Glycerol's Contribution to Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glycerol Tech Background
Glycerol, also known as glycerin or propane-1,2,3-triol, has emerged as a significant player in the global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This three-carbon compound, with its unique chemical properties, has been at the forefront of sustainable technology development for several decades. The journey of glycerol from a mere byproduct of biodiesel production to a versatile green chemical exemplifies the evolution of sustainable practices in the chemical industry.
The technological evolution of glycerol utilization can be traced back to the early 2000s when the biodiesel industry experienced rapid growth. As biodiesel production increased, so did the surplus of glycerol, prompting researchers and industry experts to explore innovative applications for this abundant byproduct. This marked the beginning of glycerol's transformation from waste to a valuable resource in the fight against climate change.
Over the years, glycerol has found applications in various sectors, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. In the energy sector, it has been used as a feedstock for the production of renewable fuels, such as biogas and hydrogen. The chemical industry has embraced glycerol as a platform molecule for the synthesis of value-added chemicals, replacing petroleum-based alternatives and reducing carbon footprints.
The agricultural sector has also benefited from glycerol-based technologies, with applications in animal feed and soil amendments that help mitigate methane emissions from livestock and improve carbon sequestration in soils. Furthermore, the construction industry has incorporated glycerol-derived materials in the development of eco-friendly building materials, contributing to reduced embodied carbon in infrastructure.
Recent technological advancements have focused on enhancing the efficiency of glycerol conversion processes, exploring novel catalysts and reaction pathways to maximize its potential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Researchers are investigating the use of glycerol in carbon capture and utilization technologies, where it serves as a precursor for the production of carbonates and other materials that can sequester CO2.
The trajectory of glycerol technology is closely aligned with global sustainability goals, particularly the Paris Agreement's target of limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius. As such, the development of glycerol-based solutions has gained momentum, attracting significant investment and research attention from both public and private sectors.
Looking ahead, the technological landscape for glycerol in greenhouse gas reduction is poised for further innovation. Emerging areas of research include the integration of glycerol-based processes with renewable energy systems, the development of glycerol-derived bioplastics, and the exploration of glycerol's role in the circular economy. These advancements are expected to further amplify glycerol's contribution to mitigating climate change and fostering a more sustainable future.
The technological evolution of glycerol utilization can be traced back to the early 2000s when the biodiesel industry experienced rapid growth. As biodiesel production increased, so did the surplus of glycerol, prompting researchers and industry experts to explore innovative applications for this abundant byproduct. This marked the beginning of glycerol's transformation from waste to a valuable resource in the fight against climate change.
Over the years, glycerol has found applications in various sectors, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. In the energy sector, it has been used as a feedstock for the production of renewable fuels, such as biogas and hydrogen. The chemical industry has embraced glycerol as a platform molecule for the synthesis of value-added chemicals, replacing petroleum-based alternatives and reducing carbon footprints.
The agricultural sector has also benefited from glycerol-based technologies, with applications in animal feed and soil amendments that help mitigate methane emissions from livestock and improve carbon sequestration in soils. Furthermore, the construction industry has incorporated glycerol-derived materials in the development of eco-friendly building materials, contributing to reduced embodied carbon in infrastructure.
Recent technological advancements have focused on enhancing the efficiency of glycerol conversion processes, exploring novel catalysts and reaction pathways to maximize its potential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Researchers are investigating the use of glycerol in carbon capture and utilization technologies, where it serves as a precursor for the production of carbonates and other materials that can sequester CO2.
The trajectory of glycerol technology is closely aligned with global sustainability goals, particularly the Paris Agreement's target of limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius. As such, the development of glycerol-based solutions has gained momentum, attracting significant investment and research attention from both public and private sectors.
Looking ahead, the technological landscape for glycerol in greenhouse gas reduction is poised for further innovation. Emerging areas of research include the integration of glycerol-based processes with renewable energy systems, the development of glycerol-derived bioplastics, and the exploration of glycerol's role in the circular economy. These advancements are expected to further amplify glycerol's contribution to mitigating climate change and fostering a more sustainable future.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for glycerol as a solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions has been steadily increasing in recent years. This trend is driven by the growing global focus on sustainability and the urgent need to mitigate climate change. Glycerol, a byproduct of biodiesel production, has emerged as a versatile and eco-friendly alternative in various industries, contributing to the reduction of carbon footprint.
