How to Integrate PEMF Therapy into Chronic Condition Management?
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PEMF Therapy Background and Objectives
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has emerged as a promising non-invasive treatment modality for chronic conditions. This technology harnesses the power of electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and regeneration, offering potential benefits for a wide range of health issues. The evolution of PEMF therapy can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with significant advancements in recent decades due to improved understanding of cellular biology and electromagnetic interactions.
The primary objective of integrating PEMF therapy into chronic condition management is to enhance traditional treatment approaches and improve patient outcomes. By leveraging the ability of electromagnetic fields to influence cellular processes, PEMF therapy aims to address underlying causes of chronic conditions rather than merely managing symptoms. This aligns with the growing trend towards holistic and personalized healthcare solutions.
Current research indicates that PEMF therapy may be particularly effective in managing pain, inflammation, and tissue repair processes associated with various chronic conditions. These include but are not limited to osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, chronic lower back pain, and non-union fractures. The therapy's potential to reduce reliance on pharmaceutical interventions and improve quality of life for patients with chronic conditions has sparked considerable interest in both medical and research communities.
The integration of PEMF therapy into chronic condition management faces several challenges and opportunities. One key objective is to establish standardized protocols for different chronic conditions, as the optimal frequency, intensity, and duration of PEMF treatments may vary depending on the specific health issue being addressed. Additionally, there is a need for more extensive clinical trials to validate the efficacy of PEMF therapy across a broader range of chronic conditions and to identify potential long-term effects.
Another important goal is to improve the accessibility and user-friendliness of PEMF devices for home use, enabling patients to incorporate this therapy into their daily routines. This involves developing more compact, affordable, and easy-to-use PEMF devices that can be seamlessly integrated into existing chronic condition management plans.
As the field of PEMF therapy continues to evolve, researchers and clinicians are exploring its potential synergies with other treatment modalities. The objective is to create comprehensive, multimodal approaches to chronic condition management that leverage the strengths of various therapies, including PEMF, to provide more effective and personalized care for patients.
The primary objective of integrating PEMF therapy into chronic condition management is to enhance traditional treatment approaches and improve patient outcomes. By leveraging the ability of electromagnetic fields to influence cellular processes, PEMF therapy aims to address underlying causes of chronic conditions rather than merely managing symptoms. This aligns with the growing trend towards holistic and personalized healthcare solutions.
Current research indicates that PEMF therapy may be particularly effective in managing pain, inflammation, and tissue repair processes associated with various chronic conditions. These include but are not limited to osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, chronic lower back pain, and non-union fractures. The therapy's potential to reduce reliance on pharmaceutical interventions and improve quality of life for patients with chronic conditions has sparked considerable interest in both medical and research communities.
The integration of PEMF therapy into chronic condition management faces several challenges and opportunities. One key objective is to establish standardized protocols for different chronic conditions, as the optimal frequency, intensity, and duration of PEMF treatments may vary depending on the specific health issue being addressed. Additionally, there is a need for more extensive clinical trials to validate the efficacy of PEMF therapy across a broader range of chronic conditions and to identify potential long-term effects.
Another important goal is to improve the accessibility and user-friendliness of PEMF devices for home use, enabling patients to incorporate this therapy into their daily routines. This involves developing more compact, affordable, and easy-to-use PEMF devices that can be seamlessly integrated into existing chronic condition management plans.
As the field of PEMF therapy continues to evolve, researchers and clinicians are exploring its potential synergies with other treatment modalities. The objective is to create comprehensive, multimodal approaches to chronic condition management that leverage the strengths of various therapies, including PEMF, to provide more effective and personalized care for patients.
Market Analysis for PEMF in Chronic Care
The market for Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy in chronic care management is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic conditions and the growing demand for non-invasive treatment options. The global PEMF therapy devices market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 7.2% from 2021 to 2028, reaching a value of $1.8 billion by the end of the forecast period.
Chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic pain are becoming more prevalent, particularly in aging populations. This demographic shift is creating a substantial market opportunity for PEMF therapy, as it offers a non-pharmacological approach to managing these conditions. The therapy's ability to reduce pain, improve circulation, and promote tissue healing aligns well with the needs of chronic care patients.
The market for PEMF in chronic care is segmented by application, with musculoskeletal disorders representing the largest share. This segment's dominance is attributed to the high incidence of conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Neurological disorders and pain management are also significant market segments, showing promising growth potential.
