PEMF Therapy: A Pathway to Enhanced Functional Capabilities
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Technology Evolution
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for bone healing, PEMF technology has expanded its applications across various medical fields. The evolution of PEMF technology can be traced through several key phases, each marked by advancements in device design, treatment protocols, and scientific understanding.
In the 1950s, the foundational work of Fukada and Yasuda established the piezoelectric properties of bone, laying the groundwork for PEMF therapy. This discovery led to the development of the first PEMF devices in the 1970s, primarily used for non-union fracture healing. These early devices were large, stationary, and limited in their application scope.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a surge in PEMF research, expanding its potential beyond bone healing. Scientists began exploring its effects on soft tissue repair, pain management, and neurological conditions. This period also marked the miniaturization of PEMF devices, making them more portable and accessible for home use.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era in PEMF technology. Advanced materials and improved electromagnetic field generation techniques allowed for more precise and targeted therapies. The introduction of pulsed radiofrequency electromagnetic field (PREF) therapy further refined the technology, offering higher frequencies and potentially greater therapeutic effects.
In recent years, PEMF technology has seen integration with other therapeutic modalities. Combination therapies, such as PEMF with photobiomodulation or electrical stimulation, have emerged, aiming to synergize treatment effects. Additionally, the advent of wearable technology has led to the development of PEMF devices that can be worn continuously, potentially enhancing treatment efficacy through prolonged exposure.
The latest frontier in PEMF evolution involves personalized medicine approaches. Researchers are now exploring ways to tailor PEMF parameters to individual patient needs, considering factors such as specific conditions, genetic profiles, and real-time physiological feedback. This personalization aims to optimize treatment outcomes and minimize potential side effects.
As PEMF technology continues to evolve, ongoing research focuses on refining treatment protocols, expanding applications, and improving device efficiency. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms promises to further enhance PEMF therapy's precision and effectiveness, potentially opening new avenues for treating a wider range of health conditions and enhancing functional capabilities.
In the 1950s, the foundational work of Fukada and Yasuda established the piezoelectric properties of bone, laying the groundwork for PEMF therapy. This discovery led to the development of the first PEMF devices in the 1970s, primarily used for non-union fracture healing. These early devices were large, stationary, and limited in their application scope.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a surge in PEMF research, expanding its potential beyond bone healing. Scientists began exploring its effects on soft tissue repair, pain management, and neurological conditions. This period also marked the miniaturization of PEMF devices, making them more portable and accessible for home use.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new era in PEMF technology. Advanced materials and improved electromagnetic field generation techniques allowed for more precise and targeted therapies. The introduction of pulsed radiofrequency electromagnetic field (PREF) therapy further refined the technology, offering higher frequencies and potentially greater therapeutic effects.
In recent years, PEMF technology has seen integration with other therapeutic modalities. Combination therapies, such as PEMF with photobiomodulation or electrical stimulation, have emerged, aiming to synergize treatment effects. Additionally, the advent of wearable technology has led to the development of PEMF devices that can be worn continuously, potentially enhancing treatment efficacy through prolonged exposure.
The latest frontier in PEMF evolution involves personalized medicine approaches. Researchers are now exploring ways to tailor PEMF parameters to individual patient needs, considering factors such as specific conditions, genetic profiles, and real-time physiological feedback. This personalization aims to optimize treatment outcomes and minimize potential side effects.
As PEMF technology continues to evolve, ongoing research focuses on refining treatment protocols, expanding applications, and improving device efficiency. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms promises to further enhance PEMF therapy's precision and effectiveness, potentially opening new avenues for treating a wider range of health conditions and enhancing functional capabilities.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of its potential benefits and a growing emphasis on non-invasive treatment options. This therapy, which uses electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and enhance overall health, has found applications in various medical fields, including orthopedics, neurology, and sports medicine.
The global PEMF therapy devices market is experiencing significant expansion, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to remain strong over the next decade. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, an aging population, and the increasing adoption of alternative therapies for pain management and rehabilitation.
One of the key drivers of market demand is the growing interest in non-pharmacological approaches to pain management and healing. As concerns about opioid addiction and the side effects of long-term medication use continue to rise, patients and healthcare providers are increasingly turning to PEMF therapy as a safe and effective alternative. This trend is particularly evident in the treatment of conditions such as osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic lower back pain.