In the chemical industry, glycerol is gaining traction as a renewable feedstock for the production of various chemicals, replacing petroleum-based raw materials. This shift is driven by the increasing demand for bio-based products and the pressure on companies to reduce their environmental impact. The market for glycerol-derived chemicals is expected to grow significantly, as industries seek more sustainable alternatives to traditional petrochemicals.
The automotive sector represents another key market for glycerol-based solutions. With stringent emissions regulations being implemented worldwide, there is a growing demand for cleaner fuel additives and lubricants. Glycerol-based products have shown promise in improving fuel efficiency and reducing harmful emissions, making them attractive to both manufacturers and consumers.
In the construction industry, glycerol is finding applications in the development of eco-friendly building materials. These materials not only contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions during production but also improve the energy efficiency of buildings. The increasing focus on green construction and sustainable urban development is driving the demand for such innovative materials.
The agriculture sector is also showing interest in glycerol-based products for soil amendment and crop protection. These applications can help reduce the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, thereby lowering the carbon footprint of agricultural practices. As sustainable farming practices gain popularity, the demand for glycerol in this sector is expected to rise.
The potential market size for glycerol in greenhouse gas reduction applications is substantial. The global glycerol market is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, with a considerable portion attributed to its use in environmentally friendly applications. This growth is supported by favorable government policies and incentives promoting the use of renewable resources and low-carbon technologies.
However, the market demand for glycerol-based solutions faces some challenges. The fluctuating prices of crude glycerol, dependent on biodiesel production, can impact the economic viability of some applications. Additionally, the need for further research and development to optimize glycerol-based products for specific industrial uses may slow market penetration in certain sectors.
In the chemical industry, glycerol is gaining traction as a renewable feedstock for the production of various chemicals, replacing petroleum-based raw materials. This shift is driven by the increasing demand for bio-based products and the pressure on companies to reduce their environmental impact. The market for glycerol-derived chemicals is expected to grow significantly, as industries seek more sustainable alternatives to traditional petrochemicals.
The automotive sector represents another key market for glycerol-based solutions. With stringent emissions regulations being implemented worldwide, there is a growing demand for cleaner fuel additives and lubricants. Glycerol-based products have shown promise in improving fuel efficiency and reducing harmful emissions, making them attractive to both manufacturers and consumers.
In the construction industry, glycerol is finding applications in the development of eco-friendly building materials. These materials not only contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions during production but also improve the energy efficiency of buildings. The increasing focus on green construction and sustainable urban development is driving the demand for such innovative materials.
The agriculture sector is also showing interest in glycerol-based products for soil amendment and crop protection. These applications can help reduce the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, thereby lowering the carbon footprint of agricultural practices. As sustainable farming practices gain popularity, the demand for glycerol in this sector is expected to rise.
The potential market size for glycerol in greenhouse gas reduction applications is substantial. The global glycerol market is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, with a considerable portion attributed to its use in environmentally friendly applications. This growth is supported by favorable government policies and incentives promoting the use of renewable resources and low-carbon technologies.
However, the market demand for glycerol-based solutions faces some challenges. The fluctuating prices of crude glycerol, dependent on biodiesel production, can impact the economic viability of some applications. Additionally, the need for further research and development to optimize glycerol-based products for specific industrial uses may slow market penetration in certain sectors.
Current Challenges
Despite the promising potential of glycerol in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, several significant challenges currently hinder its widespread adoption and effectiveness. One of the primary obstacles is the limited infrastructure for glycerol collection and processing. Many industries that produce glycerol as a byproduct lack efficient systems to capture and utilize this resource, leading to waste and missed opportunities for emission reduction.
The variability in glycerol quality poses another challenge. Depending on its source and production method, glycerol can contain impurities that affect its usability in various applications. This inconsistency necessitates additional purification processes, which can be energy-intensive and costly, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits.