Geographically, North America currently leads the PEMF therapy market, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market share. This dominance is due to the region's advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and increasing adoption of alternative therapies. Europe follows closely, with a growing acceptance of PEMF therapy in countries like Germany and the UK. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rising healthcare awareness and improving access to medical technologies.
The market is characterized by a mix of established medical device companies and specialized PEMF therapy providers. Key players include Orthofix Medical Inc., HealthyLine, and BEMER Group. These companies are focusing on product innovation and expanding their product portfolios to cater to diverse chronic care needs.
Reimbursement policies play a crucial role in market growth. While PEMF therapy is increasingly recognized for its efficacy, coverage by insurance providers varies widely. Improved reimbursement policies could significantly boost market adoption, particularly in the United States and European countries.
Consumer awareness and education remain critical factors influencing market growth. As more clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF therapy in chronic condition management becomes available, patient acceptance is likely to increase. Healthcare providers' familiarity with PEMF therapy and its integration into standard care protocols will also drive market expansion.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the PEMF therapy market. While it initially disrupted supply chains and reduced access to healthcare facilities, it has also accelerated the adoption of home-based medical devices, potentially benefiting the PEMF therapy market in the long term.
Chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic pain are becoming more prevalent, particularly in aging populations. This demographic shift is creating a substantial market opportunity for PEMF therapy, as it offers a non-pharmacological approach to managing these conditions. The therapy's ability to reduce pain, improve circulation, and promote tissue healing aligns well with the needs of chronic care patients.
The market for PEMF in chronic care is segmented by application, with musculoskeletal disorders representing the largest share. This segment's dominance is attributed to the high incidence of conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Neurological disorders and pain management are also significant market segments, showing promising growth potential.
Geographically, North America currently leads the PEMF therapy market, accounting for approximately 40% of the global market share. This dominance is due to the region's advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and increasing adoption of alternative therapies. Europe follows closely, with a growing acceptance of PEMF therapy in countries like Germany and the UK. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rising healthcare awareness and improving access to medical technologies.
The market is characterized by a mix of established medical device companies and specialized PEMF therapy providers. Key players include Orthofix Medical Inc., HealthyLine, and BEMER Group. These companies are focusing on product innovation and expanding their product portfolios to cater to diverse chronic care needs.
Reimbursement policies play a crucial role in market growth. While PEMF therapy is increasingly recognized for its efficacy, coverage by insurance providers varies widely. Improved reimbursement policies could significantly boost market adoption, particularly in the United States and European countries.
Consumer awareness and education remain critical factors influencing market growth. As more clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of PEMF therapy in chronic condition management becomes available, patient acceptance is likely to increase. Healthcare providers' familiarity with PEMF therapy and its integration into standard care protocols will also drive market expansion.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the PEMF therapy market. While it initially disrupted supply chains and reduced access to healthcare facilities, it has also accelerated the adoption of home-based medical devices, potentially benefiting the PEMF therapy market in the long term.
Current PEMF Technology and Challenges
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy has gained significant attention in recent years as a potential treatment for chronic conditions. However, the integration of this technology into mainstream chronic condition management faces several challenges and limitations.
The current PEMF technology utilizes low-frequency electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and regeneration. These devices typically operate at frequencies between 1-100 Hz and field strengths ranging from 1-100 Gauss. While the technology has shown promise in various clinical studies, there are still concerns regarding its efficacy and standardization across different conditions.
One of the primary challenges in PEMF therapy is the lack of consensus on optimal treatment parameters. Different manufacturers and researchers use varying frequencies, intensities, and treatment durations, making it difficult to establish standardized protocols for specific chronic conditions. This variability in treatment parameters has led to inconsistent results across studies and hindered widespread adoption in clinical practice.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms of action of PEMF therapy at the cellular and molecular levels. While some studies have demonstrated effects on ion channels, cell membrane potential, and gene expression, the exact pathways through which PEMF influences chronic conditions remain unclear. This knowledge gap makes it challenging to optimize treatment protocols and predict outcomes for individual patients.
The current PEMF devices also face limitations in terms of portability and ease of use. Many existing systems are bulky and require patients to remain stationary during treatment sessions, which can be inconvenient for long-term management of chronic conditions. Additionally, the cost of PEMF devices can be prohibitive for some patients, limiting access to this potential therapy.
