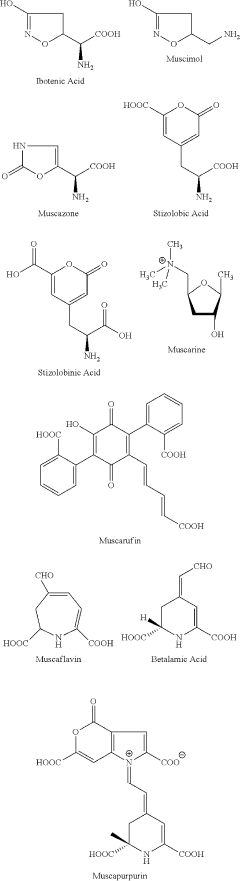
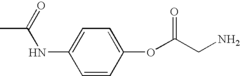
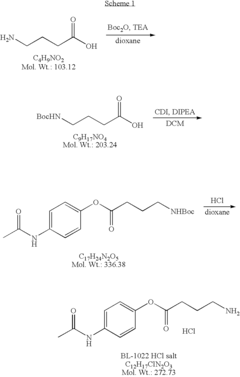
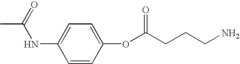
How Muscimol Impacts GABAergic Synapses
JUL 4, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
GABAergic Synapse Fundamentals and Research Objectives
GABAergic synapses are fundamental inhibitory connections in the central nervous system, playing a crucial role in regulating neuronal excitability and maintaining the balance of neural circuits. These synapses utilize gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) as their primary neurotransmitter, which binds to GABA receptors on the postsynaptic membrane to mediate inhibitory effects. The study of GABAergic synapses has been a cornerstone in neuroscience research, providing insights into various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
The primary objective of investigating muscimol's impact on GABAergic synapses is to elucidate the mechanisms by which this potent GABA agonist modulates synaptic transmission and neuronal function. Muscimol, a psychoactive alkaloid found in certain mushroom species, has garnered significant attention due to its high affinity for GABA-A receptors and its potential therapeutic applications.
Research in this field aims to uncover the precise molecular and cellular processes through which muscimol interacts with GABAergic synapses. This includes examining its effects on receptor activation, ion channel dynamics, and subsequent changes in membrane potential. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted interventions for conditions characterized by imbalances in GABAergic signaling, such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and certain neurodegenerative diseases.
Another key research objective is to investigate the long-term consequences of muscimol exposure on synaptic plasticity and network function. This involves studying how prolonged activation of GABA receptors by muscimol may lead to adaptive changes in receptor expression, synaptic strength, and overall circuit dynamics. Such insights are essential for assessing the potential therapeutic benefits and risks associated with muscimol-based treatments.
Furthermore, researchers aim to explore the differential effects of muscimol on various subtypes of GABAergic synapses and across different brain regions. This comparative approach can reveal region-specific vulnerabilities or resistances to muscimol's effects, potentially guiding more targeted and effective therapeutic strategies.
The technological advancements in neuroimaging, electrophysiology, and molecular biology have significantly enhanced our ability to study GABAergic synapses and muscimol's impact at unprecedented levels of detail. These tools allow for real-time monitoring of synaptic activity, visualization of receptor dynamics, and manipulation of specific neural circuits, providing a comprehensive understanding of muscimol's actions in the context of complex neural networks.
As research in this field progresses, it is anticipated that the findings will not only contribute to our fundamental understanding of inhibitory neurotransmission but also pave the way for novel therapeutic approaches in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. The ultimate goal is to harness the potential of muscimol and related compounds to modulate GABAergic function in a controlled and beneficial manner, opening new avenues for drug development and personalized medicine in neurology and psychiatry.
The primary objective of investigating muscimol's impact on GABAergic synapses is to elucidate the mechanisms by which this potent GABA agonist modulates synaptic transmission and neuronal function. Muscimol, a psychoactive alkaloid found in certain mushroom species, has garnered significant attention due to its high affinity for GABA-A receptors and its potential therapeutic applications.
Research in this field aims to uncover the precise molecular and cellular processes through which muscimol interacts with GABAergic synapses. This includes examining its effects on receptor activation, ion channel dynamics, and subsequent changes in membrane potential. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted interventions for conditions characterized by imbalances in GABAergic signaling, such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and certain neurodegenerative diseases.
Another key research objective is to investigate the long-term consequences of muscimol exposure on synaptic plasticity and network function. This involves studying how prolonged activation of GABA receptors by muscimol may lead to adaptive changes in receptor expression, synaptic strength, and overall circuit dynamics. Such insights are essential for assessing the potential therapeutic benefits and risks associated with muscimol-based treatments.