The sports medicine sector represents another significant area of market growth for PEMF therapy. Professional athletes and sports teams are increasingly incorporating PEMF devices into their training and recovery regimens, recognizing the therapy's potential to accelerate healing, reduce inflammation, and improve overall performance. This high-profile adoption is likely to drive further interest and demand among amateur athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
In the realm of neurological disorders, PEMF therapy is gaining traction as a complementary treatment for conditions such as depression, anxiety, and insomnia. As mental health awareness continues to grow globally, the demand for non-invasive, drug-free treatment options is expected to fuel further market expansion in this area.
The home healthcare segment is emerging as a particularly promising market for PEMF therapy devices. The increasing availability of portable, user-friendly PEMF devices for personal use is making the therapy more accessible to a broader consumer base. This trend is likely to accelerate, driven by the growing preference for home-based treatments and the rising adoption of wearable health technologies.
Geographically, North America currently leads the PEMF therapy market, followed by Europe. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure, growing awareness of alternative therapies, and the large patient population in countries like China and India.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in fully realizing the market potential of PEMF therapy. These include the need for more extensive clinical research to validate its efficacy across various applications, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and the relatively high cost of advanced PEMF devices. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for sustaining the long-term growth trajectory of the PEMF therapy market.
The global PEMF therapy devices market is experiencing significant expansion, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to remain strong over the next decade. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, an aging population, and the increasing adoption of alternative therapies for pain management and rehabilitation.
One of the key drivers of market demand is the growing interest in non-pharmacological approaches to pain management and healing. As concerns about opioid addiction and the side effects of long-term medication use continue to rise, patients and healthcare providers are increasingly turning to PEMF therapy as a safe and effective alternative. This trend is particularly evident in the treatment of conditions such as osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic lower back pain.
The sports medicine sector represents another significant area of market growth for PEMF therapy. Professional athletes and sports teams are increasingly incorporating PEMF devices into their training and recovery regimens, recognizing the therapy's potential to accelerate healing, reduce inflammation, and improve overall performance. This high-profile adoption is likely to drive further interest and demand among amateur athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
In the realm of neurological disorders, PEMF therapy is gaining traction as a complementary treatment for conditions such as depression, anxiety, and insomnia. As mental health awareness continues to grow globally, the demand for non-invasive, drug-free treatment options is expected to fuel further market expansion in this area.
The home healthcare segment is emerging as a particularly promising market for PEMF therapy devices. The increasing availability of portable, user-friendly PEMF devices for personal use is making the therapy more accessible to a broader consumer base. This trend is likely to accelerate, driven by the growing preference for home-based treatments and the rising adoption of wearable health technologies.
Geographically, North America currently leads the PEMF therapy market, followed by Europe. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure, growing awareness of alternative therapies, and the large patient population in countries like China and India.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in fully realizing the market potential of PEMF therapy. These include the need for more extensive clinical research to validate its efficacy across various applications, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and the relatively high cost of advanced PEMF devices. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for sustaining the long-term growth trajectory of the PEMF therapy market.
Current PEMF Challenges
Despite the promising potential of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy, several challenges currently hinder its widespread adoption and efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardization in PEMF devices and treatment protocols. The wide variety of available devices, each with different frequencies, intensities, and waveforms, makes it difficult for healthcare providers to determine the most effective treatment parameters for specific conditions.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which PEMF therapy influences cellular function and tissue repair. While numerous studies have demonstrated positive outcomes, the underlying biological processes remain incompletely elucidated. This knowledge gap hampers the development of more targeted and efficient PEMF therapies.
The inconsistency in research methodologies and reporting standards across PEMF studies poses a substantial obstacle to drawing definitive conclusions about its efficacy. Many studies suffer from small sample sizes, inadequate control groups, or insufficient follow-up periods, leading to skepticism within the medical community and regulatory bodies.
Regulatory hurdles present another challenge for PEMF therapy. The classification and approval processes for PEMF devices vary across different countries, creating a complex landscape for manufacturers and limiting global market access. In some regions, PEMF devices are classified as medical devices requiring rigorous clinical trials, while in others, they may be considered wellness products with less stringent regulations.
