How to Address Barriers to Adoption of PEMF Therapy in Healthcare?
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Therapy Evolution
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for bone healing applications, PEMF therapy has expanded its scope to address various health conditions, including pain management, tissue repair, and neurological disorders.
The early stages of PEMF therapy focused primarily on bone healing, with the first FDA-approved device for this purpose introduced in 1979. This breakthrough paved the way for further research and development in the field. As understanding of the therapy's mechanisms improved, researchers began exploring its potential in other areas of medicine.
During the 1980s and 1990s, PEMF therapy saw increased adoption in sports medicine and rehabilitation. Athletes and physical therapists recognized its potential for accelerating recovery from injuries and reducing inflammation. This period also marked the beginning of more rigorous scientific studies to validate the therapy's efficacy and safety.
The turn of the millennium brought about significant advancements in PEMF technology. Miniaturization of components and improved battery life led to the development of portable PEMF devices, making the therapy more accessible for home use. This shift from clinical-only applications to consumer-oriented products represented a major milestone in the therapy's evolution.
In recent years, PEMF therapy has gained traction in the treatment of chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and depression. The non-invasive nature of the therapy, coupled with its potential for reducing reliance on pharmaceutical interventions, has attracted both medical professionals and patients seeking alternative treatment options.
Technological advancements have also played a crucial role in enhancing the precision and effectiveness of PEMF therapy. Modern devices offer customizable treatment protocols, allowing for tailored approaches to individual patient needs. Additionally, integration with smartphone apps and wearable technology has improved user experience and treatment adherence.
Despite these advancements, PEMF therapy still faces challenges in widespread adoption within mainstream healthcare. Skepticism from some medical professionals, coupled with a lack of standardized protocols and limited large-scale clinical trials, has hindered its integration into standard medical practice. Addressing these barriers requires continued research, education, and collaboration between scientists, clinicians, and regulatory bodies.
Looking ahead, the evolution of PEMF therapy is likely to focus on optimizing treatment parameters, expanding applications to new medical conditions, and improving the integration of PEMF devices with other healthcare technologies. As the body of evidence supporting its efficacy grows, PEMF therapy may become an increasingly important tool in the healthcare landscape, offering a non-invasive, drug-free option for managing a wide range of health conditions.
The early stages of PEMF therapy focused primarily on bone healing, with the first FDA-approved device for this purpose introduced in 1979. This breakthrough paved the way for further research and development in the field. As understanding of the therapy's mechanisms improved, researchers began exploring its potential in other areas of medicine.
During the 1980s and 1990s, PEMF therapy saw increased adoption in sports medicine and rehabilitation. Athletes and physical therapists recognized its potential for accelerating recovery from injuries and reducing inflammation. This period also marked the beginning of more rigorous scientific studies to validate the therapy's efficacy and safety.
The turn of the millennium brought about significant advancements in PEMF technology. Miniaturization of components and improved battery life led to the development of portable PEMF devices, making the therapy more accessible for home use. This shift from clinical-only applications to consumer-oriented products represented a major milestone in the therapy's evolution.
In recent years, PEMF therapy has gained traction in the treatment of chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and depression. The non-invasive nature of the therapy, coupled with its potential for reducing reliance on pharmaceutical interventions, has attracted both medical professionals and patients seeking alternative treatment options.
Technological advancements have also played a crucial role in enhancing the precision and effectiveness of PEMF therapy. Modern devices offer customizable treatment protocols, allowing for tailored approaches to individual patient needs. Additionally, integration with smartphone apps and wearable technology has improved user experience and treatment adherence.
Despite these advancements, PEMF therapy still faces challenges in widespread adoption within mainstream healthcare. Skepticism from some medical professionals, coupled with a lack of standardized protocols and limited large-scale clinical trials, has hindered its integration into standard medical practice. Addressing these barriers requires continued research, education, and collaboration between scientists, clinicians, and regulatory bodies.
Looking ahead, the evolution of PEMF therapy is likely to focus on optimizing treatment parameters, expanding applications to new medical conditions, and improving the integration of PEMF devices with other healthcare technologies. As the body of evidence supporting its efficacy grows, PEMF therapy may become an increasingly important tool in the healthcare landscape, offering a non-invasive, drug-free option for managing a wide range of health conditions.
Healthcare Market Demand
The healthcare market for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of its potential benefits and a growing demand for non-invasive treatment options. As chronic diseases and musculoskeletal disorders become more prevalent, patients and healthcare providers are seeking alternative therapies that can complement or replace traditional treatments.
The global PEMF therapy devices market is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to exceed 5% through 2027. This growth is fueled by the rising incidence of chronic pain conditions, sports injuries, and age-related disorders, as well as the increasing adoption of PEMF therapy in rehabilitation centers and sports medicine facilities.
