How AMOLED aids in foldable smartphone durability?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED in Foldables: Background and Objectives
The evolution of foldable smartphones has been a significant milestone in mobile technology, with AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays playing a crucial role in their development and durability. This technological advancement has its roots in the early 2000s when OLED technology first emerged, offering thinner, more flexible display options compared to traditional LCD screens.
The primary objective of integrating AMOLED technology into foldable smartphones is to enhance device durability while maintaining superior display quality. AMOLED displays are inherently more flexible than their LCD counterparts, making them ideal for the unique form factor of foldable devices. This flexibility is essential in withstanding the repeated folding and unfolding actions that these smartphones must endure.
As the smartphone market has matured, manufacturers have been seeking innovative ways to differentiate their products and provide new user experiences. Foldable smartphones represent a convergence of cutting-edge display technology and novel form factors, aiming to offer users larger screen real estate without sacrificing portability.
The development of AMOLED technology for foldable devices has been driven by several key factors. Firstly, the need for displays that can bend without breaking or degrading in quality. Secondly, the demand for screens that can maintain color accuracy and brightness even when folded repeatedly. Lastly, the requirement for power efficiency, as larger screens typically consume more energy.
AMOLED's contribution to foldable smartphone durability extends beyond mere flexibility. The technology allows for the creation of ultra-thin display panels, which are less prone to damage from bending stress. Additionally, AMOLED displays can be manufactured on plastic substrates rather than glass, further enhancing their resilience to repeated folding.
The evolution of AMOLED in foldable smartphones has seen continuous improvements in areas such as crease reduction, color shift minimization, and overall lifespan of the display. Manufacturers have been working on developing specialized materials and manufacturing processes to address these challenges and improve the longevity of foldable devices.
Looking forward, the objectives for AMOLED technology in foldable smartphones include further enhancing durability, reducing the visibility of creases, improving energy efficiency, and exploring new form factors that push the boundaries of smartphone design. As the technology matures, we can expect to see more innovative applications that leverage the unique properties of AMOLED displays in foldable devices.
The primary objective of integrating AMOLED technology into foldable smartphones is to enhance device durability while maintaining superior display quality. AMOLED displays are inherently more flexible than their LCD counterparts, making them ideal for the unique form factor of foldable devices. This flexibility is essential in withstanding the repeated folding and unfolding actions that these smartphones must endure.
As the smartphone market has matured, manufacturers have been seeking innovative ways to differentiate their products and provide new user experiences. Foldable smartphones represent a convergence of cutting-edge display technology and novel form factors, aiming to offer users larger screen real estate without sacrificing portability.
The development of AMOLED technology for foldable devices has been driven by several key factors. Firstly, the need for displays that can bend without breaking or degrading in quality. Secondly, the demand for screens that can maintain color accuracy and brightness even when folded repeatedly. Lastly, the requirement for power efficiency, as larger screens typically consume more energy.
AMOLED's contribution to foldable smartphone durability extends beyond mere flexibility. The technology allows for the creation of ultra-thin display panels, which are less prone to damage from bending stress. Additionally, AMOLED displays can be manufactured on plastic substrates rather than glass, further enhancing their resilience to repeated folding.
The evolution of AMOLED in foldable smartphones has seen continuous improvements in areas such as crease reduction, color shift minimization, and overall lifespan of the display. Manufacturers have been working on developing specialized materials and manufacturing processes to address these challenges and improve the longevity of foldable devices.
Looking forward, the objectives for AMOLED technology in foldable smartphones include further enhancing durability, reducing the visibility of creases, improving energy efficiency, and exploring new form factors that push the boundaries of smartphone design. As the technology matures, we can expect to see more innovative applications that leverage the unique properties of AMOLED displays in foldable devices.
Market Analysis: Foldable Smartphone Demand
The foldable smartphone market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by consumer demand for innovative and versatile devices. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, the market for foldable smartphones is expected to expand rapidly. Industry analysts project substantial growth in this segment, with some estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% in the coming years.
Consumer interest in foldable smartphones stems from their unique value proposition. These devices offer the convenience of a compact form factor when folded, while providing a larger display for enhanced productivity and entertainment when unfolded. This dual functionality appeals to users who seek a balance between portability and screen real estate, particularly in an era where mobile devices are increasingly used for work, gaming, and content consumption.