Regulatory challenges also pose a significant hurdle in the integration of PEMF therapy. The FDA has approved some PEMF devices for specific indications, such as bone healing and pain management. However, the regulatory landscape for broader applications in chronic condition management remains complex and uncertain, potentially slowing down the adoption of this technology in clinical settings.
Furthermore, there is a need for more robust, large-scale clinical trials to establish the long-term efficacy and safety of PEMF therapy for various chronic conditions. While numerous small studies have shown promising results, the lack of comprehensive, multi-center trials has limited the acceptance of PEMF therapy within the medical community.
In conclusion, while PEMF technology shows potential for chronic condition management, several challenges must be addressed to facilitate its integration into mainstream healthcare. These include standardizing treatment protocols, elucidating mechanisms of action, improving device design and accessibility, navigating regulatory hurdles, and conducting more extensive clinical trials to validate its efficacy and safety across a range of chronic conditions.
The current PEMF technology utilizes low-frequency electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and regeneration. These devices typically operate at frequencies between 1-100 Hz and field strengths ranging from 1-100 Gauss. While the technology has shown promise in various clinical studies, there are still concerns regarding its efficacy and standardization across different conditions.
One of the primary challenges in PEMF therapy is the lack of consensus on optimal treatment parameters. Different manufacturers and researchers use varying frequencies, intensities, and treatment durations, making it difficult to establish standardized protocols for specific chronic conditions. This variability in treatment parameters has led to inconsistent results across studies and hindered widespread adoption in clinical practice.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms of action of PEMF therapy at the cellular and molecular levels. While some studies have demonstrated effects on ion channels, cell membrane potential, and gene expression, the exact pathways through which PEMF influences chronic conditions remain unclear. This knowledge gap makes it challenging to optimize treatment protocols and predict outcomes for individual patients.
The current PEMF devices also face limitations in terms of portability and ease of use. Many existing systems are bulky and require patients to remain stationary during treatment sessions, which can be inconvenient for long-term management of chronic conditions. Additionally, the cost of PEMF devices can be prohibitive for some patients, limiting access to this potential therapy.
Regulatory challenges also pose a significant hurdle in the integration of PEMF therapy. The FDA has approved some PEMF devices for specific indications, such as bone healing and pain management. However, the regulatory landscape for broader applications in chronic condition management remains complex and uncertain, potentially slowing down the adoption of this technology in clinical settings.
Furthermore, there is a need for more robust, large-scale clinical trials to establish the long-term efficacy and safety of PEMF therapy for various chronic conditions. While numerous small studies have shown promising results, the lack of comprehensive, multi-center trials has limited the acceptance of PEMF therapy within the medical community.
In conclusion, while PEMF technology shows potential for chronic condition management, several challenges must be addressed to facilitate its integration into mainstream healthcare. These include standardizing treatment protocols, elucidating mechanisms of action, improving device design and accessibility, navigating regulatory hurdles, and conducting more extensive clinical trials to validate its efficacy and safety across a range of chronic conditions.
Existing PEMF Integration Methods
01 PEMF devices for therapeutic applications
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices are designed for various therapeutic applications. These devices generate electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular activity and promote healing. They can be used for pain management, tissue repair, and improving overall well-being.- PEMF devices for therapeutic applications: Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy devices are designed for various therapeutic applications. These devices generate electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular repair and improve overall health. They can be used for pain management, tissue healing, and treating various medical conditions.
- PEMF therapy for specific medical conditions: PEMF therapy is utilized to treat specific medical conditions such as osteoarthritis, bone fractures, and neurological disorders. The therapy aims to reduce inflammation, promote tissue regeneration, and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions. Specialized PEMF devices are developed to target specific areas of the body or particular health issues.
- Wearable PEMF devices: Wearable PEMF devices are designed for convenient and continuous therapy. These devices can be worn on various parts of the body, allowing for targeted treatment while the user goes about their daily activities. Wearable PEMF devices often incorporate flexible materials and compact designs for improved comfort and usability.
- PEMF therapy combined with other treatments: PEMF therapy is often combined with other treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic effects. This may include integration with light therapy, heat therapy, or other forms of electromagnetic stimulation. The combination of treatments aims to provide synergistic benefits and improve overall treatment outcomes.