One of the key drivers of market demand is the growing body of clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF therapy in various medical applications. Studies have shown promising results in areas such as pain management, bone healing, and wound care, which has led to increased interest from both patients and healthcare professionals.
The aging population in many developed countries is also contributing to the market demand for PEMF therapy. As the elderly population grows, there is a higher prevalence of conditions such as osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and chronic pain, which are potential targets for PEMF treatment. This demographic shift is creating opportunities for PEMF device manufacturers and therapy providers to expand their market reach.
Another factor driving market demand is the increasing focus on personalized medicine and patient-centric care. PEMF therapy aligns well with this trend, as it can be tailored to individual patient needs and can be used in combination with other treatment modalities. This flexibility makes it an attractive option for healthcare providers looking to offer comprehensive care plans.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also indirectly boosted interest in PEMF therapy, as patients seek alternative treatments that can be administered at home or with minimal physical contact. This has led to an increase in demand for portable PEMF devices and home-use systems, expanding the market beyond traditional clinical settings.
Despite the growing demand, there are still barriers to widespread adoption in healthcare settings. These include the need for more extensive clinical trials, concerns about long-term effects, and the lack of standardized protocols for PEMF therapy. Addressing these barriers will be crucial for realizing the full market potential of PEMF therapy in healthcare.
The global PEMF therapy devices market is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to exceed 5% through 2027. This growth is fueled by the rising incidence of chronic pain conditions, sports injuries, and age-related disorders, as well as the increasing adoption of PEMF therapy in rehabilitation centers and sports medicine facilities.
One of the key drivers of market demand is the growing body of clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF therapy in various medical applications. Studies have shown promising results in areas such as pain management, bone healing, and wound care, which has led to increased interest from both patients and healthcare professionals.
The aging population in many developed countries is also contributing to the market demand for PEMF therapy. As the elderly population grows, there is a higher prevalence of conditions such as osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and chronic pain, which are potential targets for PEMF treatment. This demographic shift is creating opportunities for PEMF device manufacturers and therapy providers to expand their market reach.
Another factor driving market demand is the increasing focus on personalized medicine and patient-centric care. PEMF therapy aligns well with this trend, as it can be tailored to individual patient needs and can be used in combination with other treatment modalities. This flexibility makes it an attractive option for healthcare providers looking to offer comprehensive care plans.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also indirectly boosted interest in PEMF therapy, as patients seek alternative treatments that can be administered at home or with minimal physical contact. This has led to an increase in demand for portable PEMF devices and home-use systems, expanding the market beyond traditional clinical settings.
Despite the growing demand, there are still barriers to widespread adoption in healthcare settings. These include the need for more extensive clinical trials, concerns about long-term effects, and the lack of standardized protocols for PEMF therapy. Addressing these barriers will be crucial for realizing the full market potential of PEMF therapy in healthcare.
PEMF Adoption Challenges
Despite the potential benefits of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy in healthcare, several significant barriers hinder its widespread adoption. One of the primary challenges is the lack of comprehensive clinical evidence supporting its efficacy across various medical conditions. While some studies have shown promising results, the overall body of research remains limited, making it difficult for healthcare providers to confidently recommend PEMF therapy as a standard treatment option.
Another major obstacle is the regulatory landscape surrounding PEMF devices. In many countries, including the United States, PEMF therapy devices are not fully approved by regulatory bodies for all potential medical applications. This regulatory uncertainty creates hesitation among healthcare institutions and practitioners in integrating PEMF therapy into their treatment protocols.
The high cost of PEMF equipment and treatments also poses a significant barrier to adoption. Many healthcare facilities, especially smaller clinics and private practices, may find it challenging to justify the investment in PEMF technology without clear evidence of its cost-effectiveness and return on investment. Additionally, insurance coverage for PEMF therapy is often limited or non-existent, making it financially burdensome for patients to access this treatment option.
A lack of standardization in PEMF therapy protocols and device specifications further complicates its adoption. The wide variety of PEMF devices available, each with different frequencies, intensities, and application methods, makes it challenging for healthcare providers to determine the most effective approach for specific conditions. This variability also hampers the comparison of research results and the development of consistent treatment guidelines.
The limited awareness and understanding of PEMF therapy among both healthcare professionals and patients contribute to its slow adoption. Many medical practitioners are not adequately educated about the potential benefits and applications of PEMF therapy, leading to skepticism or reluctance to incorporate it into their practice. Similarly, patients may be unfamiliar with PEMF therapy or harbor misconceptions about its safety and effectiveness.
Lastly, the integration of PEMF therapy into existing healthcare workflows and treatment paradigms presents logistical challenges. Healthcare providers may struggle to incorporate PEMF treatments into their already busy schedules, and there may be concerns about how to properly train staff in the use of PEMF devices and the management of treatment protocols.