The demand for foldable smartphones is particularly strong among early adopters and tech enthusiasts who are willing to pay a premium for cutting-edge technology. However, as manufacturing processes improve and economies of scale come into play, prices are expected to decrease, making foldable devices more accessible to a broader consumer base. This trend is likely to further accelerate market growth in the mid to long term.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly countries like South Korea and China, has shown the highest adoption rates for foldable smartphones. These markets are characterized by tech-savvy consumers and strong domestic manufacturers pushing the boundaries of innovation. North America and Europe are also seeing increasing demand, albeit at a slower pace, as more options become available and consumer awareness grows.
The enterprise sector represents another significant driver of foldable smartphone demand. Businesses are recognizing the potential productivity benefits of devices that can seamlessly transition between smartphone and tablet form factors. This versatility is particularly valuable for mobile professionals, sales teams, and field workers who require both portability and screen space for their daily tasks.
Despite the positive growth trajectory, challenges remain in the foldable smartphone market. Concerns about durability, particularly regarding the folding mechanism and flexible display, have been a barrier to widespread adoption. However, advancements in materials science and engineering, including the use of AMOLED technology, are addressing these concerns and improving consumer confidence in the longevity of foldable devices.
Consumer interest in foldable smartphones stems from their unique value proposition. These devices offer the convenience of a compact form factor when folded, while providing a larger display for enhanced productivity and entertainment when unfolded. This dual functionality appeals to users who seek a balance between portability and screen real estate, particularly in an era where mobile devices are increasingly used for work, gaming, and content consumption.
The demand for foldable smartphones is particularly strong among early adopters and tech enthusiasts who are willing to pay a premium for cutting-edge technology. However, as manufacturing processes improve and economies of scale come into play, prices are expected to decrease, making foldable devices more accessible to a broader consumer base. This trend is likely to further accelerate market growth in the mid to long term.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly countries like South Korea and China, has shown the highest adoption rates for foldable smartphones. These markets are characterized by tech-savvy consumers and strong domestic manufacturers pushing the boundaries of innovation. North America and Europe are also seeing increasing demand, albeit at a slower pace, as more options become available and consumer awareness grows.
The enterprise sector represents another significant driver of foldable smartphone demand. Businesses are recognizing the potential productivity benefits of devices that can seamlessly transition between smartphone and tablet form factors. This versatility is particularly valuable for mobile professionals, sales teams, and field workers who require both portability and screen space for their daily tasks.
Despite the positive growth trajectory, challenges remain in the foldable smartphone market. Concerns about durability, particularly regarding the folding mechanism and flexible display, have been a barrier to widespread adoption. However, advancements in materials science and engineering, including the use of AMOLED technology, are addressing these concerns and improving consumer confidence in the longevity of foldable devices.
AMOLED Technology: Current State and Challenges
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has become a cornerstone in the development of foldable smartphones, offering unique advantages that contribute significantly to device durability. However, the current state of AMOLED technology in foldable devices also presents several challenges that researchers and manufacturers are actively addressing.
One of the primary advantages of AMOLED displays in foldable smartphones is their flexibility. Unlike traditional LCD screens, AMOLED panels can be bent and folded without compromising image quality or functionality. This inherent flexibility allows for the creation of innovative form factors, such as inward and outward folding designs, which have become increasingly popular in the smartphone market.
Despite these advantages, AMOLED technology in foldable devices faces several challenges. One of the most significant issues is the potential for screen damage at the folding point. Repeated folding and unfolding can cause stress on the OLED materials, leading to pixel degradation or failure along the crease. Manufacturers are working to develop more robust OLED structures and protective layers to mitigate this problem.
Another challenge is the visibility of the crease in the folded area. While AMOLED displays can fold without breaking, the folding action often leaves a visible line or indentation on the screen, which can be noticeable to users and detract from the overall visual experience. Improving the folding mechanism and developing new materials to reduce the visibility of the crease are ongoing areas of research.
Color shift and brightness uniformity across the folded and unfolded states of the display also present challenges. The bending of the OLED layers can cause slight variations in color reproduction and brightness, particularly near the folding area. Ensuring consistent display performance in all device configurations is a key focus for manufacturers.
