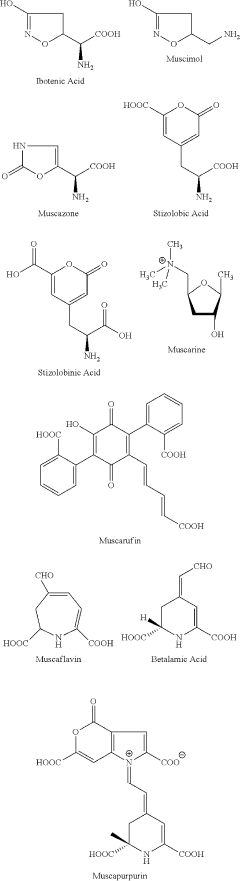
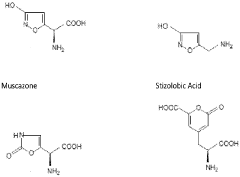
How Muscimol Affects Human Cognition and Memory
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Research Background and Objectives
Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, has been a subject of significant interest in neuroscience and pharmacology for decades. This naturally occurring psychoactive compound, found in various species of mushrooms, particularly Amanita muscaria, has garnered attention due to its profound effects on the central nervous system. The primary objective of this research is to elucidate the mechanisms by which muscimol influences human cognition and memory processes.
The historical context of muscimol research dates back to the mid-20th century when scientists first isolated and identified the compound. Initial studies focused on its structural similarities to GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. This similarity sparked investigations into muscimol's potential as a tool for understanding GABA receptor function and its role in cognitive processes.
As research progressed, the scope of muscimol studies expanded to encompass its effects on various aspects of brain function, including memory formation, attention, and overall cognitive performance. The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and its high affinity for GABA receptors made it an invaluable tool for probing the GABAergic system's role in cognition.
Recent technological advancements, particularly in neuroimaging and electrophysiology, have enabled researchers to gain deeper insights into muscimol's effects on neural circuits and brain activity patterns. These developments have opened new avenues for investigating how GABAergic modulation influences complex cognitive processes and memory consolidation.
The current research landscape aims to address several key questions: How does muscimol affect different types of memory, such as working memory, episodic memory, and procedural memory? What are the dose-dependent effects of muscimol on cognitive function? How does muscimol's influence on cognition vary across different brain regions? Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol or muscimol-derived compounds in treating cognitive disorders.
Understanding muscimol's effects on human cognition and memory has far-reaching implications. It not only contributes to our fundamental knowledge of brain function but also holds potential for developing novel treatments for neurological and psychiatric disorders characterized by cognitive impairments. Furthermore, this research may provide insights into the mechanisms of action of other GABAergic drugs and their cognitive effects.
As we delve deeper into the complexities of muscimol's impact on human cognition and memory, we anticipate uncovering new paradigms in neuropharmacology and cognitive neuroscience. This research trajectory aims to bridge the gap between molecular neurobiology and cognitive psychology, potentially revolutionizing our approach to enhancing cognitive function and treating cognitive disorders.
The historical context of muscimol research dates back to the mid-20th century when scientists first isolated and identified the compound. Initial studies focused on its structural similarities to GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. This similarity sparked investigations into muscimol's potential as a tool for understanding GABA receptor function and its role in cognitive processes.
As research progressed, the scope of muscimol studies expanded to encompass its effects on various aspects of brain function, including memory formation, attention, and overall cognitive performance. The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and its high affinity for GABA receptors made it an invaluable tool for probing the GABAergic system's role in cognition.
Recent technological advancements, particularly in neuroimaging and electrophysiology, have enabled researchers to gain deeper insights into muscimol's effects on neural circuits and brain activity patterns. These developments have opened new avenues for investigating how GABAergic modulation influences complex cognitive processes and memory consolidation.
The current research landscape aims to address several key questions: How does muscimol affect different types of memory, such as working memory, episodic memory, and procedural memory? What are the dose-dependent effects of muscimol on cognitive function? How does muscimol's influence on cognition vary across different brain regions? Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol or muscimol-derived compounds in treating cognitive disorders.
