient characteristics and treatment goals.
To address potential concerns about electromagnetic interference, healthcare facilities should implement comprehensive electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) management strategies. This includes conducting EMC assessments, establishing safe zones for PEMF therapy, and ensuring proper shielding of sensitive medical equipment.
Lastly, the development of reimbursement models and coding systems for PEMF therapy is crucial for its widespread adoption. Collaborating with insurance providers and regulatory bodies to establish clear guidelines for PEMF therapy coverage will encourage healthcare organizations to invest in this technology and integrate it into their service offerings.
By implementing these strategies, healthcare systems can effectively incorporate PEMF therapy into their existing infrastructure, potentially improving patient outcomes and expanding treatment options for various medical conditions.
Collaboration between PEMF device manufacturers and healthcare providers is crucial for seamless integration. This partnership should focus on designing user-friendly interfaces and intuitive control systems that allow medical professionals to easily incorporate PEMF therapy into their practice. Additionally, the development of compact, portable PEMF devices will enable their use in various healthcare environments, from hospitals to outpatient clinics and home care settings.
Education and training programs for healthcare professionals are essential components of successful PEMF integration. These programs should cover the principles of PEMF therapy, its applications, and proper device operation. By enhancing the knowledge and skills of medical staff, healthcare organizations can ensure the effective and safe implementation of PEMF treatments.
The integration of PEMF therapy with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems is another critical strategy. This integration will allow for seamless documentation of PEMF treatments, tracking of patient outcomes, and facilitation of data-driven decision-making in patient care. Furthermore, the development of AI-powered PEMF treatment planning tools can assist healthcare providers in optimizing treatment parameters based on individual patient characteristics and treatment goals.
To address potential concerns about electromagnetic interference, healthcare facilities should implement comprehensive electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) management strategies. This includes conducting EMC assessments, establishing safe zones for PEMF therapy, and ensuring proper shielding of sensitive medical equipment.
Lastly, the development of reimbursement models and coding systems for PEMF therapy is crucial for its widespread adoption. Collaborating with insurance providers and regulatory bodies to establish clear guidelines for PEMF therapy coverage will encourage healthcare organizations to invest in this technology and integrate it into their service offerings.
By implementing these strategies, healthcare systems can effectively incorporate PEMF therapy into their existing infrastructure, potentially improving patient outcomes and expanding treatment options for various medical conditions.
PEMF Safety Regulations
As the integration of PEMF therapy into mainstream healthcare systems continues to evolve, the development and implementation of comprehensive safety regulations become increasingly crucial. Current safety standards for PEMF devices primarily focus on electromagnetic field exposure limits and device manufacturing quality. However, future regulations are expected to address a broader range of concerns, including long-term effects, personalized treatment protocols, and integration with other medical technologies.
One key area of focus for future PEMF safety regulations is likely to be the establishment of standardized treatment protocols. This will involve defining optimal frequency ranges, intensity levels, and exposure durations for various medical conditions. Such standardization will not only enhance treatment efficacy but also minimize potential risks associated with improper use or overexposure.
Another important aspect of future safety regulations will be the development of more sophisticated monitoring systems. These systems will track patient responses to PEMF therapy in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments to treatment parameters if necessary. This adaptive approach will significantly enhance patient safety and treatment outcomes.
The integration of PEMF devices with other medical technologies and electronic health records (EHR) systems will also necessitate new safety protocols. Regulations will need to address data security, interoperability standards, and potential electromagnetic interference with other medical devices.
As PEMF therapy becomes more prevalent in home-use settings, future regulations will likely focus on ensuring safe and effective use by non-medical professionals. This may include mandatory user training programs, fail-safe mechanisms in devices, and remote monitoring capabilities for healthcare providers.
Lastly, as research into the long-term effects of PEMF therapy continues, regulations will need to evolve to address any newly discovered risks or benefits. This may involve periodic reassessment of safety standards and the establishment of long-term patient monitoring programs to detect any unforeseen effects.
In conclusion, the future of PEMF safety regulations in integrated health systems will likely be characterized by a more holistic, data-driven approach that balances the therapy's potential benefits with rigorous safety standards. This evolving regulatory landscape will play a crucial role in facilitating the widespread adoption of PEMF therapy while ensuring patient safety remains paramount.
One key area of focus for future PEMF safety regulations is likely to be the establishment of standardized treatment protocols. This will involve defining optimal frequency ranges, intensity levels, and exposure durations for various medical conditions. Such standardization will not only enhance treatment efficacy but also minimize potential risks associated with improper use or overexposure.
Another important aspect of future safety regulations will be the development of more sophisticated monitoring systems. These systems will track patient responses to PEMF therapy in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments to treatment parameters if necessary. This adaptive approach will significantly enhance patient safety and treatment outcomes.
The integration of PEMF devices with other medical technologies and electronic health records (EHR) systems will also necessitate new safety protocols. Regulations will need to address data security, interoperability standards, and potential electromagnetic interference with other medical devices.
As PEMF therapy becomes more prevalent in home-use settings, future regulations will likely focus on ensuring safe and effective use by non-medical professionals. This may include mandatory user training programs, fail-safe mechanisms in devices, and remote monitoring capabilities for healthcare providers.
Lastly, as research into the long-term effects of PEMF therapy continues, regulations will need to evolve to address any newly discovered risks or benefits. This may involve periodic reassessment of safety standards and the establishment of long-term patient monitoring programs to detect any unforeseen effects.
In conclusion, the future of PEMF safety regulations in integrated health systems will likely be characterized by a more holistic, data-driven approach that balances the therapy's potential benefits with rigorous safety standards. This evolving regulatory landscape will play a crucial role in facilitating the widespread adoption of PEMF therapy while ensuring patient safety remains paramount.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!