Durability concerns extend beyond the display itself to the touch sensors and protective layers. Integrating flexible touch sensors that can withstand repeated folding while maintaining sensitivity and accuracy is crucial. Additionally, developing scratch-resistant and impact-resistant cover materials that can flex without compromising protection is an ongoing challenge.
Power consumption and battery life are also important considerations. While AMOLED displays are generally more energy-efficient than LCDs, the larger screens of foldable devices and the power required to drive flexible display components can impact overall device efficiency. Balancing performance with power consumption remains a key challenge in foldable smartphone design.
As the technology continues to evolve, researchers are exploring advanced materials and manufacturing processes to enhance the durability and performance of AMOLED displays in foldable devices. These efforts aim to address the current limitations and push the boundaries of what is possible in flexible display technology.
One of the primary advantages of AMOLED displays in foldable smartphones is their flexibility. Unlike traditional LCD screens, AMOLED panels can be bent and folded without compromising image quality or functionality. This inherent flexibility allows for the creation of innovative form factors, such as inward and outward folding designs, which have become increasingly popular in the smartphone market.
Despite these advantages, AMOLED technology in foldable devices faces several challenges. One of the most significant issues is the potential for screen damage at the folding point. Repeated folding and unfolding can cause stress on the OLED materials, leading to pixel degradation or failure along the crease. Manufacturers are working to develop more robust OLED structures and protective layers to mitigate this problem.
Another challenge is the visibility of the crease in the folded area. While AMOLED displays can fold without breaking, the folding action often leaves a visible line or indentation on the screen, which can be noticeable to users and detract from the overall visual experience. Improving the folding mechanism and developing new materials to reduce the visibility of the crease are ongoing areas of research.
Color shift and brightness uniformity across the folded and unfolded states of the display also present challenges. The bending of the OLED layers can cause slight variations in color reproduction and brightness, particularly near the folding area. Ensuring consistent display performance in all device configurations is a key focus for manufacturers.
Durability concerns extend beyond the display itself to the touch sensors and protective layers. Integrating flexible touch sensors that can withstand repeated folding while maintaining sensitivity and accuracy is crucial. Additionally, developing scratch-resistant and impact-resistant cover materials that can flex without compromising protection is an ongoing challenge.
Power consumption and battery life are also important considerations. While AMOLED displays are generally more energy-efficient than LCDs, the larger screens of foldable devices and the power required to drive flexible display components can impact overall device efficiency. Balancing performance with power consumption remains a key challenge in foldable smartphone design.
As the technology continues to evolve, researchers are exploring advanced materials and manufacturing processes to enhance the durability and performance of AMOLED displays in foldable devices. These efforts aim to address the current limitations and push the boundaries of what is possible in flexible display technology.
AMOLED Solutions for Foldable Durability
01 Pixel compensation techniques
Various pixel compensation techniques are employed to improve AMOLED durability. These methods address issues such as pixel aging, non-uniformity, and degradation over time. Compensation algorithms and circuits are implemented to adjust pixel voltages or currents, ensuring consistent display performance and extending the overall lifespan of AMOLED panels.- Pixel compensation techniques: Various pixel compensation techniques are employed to improve AMOLED durability. These methods address issues such as pixel aging, non-uniformity, and degradation over time. Compensation algorithms and circuits are implemented to adjust pixel voltages or currents, ensuring consistent display quality and extending the overall lifespan of AMOLED panels.
- Structural improvements for AMOLED displays: Enhancements in AMOLED display structure contribute to improved durability. This includes advancements in thin-film transistor (TFT) designs, pixel layouts, and protective layers. These structural improvements aim to reduce stress on individual components, enhance resistance to environmental factors, and prolong the operational life of AMOLED displays.
- Power management and thermal control: Effective power management and thermal control strategies are crucial for AMOLED durability. These techniques involve optimizing power consumption, implementing efficient heat dissipation methods, and utilizing adaptive brightness control. By managing power and temperature, the degradation of OLED materials is minimized, thereby extending the display's lifespan.
