The Role of PEMF Therapy in Interdisciplinary Health Teams
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Therapy Evolution
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for bone healing, PEMF therapy has expanded its applications across various medical fields, demonstrating its potential in interdisciplinary health teams.
The early stages of PEMF therapy focused primarily on orthopedic applications, particularly in the treatment of non-union fractures. Researchers discovered that specific electromagnetic frequencies could stimulate bone growth and accelerate healing processes. This breakthrough led to the FDA approval of PEMF devices for bone healing in 1979, marking a significant milestone in the therapy's evolution.
As research progressed, the scope of PEMF therapy broadened to include soft tissue repair and pain management. In the 1990s, studies began to explore its efficacy in treating chronic pain conditions such as osteoarthritis and fibromyalgia. This expansion of applications highlighted the therapy's potential for addressing a wider range of health issues, paving the way for its integration into multidisciplinary treatment approaches.
The turn of the millennium saw a surge in PEMF research, with advancements in technology allowing for more precise and targeted treatments. Researchers began investigating the therapy's effects on cellular processes, including inflammation reduction, improved circulation, and enhanced tissue oxygenation. These findings opened up new possibilities for PEMF therapy in areas such as wound healing, neurological disorders, and even mental health.
In recent years, the evolution of PEMF therapy has been characterized by miniaturization and increased portability of devices. This development has made the therapy more accessible for home use and outpatient settings, facilitating its integration into comprehensive care plans. Additionally, the advent of wearable PEMF devices has enabled continuous treatment, potentially enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
The growing body of evidence supporting PEMF therapy's efficacy across multiple medical disciplines has led to its increased adoption in interdisciplinary health teams. Orthopedists, pain specialists, neurologists, and physical therapists are now collaborating to incorporate PEMF therapy into holistic treatment strategies. This interdisciplinary approach allows for more comprehensive patient care, addressing various aspects of health and well-being simultaneously.
As PEMF therapy continues to evolve, ongoing research is exploring its potential in emerging fields such as regenerative medicine and anti-aging therapies. The therapy's ability to influence cellular processes at a fundamental level suggests promising applications in these cutting-edge areas of healthcare. Furthermore, the integration of PEMF therapy with other complementary treatments, such as acupuncture and cognitive behavioral therapy, is being investigated to enhance overall treatment efficacy.
The early stages of PEMF therapy focused primarily on orthopedic applications, particularly in the treatment of non-union fractures. Researchers discovered that specific electromagnetic frequencies could stimulate bone growth and accelerate healing processes. This breakthrough led to the FDA approval of PEMF devices for bone healing in 1979, marking a significant milestone in the therapy's evolution.
As research progressed, the scope of PEMF therapy broadened to include soft tissue repair and pain management. In the 1990s, studies began to explore its efficacy in treating chronic pain conditions such as osteoarthritis and fibromyalgia. This expansion of applications highlighted the therapy's potential for addressing a wider range of health issues, paving the way for its integration into multidisciplinary treatment approaches.
The turn of the millennium saw a surge in PEMF research, with advancements in technology allowing for more precise and targeted treatments. Researchers began investigating the therapy's effects on cellular processes, including inflammation reduction, improved circulation, and enhanced tissue oxygenation. These findings opened up new possibilities for PEMF therapy in areas such as wound healing, neurological disorders, and even mental health.
In recent years, the evolution of PEMF therapy has been characterized by miniaturization and increased portability of devices. This development has made the therapy more accessible for home use and outpatient settings, facilitating its integration into comprehensive care plans. Additionally, the advent of wearable PEMF devices has enabled continuous treatment, potentially enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
The growing body of evidence supporting PEMF therapy's efficacy across multiple medical disciplines has led to its increased adoption in interdisciplinary health teams. Orthopedists, pain specialists, neurologists, and physical therapists are now collaborating to incorporate PEMF therapy into holistic treatment strategies. This interdisciplinary approach allows for more comprehensive patient care, addressing various aspects of health and well-being simultaneously.
As PEMF therapy continues to evolve, ongoing research is exploring its potential in emerging fields such as regenerative medicine and anti-aging therapies. The therapy's ability to influence cellular processes at a fundamental level suggests promising applications in these cutting-edge areas of healthcare. Furthermore, the integration of PEMF therapy with other complementary treatments, such as acupuncture and cognitive behavioral therapy, is being investigated to enhance overall treatment efficacy.