- Advanced PEMF control systems: Advanced control systems are developed for PEMF devices to optimize treatment parameters. These systems may include programmable settings, real-time monitoring, and adaptive algorithms to adjust the electromagnetic field based on the patient's response or specific treatment requirements. Such advancements aim to improve the efficacy and personalization of PEMF therapy.
02 PEMF therapy for specific medical conditions
PEMF therapy is utilized to treat specific medical conditions. It has shown efficacy in addressing issues such as bone healing, wound repair, and reducing inflammation. The therapy can be tailored to target particular areas of the body or specific health concerns.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advancements in PEMF technology
Recent advancements in PEMF technology have led to more sophisticated and efficient devices. These improvements include better control over field intensity, frequency modulation, and treatment protocols. New designs also focus on enhancing user experience and treatment effectiveness.Expand Specific Solutions04 Portable and wearable PEMF devices
The development of portable and wearable PEMF devices has made the therapy more accessible for home use. These compact devices allow for continuous treatment and can be easily integrated into daily routines, providing convenience and flexibility for users.Expand Specific Solutions05 Combination of PEMF with other therapies
PEMF therapy is being combined with other treatment modalities to enhance therapeutic outcomes. This includes integration with light therapy, heat therapy, or other forms of electromagnetic stimulation. Such combinations aim to provide synergistic effects and improve overall treatment efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PEMF Device Manufacturers and Providers
The integration of PEMF therapy into chronic condition management is in an early development stage, with a growing market and evolving technological landscape. Major players like Koninklijke Philips NV, Medtronic, and General Electric Company are investing in this field, leveraging their expertise in medical devices and healthcare technology. The market size is expanding as more healthcare providers recognize PEMF's potential benefits. However, the technology's maturity varies, with companies like Regenesis Biomedical and SofPulse focusing on specific applications. Research institutions such as Jilin University and the National University of Singapore are contributing to the scientific understanding of PEMF, potentially accelerating its adoption in chronic condition management.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Technical Solution: Philips has developed advanced PEMF therapy devices for chronic condition management. Their technology utilizes precise electromagnetic field generation to stimulate cellular repair and reduce inflammation. The devices are designed for home use, featuring adjustable intensity levels and pre-programmed treatment protocols for various chronic conditions. Philips' PEMF systems incorporate smart connectivity, allowing for remote monitoring and data analysis to track treatment efficacy over time[1][3]. The company has also invested in clinical trials to validate the effectiveness of PEMF therapy in managing specific chronic conditions, such as osteoarthritis and chronic pain[2].
Strengths: Strong brand reputation, extensive R&D capabilities, and global distribution network. Weaknesses: High cost of devices may limit accessibility for some patients.
Regenesis Biomedical, Inc.
Technical Solution: Regenesis Biomedical specializes in PEMF therapy for chronic wound healing and pain management. Their flagship product, the Provant Therapy System, uses a proprietary PEMF technology called PEMF64 to stimulate cellular repair and reduce inflammation. The device is FDA-cleared for treating post-operative pain and edema[6]. Regenesis has developed a portable, rechargeable PEMF device that allows for continuous treatment, even while patients are mobile. The company has conducted several clinical studies demonstrating the efficacy of their PEMF technology in accelerating wound healing and reducing chronic pain in conditions such as diabetic foot ulcers and venous stasis ulcers[7].
Strengths: Focused expertise in PEMF therapy for specific chronic conditions, FDA-cleared products. Weaknesses: Limited product range compared to larger medical device companies.