- Material innovations for AMOLED displays: Advancements in OLED materials play a significant role in enhancing AMOLED durability. This includes the development of more stable organic compounds, improved electron transport layers, and novel encapsulation materials. These material innovations aim to increase resistance to degradation factors such as moisture, oxygen, and electrical stress.
- Burn-in prevention and mitigation: Techniques to prevent and mitigate burn-in effects are essential for AMOLED durability. These methods include pixel shifting, adaptive refresh rates, and intelligent content analysis to distribute pixel wear evenly. Additionally, compensation algorithms are employed to detect and correct burn-in artifacts, ensuring a longer-lasting and more consistent display quality.
02 Structural improvements for AMOLED displays
Enhancements to the physical structure of AMOLED displays contribute to improved durability. These include optimized layer compositions, protective encapsulation techniques, and innovative electrode designs. Such structural improvements help protect the organic materials from environmental factors, reduce mechanical stress, and enhance overall device longevity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Power management and thermal control
Effective power management and thermal control strategies are crucial for AMOLED durability. These techniques involve optimizing power consumption, implementing efficient driving schemes, and managing heat dissipation. By reducing thermal stress and minimizing power-related degradation, these approaches help extend the operational life of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advanced materials for AMOLED longevity
The development and use of advanced materials play a significant role in enhancing AMOLED durability. This includes the incorporation of more stable organic compounds, improved electrode materials, and novel encapsulation substances. These materials contribute to better resistance against environmental factors, reduced degradation rates, and overall improved long-term performance of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions05 Intelligent display management systems
Intelligent display management systems are implemented to enhance AMOLED durability. These systems incorporate sensors, real-time monitoring, and adaptive algorithms to optimize display performance over time. By dynamically adjusting display parameters based on usage patterns, environmental conditions, and device status, these systems help maintain display quality and extend the operational lifespan of AMOLED panels.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Foldable AMOLED Industry
The AMOLED technology for foldable smartphone durability is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and advancing technical maturity. Major players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and LG Electronics are driving innovation in this field. The market is expanding as more smartphone manufacturers adopt foldable designs, creating demand for durable AMOLED displays. Technical advancements focus on improving flexibility, reducing creases, and enhancing overall durability. Companies are investing heavily in R&D to overcome challenges related to repeated folding and unfolding, with progress being made in materials and manufacturing processes.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed a flexible AMOLED display technology specifically for foldable smartphones, focusing on improving durability through innovative materials and structures. Their displays utilize a multi-layer structure that includes a flexible substrate, a thin-film encapsulation layer, and a specially designed touch sensor layer that can withstand repeated bending[4]. BOE's AMOLED panels for foldables feature a unique pixel compensation technology that helps maintain display quality and brightness uniformity even after thousands of folding cycles. The company has also introduced a "soft hard layer" design that combines flexible and rigid elements to enhance overall durability while maintaining the display's foldability[5].
Strengths: Advanced flexible AMOLED technology, innovative multi-layer structure. Weaknesses: Less market presence in foldables compared to Samsung, potential for higher defect rates in mass production.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has pioneered AMOLED technology for foldable smartphones, developing Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG) to enhance durability. Their latest foldable devices feature a layer of UTG that's just 30 micrometers thick, covered by a protective plastic layer[1]. This combination provides flexibility while improving scratch resistance. Samsung's AMOLED displays for foldables also incorporate a shock-absorbing layer and a reinforced panel structure to distribute impact forces, significantly reducing the risk of damage from drops or external pressure[2]. The company has implemented advanced pixel layouts and materials that can withstand repeated folding, with some models tested to withstand up to 200,000 folds without degradation[3].
Strengths: Industry-leading AMOLED technology, proprietary UTG development, extensive durability testing. Weaknesses: Higher production costs, potential for visible crease over time.
Core Innovations in Flexible AMOLED
Active matrix organic light emitting diode panel
PatentInactiveUS20200185645A1
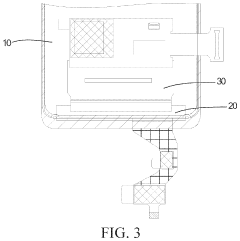
Innovation
- An AMOLED panel design featuring a hydrogel layer coated between two backing plates at the bent portion, which is then solidified with ultraviolet light, providing structural strength and toughness to the fillet formed when the panel is folded, thereby preventing deformation and breakage.