The high cost of advanced PEMF devices and treatments is a significant barrier to accessibility for many patients. Insurance coverage for PEMF therapy is often limited or non-existent, further restricting its adoption in mainstream healthcare settings.
There is also a notable lack of long-term safety data for PEMF therapy, particularly concerning its effects on various patient populations, such as pregnant women, children, or individuals with implanted electronic devices. This gap in safety information raises concerns among healthcare providers and patients alike.
Lastly, the integration of PEMF therapy into existing healthcare practices and treatment protocols remains a challenge. Many healthcare professionals are unfamiliar with PEMF technology or skeptical of its benefits, leading to slow adoption rates in clinical settings. Overcoming this resistance requires extensive education and training programs for healthcare providers, as well as more robust clinical evidence to support PEMF's efficacy across various medical conditions.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which PEMF therapy influences cellular function and tissue repair. While numerous studies have demonstrated positive outcomes, the underlying biological processes remain incompletely elucidated. This knowledge gap hampers the development of more targeted and efficient PEMF therapies.
The inconsistency in research methodologies and reporting standards across PEMF studies poses a substantial obstacle to drawing definitive conclusions about its efficacy. Many studies suffer from small sample sizes, inadequate control groups, or insufficient follow-up periods, leading to skepticism within the medical community and regulatory bodies.
Regulatory hurdles present another challenge for PEMF therapy. The classification and approval processes for PEMF devices vary across different countries, creating a complex landscape for manufacturers and limiting global market access. In some regions, PEMF devices are classified as medical devices requiring rigorous clinical trials, while in others, they may be considered wellness products with less stringent regulations.
The high cost of advanced PEMF devices and treatments is a significant barrier to accessibility for many patients. Insurance coverage for PEMF therapy is often limited or non-existent, further restricting its adoption in mainstream healthcare settings.
There is also a notable lack of long-term safety data for PEMF therapy, particularly concerning its effects on various patient populations, such as pregnant women, children, or individuals with implanted electronic devices. This gap in safety information raises concerns among healthcare providers and patients alike.
Lastly, the integration of PEMF therapy into existing healthcare practices and treatment protocols remains a challenge. Many healthcare professionals are unfamiliar with PEMF technology or skeptical of its benefits, leading to slow adoption rates in clinical settings. Overcoming this resistance requires extensive education and training programs for healthcare providers, as well as more robust clinical evidence to support PEMF's efficacy across various medical conditions.
PEMF Treatment Protocols
01 Pain management and tissue healing
PEMF therapy is utilized for managing pain and promoting tissue healing. It can reduce inflammation, accelerate wound healing, and alleviate various types of pain, including chronic and acute conditions. The therapy works by stimulating cellular repair and regeneration processes, improving blood circulation, and modulating pain signals.- Pain management and tissue healing: PEMF therapy is utilized for managing pain and promoting tissue healing. It can reduce inflammation, accelerate wound healing, and alleviate various types of pain, including chronic and acute conditions. The therapy works by stimulating cellular repair processes and improving blood circulation in affected areas.
- Bone and joint health improvement: PEMF therapy has shown efficacy in improving bone density and joint health. It can stimulate bone formation, enhance calcium uptake, and accelerate the healing of fractures. This therapy is also beneficial for treating osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other joint-related conditions by reducing inflammation and promoting cartilage regeneration.
- Neurological and cognitive function enhancement: PEMF therapy has potential applications in enhancing neurological and cognitive functions. It may improve memory, focus, and overall brain health by stimulating neural activity and increasing cerebral blood flow. This therapy is being explored for its potential benefits in treating neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and depression.
- Cardiovascular health improvement: PEMF therapy can contribute to cardiovascular health by improving blood circulation, reducing blood pressure, and enhancing overall heart function. It may help in the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions by promoting the formation of new blood vessels and reducing the risk of blood clots.
- Sleep quality and stress reduction: PEMF therapy has been found to improve sleep quality and reduce stress levels. It can help regulate circadian rhythms, promote relaxation, and alleviate insomnia. The therapy may also have a positive impact on mood disorders and anxiety by modulating neurotransmitter activity and reducing cortisol levels.