Economic factors also play a crucial role in the current challenges. The fluctuating market price of glycerol, influenced by supply and demand dynamics in the biodiesel industry, creates uncertainty for investors and businesses considering glycerol-based solutions. This volatility can discourage long-term commitments and investments in glycerol utilization technologies.
Technical limitations in glycerol conversion processes present another hurdle. While several promising pathways exist for converting glycerol into value-added products or energy sources, many of these technologies are still in the early stages of development or face scalability issues. Improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these conversion processes is essential for maximizing glycerol's potential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Regulatory frameworks and policy support also pose challenges. In many regions, there is a lack of clear guidelines or incentives for glycerol utilization in emission reduction strategies. This regulatory uncertainty can impede investment and innovation in glycerol-based solutions.
Furthermore, there is a knowledge gap among stakeholders regarding the full potential of glycerol in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Many industries and policymakers are not fully aware of the latest advancements in glycerol utilization or its environmental benefits, leading to underutilization of this resource.
Lastly, competition from other renewable energy sources and emission reduction technologies presents a challenge for glycerol. As various alternatives vie for attention and investment, glycerol must demonstrate its unique advantages and cost-effectiveness to secure its place in the broader strategy for combating climate change.
The variability in glycerol quality poses another challenge. Depending on its source and production method, glycerol can contain impurities that affect its usability in various applications. This inconsistency necessitates additional purification processes, which can be energy-intensive and costly, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits.
Economic factors also play a crucial role in the current challenges. The fluctuating market price of glycerol, influenced by supply and demand dynamics in the biodiesel industry, creates uncertainty for investors and businesses considering glycerol-based solutions. This volatility can discourage long-term commitments and investments in glycerol utilization technologies.
Technical limitations in glycerol conversion processes present another hurdle. While several promising pathways exist for converting glycerol into value-added products or energy sources, many of these technologies are still in the early stages of development or face scalability issues. Improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these conversion processes is essential for maximizing glycerol's potential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Regulatory frameworks and policy support also pose challenges. In many regions, there is a lack of clear guidelines or incentives for glycerol utilization in emission reduction strategies. This regulatory uncertainty can impede investment and innovation in glycerol-based solutions.
Furthermore, there is a knowledge gap among stakeholders regarding the full potential of glycerol in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Many industries and policymakers are not fully aware of the latest advancements in glycerol utilization or its environmental benefits, leading to underutilization of this resource.
Lastly, competition from other renewable energy sources and emission reduction technologies presents a challenge for glycerol. As various alternatives vie for attention and investment, glycerol must demonstrate its unique advantages and cost-effectiveness to secure its place in the broader strategy for combating climate change.
Existing GHG Solutions
01 Glycerol as a renewable feedstock for reducing greenhouse gas emissions
Glycerol, a byproduct of biodiesel production, can be used as a renewable feedstock in various industrial processes. This utilization helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions by replacing fossil fuel-based raw materials and providing a sustainable alternative in chemical manufacturing.- Glycerol as a renewable feedstock for reducing greenhouse gas emissions: Glycerol, a byproduct of biodiesel production, can be used as a renewable feedstock to produce various chemicals and materials. This approach helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions by replacing fossil fuel-based raw materials with a sustainable alternative. The utilization of glycerol in this manner contributes to the circular economy and reduces the carbon footprint of industrial processes.
- Carbon capture and storage using glycerol-based solvents: Glycerol-based solvents can be used in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These solvents have shown potential for efficiently capturing CO2 from industrial processes and power plants. The use of glycerol in CCS applications provides a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional amine-based solvents.
- Glycerol as a fuel additive for reducing emissions: Incorporating glycerol as a fuel additive in internal combustion engines can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When blended with conventional fuels, glycerol can improve combustion efficiency and reduce the formation of harmful emissions. This application of glycerol provides a way to utilize excess glycerol from biodiesel production while simultaneously addressing environmental concerns.
- Life cycle assessment of glycerol production and utilization: Conducting life cycle assessments of glycerol production and utilization helps quantify its overall impact on greenhouse gas emissions. These assessments consider factors such as raw material sourcing, production processes, and end-use applications. By analyzing the entire life cycle, researchers can identify opportunities to optimize glycerol-based processes and further reduce their environmental impact.