Healthcare Integration
The integration of PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy into interdisciplinary health teams represents a significant advancement in healthcare delivery. This approach combines the expertise of various healthcare professionals with the potential benefits of PEMF therapy, creating a more comprehensive and patient-centered treatment model. Interdisciplinary teams typically include physicians, nurses, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and other specialists who collaborate to address complex health issues.
PEMF therapy, known for its potential to promote cellular repair and reduce inflammation, can complement traditional medical treatments across multiple disciplines. In pain management, for instance, PEMF therapy may be used alongside pharmacological interventions and physical therapy to provide a multi-faceted approach to chronic pain relief. This integration allows for a more holistic treatment plan that addresses both the symptoms and underlying causes of pain.
In rehabilitation settings, PEMF therapy can be incorporated into post-surgical recovery protocols or injury treatment plans. Physical therapists and occupational therapists may utilize PEMF devices to enhance tissue healing and reduce recovery time, while simultaneously applying their expertise in movement and functional restoration. This synergy between PEMF therapy and traditional rehabilitation techniques can potentially lead to improved patient outcomes and faster return to normal activities.
The integration of PEMF therapy also extends to mental health treatment. Psychiatrists and psychologists may explore the use of PEMF therapy as an adjunct to conventional treatments for conditions such as depression and anxiety. The potential of PEMF to modulate brain activity and neurotransmitter levels offers an additional tool in the mental health professional's arsenal, potentially enhancing the efficacy of psychotherapy and medication-based treatments.
Furthermore, the incorporation of PEMF therapy into interdisciplinary teams can foster innovation in treatment protocols. As healthcare professionals from different specialties collaborate and share their observations on the effects of PEMF therapy, new applications and treatment combinations may emerge. This cross-pollination of ideas can lead to the development of novel therapeutic approaches that leverage the strengths of both PEMF technology and traditional medical practices.
However, the successful integration of PEMF therapy into interdisciplinary health teams requires careful coordination and education. Team members must be trained in the proper application of PEMF therapy, its potential benefits, and its limitations. Regular communication and case conferences among team members are essential to ensure that PEMF therapy is appropriately incorporated into each patient's treatment plan and that its effects are monitored and evaluated in conjunction with other interventions.
PEMF therapy, known for its potential to promote cellular repair and reduce inflammation, can complement traditional medical treatments across multiple disciplines. In pain management, for instance, PEMF therapy may be used alongside pharmacological interventions and physical therapy to provide a multi-faceted approach to chronic pain relief. This integration allows for a more holistic treatment plan that addresses both the symptoms and underlying causes of pain.
In rehabilitation settings, PEMF therapy can be incorporated into post-surgical recovery protocols or injury treatment plans. Physical therapists and occupational therapists may utilize PEMF devices to enhance tissue healing and reduce recovery time, while simultaneously applying their expertise in movement and functional restoration. This synergy between PEMF therapy and traditional rehabilitation techniques can potentially lead to improved patient outcomes and faster return to normal activities.
The integration of PEMF therapy also extends to mental health treatment. Psychiatrists and psychologists may explore the use of PEMF therapy as an adjunct to conventional treatments for conditions such as depression and anxiety. The potential of PEMF to modulate brain activity and neurotransmitter levels offers an additional tool in the mental health professional's arsenal, potentially enhancing the efficacy of psychotherapy and medication-based treatments.
Furthermore, the incorporation of PEMF therapy into interdisciplinary teams can foster innovation in treatment protocols. As healthcare professionals from different specialties collaborate and share their observations on the effects of PEMF therapy, new applications and treatment combinations may emerge. This cross-pollination of ideas can lead to the development of novel therapeutic approaches that leverage the strengths of both PEMF technology and traditional medical practices.
However, the successful integration of PEMF therapy into interdisciplinary health teams requires careful coordination and education. Team members must be trained in the proper application of PEMF therapy, its potential benefits, and its limitations. Regular communication and case conferences among team members are essential to ensure that PEMF therapy is appropriately incorporated into each patient's treatment plan and that its effects are monitored and evaluated in conjunction with other interventions.