Addressing these barriers requires a multifaceted approach involving further research, regulatory clarity, cost reduction strategies, standardization efforts, educational initiatives, and practical implementation solutions. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of PEMF therapy in healthcare and improving patient outcomes across various medical conditions.
Another major obstacle is the regulatory landscape surrounding PEMF devices. In many countries, including the United States, PEMF therapy devices are not fully approved by regulatory bodies for all potential medical applications. This regulatory uncertainty creates hesitation among healthcare institutions and practitioners in integrating PEMF therapy into their treatment protocols.
The high cost of PEMF equipment and treatments also poses a significant barrier to adoption. Many healthcare facilities, especially smaller clinics and private practices, may find it challenging to justify the investment in PEMF technology without clear evidence of its cost-effectiveness and return on investment. Additionally, insurance coverage for PEMF therapy is often limited or non-existent, making it financially burdensome for patients to access this treatment option.
A lack of standardization in PEMF therapy protocols and device specifications further complicates its adoption. The wide variety of PEMF devices available, each with different frequencies, intensities, and application methods, makes it challenging for healthcare providers to determine the most effective approach for specific conditions. This variability also hampers the comparison of research results and the development of consistent treatment guidelines.
The limited awareness and understanding of PEMF therapy among both healthcare professionals and patients contribute to its slow adoption. Many medical practitioners are not adequately educated about the potential benefits and applications of PEMF therapy, leading to skepticism or reluctance to incorporate it into their practice. Similarly, patients may be unfamiliar with PEMF therapy or harbor misconceptions about its safety and effectiveness.
Lastly, the integration of PEMF therapy into existing healthcare workflows and treatment paradigms presents logistical challenges. Healthcare providers may struggle to incorporate PEMF treatments into their already busy schedules, and there may be concerns about how to properly train staff in the use of PEMF devices and the management of treatment protocols.
Addressing these barriers requires a multifaceted approach involving further research, regulatory clarity, cost reduction strategies, standardization efforts, educational initiatives, and practical implementation solutions. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of PEMF therapy in healthcare and improving patient outcomes across various medical conditions.
Current PEMF Solutions
01 PEMF therapy devices and systems
Various devices and systems have been developed for delivering Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy. These include portable devices, wearable applicators, and integrated systems that can be used in clinical settings or at home. The devices are designed to generate specific electromagnetic fields to promote healing and wellness.- PEMF therapy devices and systems: Various devices and systems have been developed for delivering Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy. These include portable devices, wearable applicators, and integrated systems that can be used in clinical settings or at home. The devices are designed to generate and apply electromagnetic fields to specific areas of the body for therapeutic purposes.
- PEMF therapy applications in healthcare: PEMF therapy has been adopted for various healthcare applications, including pain management, wound healing, bone regeneration, and treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. Research indicates potential benefits in reducing inflammation, improving circulation, and promoting cellular repair. The therapy is being explored for both acute and chronic conditions.
- Integration of PEMF therapy with other technologies: There is a growing trend in integrating PEMF therapy with other technologies and treatment modalities. This includes combining PEMF with biofeedback systems, virtual reality, and other forms of electromagnetic therapies. Such integrations aim to enhance the overall therapeutic effect and provide more comprehensive treatment options.
- PEMF therapy in veterinary and agricultural applications: The adoption of PEMF therapy has extended beyond human healthcare to veterinary medicine and agriculture. PEMF devices are being used for treating animals, particularly in equine therapy. In agriculture, PEMF technology is explored for enhancing plant growth and crop yield.
- Advancements in PEMF therapy control and personalization: Recent developments in PEMF therapy focus on improving control mechanisms and personalizing treatment protocols. This includes the use of AI and machine learning algorithms to optimize therapy settings, as well as the development of smart devices that can adapt to individual patient needs. These advancements aim to enhance the efficacy and user-friendliness of PEMF therapy.
02 PEMF therapy applications in healthcare
PEMF therapy has been adopted in various healthcare applications, including pain management, wound healing, bone regeneration, and treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. Research indicates its potential in improving circulation, reducing inflammation, and accelerating tissue repair processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of PEMF therapy with other technologies
There is a growing trend in integrating PEMF therapy with other technologies and treatment modalities. This includes combining PEMF with biofeedback systems, virtual reality, and other forms of electromagnetic therapies to enhance overall treatment efficacy and patient experience.Expand Specific Solutions04 PEMF therapy in veterinary and agricultural applications
The adoption of PEMF therapy has extended beyond human healthcare to veterinary medicine and agriculture. It is being used for treating animals, improving plant growth, and enhancing crop yields. This expansion demonstrates the versatility and potential of PEMF technology in various fields.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advancements in PEMF therapy control and customization
Recent developments in PEMF therapy focus on improving control mechanisms and customization options. This includes software-driven systems that allow for precise adjustment of treatment parameters, personalized therapy protocols, and remote monitoring capabilities, enhancing the effectiveness and user-friendliness of PEMF treatments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Industry Players
The adoption of PEMF therapy in healthcare is currently in a transitional phase, with the market showing promising growth potential. The global PEMF therapy devices market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, driven by increasing awareness of non-invasive treatment options and growing applications in pain management and rehabilitation. However, the technology's maturity varies across different applications. Companies like Medtronic AF Luxembourg SARL and Regenesis Biomedical, Inc. are at the forefront of PEMF technology development, with established products in specific medical fields. Emerging players such as Venus Concept Ltd. and SofPulse, Inc. are introducing innovative PEMF solutions, indicating a competitive and evolving landscape. The industry faces challenges in standardization and clinical validation, which are crucial for wider acceptance in mainstream healthcare settings.