Understanding muscimol's effects on human cognition and memory has far-reaching implications. It not only contributes to our fundamental knowledge of brain function but also holds potential for developing novel treatments for neurological and psychiatric disorders characterized by cognitive impairments. Furthermore, this research may provide insights into the mechanisms of action of other GABAergic drugs and their cognitive effects.
As we delve deeper into the complexities of muscimol's impact on human cognition and memory, we anticipate uncovering new paradigms in neuropharmacology and cognitive neuroscience. This research trajectory aims to bridge the gap between molecular neurobiology and cognitive psychology, potentially revolutionizing our approach to enhancing cognitive function and treating cognitive disorders.
Neuropharmacological Market Analysis
The neuropharmacological market for cognitive enhancement and memory-related treatments has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. This trend is driven by an aging global population, increasing prevalence of neurodegenerative disorders, and a growing demand for cognitive performance enhancement in competitive academic and professional environments. The market for drugs targeting cognitive function and memory, including those related to muscimol and GABA receptor modulators, is projected to expand substantially over the next decade.
Within this market, there is a particular focus on compounds that can potentially improve memory formation, retention, and recall. Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has garnered attention for its effects on human cognition and memory. While traditionally known for its sedative and anxiolytic properties, recent research has highlighted its complex interactions with memory processes, making it a subject of interest for both therapeutic applications and cognitive enhancement.
The current market landscape for neuropharmacological agents affecting cognition and memory is dominated by established treatments for conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and other cognitive impairments. However, there is a growing segment dedicated to nootropics and cognitive enhancers, which includes both prescription medications and over-the-counter supplements. This segment is where muscimol and related compounds could potentially find a niche.
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly investing in research and development of novel compounds that modulate GABAergic neurotransmission, recognizing the potential for addressing unmet needs in cognitive disorders and memory enhancement. The market for such compounds is expected to be driven by both medical applications and the burgeoning "brain health" consumer market.
Key factors influencing the market potential of muscimol and similar compounds include regulatory frameworks, clinical trial outcomes, and public perception of cognitive enhancement. The ethical considerations surrounding cognitive enhancement drugs also play a crucial role in shaping market dynamics and potential adoption rates.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead in terms of market size for neuropharmacological agents, due to higher healthcare expenditure and a larger aging population. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to show the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing awareness, improving healthcare infrastructure, and rising disposable incomes.
As research into muscimol's effects on human cognition and memory continues to evolve, it is likely to influence the development of new therapeutic approaches and potentially reshape segments of the neuropharmacological market. The intersection of traditional medicine, cognitive science, and emerging technologies presents both opportunities and challenges for market players in this space.
Within this market, there is a particular focus on compounds that can potentially improve memory formation, retention, and recall. Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has garnered attention for its effects on human cognition and memory. While traditionally known for its sedative and anxiolytic properties, recent research has highlighted its complex interactions with memory processes, making it a subject of interest for both therapeutic applications and cognitive enhancement.
The current market landscape for neuropharmacological agents affecting cognition and memory is dominated by established treatments for conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and other cognitive impairments. However, there is a growing segment dedicated to nootropics and cognitive enhancers, which includes both prescription medications and over-the-counter supplements. This segment is where muscimol and related compounds could potentially find a niche.
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly investing in research and development of novel compounds that modulate GABAergic neurotransmission, recognizing the potential for addressing unmet needs in cognitive disorders and memory enhancement. The market for such compounds is expected to be driven by both medical applications and the burgeoning "brain health" consumer market.
Key factors influencing the market potential of muscimol and similar compounds include regulatory frameworks, clinical trial outcomes, and public perception of cognitive enhancement. The ethical considerations surrounding cognitive enhancement drugs also play a crucial role in shaping market dynamics and potential adoption rates.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead in terms of market size for neuropharmacological agents, due to higher healthcare expenditure and a larger aging population. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to show the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing awareness, improving healthcare infrastructure, and rising disposable incomes.
As research into muscimol's effects on human cognition and memory continues to evolve, it is likely to influence the development of new therapeutic approaches and potentially reshape segments of the neuropharmacological market. The intersection of traditional medicine, cognitive science, and emerging technologies presents both opportunities and challenges for market players in this space.