Array substrate, display device, and method for manufacturing array substrate
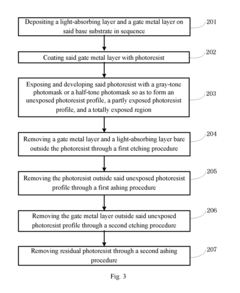
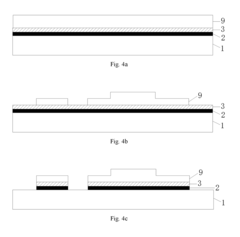
PatentActiveUS20170148862A1
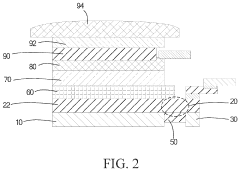
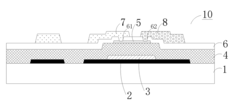
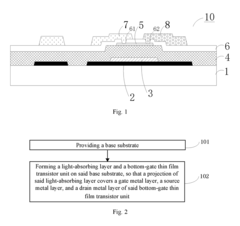
Innovation
- An array substrate with a light-absorbing layer covering the gate, source, and drain metal layers of a bottom-gate thin film transistor unit, preventing ambient light irradiation while allowing useful light to pass through.
Supply Chain Considerations for Foldable AMOLEDs
The supply chain for foldable AMOLEDs presents unique challenges and considerations due to the specialized nature of these displays. Sourcing high-quality flexible substrates is crucial, as these form the foundation of the foldable display. Manufacturers must establish reliable partnerships with suppliers who can consistently deliver materials that meet the stringent requirements for flexibility, durability, and optical performance.
Production of foldable AMOLED panels requires advanced manufacturing facilities with specialized equipment. This necessitates significant capital investment and may lead to limited production capacity in the short term. As demand for foldable smartphones grows, manufacturers must carefully balance capacity expansion with market demand to avoid oversupply or shortages.
Quality control is paramount in the foldable AMOLED supply chain. The complex structure of these displays, combining multiple layers of sensitive materials, demands rigorous testing at each stage of production. Manufacturers must implement comprehensive quality assurance processes to detect defects early and minimize waste, which is particularly important given the high cost of materials and production.
Logistics and transportation of foldable AMOLED panels require special attention. The delicate nature of these displays necessitates careful handling and packaging to prevent damage during transit. This may involve custom-designed packaging solutions and specialized shipping procedures, potentially increasing logistics costs and complexity.
The supply chain must also account for the need for rapid innovation and iteration in foldable AMOLED technology. Close collaboration between display manufacturers, smartphone brands, and material suppliers is essential to drive continuous improvements in durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness. This may involve co-development of new materials or manufacturing processes, requiring agile supply chain management to quickly adapt to technological advancements.
Inventory management presents another challenge in the foldable AMOLED supply chain. The high value of these components, combined with their potential for rapid technological obsolescence, requires careful balancing of stock levels. Just-in-time manufacturing principles may need to be adapted to ensure sufficient supply without excessive inventory costs.
As the foldable smartphone market matures, supply chain diversification becomes increasingly important. Reliance on a limited number of suppliers for critical components can pose risks to production continuity. Manufacturers must work to develop alternative sources for key materials and components to mitigate supply chain disruptions and enhance negotiating power.
Production of foldable AMOLED panels requires advanced manufacturing facilities with specialized equipment. This necessitates significant capital investment and may lead to limited production capacity in the short term. As demand for foldable smartphones grows, manufacturers must carefully balance capacity expansion with market demand to avoid oversupply or shortages.
Quality control is paramount in the foldable AMOLED supply chain. The complex structure of these displays, combining multiple layers of sensitive materials, demands rigorous testing at each stage of production. Manufacturers must implement comprehensive quality assurance processes to detect defects early and minimize waste, which is particularly important given the high cost of materials and production.
Logistics and transportation of foldable AMOLED panels require special attention. The delicate nature of these displays necessitates careful handling and packaging to prevent damage during transit. This may involve custom-designed packaging solutions and specialized shipping procedures, potentially increasing logistics costs and complexity.