Core PEMF Mechanisms in Chronic Conditions
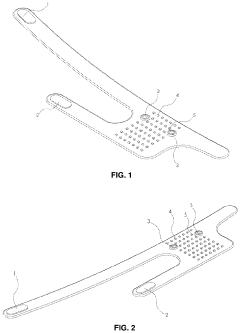
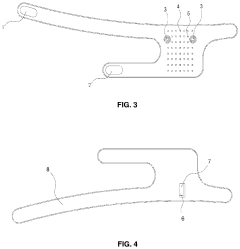
Flexible Photobiomodulation and Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy Device
PatentPendingUS20230001222A1
Innovation
- A flexible wearable device that combines PEMF and PBM therapies, featuring a flexible substrate with electromagnetic coils and light-emitting diodes, controlled by a single module that can switch between pre-set frequency sequences, and is wirelessly enabled for remote control.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy Whole Body Wellness Device to increase cells energy, strengthen immune system and promote cell regeneration
PatentInactiveUS20190054308A1
Innovation
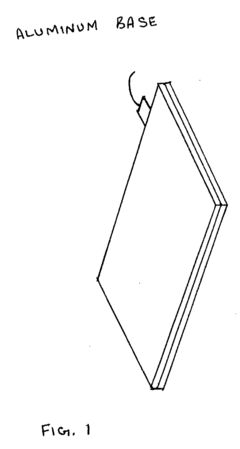
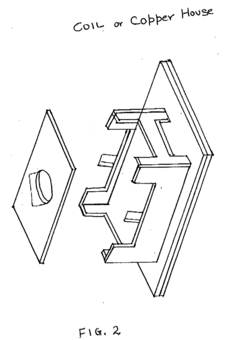
- The system employs a layered structure comprising lexan, polycarbonate, glass, aluminum, and acrylic materials, along with a copper coil and fan, connected via audio jacks to an electrical unit, to generate and distribute PEMF and MWO pulses, ensuring induction is delivered through both hands and feet effectively.
Regulatory Framework for PEMF Medical Devices
The regulatory framework for PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field) medical devices plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of these devices in chronic condition management. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of PEMF devices, classifying them as Class II or Class III medical devices depending on their intended use and potential risks.
Class II PEMF devices, which are considered to pose moderate risk, typically require a 510(k) premarket notification submission to the FDA. This process involves demonstrating that the new device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device. Manufacturers must provide evidence of safety and effectiveness, including clinical data if necessary, to support their claims.
For Class III PEMF devices, which are deemed to pose a higher risk or are intended for novel uses, a more rigorous premarket approval (PMA) process is required. This involves submitting comprehensive clinical trial data to demonstrate the device's safety and efficacy for its intended use in chronic condition management.
The regulatory framework also encompasses quality system regulations (QSRs) that manufacturers must adhere to throughout the product lifecycle. These regulations ensure consistent production of safe and effective devices through proper design controls, manufacturing processes, and post-market surveillance.
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into full effect in May 2021. The MDR imposes stricter requirements for clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and traceability compared to its predecessor, the Medical Device Directive (MDD).
Under the MDR, PEMF devices are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their intended use and potential risks. Manufacturers must obtain CE marking by demonstrating compliance with the MDR's essential requirements, which include clinical evaluation, risk management, and technical documentation.
The regulatory landscape for PEMF devices also extends to other major markets, such as Japan, where the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) oversees the approval process, and China, where the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) regulates medical devices.
As PEMF therapy gains traction in chronic condition management, regulatory bodies are continually adapting their frameworks to address emerging technologies and applications. This includes developing specific guidance documents for PEMF devices and considering their unique characteristics in the regulatory review process.
Manufacturers and healthcare providers integrating PEMF therapy into chronic condition management must navigate these complex regulatory environments to ensure compliance and patient safety. This often involves engaging with regulatory agencies early in the development process, conducting appropriate clinical studies, and maintaining robust quality management systems throughout the product lifecycle.
Class II PEMF devices, which are considered to pose moderate risk, typically require a 510(k) premarket notification submission to the FDA. This process involves demonstrating that the new device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device. Manufacturers must provide evidence of safety and effectiveness, including clinical data if necessary, to support their claims.
For Class III PEMF devices, which are deemed to pose a higher risk or are intended for novel uses, a more rigorous premarket approval (PMA) process is required. This involves submitting comprehensive clinical trial data to demonstrate the device's safety and efficacy for its intended use in chronic condition management.
The regulatory framework also encompasses quality system regulations (QSRs) that manufacturers must adhere to throughout the product lifecycle. These regulations ensure consistent production of safe and effective devices through proper design controls, manufacturing processes, and post-market surveillance.
In the European Union, PEMF devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into full effect in May 2021. The MDR imposes stricter requirements for clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and traceability compared to its predecessor, the Medical Device Directive (MDD).
Under the MDR, PEMF devices are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their intended use and potential risks. Manufacturers must obtain CE marking by demonstrating compliance with the MDR's essential requirements, which include clinical evaluation, risk management, and technical documentation.