- Glycerol-based polymers for sustainable packaging: Developing glycerol-based polymers for sustainable packaging applications can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. These biodegradable materials offer an alternative to conventional plastics derived from fossil fuels. By utilizing glycerol in polymer production, the packaging industry can decrease its reliance on non-renewable resources and minimize its carbon footprint.
02 Carbon capture and storage using glycerol-based solvents
Glycerol-based solvents can be employed in carbon capture and storage technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These solvents demonstrate high CO2 absorption capacity and can be used in industrial processes to capture and sequester carbon dioxide, thereby mitigating climate change impacts.Expand Specific Solutions03 Glycerol conversion to value-added products with lower environmental impact
Converting glycerol into value-added products, such as propylene glycol or acrolein, can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These processes utilize renewable glycerol as a starting material, potentially replacing petrochemical-based production methods and reducing the carbon footprint of various industries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Glycerol-based biofuels for reducing transportation emissions
Glycerol can be used to produce biofuels, which can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the transportation sector. These glycerol-based biofuels serve as alternatives to conventional fossil fuels, potentially lowering the carbon intensity of vehicles and contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.Expand Specific Solutions05 Life cycle assessment of glycerol production and utilization
Life cycle assessments of glycerol production and utilization help quantify the overall environmental impact and greenhouse gas emissions associated with glycerol-based processes. These assessments consider factors such as raw material sourcing, production methods, and end-use applications to evaluate the sustainability of glycerol in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The glycerol market for reducing greenhouse gas emissions is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Danstar Ferment AG, CJ CheilJedang Corp., and Virent, Inc. leading innovation. Academic institutions such as Rice University and North Carolina State University are contributing to research and development. Major players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. and Mitsui Chemicals, Inc. are investing in sustainable solutions, while specialized firms like SeaChange Group LLC focus on niche applications. The involvement of diverse stakeholders indicates a maturing technology landscape with promising environmental impact.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a novel process for converting glycerol to high-value chemicals, contributing to greenhouse gas reduction. Their approach involves catalytic conversion of glycerol to propylene glycol and other value-added products[1]. The process utilizes a proprietary catalyst system that enables high selectivity and yield. Sinopec has also integrated this technology into their existing refinery operations, allowing for efficient use of glycerol byproducts from biodiesel production[2]. The company has reported a significant reduction in carbon emissions through this process, as it replaces traditional petroleum-based routes for producing these chemicals[3].
Strengths: Integrated with existing infrastructure, high efficiency, and direct contribution to emissions reduction. Weaknesses: Dependent on biodiesel production for feedstock, potential scalability issues.
Arkema France SA
Technical Solution: Arkema France SA has pioneered a bio-based glycerol carbonate production process that significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Their innovative approach involves the direct carbonation of glycerol using CO2 as a reactant, effectively sequestering carbon dioxide in the process[4]. The company has optimized reaction conditions to achieve high conversion rates and selectivity. Arkema's technology not only utilizes glycerol, a biodiesel byproduct, but also consumes CO2, making it a dual-action approach to emissions reduction[5]. The resulting glycerol carbonate has applications in various industries, including polymers, solvents, and personal care products, replacing traditional petroleum-derived alternatives[6].
Strengths: Dual carbon reduction (glycerol use and CO2 consumption), versatile end-product applications. Weaknesses: Potential high energy requirements for the carbonation process, dependency on CO2 availability.
Glycerol Innovations
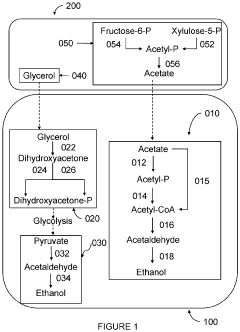
Bacterial and yeast combinations for reducing greenhouse gas production during fermentation of biomass comprising hexoses
PatentPendingUS20240191263A1
Innovation
- A combination of a bacterial host cell and a yeast host cell is used, where the bacterial host cell converts acetate and glycerol into ethanol, reducing CO2 production, and the yeast host cell generates acetate and glycerol, optimizing the metabolic pathways to enhance ethanol production while minimizing CO2 emissions.
