How Enhanced Solenoid Valve Design Affects Power Plant Operations
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Solenoid Valve Evolution
Solenoid valves have undergone significant evolution since their inception, playing a crucial role in power plant operations. The journey of solenoid valve design has been marked by continuous improvements in efficiency, reliability, and performance.
In the early stages, solenoid valves were relatively simple devices with limited control capabilities. They primarily served basic on/off functions in power plant systems. As the demands of power generation increased, so did the need for more sophisticated valve designs.
The 1960s and 1970s saw the introduction of more robust solenoid valves capable of handling higher pressures and temperatures. This development was crucial for power plants, as it allowed for better control of steam and water flow in critical systems. The incorporation of improved materials, such as high-grade stainless steel and advanced polymers, enhanced the durability and lifespan of these valves.
The 1980s marked a significant leap in solenoid valve technology with the integration of electronic controls. This advancement enabled more precise operation and remote monitoring capabilities, which were particularly beneficial for large-scale power plants. The ability to fine-tune valve operations led to improved efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, the focus shifted towards miniaturization and increased responsiveness. Compact solenoid valves with faster actuation times were developed, allowing for more rapid adjustments in power plant processes. This era also saw the introduction of proportional solenoid valves, which offered variable flow control, a feature that proved invaluable in optimizing power plant operations.
Recent years have witnessed a revolution in solenoid valve design, driven by the need for smarter and more efficient power plants. The integration of advanced sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities has transformed solenoid valves into intelligent components of the power generation ecosystem. These smart valves can now provide real-time data on their performance, predict maintenance needs, and automatically adjust to changing operational conditions.
Furthermore, the latest solenoid valve designs incorporate energy-efficient actuators and low-power consumption electronics. This not only reduces the overall energy footprint of power plants but also enhances the reliability of valve operations during critical situations, such as power outages or system failures.
The evolution of solenoid valve design has also been influenced by environmental concerns and regulatory requirements. Modern valves are designed to minimize leakage, reduce emissions, and comply with stringent safety standards. This has led to the development of eco-friendly materials and sealing technologies that ensure both performance and environmental responsibility.
As power plants continue to evolve towards more sustainable and efficient operations, solenoid valve design is expected to advance further. Future developments may include self-diagnosing valves, AI-driven predictive maintenance systems, and even more energy-efficient actuation mechanisms. These enhancements will continue to play a vital role in improving the overall efficiency, reliability, and environmental impact of power plant operations.
In the early stages, solenoid valves were relatively simple devices with limited control capabilities. They primarily served basic on/off functions in power plant systems. As the demands of power generation increased, so did the need for more sophisticated valve designs.
The 1960s and 1970s saw the introduction of more robust solenoid valves capable of handling higher pressures and temperatures. This development was crucial for power plants, as it allowed for better control of steam and water flow in critical systems. The incorporation of improved materials, such as high-grade stainless steel and advanced polymers, enhanced the durability and lifespan of these valves.
The 1980s marked a significant leap in solenoid valve technology with the integration of electronic controls. This advancement enabled more precise operation and remote monitoring capabilities, which were particularly beneficial for large-scale power plants. The ability to fine-tune valve operations led to improved efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, the focus shifted towards miniaturization and increased responsiveness. Compact solenoid valves with faster actuation times were developed, allowing for more rapid adjustments in power plant processes. This era also saw the introduction of proportional solenoid valves, which offered variable flow control, a feature that proved invaluable in optimizing power plant operations.
Recent years have witnessed a revolution in solenoid valve design, driven by the need for smarter and more efficient power plants. The integration of advanced sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities has transformed solenoid valves into intelligent components of the power generation ecosystem. These smart valves can now provide real-time data on their performance, predict maintenance needs, and automatically adjust to changing operational conditions.
Furthermore, the latest solenoid valve designs incorporate energy-efficient actuators and low-power consumption electronics. This not only reduces the overall energy footprint of power plants but also enhances the reliability of valve operations during critical situations, such as power outages or system failures.