Technical Challenges
PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy, while promising, faces several technical challenges in its integration into interdisciplinary health teams. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardization in PEMF devices and treatment protocols. The wide variety of devices available, each with different frequencies, intensities, and waveforms, makes it difficult to establish consistent treatment guidelines across different healthcare disciplines.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms of action of PEMF therapy at the cellular and molecular levels. While studies have shown positive effects on various physiological processes, the exact pathways through which PEMF influences cellular function and tissue repair remain incompletely understood. This knowledge gap hinders the development of targeted therapies and the optimization of treatment parameters for specific health conditions.
The dosimetry of PEMF therapy also presents technical difficulties. Determining the optimal dose, duration, and frequency of treatments for different health conditions and individual patients is complex. The lack of standardized dosing protocols makes it challenging for healthcare professionals from various disciplines to confidently prescribe and administer PEMF therapy as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Furthermore, the integration of PEMF devices with existing medical equipment and electronic health record systems poses technical hurdles. Ensuring compatibility and seamless data exchange between PEMF devices and other medical technologies used by interdisciplinary teams is crucial for effective patient care and treatment monitoring.
The long-term effects and potential interactions of PEMF therapy with other treatments and medications are not fully elucidated. This uncertainty creates challenges in developing comprehensive treatment plans that incorporate PEMF therapy alongside other interventions commonly used by interdisciplinary health teams.
Additionally, the development of portable, user-friendly PEMF devices suitable for home use presents technical challenges. Creating devices that are both effective and safe for patients to use independently, while still allowing for remote monitoring by healthcare professionals, requires advanced engineering and design solutions.
Lastly, the need for more robust clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF therapy across various health conditions remains a significant challenge. While some studies have shown promising results, the lack of large-scale, randomized controlled trials in many areas limits the widespread acceptance and integration of PEMF therapy into standard care protocols used by interdisciplinary health teams.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms of action of PEMF therapy at the cellular and molecular levels. While studies have shown positive effects on various physiological processes, the exact pathways through which PEMF influences cellular function and tissue repair remain incompletely understood. This knowledge gap hinders the development of targeted therapies and the optimization of treatment parameters for specific health conditions.
The dosimetry of PEMF therapy also presents technical difficulties. Determining the optimal dose, duration, and frequency of treatments for different health conditions and individual patients is complex. The lack of standardized dosing protocols makes it challenging for healthcare professionals from various disciplines to confidently prescribe and administer PEMF therapy as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Furthermore, the integration of PEMF devices with existing medical equipment and electronic health record systems poses technical hurdles. Ensuring compatibility and seamless data exchange between PEMF devices and other medical technologies used by interdisciplinary teams is crucial for effective patient care and treatment monitoring.
The long-term effects and potential interactions of PEMF therapy with other treatments and medications are not fully elucidated. This uncertainty creates challenges in developing comprehensive treatment plans that incorporate PEMF therapy alongside other interventions commonly used by interdisciplinary health teams.
Additionally, the development of portable, user-friendly PEMF devices suitable for home use presents technical challenges. Creating devices that are both effective and safe for patients to use independently, while still allowing for remote monitoring by healthcare professionals, requires advanced engineering and design solutions.
Lastly, the need for more robust clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF therapy across various health conditions remains a significant challenge. While some studies have shown promising results, the lack of large-scale, randomized controlled trials in many areas limits the widespread acceptance and integration of PEMF therapy into standard care protocols used by interdisciplinary health teams.
Current PEMF Solutions
01 PEMF devices for therapeutic applications
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices are designed for various therapeutic applications. These devices generate electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular activity and promote healing. They can be used for pain management, tissue repair, and improving overall well-being.- PEMF devices for therapeutic applications: Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices are designed for various therapeutic applications. These devices generate electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and regeneration, potentially treating conditions such as pain, inflammation, and bone healing. The devices can be configured for different body parts and treatment protocols.
- PEMF therapy for pain management and tissue healing: PEMF therapy is utilized for pain management and tissue healing. The electromagnetic fields generated by PEMF devices can help reduce pain, improve circulation, and accelerate the healing process of various tissues, including bones, muscles, and soft tissues. This non-invasive treatment approach is applied to conditions such as arthritis, fractures, and chronic pain syndromes.