02 Bone and joint health improvement
PEMF therapy has shown efficacy in improving bone density, accelerating fracture healing, and managing joint-related conditions such as osteoarthritis. It stimulates osteoblast activity, enhances calcium uptake, and promotes the production of cartilage and connective tissues, leading to better overall bone and joint health.Expand Specific Solutions03 Neurological and cognitive function enhancement
PEMF therapy has potential applications in enhancing neurological and cognitive functions. It may improve memory, concentration, and overall brain function. The therapy is being explored for its effects on neurodegenerative disorders, stroke recovery, and mental health conditions by promoting neuroplasticity and neuroprotection.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cardiovascular health and circulation improvement
PEMF therapy can enhance cardiovascular health by improving blood circulation, reducing blood pressure, and promoting the formation of new blood vessels. It may help in managing conditions such as peripheral artery disease and improving overall cardiovascular function by stimulating nitric oxide production and enhancing cellular energy production.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sleep quality and stress reduction
PEMF therapy has been found to improve sleep quality and reduce stress levels. It can help regulate circadian rhythms, promote relaxation, and alleviate insomnia symptoms. The therapy may also have positive effects on mood disorders and anxiety by modulating neurotransmitter activity and promoting a sense of well-being.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Industry Players
The PEMF therapy market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing awareness of non-invasive treatment options and technological advancements. The global market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 5%. Technologically, PEMF therapy is maturing, with companies like Venus Concept Ltd., Regenesis Biomedical, Inc., and SofPulse, Inc. leading innovation. These firms are developing more sophisticated devices with improved efficacy and user-friendliness. Academic institutions such as the National University of Singapore and Emory University are contributing to the scientific understanding of PEMF, while established medical technology companies like Medtronic and Orthofix are exploring its integration into broader treatment modalities, indicating a trend towards mainstream adoption in healthcare.
Venus Concept Ltd.
Technical Solution: Venus Concept has developed advanced PEMF therapy devices that utilize proprietary RP3 technology. This technology delivers uniform electromagnetic fields to penetrate deep into tissues, promoting cellular repair and regeneration. Their systems incorporate adjustable frequency and intensity settings, allowing for personalized treatment protocols. The company's PEMF devices are designed for both clinical and home use, featuring user-friendly interfaces and pre-programmed treatment options for various conditions[1][3].
Strengths: Proprietary technology, versatile applications, user-friendly design. Weaknesses: Limited clinical evidence for some applications, potential high cost for advanced systems.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical specializes in PEMF therapy for wound healing and pain management. Their flagship product, the Provant Therapy System, utilizes a specific pulsed electromagnetic field to stimulate cellular activity and promote tissue repair. The device operates at a frequency of 27.12 MHz, which has been shown to effectively penetrate tissues and enhance cellular energy production. Regenesis has conducted extensive clinical trials demonstrating the efficacy of their PEMF technology in accelerating wound healing, particularly in diabetic foot ulcers and post-operative recovery[2][4].
Strengths: Focused application in wound healing, strong clinical evidence base. Weaknesses: Limited scope of applications compared to broader PEMF systems.
PEMF Core Innovations
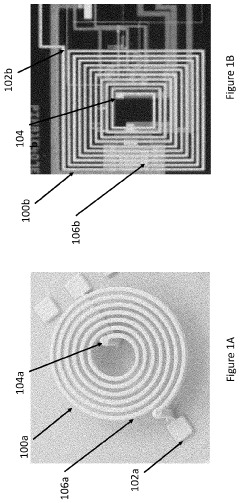
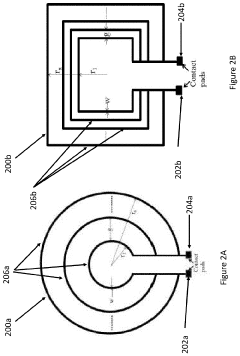
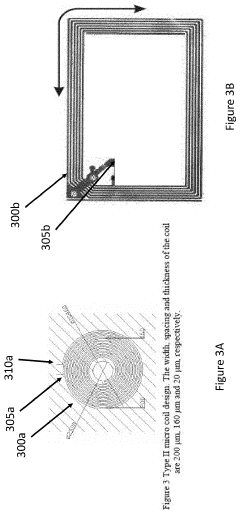
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Devices Integrated into Adjustable Clothing
PatentPendingUS20230104434A1
Innovation
- A pulsed electromagnetic field device integrated into wearable clothing, using arrays of planar microcoils that generate controlled, homogenous magnetic fields, allowing for comfortable, long-term use and targeted treatment of various brain-related disorders and conditions.
Pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) therapy whole body wellness device to increase cells energy, strengthen immune system and promote cell regeneration
PatentInactiveIN201814011740A
Innovation
- A self-contained portable PEMF device, PEMF-DS100, generates pulsed electromagnetic fields that penetrate the body through the hands and feet, utilizing Multiple-Wave Oscillation technology to synchronize cellular vibrations, enhance energy potential, and promote self-healing, while being designed to avoid adaptation and maintain effectiveness over time.
PEMF Safety Regulations
The regulatory landscape for Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices is complex and varies across different regions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies PEMF devices as Class II medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) clearance before they can be legally marketed. These devices must demonstrate substantial equivalence to a predicate device already on the market.
The FDA has established specific guidelines for PEMF devices, including requirements for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing to ensure they do not interfere with other electronic devices. Additionally, manufacturers must provide clinical evidence supporting the safety and efficacy of their devices for the intended use. The FDA also mandates that PEMF devices comply with radiation safety standards set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). Manufacturers must obtain CE marking by demonstrating compliance with essential requirements for safety and performance. This process involves conducting a clinical evaluation, risk management, and quality management system implementation. The EU also requires post-market surveillance to monitor device performance and safety in real-world use.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) regulates PEMF devices under the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act. Manufacturers must obtain marketing authorization through a rigorous review process, which includes evaluating safety data, efficacy claims, and quality control measures.
International standards play a crucial role in PEMF device regulation. The IEC 60601 series of standards, particularly IEC 60601-1 for general safety and IEC 60601-1-2 for EMC, are widely recognized and often adopted by regulatory bodies worldwide. These standards set limits for electromagnetic emissions and immunity, ensuring PEMF devices can operate safely in various environments.
Safety regulations also address potential biological effects of PEMF exposure. The International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) provides guidelines for limiting exposure to electromagnetic fields, which many countries use as a basis for their national regulations. These guidelines set specific absorption rate (SAR) limits to prevent adverse health effects from tissue heating.
As PEMF technology advances, regulatory bodies are continually updating their requirements. Recent trends include increased focus on cybersecurity for connected PEMF devices and more stringent requirements for clinical evidence, particularly for devices claiming therapeutic benefits. Manufacturers must stay abreast of these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and market access for their PEMF devices.
The FDA has established specific guidelines for PEMF devices, including requirements for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing to ensure they do not interfere with other electronic devices. Additionally, manufacturers must provide clinical evidence supporting the safety and efficacy of their devices for the intended use. The FDA also mandates that PEMF devices comply with radiation safety standards set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). Manufacturers must obtain CE marking by demonstrating compliance with essential requirements for safety and performance. This process involves conducting a clinical evaluation, risk management, and quality management system implementation. The EU also requires post-market surveillance to monitor device performance and safety in real-world use.
Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) regulates PEMF devices under the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act. Manufacturers must obtain marketing authorization through a rigorous review process, which includes evaluating safety data, efficacy claims, and quality control measures.
International standards play a crucial role in PEMF device regulation. The IEC 60601 series of standards, particularly IEC 60601-1 for general safety and IEC 60601-1-2 for EMC, are widely recognized and often adopted by regulatory bodies worldwide. These standards set limits for electromagnetic emissions and immunity, ensuring PEMF devices can operate safely in various environments.
Safety regulations also address potential biological effects of PEMF exposure. The International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) provides guidelines for limiting exposure to electromagnetic fields, which many countries use as a basis for their national regulations. These guidelines set specific absorption rate (SAR) limits to prevent adverse health effects from tissue heating.