The evolution of solenoid valve design has also been influenced by environmental concerns and regulatory requirements. Modern valves are designed to minimize leakage, reduce emissions, and comply with stringent safety standards. This has led to the development of eco-friendly materials and sealing technologies that ensure both performance and environmental responsibility.
As power plants continue to evolve towards more sustainable and efficient operations, solenoid valve design is expected to advance further. Future developments may include self-diagnosing valves, AI-driven predictive maintenance systems, and even more energy-efficient actuation mechanisms. These enhancements will continue to play a vital role in improving the overall efficiency, reliability, and environmental impact of power plant operations.
Power Plant Efficiency Demands
Power plants worldwide are facing increasing pressure to improve their operational efficiency and reduce environmental impact. This demand for enhanced efficiency is driven by several factors, including rising fuel costs, stricter environmental regulations, and the need to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving energy market. As a result, power plant operators are constantly seeking innovative solutions to optimize their processes and maximize output while minimizing resource consumption.
One of the key areas of focus for improving power plant efficiency is the optimization of fluid control systems, particularly solenoid valves. These components play a crucial role in regulating the flow of various fluids and gases throughout the power generation process. Enhanced solenoid valve designs can significantly impact power plant operations by improving precision, reducing energy consumption, and increasing overall system reliability.
The demand for more efficient power plants has led to the development of advanced solenoid valve technologies that offer faster response times, higher flow rates, and improved durability. These enhancements contribute to better control of critical processes such as fuel injection, steam regulation, and cooling systems. By optimizing these processes, power plants can achieve higher thermal efficiency, reduced emissions, and improved load-following capabilities.
Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies and digital control systems has enabled more precise and adaptive operation of solenoid valves. This allows for real-time monitoring and adjustment of valve performance, leading to optimized fluid flow and reduced energy waste. The ability to fine-tune valve operations based on changing plant conditions and demand patterns contributes significantly to overall plant efficiency.
Another driving factor in the demand for enhanced solenoid valve design is the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and the need for flexible power generation. As power plants are required to operate more dynamically to accommodate fluctuations in renewable energy supply, the role of efficient and responsive fluid control systems becomes even more critical. Advanced solenoid valves can help power plants quickly adjust their output and maintain stability in the face of varying load conditions.
The push for greater efficiency also extends to the maintenance and lifecycle management of power plant components. Enhanced solenoid valve designs that offer improved reliability and longer service life can reduce downtime and maintenance costs, contributing to overall plant efficiency. This aspect is particularly important as power plants seek to maximize their operational availability and minimize unplanned outages.
One of the key areas of focus for improving power plant efficiency is the optimization of fluid control systems, particularly solenoid valves. These components play a crucial role in regulating the flow of various fluids and gases throughout the power generation process. Enhanced solenoid valve designs can significantly impact power plant operations by improving precision, reducing energy consumption, and increasing overall system reliability.
The demand for more efficient power plants has led to the development of advanced solenoid valve technologies that offer faster response times, higher flow rates, and improved durability. These enhancements contribute to better control of critical processes such as fuel injection, steam regulation, and cooling systems. By optimizing these processes, power plants can achieve higher thermal efficiency, reduced emissions, and improved load-following capabilities.
Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies and digital control systems has enabled more precise and adaptive operation of solenoid valves. This allows for real-time monitoring and adjustment of valve performance, leading to optimized fluid flow and reduced energy waste. The ability to fine-tune valve operations based on changing plant conditions and demand patterns contributes significantly to overall plant efficiency.
Another driving factor in the demand for enhanced solenoid valve design is the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and the need for flexible power generation. As power plants are required to operate more dynamically to accommodate fluctuations in renewable energy supply, the role of efficient and responsive fluid control systems becomes even more critical. Advanced solenoid valves can help power plants quickly adjust their output and maintain stability in the face of varying load conditions.