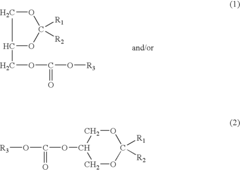
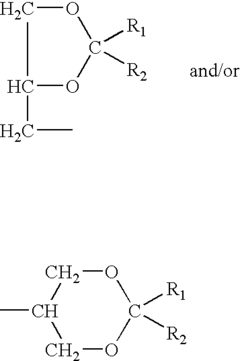
Diesel fuel compositions that contain glycerol acetal carbonates
PatentInactiveUS7097674B2
Innovation
- Incorporating glycerol acetal carbonates into diesel fuel compositions, which are synthesized through specific reactions and introduced at suitable concentrations to enhance solubility and reduce pollutant emissions.
Environmental Policies
Environmental policies play a crucial role in shaping the adoption and implementation of technologies that contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, such as the utilization of glycerol. Governments worldwide have been increasingly recognizing the potential of biofuels and bio-based products in mitigating climate change, leading to the development of supportive policy frameworks.
Many countries have implemented renewable fuel standards or mandates that require a certain percentage of transportation fuels to be derived from renewable sources. These policies have indirectly promoted the production of biodiesel, which generates glycerol as a by-product. As a result, there has been a surge in glycerol availability, creating opportunities for its utilization in various applications that can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems, have also been instrumental in driving the adoption of glycerol-based technologies. By putting a price on carbon emissions, these policies create economic incentives for industries to seek alternative, low-carbon solutions. Glycerol, being a renewable and potentially carbon-neutral feedstock, becomes an attractive option for various industrial processes under such policy frameworks.
Several countries have implemented specific policies to promote the use of bio-based chemicals and materials. For instance, the European Union's Bioeconomy Strategy aims to reduce dependence on fossil resources and promote the use of renewable biological resources, including glycerol. Such policies often include funding for research and development, tax incentives, and preferential procurement practices for bio-based products.
Environmental regulations targeting specific industries have also indirectly boosted the demand for glycerol-based solutions. For example, stringent emissions standards in the automotive sector have led to increased interest in glycerol-derived additives for cleaner-burning fuels. Similarly, regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) have spurred the development of glycerol-based solvents as environmentally friendly alternatives.
Waste management policies have further influenced the glycerol market. As governments implement stricter regulations on waste disposal and promote circular economy principles, there is growing pressure to find valuable uses for by-products like crude glycerol from biodiesel production. This has catalyzed research and innovation in glycerol valorization technologies.
International climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, have set the stage for more ambitious national policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. These overarching commitments have cascaded down to sector-specific policies that favor low-carbon technologies, including those utilizing glycerol.
Many countries have implemented renewable fuel standards or mandates that require a certain percentage of transportation fuels to be derived from renewable sources. These policies have indirectly promoted the production of biodiesel, which generates glycerol as a by-product. As a result, there has been a surge in glycerol availability, creating opportunities for its utilization in various applications that can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems, have also been instrumental in driving the adoption of glycerol-based technologies. By putting a price on carbon emissions, these policies create economic incentives for industries to seek alternative, low-carbon solutions. Glycerol, being a renewable and potentially carbon-neutral feedstock, becomes an attractive option for various industrial processes under such policy frameworks.
Several countries have implemented specific policies to promote the use of bio-based chemicals and materials. For instance, the European Union's Bioeconomy Strategy aims to reduce dependence on fossil resources and promote the use of renewable biological resources, including glycerol. Such policies often include funding for research and development, tax incentives, and preferential procurement practices for bio-based products.
Environmental regulations targeting specific industries have also indirectly boosted the demand for glycerol-based solutions. For example, stringent emissions standards in the automotive sector have led to increased interest in glycerol-derived additives for cleaner-burning fuels. Similarly, regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) have spurred the development of glycerol-based solvents as environmentally friendly alternatives.