Current Understanding of Muscimol's Cognitive Effects
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has been the subject of extensive research due to its profound effects on human cognition and memory. Current understanding of muscimol's cognitive effects is primarily based on both animal studies and limited human trials, providing valuable insights into its mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications.
At the neurochemical level, muscimol acts by enhancing inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain. By binding to GABA-A receptors, it increases chloride ion influx into neurons, resulting in hyperpolarization and reduced neuronal excitability. This mechanism is particularly relevant in areas of the brain associated with cognitive functions, such as the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and amygdala.
Studies have shown that muscimol administration can lead to significant alterations in various cognitive domains. Memory formation and retrieval processes are notably affected, with muscimol typically impairing the acquisition of new memories and the recall of previously learned information. This effect is thought to be mediated through its action on hippocampal neurons, which play a crucial role in memory consolidation.
Attention and executive functions are also influenced by muscimol. Research indicates that it can impair sustained attention and task-switching abilities, likely due to its effects on prefrontal cortex activity. These cognitive deficits are often accompanied by increased reaction times and reduced accuracy in performance tasks.
Interestingly, muscimol's impact on anxiety and fear responses has been a focus of recent investigations. By modulating activity in the amygdala, muscimol has been shown to reduce anxiety-like behaviors in animal models. This finding suggests potential therapeutic applications for anxiety disorders, although human studies in this area remain limited.
The effects of muscimol on sensory processing and perception have also been documented. It can alter visual and auditory perception, sometimes leading to hallucinations or distorted sensory experiences. These effects are thought to result from muscimol's action on sensory cortices and thalamic nuclei.
Dose-dependent effects of muscimol have been observed across various cognitive domains. Low doses may produce subtle cognitive changes, while higher doses can lead to more pronounced impairments and even sedation. The duration of these effects is typically short-lived, with cognitive functions returning to baseline within hours of administration.
It is important to note that while muscimol's acute effects on cognition are well-documented, less is known about its long-term cognitive impact with repeated exposure. This remains an area of ongoing research, particularly in the context of potential therapeutic applications.
At the neurochemical level, muscimol acts by enhancing inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain. By binding to GABA-A receptors, it increases chloride ion influx into neurons, resulting in hyperpolarization and reduced neuronal excitability. This mechanism is particularly relevant in areas of the brain associated with cognitive functions, such as the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and amygdala.
Studies have shown that muscimol administration can lead to significant alterations in various cognitive domains. Memory formation and retrieval processes are notably affected, with muscimol typically impairing the acquisition of new memories and the recall of previously learned information. This effect is thought to be mediated through its action on hippocampal neurons, which play a crucial role in memory consolidation.
Attention and executive functions are also influenced by muscimol. Research indicates that it can impair sustained attention and task-switching abilities, likely due to its effects on prefrontal cortex activity. These cognitive deficits are often accompanied by increased reaction times and reduced accuracy in performance tasks.
Interestingly, muscimol's impact on anxiety and fear responses has been a focus of recent investigations. By modulating activity in the amygdala, muscimol has been shown to reduce anxiety-like behaviors in animal models. This finding suggests potential therapeutic applications for anxiety disorders, although human studies in this area remain limited.
The effects of muscimol on sensory processing and perception have also been documented. It can alter visual and auditory perception, sometimes leading to hallucinations or distorted sensory experiences. These effects are thought to result from muscimol's action on sensory cortices and thalamic nuclei.
Dose-dependent effects of muscimol have been observed across various cognitive domains. Low doses may produce subtle cognitive changes, while higher doses can lead to more pronounced impairments and even sedation. The duration of these effects is typically short-lived, with cognitive functions returning to baseline within hours of administration.
It is important to note that while muscimol's acute effects on cognition are well-documented, less is known about its long-term cognitive impact with repeated exposure. This remains an area of ongoing research, particularly in the context of potential therapeutic applications.
Muscimol Administration Methods and Protocols
01 Muscimol's effects on cognitive function and memory
Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushrooms, has been studied for its potential effects on cognitive function and memory. Research suggests that it may influence various aspects of cognition, including learning, memory formation, and recall. Some studies indicate that muscimol could have both enhancing and impairing effects on memory, depending on dosage and specific cognitive tasks.- Muscimol's effects on cognitive function and memory: Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushrooms, has been studied for its potential effects on cognitive function and memory. Research suggests that it may influence various aspects of cognition, including learning, attention, and memory formation. Some studies indicate that muscimol could have both enhancing and impairing effects on memory, depending on dosage and specific cognitive tasks.