Medtronic AF Luxembourg SARL
Technical Solution: Medtronic's approach to addressing barriers in PEMF therapy adoption focuses on developing advanced, user-friendly devices and conducting extensive clinical research. They have introduced portable PEMF devices that can be used at home, improving accessibility and patient compliance. Medtronic has invested in large-scale clinical trials to demonstrate the efficacy of PEMF therapy in various conditions, particularly in bone healing and pain management [1][3]. Their devices incorporate smart technology for treatment tracking and remote monitoring, allowing healthcare providers to adjust treatments remotely and ensure optimal outcomes [2]. Medtronic also emphasizes education programs for both patients and healthcare professionals to increase awareness and understanding of PEMF therapy benefits and proper usage.
Strengths: Strong research backing, advanced technology integration, and global distribution network. Weaknesses: Higher cost of devices compared to some competitors, which may limit adoption in cost-sensitive markets.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical addresses PEMF therapy adoption barriers through their innovative Provant Therapy System. This FDA-cleared device is designed for easy use in various healthcare settings, from hospitals to home care. The system utilizes a proprietary pulsed radio frequency energy (PRFE) technology, which is a form of PEMF therapy optimized for tissue healing and pain reduction [4]. Regenesis focuses on specific indications such as postoperative pain and edema reduction, which helps in targeting key medical areas where PEMF can provide significant benefits. They have developed a comprehensive reimbursement support program to assist healthcare providers and patients in navigating insurance coverage, addressing one of the major barriers to adoption [5]. Additionally, Regenesis provides extensive training and support materials for healthcare professionals, enhancing their ability to effectively integrate PEMF therapy into treatment protocols.