As PEMF technology advances, regulatory bodies are continually updating their requirements. Recent trends include increased focus on cybersecurity for connected PEMF devices and more stringent requirements for clinical evidence, particularly for devices claiming therapeutic benefits. Manufacturers must stay abreast of these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and market access for their PEMF devices.
PEMF Cost-Benefit Analysis
The cost-benefit analysis of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy reveals a complex interplay of economic factors and health outcomes. Initial investment in PEMF devices can be substantial, with high-quality systems ranging from $1,000 to $20,000. However, this upfront cost should be weighed against potential long-term savings in healthcare expenses and improved quality of life.
PEMF therapy has shown promise in treating various conditions, including chronic pain, osteoarthritis, and non-union fractures. Studies indicate that regular PEMF use can lead to reduced reliance on pain medications, fewer doctor visits, and decreased need for surgical interventions. These outcomes translate to significant cost savings for both individuals and healthcare systems over time.
The non-invasive nature of PEMF therapy also contributes to its cost-effectiveness. Unlike surgical procedures or pharmaceutical treatments, PEMF therapy has minimal side effects and can be self-administered at home, reducing the need for frequent medical appointments and associated costs.
In terms of productivity gains, PEMF therapy's potential to alleviate chronic pain and improve mobility can lead to fewer sick days and enhanced work performance. This indirect economic benefit should be factored into the overall cost-benefit analysis, as it impacts both individual earning potential and broader economic productivity.
However, it's important to note that the efficacy of PEMF therapy can vary depending on the specific condition being treated and the individual's response. This variability introduces an element of uncertainty into the cost-benefit calculation, as not all users may experience the same level of improvement or cost savings.
Insurance coverage for PEMF therapy is currently limited, which affects its accessibility and perceived value. As more clinical evidence accumulates, there may be increased pressure on insurance providers to cover PEMF treatments, potentially altering the cost-benefit equation for many patients.
When considering the long-term benefits, the durability and lifespan of PEMF devices become crucial factors. High-quality devices can last for many years with proper maintenance, spreading the initial investment over a longer period and improving the overall cost-effectiveness.
In conclusion, while the upfront costs of PEMF therapy can be significant, the potential for long-term health improvements and associated cost savings make it a compelling option for many individuals and healthcare providers. As research continues to validate its efficacy across various conditions, the cost-benefit ratio of PEMF therapy is likely to improve further, potentially establishing it as a standard treatment option in the future of healthcare.
PEMF therapy has shown promise in treating various conditions, including chronic pain, osteoarthritis, and non-union fractures. Studies indicate that regular PEMF use can lead to reduced reliance on pain medications, fewer doctor visits, and decreased need for surgical interventions. These outcomes translate to significant cost savings for both individuals and healthcare systems over time.
The non-invasive nature of PEMF therapy also contributes to its cost-effectiveness. Unlike surgical procedures or pharmaceutical treatments, PEMF therapy has minimal side effects and can be self-administered at home, reducing the need for frequent medical appointments and associated costs.
In terms of productivity gains, PEMF therapy's potential to alleviate chronic pain and improve mobility can lead to fewer sick days and enhanced work performance. This indirect economic benefit should be factored into the overall cost-benefit analysis, as it impacts both individual earning potential and broader economic productivity.
However, it's important to note that the efficacy of PEMF therapy can vary depending on the specific condition being treated and the individual's response. This variability introduces an element of uncertainty into the cost-benefit calculation, as not all users may experience the same level of improvement or cost savings.
Insurance coverage for PEMF therapy is currently limited, which affects its accessibility and perceived value. As more clinical evidence accumulates, there may be increased pressure on insurance providers to cover PEMF treatments, potentially altering the cost-benefit equation for many patients.
When considering the long-term benefits, the durability and lifespan of PEMF devices become crucial factors. High-quality devices can last for many years with proper maintenance, spreading the initial investment over a longer period and improving the overall cost-effectiveness.
In conclusion, while the upfront costs of PEMF therapy can be significant, the potential for long-term health improvements and associated cost savings make it a compelling option for many individuals and healthcare providers. As research continues to validate its efficacy across various conditions, the cost-benefit ratio of PEMF therapy is likely to improve further, potentially establishing it as a standard treatment option in the future of healthcare.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!