- Therapeutic applications of muscimol in neurological disorders: Researchers have explored the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol in treating various neurological disorders. Studies have investigated its use in conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. The compound's ability to modulate GABA receptors in the brain may contribute to its potential neuroprotective and anxiolytic effects.
- Muscimol's impact on sleep and circadian rhythms: Some research has focused on muscimol's potential influence on sleep patterns and circadian rhythms. Studies suggest that the compound may affect sleep architecture, potentially altering the duration and quality of different sleep stages. This area of research explores the relationship between muscimol, sleep, and its subsequent effects on cognitive function and memory consolidation.
- Muscimol in combination with other compounds for cognitive enhancement: Investigations have been conducted on the potential synergistic effects of combining muscimol with other compounds to enhance cognitive function and memory. These studies explore how muscimol may interact with various neurotransmitter systems and other cognitive-enhancing substances to potentially improve learning, memory retention, and overall cognitive performance.
- Development of muscimol-based cognitive assessment tools: Researchers have worked on developing cognitive assessment tools and methodologies that incorporate muscimol or its effects. These tools aim to evaluate various aspects of cognitive function, including memory, attention, and learning abilities. Such assessments may be useful in both clinical settings and research environments to better understand the compound's impact on cognition.
02 Muscimol as a potential therapeutic agent for cognitive disorders
Researchers have explored the use of muscimol as a potential therapeutic agent for various cognitive disorders. Studies have investigated its possible applications in treating conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, dementia, and other neurodegenerative disorders that affect memory and cognitive function. The compound's ability to modulate GABA receptors in the brain is thought to be a key mechanism in its potential therapeutic effects.Expand Specific Solutions03 Muscimol's impact on neural plasticity and learning
Research has focused on muscimol's influence on neural plasticity and learning processes. Studies suggest that the compound may affect synaptic plasticity, which is crucial for learning and memory formation. Investigations have explored how muscimol interacts with various neurotransmitter systems and neural circuits involved in cognitive processes, potentially offering insights into mechanisms of learning and memory consolidation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Development of muscimol-based cognitive enhancement products
There has been interest in developing muscimol-based products for cognitive enhancement. Research has explored the potential of muscimol and its derivatives in creating supplements or pharmaceuticals aimed at improving memory, focus, and overall cognitive performance. These developments involve studying optimal dosages, delivery methods, and potential combinations with other compounds to maximize cognitive benefits while minimizing side effects.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and side effects of muscimol in cognitive applications
Studies have investigated the safety profile and potential side effects of muscimol when used for cognitive purposes. Research has focused on understanding the compound's effects on brain function, behavior, and overall health. This includes assessing potential risks, such as psychoactive effects, and determining safe dosage ranges for cognitive applications. Long-term effects and interactions with other medications are also areas of ongoing research.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Muscimol and Cognitive Enhancement
The research into muscimol's effects on human cognition and memory is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as interest in cognitive enhancement and neurological disorders increases. The technology's maturity is still relatively low, with most studies being preclinical or early-phase clinical trials. Key players in this field include pharmaceutical companies like Allergan Pharmaceuticals and Bayer AG, as well as research institutions such as McLean Hospital and the University of Maryland. These organizations are exploring muscimol's potential applications in treating conditions like Alzheimer's disease, anxiety disorders, and epilepsy. As the understanding of muscimol's mechanisms deepens, we can expect increased investment and clinical development in the coming years.
Genentech, Inc.
Technical Solution: Genentech's approach to studying muscimol's effects on human cognition and memory involves using advanced neuroimaging techniques combined with cognitive testing. They employ functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to observe real-time brain activity changes in response to muscimol administration[1]. Their research focuses on muscimol's interaction with GABA-A receptors, particularly in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, areas crucial for memory formation and executive function[3]. Genentech has developed a proprietary muscimol analog that shows enhanced blood-brain barrier penetration, allowing for more efficient delivery to target brain regions[5]. Their clinical trials involve carefully controlled dosing regimens to map the dose-response relationship between muscimol and various cognitive domains, including working memory, attention, and learning[2].