Strengths: Focused application in specific medical areas, strong reimbursement support program. Weaknesses: Limited range of PEMF devices compared to larger competitors, potentially limiting broader market penetration.
PEMF Research Insights
Treatment of conditions susceptible to pulsed electromagnetic field therapy
PatentActiveUS20170354830A1
Innovation
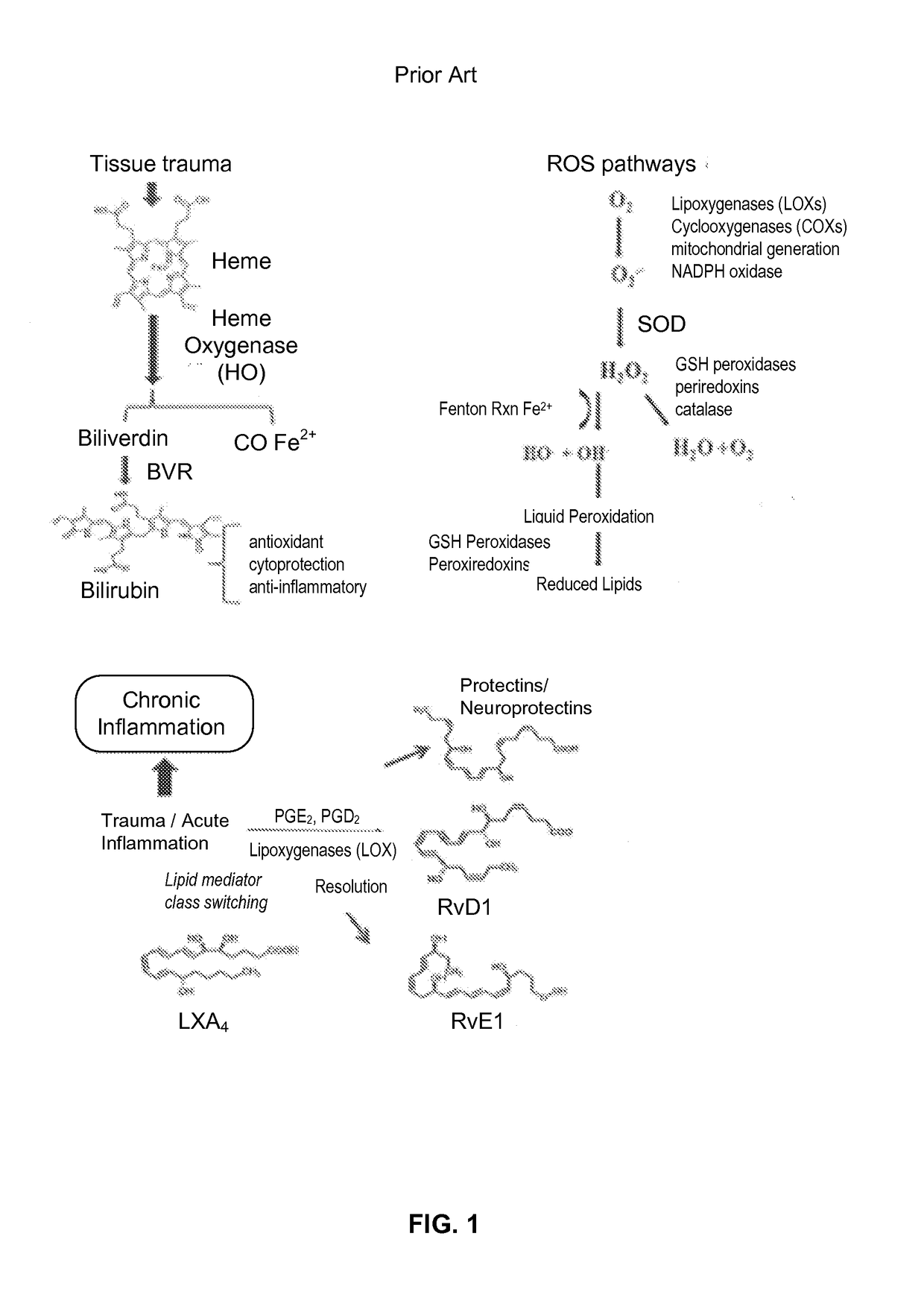
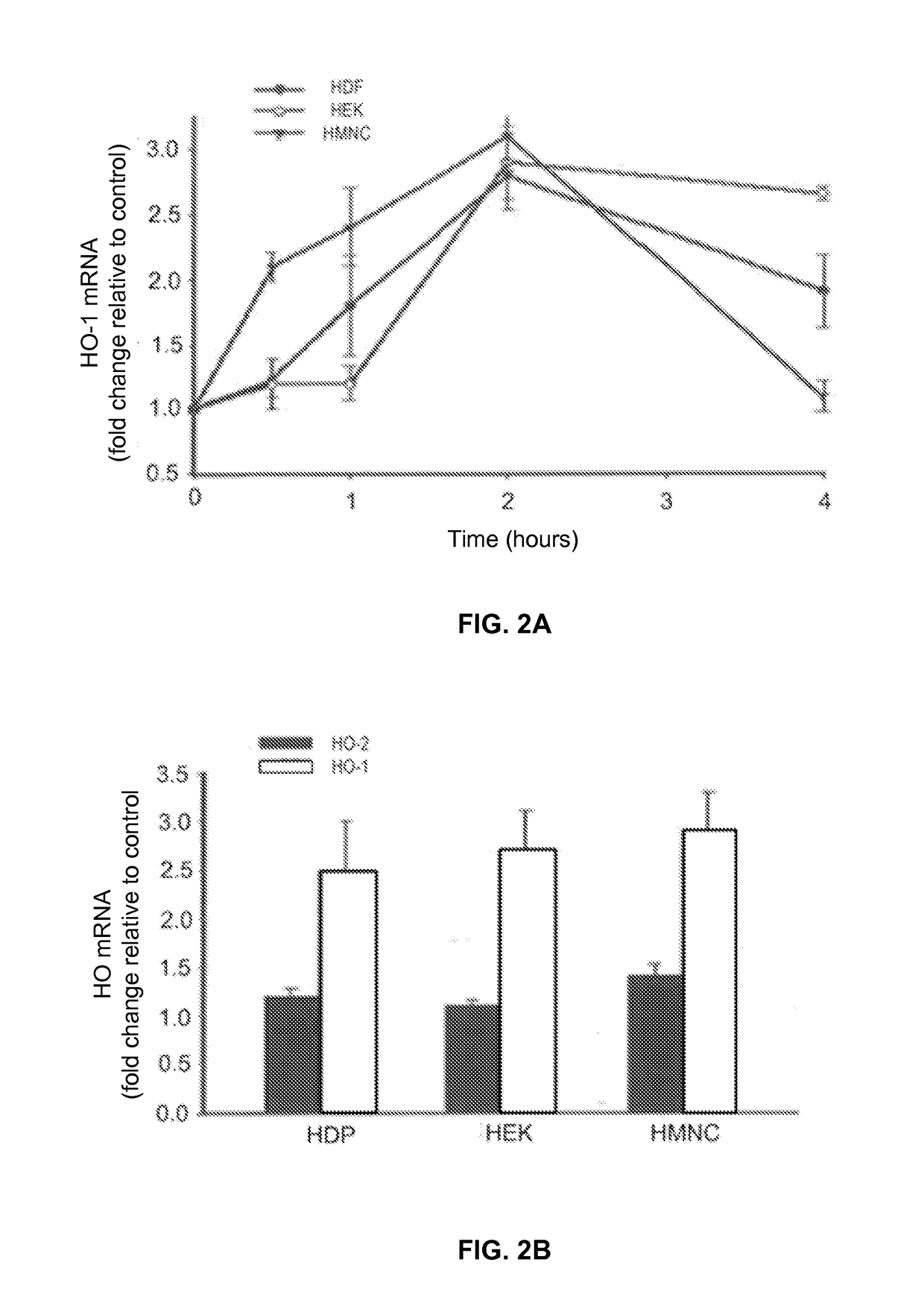
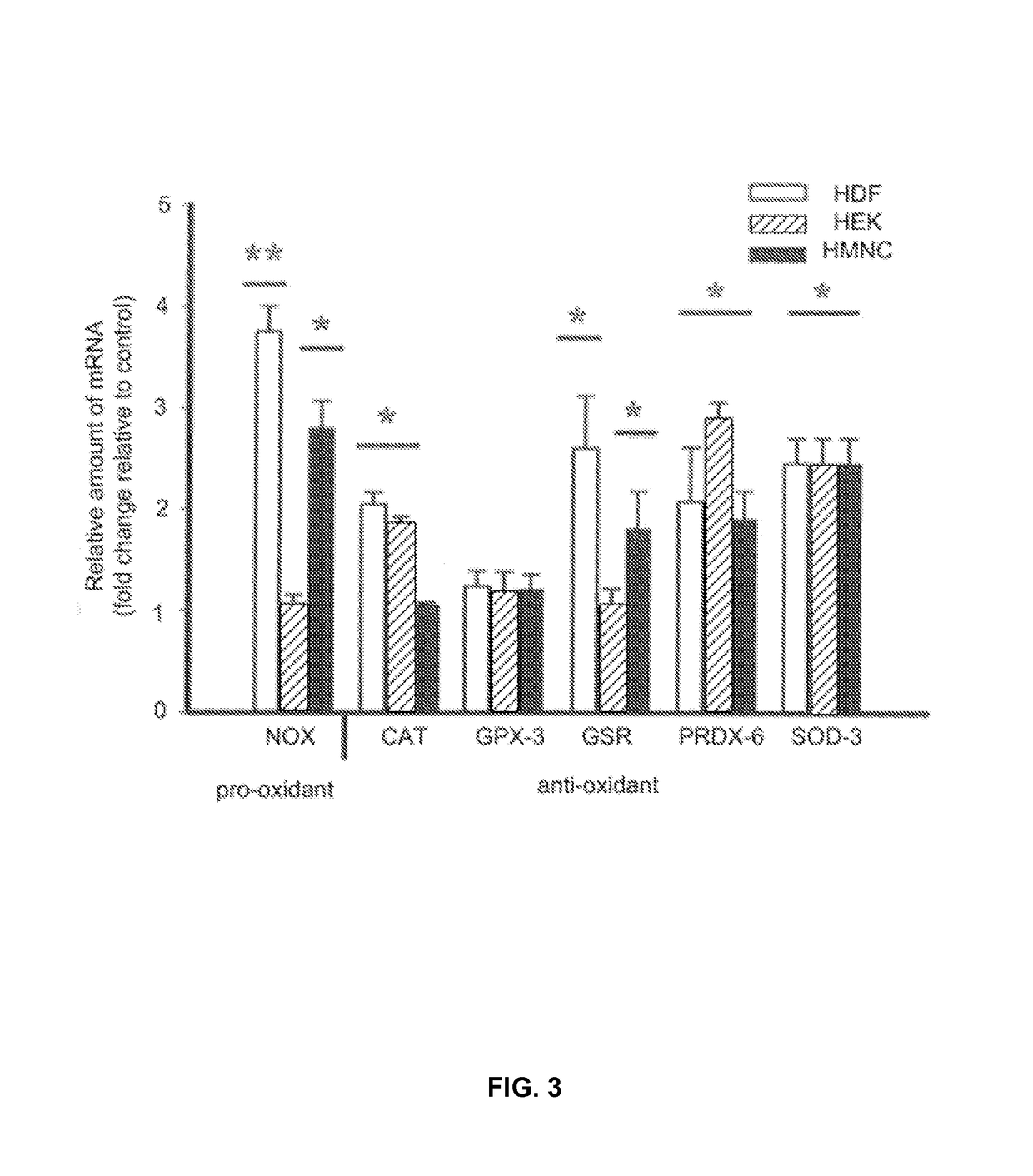
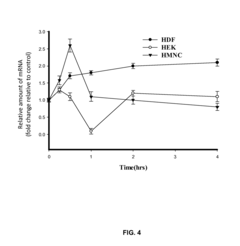
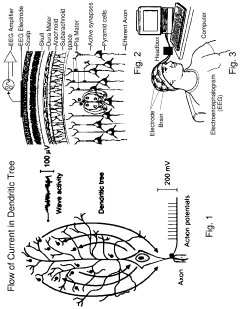
- PEMF therapy is administered to modulate gene expression associated with inflammation pathways, including heme oxygenase, antioxidant enzymes, lipid mediator biosynthesis, and cytokines, using specific parameters such as electric field strength, pulse rate, and duration to produce measurable clinical effects on pain, nerve function, and wound healing.