Waste management policies have further influenced the glycerol market. As governments implement stricter regulations on waste disposal and promote circular economy principles, there is growing pressure to find valuable uses for by-products like crude glycerol from biodiesel production. This has catalyzed research and innovation in glycerol valorization technologies.
International climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, have set the stage for more ambitious national policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. These overarching commitments have cascaded down to sector-specific policies that favor low-carbon technologies, including those utilizing glycerol.
Lifecycle Assessment
Lifecycle Assessment (LCA) plays a crucial role in evaluating glycerol's potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This comprehensive approach examines the environmental impacts associated with all stages of glycerol production and utilization, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
The LCA of glycerol begins with the sourcing of feedstocks, typically derived from biodiesel production or other industrial processes. The environmental impacts of these feedstocks, including land use changes and agricultural practices, are carefully considered. The production phase encompasses the energy and resource inputs required for glycerol purification and processing, which can vary significantly depending on the source and desired purity level.
Transportation and distribution of glycerol to end-users contribute to the overall carbon footprint. However, glycerol's high energy density and stability make it an efficient product to transport, potentially offsetting some emissions compared to alternative materials.
The use phase of glycerol in various applications, such as biofuels, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals, is a critical component of the LCA. Here, the potential for greenhouse gas reduction becomes evident. For instance, when used as a biofuel additive, glycerol can enhance combustion efficiency and reduce overall emissions from vehicles.
End-of-life considerations for glycerol-based products are generally favorable, as many applications result in biodegradable or recyclable materials. This aspect of the lifecycle can contribute positively to the overall environmental impact assessment.
Comparative LCAs between glycerol-based products and their fossil fuel-derived counterparts often reveal significant potential for greenhouse gas reduction. These studies typically show lower carbon footprints for glycerol-based alternatives, particularly when considering the entire lifecycle.
However, it is essential to note that the environmental benefits of glycerol can vary depending on its source and application. Crude glycerol from biodiesel production may have a more favorable LCA profile compared to synthetic glycerol produced from fossil fuels. Additionally, the energy mix used in glycerol processing and the efficiency of production processes can significantly influence the overall environmental impact.
To maximize glycerol's contribution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, ongoing research focuses on optimizing production processes, improving purification techniques, and developing novel applications that leverage glycerol's unique properties. These efforts aim to enhance the lifecycle performance of glycerol-based products and further reduce their environmental footprint.
The LCA of glycerol begins with the sourcing of feedstocks, typically derived from biodiesel production or other industrial processes. The environmental impacts of these feedstocks, including land use changes and agricultural practices, are carefully considered. The production phase encompasses the energy and resource inputs required for glycerol purification and processing, which can vary significantly depending on the source and desired purity level.
Transportation and distribution of glycerol to end-users contribute to the overall carbon footprint. However, glycerol's high energy density and stability make it an efficient product to transport, potentially offsetting some emissions compared to alternative materials.
The use phase of glycerol in various applications, such as biofuels, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals, is a critical component of the LCA. Here, the potential for greenhouse gas reduction becomes evident. For instance, when used as a biofuel additive, glycerol can enhance combustion efficiency and reduce overall emissions from vehicles.
End-of-life considerations for glycerol-based products are generally favorable, as many applications result in biodegradable or recyclable materials. This aspect of the lifecycle can contribute positively to the overall environmental impact assessment.
Comparative LCAs between glycerol-based products and their fossil fuel-derived counterparts often reveal significant potential for greenhouse gas reduction. These studies typically show lower carbon footprints for glycerol-based alternatives, particularly when considering the entire lifecycle.
However, it is essential to note that the environmental benefits of glycerol can vary depending on its source and application. Crude glycerol from biodiesel production may have a more favorable LCA profile compared to synthetic glycerol produced from fossil fuels. Additionally, the energy mix used in glycerol processing and the efficiency of production processes can significantly influence the overall environmental impact.
To maximize glycerol's contribution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, ongoing research focuses on optimizing production processes, improving purification techniques, and developing novel applications that leverage glycerol's unique properties. These efforts aim to enhance the lifecycle performance of glycerol-based products and further reduce their environmental footprint.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!