The supply chain must also account for the need for rapid innovation and iteration in foldable AMOLED technology. Close collaboration between display manufacturers, smartphone brands, and material suppliers is essential to drive continuous improvements in durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness. This may involve co-development of new materials or manufacturing processes, requiring agile supply chain management to quickly adapt to technological advancements.
Inventory management presents another challenge in the foldable AMOLED supply chain. The high value of these components, combined with their potential for rapid technological obsolescence, requires careful balancing of stock levels. Just-in-time manufacturing principles may need to be adapted to ensure sufficient supply without excessive inventory costs.
As the foldable smartphone market matures, supply chain diversification becomes increasingly important. Reliance on a limited number of suppliers for critical components can pose risks to production continuity. Manufacturers must work to develop alternative sources for key materials and components to mitigate supply chain disruptions and enhance negotiating power.
Environmental Impact of Foldable AMOLED Production
The production of foldable AMOLED displays for smartphones has significant environmental implications, both positive and negative. On the positive side, the durability and longevity of AMOLED technology in foldable devices can potentially reduce electronic waste by extending the lifespan of smartphones. The flexible nature of AMOLED displays allows for more efficient use of materials, potentially reducing the overall environmental footprint of device manufacturing.
However, the production process of foldable AMOLED displays involves several environmentally challenging aspects. The manufacturing of these displays requires rare earth elements and precious metals, which are often mined using environmentally destructive methods. The extraction and processing of these materials can lead to soil degradation, water pollution, and habitat destruction in mining areas.
The production of AMOLED displays also involves energy-intensive processes, contributing to increased carbon emissions. The complex layering and precise manufacturing techniques required for foldable displays demand substantial energy input, often sourced from fossil fuels in many production regions. This energy consumption contributes to the overall carbon footprint of smartphone production.
Chemical usage in AMOLED production poses another environmental concern. The manufacturing process involves various solvents, acids, and other potentially hazardous chemicals. Improper handling or disposal of these substances can lead to soil and water contamination, affecting local ecosystems and human health.
Water usage is a significant factor in AMOLED production, with large quantities required for cleaning and cooling processes. In water-stressed regions, this high water demand can exacerbate local water scarcity issues and impact surrounding communities and ecosystems.
The complexity of foldable AMOLED displays also presents recycling challenges. The intricate integration of various materials makes it difficult to separate and recycle components effectively at the end of a device's life cycle. This complexity can lead to increased e-waste if proper recycling technologies and infrastructure are not developed in tandem with the technology.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, manufacturers are exploring more sustainable production methods. These include developing recycling techniques specific to foldable AMOLED displays, investing in renewable energy sources for production facilities, and researching alternative, more environmentally friendly materials for display components. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the efficiency of production processes to reduce energy and water consumption.
However, the production process of foldable AMOLED displays involves several environmentally challenging aspects. The manufacturing of these displays requires rare earth elements and precious metals, which are often mined using environmentally destructive methods. The extraction and processing of these materials can lead to soil degradation, water pollution, and habitat destruction in mining areas.
The production of AMOLED displays also involves energy-intensive processes, contributing to increased carbon emissions. The complex layering and precise manufacturing techniques required for foldable displays demand substantial energy input, often sourced from fossil fuels in many production regions. This energy consumption contributes to the overall carbon footprint of smartphone production.
Chemical usage in AMOLED production poses another environmental concern. The manufacturing process involves various solvents, acids, and other potentially hazardous chemicals. Improper handling or disposal of these substances can lead to soil and water contamination, affecting local ecosystems and human health.
Water usage is a significant factor in AMOLED production, with large quantities required for cleaning and cooling processes. In water-stressed regions, this high water demand can exacerbate local water scarcity issues and impact surrounding communities and ecosystems.
The complexity of foldable AMOLED displays also presents recycling challenges. The intricate integration of various materials makes it difficult to separate and recycle components effectively at the end of a device's life cycle. This complexity can lead to increased e-waste if proper recycling technologies and infrastructure are not developed in tandem with the technology.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, manufacturers are exploring more sustainable production methods. These include developing recycling techniques specific to foldable AMOLED displays, investing in renewable energy sources for production facilities, and researching alternative, more environmentally friendly materials for display components. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the efficiency of production processes to reduce energy and water consumption.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!