The push for greater efficiency also extends to the maintenance and lifecycle management of power plant components. Enhanced solenoid valve designs that offer improved reliability and longer service life can reduce downtime and maintenance costs, contributing to overall plant efficiency. This aspect is particularly important as power plants seek to maximize their operational availability and minimize unplanned outages.
Current Solenoid Valve Limitations
Solenoid valves play a crucial role in power plant operations, controlling the flow of various fluids and gases throughout the system. However, current solenoid valve designs face several limitations that impact their performance and reliability in power plant environments.
One of the primary limitations is the susceptibility to high temperatures. Many power plant processes involve extreme heat, which can degrade the materials used in conventional solenoid valves. This thermal stress often leads to premature failure, reduced lifespan, and increased maintenance requirements. The coil windings and insulation materials are particularly vulnerable to heat-induced degradation, potentially causing electrical shorts or loss of magnetic properties.
Another significant limitation is the power consumption of traditional solenoid valves. These valves typically require continuous power to maintain their open or closed state, resulting in substantial energy usage over time. In large-scale power plant operations, this constant power draw can contribute to increased operational costs and reduced overall plant efficiency.
Corrosion resistance presents another challenge for current solenoid valve designs. Power plants often deal with corrosive fluids and gases, which can rapidly deteriorate valve components. Standard materials used in solenoid valves may not provide adequate protection against these harsh environments, leading to leaks, stuck valves, or complete failure.
The response time of conventional solenoid valves is another area of concern. In critical power plant applications, rapid actuation is essential for safety and process control. However, many existing valve designs struggle to meet the demanding response time requirements, potentially compromising system performance and safety protocols.
Size and weight limitations also pose challenges in power plant settings. Traditional solenoid valves can be bulky and heavy, making installation and maintenance in confined spaces difficult. This can lead to suboptimal placement of valves within the plant, affecting overall system efficiency and accessibility for maintenance.
Furthermore, the limited flow capacity of standard solenoid valves can restrict their application in large-scale power plant operations. Many processes require high flow rates, which current valve designs may struggle to accommodate without significant pressure drops or the need for multiple valves in parallel.
Lastly, the reliability and longevity of solenoid valves in continuous operation scenarios remain a concern. Power plants often run 24/7, and valve failures can lead to costly downtime and potential safety hazards. The current designs may not always meet the stringent reliability requirements of modern power plant operations, necessitating frequent replacements and maintenance interventions.
One of the primary limitations is the susceptibility to high temperatures. Many power plant processes involve extreme heat, which can degrade the materials used in conventional solenoid valves. This thermal stress often leads to premature failure, reduced lifespan, and increased maintenance requirements. The coil windings and insulation materials are particularly vulnerable to heat-induced degradation, potentially causing electrical shorts or loss of magnetic properties.
Another significant limitation is the power consumption of traditional solenoid valves. These valves typically require continuous power to maintain their open or closed state, resulting in substantial energy usage over time. In large-scale power plant operations, this constant power draw can contribute to increased operational costs and reduced overall plant efficiency.
Corrosion resistance presents another challenge for current solenoid valve designs. Power plants often deal with corrosive fluids and gases, which can rapidly deteriorate valve components. Standard materials used in solenoid valves may not provide adequate protection against these harsh environments, leading to leaks, stuck valves, or complete failure.
The response time of conventional solenoid valves is another area of concern. In critical power plant applications, rapid actuation is essential for safety and process control. However, many existing valve designs struggle to meet the demanding response time requirements, potentially compromising system performance and safety protocols.
Size and weight limitations also pose challenges in power plant settings. Traditional solenoid valves can be bulky and heavy, making installation and maintenance in confined spaces difficult. This can lead to suboptimal placement of valves within the plant, affecting overall system efficiency and accessibility for maintenance.
Furthermore, the limited flow capacity of standard solenoid valves can restrict their application in large-scale power plant operations. Many processes require high flow rates, which current valve designs may struggle to accommodate without significant pressure drops or the need for multiple valves in parallel.