- Combination of PEMF with other therapies: PEMF therapy is often combined with other treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic outcomes. This may include integration with light therapy, heat therapy, or other forms of electromagnetic stimulation. The synergistic effects of these combinations can potentially improve treatment efficacy for various health conditions.
- PEMF technology advancements and device designs: Ongoing advancements in PEMF technology focus on improving device designs, treatment protocols, and user experience. This includes the development of portable and wearable PEMF devices, smart control systems, and customizable treatment programs. These innovations aim to enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of PEMF therapy for various applications.
- PEMF applications in veterinary and agricultural fields: PEMF therapy is expanding into veterinary medicine and agriculture. In veterinary applications, it is used for treating animals with conditions similar to those in humans, such as joint pain and wound healing. In agriculture, PEMF technology is explored for potential benefits in plant growth, crop yield improvement, and pest control.
02 PEMF therapy for specific medical conditions
PEMF therapy is utilized to treat specific medical conditions. It has shown efficacy in managing chronic pain, reducing inflammation, accelerating bone healing, and improving circulation. The therapy can be tailored to address various health issues by adjusting the frequency and intensity of the electromagnetic fields.Expand Specific Solutions03 Portable and wearable PEMF devices
Advancements in PEMF technology have led to the development of portable and wearable devices. These compact units allow for convenient at-home use or on-the-go treatments. Wearable PEMF devices can be integrated into clothing or accessories, enabling continuous therapy throughout the day.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination of PEMF with other therapies
PEMF therapy is often combined with other treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic outcomes. This may include integration with light therapy, heat therapy, or other forms of electromagnetic stimulation. The synergistic effects of combined therapies can potentially improve treatment efficacy for various conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 PEMF technology advancements and control systems
Ongoing research focuses on improving PEMF technology and control systems. This includes developing more precise field generation methods, optimizing treatment protocols, and creating user-friendly interfaces. Advanced control systems allow for personalized therapy settings and treatment tracking.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Manufacturers
The field of PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy in interdisciplinary health teams is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global PEMF therapy market is expanding due to rising awareness of non-invasive treatment options and growing applications in pain management and rehabilitation. Companies like Regenesis Biomedical, SofPulse, and Venus Concept are at the forefront, developing innovative PEMF devices and systems. The technology's maturity is progressing, with established players like Medtronic and emerging companies such as Galvanize Therapeutics contributing to its evolution. As interdisciplinary health teams increasingly adopt PEMF therapy, collaboration between medical device manufacturers, healthcare providers, and research institutions is driving further advancements in this promising field.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical specializes in PEMF therapy devices for wound healing and pain management. Their Provant Therapy System utilizes a proprietary pulsed electromagnetic field technology that operates at 27.12 MHz[1]. This frequency is believed to stimulate cellular repair and reduce inflammation. The device is designed for easy integration into clinical settings, allowing for non-invasive treatment sessions lasting 30 minutes, which can be administered twice daily[2]. The technology aims to accelerate tissue repair by enhancing mitochondrial function and promoting the body's natural healing processes.
Strengths: FDA-cleared technology, non-invasive treatment, easy integration into clinical workflows. Weaknesses: Limited to specific frequency, may require multiple daily treatments for optimal results.
SofPulse, Inc.
Technical Solution: SofPulse has developed a portable PEMF therapy device specifically designed for post-operative pain management and edema reduction. Their technology utilizes targeted electromagnetic field pulses at a frequency of 27.12 MHz, similar to Regenesis[3]. However, SofPulse's device is uniquely designed for wearable application, allowing for continuous treatment. The device delivers short treatment cycles of 15 minutes every 2 hours, automatically repeating throughout the day[4]. This approach aims to provide consistent anti-inflammatory effects and pain relief without the need for constant user intervention, making it particularly suitable for post-surgical recovery in both clinical and home settings.
Strengths: Wearable design for continuous treatment, automated cycling for consistent therapy. Weaknesses: May be limited to post-operative applications, potential for user compliance issues in home settings.