The regulatory landscape for PEMF devices also extends to other major markets, such as Japan, where the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) oversees the approval process, and China, where the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) regulates medical devices.
As PEMF therapy gains traction in chronic condition management, regulatory bodies are continually adapting their frameworks to address emerging technologies and applications. This includes developing specific guidance documents for PEMF devices and considering their unique characteristics in the regulatory review process.
Manufacturers and healthcare providers integrating PEMF therapy into chronic condition management must navigate these complex regulatory environments to ensure compliance and patient safety. This often involves engaging with regulatory agencies early in the development process, conducting appropriate clinical studies, and maintaining robust quality management systems throughout the product lifecycle.
Cost-Effectiveness of PEMF in Healthcare
The cost-effectiveness of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy in healthcare is a crucial consideration for its integration into chronic condition management. PEMF therapy has shown promising results in treating various chronic conditions, potentially offering a non-invasive and drug-free alternative to traditional treatments. However, to fully assess its economic viability, a comprehensive analysis of its costs and benefits is necessary.
Initial investment in PEMF devices can be substantial, with prices ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. This upfront cost may seem high, but it should be evaluated against the long-term savings potential. PEMF therapy can be administered at home, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and associated costs. This aspect is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions who require ongoing treatment.
The reduction in medication usage is another significant factor contributing to the cost-effectiveness of PEMF therapy. Many chronic conditions require long-term medication, which can be expensive and may have side effects. PEMF therapy has been shown to alleviate symptoms and improve overall health, potentially reducing the reliance on pharmaceuticals. This not only decreases direct medication costs but also minimizes expenses related to managing drug side effects.
Furthermore, PEMF therapy's potential to accelerate healing and reduce recovery time can lead to substantial indirect cost savings. Faster recovery means less time off work, increased productivity, and reduced burden on caregivers. For chronic conditions that often lead to disability or reduced quality of life, PEMF therapy's ability to improve functionality and well-being can result in significant long-term economic benefits for both individuals and healthcare systems.
When comparing PEMF therapy to other treatment modalities, its non-invasive nature and low risk of complications contribute to its cost-effectiveness. Traditional treatments for chronic conditions often involve surgeries, extensive physical therapy, or ongoing medication regimens, all of which can be costly and may carry risks. PEMF therapy offers a safer alternative with fewer potential complications, potentially reducing the overall cost of care.
However, it is important to note that the cost-effectiveness of PEMF therapy can vary depending on the specific condition being treated and the individual patient's response. More research is needed to establish definitive cost-benefit ratios for different chronic conditions. Additionally, as PEMF technology continues to advance and become more widely adopted, economies of scale may further improve its cost-effectiveness in healthcare settings.
Initial investment in PEMF devices can be substantial, with prices ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. This upfront cost may seem high, but it should be evaluated against the long-term savings potential. PEMF therapy can be administered at home, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and associated costs. This aspect is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions who require ongoing treatment.
The reduction in medication usage is another significant factor contributing to the cost-effectiveness of PEMF therapy. Many chronic conditions require long-term medication, which can be expensive and may have side effects. PEMF therapy has been shown to alleviate symptoms and improve overall health, potentially reducing the reliance on pharmaceuticals. This not only decreases direct medication costs but also minimizes expenses related to managing drug side effects.
Furthermore, PEMF therapy's potential to accelerate healing and reduce recovery time can lead to substantial indirect cost savings. Faster recovery means less time off work, increased productivity, and reduced burden on caregivers. For chronic conditions that often lead to disability or reduced quality of life, PEMF therapy's ability to improve functionality and well-being can result in significant long-term economic benefits for both individuals and healthcare systems.
When comparing PEMF therapy to other treatment modalities, its non-invasive nature and low risk of complications contribute to its cost-effectiveness. Traditional treatments for chronic conditions often involve surgeries, extensive physical therapy, or ongoing medication regimens, all of which can be costly and may carry risks. PEMF therapy offers a safer alternative with fewer potential complications, potentially reducing the overall cost of care.
However, it is important to note that the cost-effectiveness of PEMF therapy can vary depending on the specific condition being treated and the individual patient's response. More research is needed to establish definitive cost-benefit ratios for different chronic conditions. Additionally, as PEMF technology continues to advance and become more widely adopted, economies of scale may further improve its cost-effectiveness in healthcare settings.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!