Lastly, the reliability and longevity of solenoid valves in continuous operation scenarios remain a concern. Power plants often run 24/7, and valve failures can lead to costly downtime and potential safety hazards. The current designs may not always meet the stringent reliability requirements of modern power plant operations, necessitating frequent replacements and maintenance interventions.
Enhanced Solenoid Valve Solutions
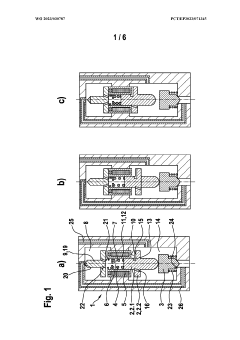
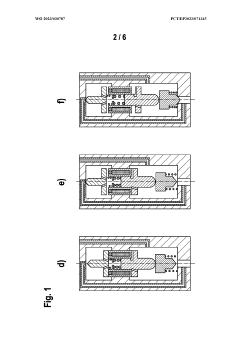
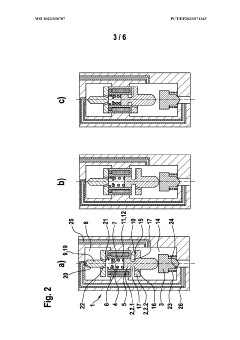
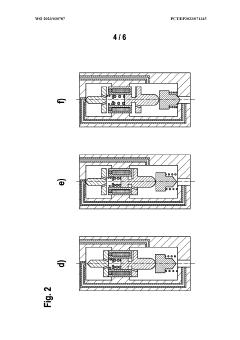
01 Electromagnetic actuation mechanism
Solenoid valves utilize electromagnetic force for actuation. The design typically includes a coil, plunger, and spring mechanism. When the coil is energized, it creates a magnetic field that moves the plunger, opening or closing the valve. The spring returns the plunger to its original position when the coil is de-energized, ensuring reliable operation.- Valve body and armature design: The design of the valve body and armature is crucial for solenoid valve performance. This includes optimizing the shape and material of the valve body to improve fluid flow and reduce pressure drop. The armature design focuses on enhancing magnetic response and reducing friction for faster and more efficient operation.
- Electromagnetic coil configuration: The electromagnetic coil configuration plays a vital role in solenoid valve design. This involves selecting appropriate wire gauge, number of turns, and coil geometry to generate the required magnetic field strength. Optimizing the coil design can improve valve response time, power efficiency, and overall performance.
- Sealing mechanism improvements: Enhancing the sealing mechanism is essential for preventing leakage and ensuring proper valve function. This includes developing advanced seal materials, optimizing seal geometry, and implementing innovative sealing techniques to improve valve reliability and longevity across various operating conditions.
- Integration of smart features: Incorporating smart features into solenoid valve design can enhance functionality and control. This may include integrating sensors for position feedback, implementing digital control interfaces, and adding diagnostic capabilities for predictive maintenance and improved system integration.
- Energy efficiency and power management: Improving energy efficiency and power management in solenoid valve design is crucial for reducing power consumption and heat generation. This involves optimizing the magnetic circuit, implementing power-saving modes, and developing low-power actuation mechanisms to enhance overall valve performance and longevity.