PEMF Research Insights
A pulsed electromagnetic field apparatus and method for generating frequencies
PatentWO2024127242A1
Innovation
- A PEMF apparatus with a pulse generator and electromagnetic field generation means that uses modified sawtooth waveforms with pre-stress and relaxation periods, and quasi-sine signals with pulse width modulation, along with a feedback circuit for frequency stability and precision, and a bifilar antenna for scalar wave generation.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy Whole Body Wellness Device to increase cells energy, strengthen immune system and promote cell regeneration
PatentInactiveUS20190054308A1
Innovation
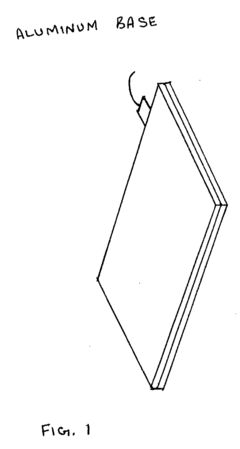
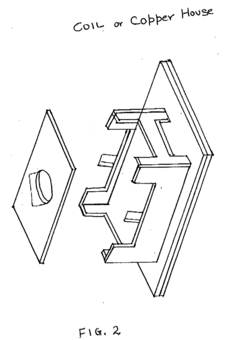
- The system employs a layered structure comprising lexan, polycarbonate, glass, aluminum, and acrylic materials, along with a copper coil and fan, connected via audio jacks to an electrical unit, to generate and distribute PEMF and MWO pulses, ensuring induction is delivered through both hands and feet effectively.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy in interdisciplinary health teams is complex and multifaceted, involving various governing bodies and standards. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating PEMF devices. These devices are typically classified as Class II medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) clearance before they can be legally marketed and sold.
The FDA has established specific guidelines for PEMF devices, including requirements for safety, effectiveness, and labeling. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their devices are substantially equivalent to predicate devices already on the market. This process involves submitting detailed technical documentation, clinical data, and risk assessments to the FDA for review.
Internationally, regulatory approaches to PEMF therapy vary. The European Union, for instance, regulates PEMF devices under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into effect in May 2021. This regulation imposes stricter requirements on manufacturers, including enhanced clinical evidence and post-market surveillance.
In the context of interdisciplinary health teams, the use of PEMF therapy must comply with professional practice guidelines and standards of care. Healthcare providers incorporating PEMF therapy into their practice must ensure they are operating within their scope of practice and adhering to relevant professional codes of conduct.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses reimbursement policies for PEMF therapy. In many jurisdictions, insurance coverage for PEMF treatments remains limited, with policies varying widely among private insurers and public health systems. This inconsistency in reimbursement can impact the integration of PEMF therapy into interdisciplinary care models.
As PEMF therapy gains traction in various medical fields, regulatory bodies are continually reassessing their approaches. There is an ongoing need for updated guidelines that address the evolving applications of PEMF technology, particularly in interdisciplinary settings. This includes considerations for combination therapies, where PEMF is used alongside other treatment modalities.
The regulatory framework also extends to the manufacturing and quality control processes for PEMF devices. Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations, ensuring consistent product quality and safety. This is particularly crucial for devices used in clinical settings by interdisciplinary teams, where reliability and consistency are paramount.
The FDA has established specific guidelines for PEMF devices, including requirements for safety, effectiveness, and labeling. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their devices are substantially equivalent to predicate devices already on the market. This process involves submitting detailed technical documentation, clinical data, and risk assessments to the FDA for review.
Internationally, regulatory approaches to PEMF therapy vary. The European Union, for instance, regulates PEMF devices under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into effect in May 2021. This regulation imposes stricter requirements on manufacturers, including enhanced clinical evidence and post-market surveillance.
In the context of interdisciplinary health teams, the use of PEMF therapy must comply with professional practice guidelines and standards of care. Healthcare providers incorporating PEMF therapy into their practice must ensure they are operating within their scope of practice and adhering to relevant professional codes of conduct.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses reimbursement policies for PEMF therapy. In many jurisdictions, insurance coverage for PEMF treatments remains limited, with policies varying widely among private insurers and public health systems. This inconsistency in reimbursement can impact the integration of PEMF therapy into interdisciplinary care models.