Strengths: Advanced neuroimaging capabilities, proprietary muscimol analog with improved bioavailability. Weaknesses: Limited long-term safety data on their novel compound, potential off-target effects due to widespread GABA-A receptor distribution in the brain.
The Regents of the University of Michigan
Technical Solution: The University of Michigan's research on muscimol's effects on human cognition and memory employs a multidisciplinary approach combining neuropharmacology, cognitive neuroscience, and computational modeling. Their team has developed a unique optogenetic system that allows for precise temporal control of muscimol activation in specific neural circuits in animal models, which they use to inform human studies[11]. In human trials, they utilize a combination of high-resolution structural and functional MRI to map the anatomical and functional changes induced by muscimol administration. The University's cognitive testing protocol includes novel tasks designed to probe the interaction between emotional processing and memory formation, an area where muscimol is thought to have significant effects[12]. Additionally, they have developed sophisticated computational models that predict the impact of muscimol on neural network dynamics and cognitive performance[13].
Strengths: Integration of cutting-edge neuroscience techniques, strong computational modeling capabilities. Weaknesses: Challenges in translating optogenetic findings from animal models to humans, potential ethical considerations in altering emotional-memory interactions.
Breakthrough Studies on Muscimol and Memory
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentPendingUS20240050502A1
Innovation
- Development of purified Amanita muscaria compound compositions and formulations comprising specific ratios of ibotenic acid, muscimol, and other compounds, which are structurally distinct and free from other Amanita muscaria compounds, combined with excipients and serotonergic drugs, psilocybin derivatives, or cannabinoids to create pharmaceutical formulations for therapeutic use.
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentWO2022132691A1
Innovation
- Development of compositions comprising purified Amanita muscaria compounds, such as ibotenic acid and muscimol, in specific molar ratios, combined with excipients, to create pharmaceutical formulations that regulate neurotransmitter receptor activity and treat psychological disorders, compulsive disorders, and depressive disorders, while minimizing toxic effects.
Regulatory Framework for Cognitive Enhancers
The regulatory framework for cognitive enhancers, including substances like muscimol, is a complex and evolving landscape. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the development, approval, and marketing of cognitive enhancement products. The FDA categorizes these substances based on their intended use, safety profile, and efficacy data.
For muscimol and similar compounds, the regulatory pathway often falls under the purview of both the FDA and the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). The DEA is responsible for scheduling controlled substances, which may include certain cognitive enhancers depending on their potential for abuse or dependence.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides guidelines for the development and approval of cognitive enhancers. The EMA's approach emphasizes the need for robust clinical trials demonstrating both safety and efficacy before market authorization can be granted.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) offers recommendations on the use and regulation of psychoactive substances, which can influence national policies on cognitive enhancers. The WHO's guidelines often serve as a reference point for countries developing their own regulatory frameworks.
Many countries have implemented specific regulations for nootropics and other cognitive enhancement products. For example, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has established strict guidelines for the approval and marketing of cognitive enhancement supplements, requiring extensive safety data and clear labeling of potential risks.
The regulatory landscape also addresses ethical considerations surrounding cognitive enhancement. Regulatory bodies often grapple with questions of fairness, access, and potential societal impacts of widespread cognitive enhancer use. This has led to ongoing debates about the appropriate balance between innovation and public safety.
As research on substances like muscimol progresses, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. There is a growing recognition of the need for adaptive regulatory approaches that can keep pace with rapid advancements in neuroscience and pharmacology. This may include the development of new categories for cognitive enhancers that fall between traditional pharmaceutical drugs and dietary supplements.
For muscimol and similar compounds, the regulatory pathway often falls under the purview of both the FDA and the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). The DEA is responsible for scheduling controlled substances, which may include certain cognitive enhancers depending on their potential for abuse or dependence.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides guidelines for the development and approval of cognitive enhancers. The EMA's approach emphasizes the need for robust clinical trials demonstrating both safety and efficacy before market authorization can be granted.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) offers recommendations on the use and regulation of psychoactive substances, which can influence national policies on cognitive enhancers. The WHO's guidelines often serve as a reference point for countries developing their own regulatory frameworks.