02 Valve sealing and flow control
Effective sealing and precise flow control are crucial in solenoid valve design. This involves careful selection of materials for valve seats and seals, optimizing the shape and size of flow passages, and incorporating features like balanced poppet designs. These elements work together to minimize leakage, reduce pressure drop, and provide accurate flow regulation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Energy efficiency and power management
Modern solenoid valve designs focus on improving energy efficiency and power management. This includes using low-power coils, implementing pulse-width modulation (PWM) control, and incorporating energy-saving modes. Some designs also feature smart power management systems that optimize power consumption based on operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of sensors and control systems
Advanced solenoid valve designs incorporate sensors and sophisticated control systems. These may include position sensors to monitor valve status, pressure sensors for feedback control, and microcontrollers for intelligent operation. Such integration enables features like self-diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and adaptive control strategies.Expand Specific Solutions05 Material selection and manufacturing techniques
The choice of materials and manufacturing methods significantly impacts solenoid valve performance and durability. Designers consider factors such as corrosion resistance, thermal properties, and magnetic characteristics when selecting materials for various components. Advanced manufacturing techniques, including 3D printing and precision machining, are employed to achieve complex geometries and tight tolerances.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Solenoid Valve Manufacturers
The enhanced solenoid valve design market for power plant operations is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for efficient and reliable control systems in the energy sector. The market size is expanding, with projections indicating substantial growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Robert Bosch GmbH, Eaton Corp., and DENSO Corp. leading innovation. These firms are developing more sophisticated, energy-efficient, and durable solenoid valve designs, incorporating smart technologies and advanced materials. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established industrial giants and specialized valve manufacturers, each striving to enhance performance and reliability in power plant applications.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has developed advanced solenoid valve designs specifically for power plant applications. Their enhanced solenoid valves incorporate precision-engineered components and smart control systems to optimize fluid flow and pressure regulation. The company's latest designs feature integrated sensors and digital interfaces for real-time monitoring and adjustment, allowing for more efficient and responsive operation in power plant systems[1][3]. Bosch's solenoid valves utilize high-performance materials and coatings to withstand harsh operating conditions, including extreme temperatures and corrosive environments often found in power plants[2]. Additionally, they have implemented energy-efficient actuation mechanisms that reduce power consumption during valve operation, contributing to overall plant efficiency[4].
Strengths: Precision control, durability in harsh conditions, and energy efficiency. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial cost and complexity in implementation compared to simpler valve designs.
Eaton Corp.
Technical Solution: Eaton has developed a range of enhanced solenoid valves tailored for power plant operations. Their designs focus on improving reliability and efficiency in critical systems. Eaton's solenoid valves incorporate advanced materials and coatings to resist wear and corrosion, ensuring longevity in demanding power plant environments[1]. The company has also implemented smart diagnostics and predictive maintenance features, allowing for proactive valve management and reduced downtime[2]. Eaton's valves are designed with optimized flow paths and rapid response times, contributing to improved overall system performance in power plants[3]. Additionally, they have developed energy-efficient actuation systems that minimize power consumption during valve operation, aligning with the industry's focus on energy conservation[4].
Strengths: High reliability, smart diagnostics, and energy efficiency. Weaknesses: Potential complexity in integration with existing systems and higher initial investment.
Innovative Solenoid Technologies
Solenoid valve
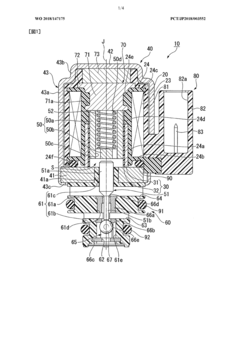
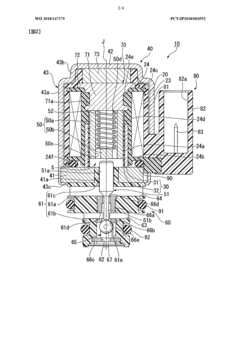
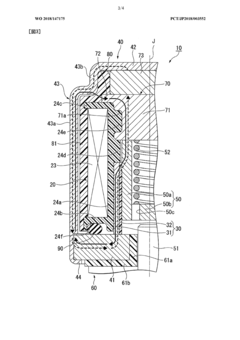
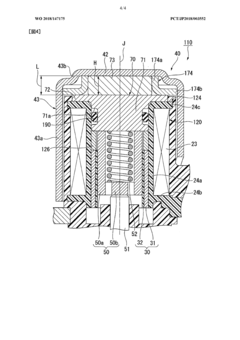
PatentWO2018147175A1
Innovation
- The solenoid valve design includes a cylindrical guide part, a magnetic body part, a yoke member, a magnet, an elastic member, and a valve part, where the yoke member is positioned radially outward from the magnet, allowing for a magnetic circuit that reduces power consumption by optimizing magnetic flux pathways and eliminating the need for continuous current supply to maintain valve states.