Method and apparatus for neuroenhancement to enhance emotional response
PatentPendingUS20230191073A1
Innovation
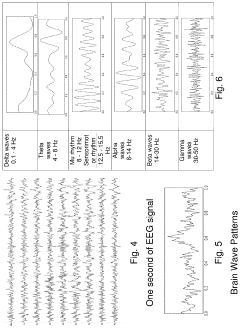
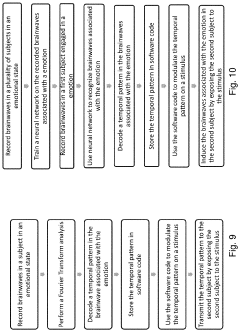
- Development of devices and systems that selectively induce brainwave activity patterns associated with specific emotions by targeting specific frequency and location in the brain, utilizing non-invasive neuromodulation techniques to enhance emotional responses.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy plays a crucial role in its adoption within healthcare systems. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has classified PEMF devices as Class III medical devices, requiring rigorous clinical trials and extensive documentation for approval. This classification presents a significant barrier to entry for new PEMF technologies and limits their widespread use in clinical settings.
European regulations, governed by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), also impose strict requirements on PEMF devices. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with safety and performance standards, conduct clinical evaluations, and obtain CE marking before marketing their products. These regulatory hurdles can be time-consuming and costly, potentially deterring smaller companies from entering the market.
In many countries, the lack of standardized protocols for PEMF therapy application further complicates regulatory compliance. Without clear guidelines on treatment parameters, dosage, and duration, healthcare providers may be hesitant to incorporate PEMF therapy into their practice, fearing potential liability issues.
Reimbursement policies also present a significant barrier to PEMF therapy adoption. Many insurance providers and national health systems do not cover PEMF treatments, citing insufficient evidence of efficacy for certain conditions. This lack of coverage can make PEMF therapy financially inaccessible to many patients, limiting its potential reach and impact.
To address these regulatory barriers, a multi-faceted approach is necessary. First, collaboration between industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and research institutions is crucial to establish standardized protocols and treatment guidelines for PEMF therapy. This would provide a clear framework for both manufacturers and healthcare providers, streamlining the approval process and enhancing clinical confidence.
Secondly, investment in high-quality clinical trials is essential to build a robust evidence base for PEMF therapy's efficacy across various medical conditions. This evidence can support regulatory approvals, influence reimbursement policies, and encourage wider acceptance among healthcare professionals.
Lastly, advocacy efforts aimed at educating policymakers and insurance providers about the potential benefits and cost-effectiveness of PEMF therapy could help reshape reimbursement policies. By demonstrating the long-term health and economic benefits of PEMF treatments, stakeholders can work towards more favorable coverage decisions, ultimately improving patient access to this promising therapy.
European regulations, governed by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), also impose strict requirements on PEMF devices. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with safety and performance standards, conduct clinical evaluations, and obtain CE marking before marketing their products. These regulatory hurdles can be time-consuming and costly, potentially deterring smaller companies from entering the market.
In many countries, the lack of standardized protocols for PEMF therapy application further complicates regulatory compliance. Without clear guidelines on treatment parameters, dosage, and duration, healthcare providers may be hesitant to incorporate PEMF therapy into their practice, fearing potential liability issues.
Reimbursement policies also present a significant barrier to PEMF therapy adoption. Many insurance providers and national health systems do not cover PEMF treatments, citing insufficient evidence of efficacy for certain conditions. This lack of coverage can make PEMF therapy financially inaccessible to many patients, limiting its potential reach and impact.
To address these regulatory barriers, a multi-faceted approach is necessary. First, collaboration between industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and research institutions is crucial to establish standardized protocols and treatment guidelines for PEMF therapy. This would provide a clear framework for both manufacturers and healthcare providers, streamlining the approval process and enhancing clinical confidence.