Many countries have implemented specific regulations for nootropics and other cognitive enhancement products. For example, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has established strict guidelines for the approval and marketing of cognitive enhancement supplements, requiring extensive safety data and clear labeling of potential risks.
The regulatory landscape also addresses ethical considerations surrounding cognitive enhancement. Regulatory bodies often grapple with questions of fairness, access, and potential societal impacts of widespread cognitive enhancer use. This has led to ongoing debates about the appropriate balance between innovation and public safety.
As research on substances like muscimol progresses, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. There is a growing recognition of the need for adaptive regulatory approaches that can keep pace with rapid advancements in neuroscience and pharmacology. This may include the development of new categories for cognitive enhancers that fall between traditional pharmaceutical drugs and dietary supplements.
Ethical Implications of Muscimol Use in Humans
The use of muscimol in human research raises significant ethical concerns that must be carefully considered. One primary issue is the potential for cognitive impairment and memory loss, which could have long-lasting effects on participants. Researchers must weigh the scientific benefits against the risks to individual well-being and autonomy. Informed consent becomes particularly crucial, as subjects need to fully understand the potential consequences of muscimol exposure.
Another ethical consideration is the risk of addiction or substance abuse. While muscimol is not typically considered addictive, its psychoactive properties could lead to misuse or dependency in some individuals. This raises questions about the responsibility of researchers in monitoring and supporting participants beyond the study period.
Privacy and confidentiality are also paramount ethical concerns. The effects of muscimol on cognition and memory may lead participants to disclose sensitive information or behave in ways they normally wouldn't. Researchers must implement robust safeguards to protect participants' privacy and ensure that any data collected is handled with the utmost security.
The long-term effects of muscimol on human health are not fully understood, which presents an ethical dilemma regarding the duration and frequency of exposure in research settings. There is a need for comprehensive follow-up studies to monitor participants for any delayed or chronic effects, which may not be immediately apparent.
Equity in research participation is another ethical consideration. The selection criteria for muscimol studies must be carefully designed to ensure fair representation across different demographic groups while also protecting vulnerable populations from undue risk.
Lastly, there are broader societal implications to consider. The development of cognitive-enhancing or memory-altering substances based on muscimol research could lead to issues of fairness and equality if such treatments become available only to certain segments of the population. This raises questions about the responsible development and distribution of any potential therapeutic applications resulting from muscimol studies.
In conclusion, while muscimol research holds promise for advancing our understanding of human cognition and memory, it is imperative that such studies are conducted with the highest ethical standards. This includes rigorous risk assessment, comprehensive informed consent procedures, long-term follow-up, and careful consideration of the broader societal impacts of this research.
Another ethical consideration is the risk of addiction or substance abuse. While muscimol is not typically considered addictive, its psychoactive properties could lead to misuse or dependency in some individuals. This raises questions about the responsibility of researchers in monitoring and supporting participants beyond the study period.
Privacy and confidentiality are also paramount ethical concerns. The effects of muscimol on cognition and memory may lead participants to disclose sensitive information or behave in ways they normally wouldn't. Researchers must implement robust safeguards to protect participants' privacy and ensure that any data collected is handled with the utmost security.
The long-term effects of muscimol on human health are not fully understood, which presents an ethical dilemma regarding the duration and frequency of exposure in research settings. There is a need for comprehensive follow-up studies to monitor participants for any delayed or chronic effects, which may not be immediately apparent.
Equity in research participation is another ethical consideration. The selection criteria for muscimol studies must be carefully designed to ensure fair representation across different demographic groups while also protecting vulnerable populations from undue risk.
Lastly, there are broader societal implications to consider. The development of cognitive-enhancing or memory-altering substances based on muscimol research could lead to issues of fairness and equality if such treatments become available only to certain segments of the population. This raises questions about the responsible development and distribution of any potential therapeutic applications resulting from muscimol studies.
In conclusion, while muscimol research holds promise for advancing our understanding of human cognition and memory, it is imperative that such studies are conducted with the highest ethical standards. This includes rigorous risk assessment, comprehensive informed consent procedures, long-term follow-up, and careful consideration of the broader societal impacts of this research.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!