Solenoid valve and hydrogen tank system comprising solenoid valve
PatentWO2023030787A1
Innovation
- A solenoid valve design featuring a magnet armature with both plunger and flat sections, utilizing a pressure difference between a pressure chamber and a valve chamber to enhance magnetic force, optimized field line configuration, and a servo-controlled mechanism to manage pneumatic and magnetic forces efficiently.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact of enhanced solenoid valve design in power plant operations is a critical consideration that extends beyond operational efficiency. These valves play a crucial role in controlling fluid flow and pressure within power plant systems, and their improved design can significantly influence environmental outcomes.
Enhanced solenoid valve designs contribute to reduced energy consumption in power plants. By optimizing valve response times and improving precision in flow control, these valves minimize energy losses associated with fluid regulation. This increased efficiency translates to lower overall power consumption by the plant, thereby reducing the carbon footprint and greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation.
Water conservation is another key environmental benefit of advanced solenoid valve designs. Improved sealing mechanisms and more precise control over water flow can substantially reduce water waste in cooling systems and steam generation processes. This is particularly important in regions facing water scarcity, where power plants often compete with other sectors for limited water resources.
The enhanced durability and reliability of modern solenoid valves also have positive environmental implications. Longer-lasting valves require less frequent replacement, reducing the demand for raw materials and energy associated with manufacturing and transportation of replacement parts. This contributes to a decrease in the overall lifecycle environmental impact of power plant operations.
Improved solenoid valve designs can also lead to better containment of potentially harmful substances used in power plant processes. More effective sealing and control mechanisms minimize the risk of leaks or unintended releases of chemicals, oils, or other pollutants into the environment. This enhanced containment capability is crucial for protecting local ecosystems and water sources from contamination.
Furthermore, the precise control offered by advanced solenoid valves can optimize combustion processes in fossil fuel power plants. This optimization can lead to more complete fuel burning, reducing the emission of particulate matter and other air pollutants. While the ultimate goal may be transitioning away from fossil fuels, these improvements can mitigate environmental impacts in the interim.
In the context of renewable energy integration, enhanced solenoid valves can play a role in improving the flexibility and responsiveness of power plants. This is particularly relevant for plants that need to adjust their output to accommodate fluctuations in renewable energy sources. By enabling more rapid and precise adjustments to plant operations, these valves can support a smoother integration of renewable energy into the grid, indirectly contributing to a reduction in overall environmental impact.
Enhanced solenoid valve designs contribute to reduced energy consumption in power plants. By optimizing valve response times and improving precision in flow control, these valves minimize energy losses associated with fluid regulation. This increased efficiency translates to lower overall power consumption by the plant, thereby reducing the carbon footprint and greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation.
Water conservation is another key environmental benefit of advanced solenoid valve designs. Improved sealing mechanisms and more precise control over water flow can substantially reduce water waste in cooling systems and steam generation processes. This is particularly important in regions facing water scarcity, where power plants often compete with other sectors for limited water resources.
The enhanced durability and reliability of modern solenoid valves also have positive environmental implications. Longer-lasting valves require less frequent replacement, reducing the demand for raw materials and energy associated with manufacturing and transportation of replacement parts. This contributes to a decrease in the overall lifecycle environmental impact of power plant operations.
Improved solenoid valve designs can also lead to better containment of potentially harmful substances used in power plant processes. More effective sealing and control mechanisms minimize the risk of leaks or unintended releases of chemicals, oils, or other pollutants into the environment. This enhanced containment capability is crucial for protecting local ecosystems and water sources from contamination.