Secondly, investment in high-quality clinical trials is essential to build a robust evidence base for PEMF therapy's efficacy across various medical conditions. This evidence can support regulatory approvals, influence reimbursement policies, and encourage wider acceptance among healthcare professionals.
Lastly, advocacy efforts aimed at educating policymakers and insurance providers about the potential benefits and cost-effectiveness of PEMF therapy could help reshape reimbursement policies. By demonstrating the long-term health and economic benefits of PEMF treatments, stakeholders can work towards more favorable coverage decisions, ultimately improving patient access to this promising therapy.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Conducting a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is crucial for addressing barriers to the adoption of PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) therapy in healthcare. This analysis involves evaluating both the financial and non-financial aspects of implementing PEMF therapy in various healthcare settings.
From a cost perspective, the initial investment in PEMF devices and equipment can be substantial. Healthcare facilities need to consider the purchase price of PEMF machines, which can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on the sophistication and intended use. Additionally, there are ongoing costs associated with maintenance, staff training, and potential upgrades as technology advances.
However, these costs should be weighed against the potential benefits. PEMF therapy has shown promise in treating various conditions, including chronic pain, bone healing, and wound care. By incorporating PEMF therapy, healthcare providers may reduce the need for certain medications or surgical interventions, potentially leading to cost savings in the long run. Moreover, improved patient outcomes and faster recovery times could result in shorter hospital stays and reduced overall healthcare costs.
The non-financial benefits of PEMF therapy should also be considered. Patients may experience improved quality of life, reduced pain, and enhanced mobility. These outcomes can lead to increased patient satisfaction and potentially better overall health outcomes. For healthcare providers, offering PEMF therapy could differentiate their services, attracting more patients and potentially increasing revenue.
It's important to note that the cost-benefit ratio may vary depending on the specific healthcare setting and patient population. For example, orthopedic clinics or rehabilitation centers might see a more immediate return on investment compared to general hospitals. Therefore, a tailored analysis for each healthcare facility is necessary to determine the viability of adopting PEMF therapy.
To overcome adoption barriers, healthcare providers should consider phased implementation strategies. Starting with a pilot program in specific departments or for certain conditions can help demonstrate the therapy's effectiveness and financial viability on a smaller scale before full-scale adoption. This approach allows for data collection on patient outcomes and cost savings, which can be used to justify broader implementation.
Furthermore, exploring alternative financing options, such as leasing equipment or partnering with PEMF device manufacturers, could help mitigate the initial financial burden. Collaborating with insurance companies to include PEMF therapy in coverage plans could also increase accessibility and adoption rates.
In conclusion, a thorough cost-benefit analysis that considers both short-term investments and long-term gains is essential for addressing barriers to PEMF therapy adoption. By carefully evaluating financial implications, patient outcomes, and operational efficiencies, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about integrating this promising therapy into their practice.
From a cost perspective, the initial investment in PEMF devices and equipment can be substantial. Healthcare facilities need to consider the purchase price of PEMF machines, which can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on the sophistication and intended use. Additionally, there are ongoing costs associated with maintenance, staff training, and potential upgrades as technology advances.
However, these costs should be weighed against the potential benefits. PEMF therapy has shown promise in treating various conditions, including chronic pain, bone healing, and wound care. By incorporating PEMF therapy, healthcare providers may reduce the need for certain medications or surgical interventions, potentially leading to cost savings in the long run. Moreover, improved patient outcomes and faster recovery times could result in shorter hospital stays and reduced overall healthcare costs.
The non-financial benefits of PEMF therapy should also be considered. Patients may experience improved quality of life, reduced pain, and enhanced mobility. These outcomes can lead to increased patient satisfaction and potentially better overall health outcomes. For healthcare providers, offering PEMF therapy could differentiate their services, attracting more patients and potentially increasing revenue.
It's important to note that the cost-benefit ratio may vary depending on the specific healthcare setting and patient population. For example, orthopedic clinics or rehabilitation centers might see a more immediate return on investment compared to general hospitals. Therefore, a tailored analysis for each healthcare facility is necessary to determine the viability of adopting PEMF therapy.
To overcome adoption barriers, healthcare providers should consider phased implementation strategies. Starting with a pilot program in specific departments or for certain conditions can help demonstrate the therapy's effectiveness and financial viability on a smaller scale before full-scale adoption. This approach allows for data collection on patient outcomes and cost savings, which can be used to justify broader implementation.
Furthermore, exploring alternative financing options, such as leasing equipment or partnering with PEMF device manufacturers, could help mitigate the initial financial burden. Collaborating with insurance companies to include PEMF therapy in coverage plans could also increase accessibility and adoption rates.
In conclusion, a thorough cost-benefit analysis that considers both short-term investments and long-term gains is essential for addressing barriers to PEMF therapy adoption. By carefully evaluating financial implications, patient outcomes, and operational efficiencies, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about integrating this promising therapy into their practice.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!