As PEMF therapy gains traction in various medical fields, regulatory bodies are continually reassessing their approaches. There is an ongoing need for updated guidelines that address the evolving applications of PEMF technology, particularly in interdisciplinary settings. This includes considerations for combination therapies, where PEMF is used alongside other treatment modalities.
The regulatory framework also extends to the manufacturing and quality control processes for PEMF devices. Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations, ensuring consistent product quality and safety. This is particularly crucial for devices used in clinical settings by interdisciplinary teams, where reliability and consistency are paramount.
Interdisciplinary Impact
PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy has emerged as a versatile and promising treatment modality that can significantly enhance the effectiveness of interdisciplinary health teams. By integrating PEMF therapy into various healthcare disciplines, teams can achieve more comprehensive and holistic patient care, leading to improved outcomes and patient satisfaction.
In the context of interdisciplinary health teams, PEMF therapy serves as a bridge between different medical specialties. For instance, in pain management, PEMF can complement traditional pharmacological approaches by offering a non-invasive, drug-free alternative. This allows pain specialists to work closely with physical therapists and rehabilitation experts to develop more effective treatment plans that address both immediate pain relief and long-term functional improvement.
The integration of PEMF therapy in orthopedics and sports medicine has fostered closer collaboration between surgeons, physiotherapists, and athletic trainers. By incorporating PEMF treatments into pre- and post-operative care protocols, teams can potentially accelerate healing, reduce inflammation, and improve overall recovery times. This collaborative approach enables a more seamless transition from surgical intervention to rehabilitation and return to activity.
In the field of neurology, PEMF therapy has shown promise in addressing various neurological conditions. Its application in this domain encourages neurologists to work more closely with occupational therapists and mental health professionals. This interdisciplinary approach can lead to more comprehensive treatment strategies for conditions such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive disorders, addressing both the neurological and psychological aspects of these conditions.
The versatility of PEMF therapy also extends to its potential applications in wound care and dermatology. By incorporating PEMF treatments into wound healing protocols, interdisciplinary teams comprising wound care specialists, dermatologists, and nurses can develop more effective strategies for managing chronic wounds and skin conditions. This collaboration can lead to faster healing times and improved patient outcomes.
Furthermore, the integration of PEMF therapy in geriatric care has fostered a more holistic approach to managing age-related conditions. Geriatricians, working alongside physical therapists, occupational therapists, and nutritionists, can utilize PEMF therapy to address multiple aspects of elderly health, including bone health, mobility, and cognitive function. This comprehensive approach can significantly enhance the quality of life for older patients and promote healthy aging.
In the context of interdisciplinary health teams, PEMF therapy serves as a bridge between different medical specialties. For instance, in pain management, PEMF can complement traditional pharmacological approaches by offering a non-invasive, drug-free alternative. This allows pain specialists to work closely with physical therapists and rehabilitation experts to develop more effective treatment plans that address both immediate pain relief and long-term functional improvement.
The integration of PEMF therapy in orthopedics and sports medicine has fostered closer collaboration between surgeons, physiotherapists, and athletic trainers. By incorporating PEMF treatments into pre- and post-operative care protocols, teams can potentially accelerate healing, reduce inflammation, and improve overall recovery times. This collaborative approach enables a more seamless transition from surgical intervention to rehabilitation and return to activity.
In the field of neurology, PEMF therapy has shown promise in addressing various neurological conditions. Its application in this domain encourages neurologists to work more closely with occupational therapists and mental health professionals. This interdisciplinary approach can lead to more comprehensive treatment strategies for conditions such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive disorders, addressing both the neurological and psychological aspects of these conditions.
The versatility of PEMF therapy also extends to its potential applications in wound care and dermatology. By incorporating PEMF treatments into wound healing protocols, interdisciplinary teams comprising wound care specialists, dermatologists, and nurses can develop more effective strategies for managing chronic wounds and skin conditions. This collaboration can lead to faster healing times and improved patient outcomes.
Furthermore, the integration of PEMF therapy in geriatric care has fostered a more holistic approach to managing age-related conditions. Geriatricians, working alongside physical therapists, occupational therapists, and nutritionists, can utilize PEMF therapy to address multiple aspects of elderly health, including bone health, mobility, and cognitive function. This comprehensive approach can significantly enhance the quality of life for older patients and promote healthy aging.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!