Furthermore, the precise control offered by advanced solenoid valves can optimize combustion processes in fossil fuel power plants. This optimization can lead to more complete fuel burning, reducing the emission of particulate matter and other air pollutants. While the ultimate goal may be transitioning away from fossil fuels, these improvements can mitigate environmental impacts in the interim.
In the context of renewable energy integration, enhanced solenoid valves can play a role in improving the flexibility and responsiveness of power plants. This is particularly relevant for plants that need to adjust their output to accommodate fluctuations in renewable energy sources. By enabling more rapid and precise adjustments to plant operations, these valves can support a smoother integration of renewable energy into the grid, indirectly contributing to a reduction in overall environmental impact.
Regulatory Compliance Challenges
The regulatory landscape surrounding power plant operations is complex and ever-evolving, presenting significant challenges for enhanced solenoid valve design implementation. Compliance with environmental regulations, such as the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act, requires power plants to continuously monitor and control emissions, where solenoid valves play a crucial role in managing fluid flow and pressure. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regularly updates its standards, necessitating ongoing adaptations in valve technology to meet stricter emission limits.
Safety regulations, including those set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), demand rigorous testing and certification processes for solenoid valves used in critical power plant systems. These valves must demonstrate reliability under extreme conditions and fail-safe operation to prevent accidents and ensure worker safety. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) imposes additional stringent requirements for valves used in nuclear power plants, emphasizing radiation resistance and long-term reliability.
Energy efficiency standards, such as those outlined in the Energy Policy Act, push for continuous improvements in power plant performance. Enhanced solenoid valve designs must contribute to overall system efficiency while maintaining compliance with these regulations. This often requires a delicate balance between optimizing valve performance and meeting regulatory thresholds.
The increasing focus on cybersecurity in critical infrastructure has led to new regulations addressing the vulnerability of digitally controlled systems. As solenoid valves become more integrated with smart control systems, they must adhere to cybersecurity standards to prevent potential breaches that could compromise plant operations or safety.
International regulations add another layer of complexity for multinational power plant operators. Variations in standards across different countries require valve designs that can be easily adapted or reconfigured to meet diverse regulatory requirements. This challenge is particularly evident in emerging markets where environmental regulations are rapidly evolving.
Compliance with these multifaceted regulations often results in increased costs and longer development cycles for enhanced solenoid valve designs. Manufacturers must invest in extensive testing, documentation, and certification processes to ensure their products meet all applicable standards. Additionally, the need for frequent updates to keep pace with regulatory changes can impact the long-term viability of certain valve designs.
Safety regulations, including those set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), demand rigorous testing and certification processes for solenoid valves used in critical power plant systems. These valves must demonstrate reliability under extreme conditions and fail-safe operation to prevent accidents and ensure worker safety. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) imposes additional stringent requirements for valves used in nuclear power plants, emphasizing radiation resistance and long-term reliability.
Energy efficiency standards, such as those outlined in the Energy Policy Act, push for continuous improvements in power plant performance. Enhanced solenoid valve designs must contribute to overall system efficiency while maintaining compliance with these regulations. This often requires a delicate balance between optimizing valve performance and meeting regulatory thresholds.
The increasing focus on cybersecurity in critical infrastructure has led to new regulations addressing the vulnerability of digitally controlled systems. As solenoid valves become more integrated with smart control systems, they must adhere to cybersecurity standards to prevent potential breaches that could compromise plant operations or safety.
International regulations add another layer of complexity for multinational power plant operators. Variations in standards across different countries require valve designs that can be easily adapted or reconfigured to meet diverse regulatory requirements. This challenge is particularly evident in emerging markets where environmental regulations are rapidly evolving.
Compliance with these multifaceted regulations often results in increased costs and longer development cycles for enhanced solenoid valve designs. Manufacturers must invest in extensive testing, documentation, and certification processes to ensure their products meet all applicable standards. Additionally, the need for frequent updates to keep pace with regulatory changes can impact the long-term viability of certain valve designs.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!