Furthermore, researchers aim to explore the differential effects of muscimol on various subtypes of GABAergic synapses and across different brain regions. This comparative approach can reveal region-specific vulnerabilities or resistances to muscimol's effects, potentially guiding more targeted and effective therapeutic strategies.
The technological advancements in neuroimaging, electrophysiology, and molecular biology have significantly enhanced our ability to study GABAergic synapses and muscimol's impact at unprecedented levels of detail. These tools allow for real-time monitoring of synaptic activity, visualization of receptor dynamics, and manipulation of specific neural circuits, providing a comprehensive understanding of muscimol's actions in the context of complex neural networks.
As research in this field progresses, it is anticipated that the findings will not only contribute to our fundamental understanding of inhibitory neurotransmission but also pave the way for novel therapeutic approaches in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. The ultimate goal is to harness the potential of muscimol and related compounds to modulate GABAergic function in a controlled and beneficial manner, opening new avenues for drug development and personalized medicine in neurology and psychiatry.
Muscimol Market and Neuropharmacological Applications
The muscimol market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing research and development activities in neuropharmacology. As a potent GABA receptor agonist, muscimol has garnered attention for its potential therapeutic applications in various neurological and psychiatric disorders. The global market for GABA receptor agonists, including muscimol, is projected to expand at a steady rate due to the rising prevalence of anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and other neurological conditions.
In the pharmaceutical industry, muscimol has emerged as a promising compound for developing novel treatments. Its ability to modulate GABAergic synapses makes it an attractive candidate for addressing conditions characterized by imbalances in inhibitory neurotransmission. Several pharmaceutical companies have initiated clinical trials to explore muscimol's efficacy in treating anxiety disorders, insomnia, and certain forms of epilepsy. These ongoing studies are expected to drive market growth and potentially lead to new drug approvals in the coming years.
The research community has shown increased interest in muscimol's neuropharmacological applications. Academic institutions and biotechnology firms are investigating its potential in neuroprotection, cognitive enhancement, and pain management. Preclinical studies have demonstrated muscimol's ability to reduce neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, suggesting its potential use in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. This expanding research landscape is likely to create new opportunities for market growth and diversification.
In the field of neuroscience tools and reagents, muscimol has found applications as a valuable research tool. Its selective activation of GABA receptors makes it useful for studying inhibitory neurotransmission in vitro and in vivo. The demand for high-purity muscimol for research purposes has led to the development of specialized synthesis and purification techniques, creating a niche market within the broader neuroscience research supplies sector.
The muscimol market faces challenges related to regulatory hurdles and potential side effects associated with GABA receptor modulation. However, ongoing research into targeted delivery methods and novel formulations aims to mitigate these concerns. Advancements in drug delivery technologies, such as nanoparticle-based systems and site-specific targeting, are expected to enhance muscimol's therapeutic potential while minimizing systemic effects.
As the understanding of GABAergic synapses and their role in various neurological processes deepens, the muscimol market is poised for further expansion. The convergence of neuropharmacology, precision medicine, and advanced drug delivery technologies is likely to drive innovation in muscimol-based therapies. This evolving landscape presents opportunities for both established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms to develop novel treatments and diagnostic tools leveraging muscimol's unique properties.
In the pharmaceutical industry, muscimol has emerged as a promising compound for developing novel treatments. Its ability to modulate GABAergic synapses makes it an attractive candidate for addressing conditions characterized by imbalances in inhibitory neurotransmission. Several pharmaceutical companies have initiated clinical trials to explore muscimol's efficacy in treating anxiety disorders, insomnia, and certain forms of epilepsy. These ongoing studies are expected to drive market growth and potentially lead to new drug approvals in the coming years.
The research community has shown increased interest in muscimol's neuropharmacological applications. Academic institutions and biotechnology firms are investigating its potential in neuroprotection, cognitive enhancement, and pain management. Preclinical studies have demonstrated muscimol's ability to reduce neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, suggesting its potential use in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. This expanding research landscape is likely to create new opportunities for market growth and diversification.
In the field of neuroscience tools and reagents, muscimol has found applications as a valuable research tool. Its selective activation of GABA receptors makes it useful for studying inhibitory neurotransmission in vitro and in vivo. The demand for high-purity muscimol for research purposes has led to the development of specialized synthesis and purification techniques, creating a niche market within the broader neuroscience research supplies sector.
The muscimol market faces challenges related to regulatory hurdles and potential side effects associated with GABA receptor modulation. However, ongoing research into targeted delivery methods and novel formulations aims to mitigate these concerns. Advancements in drug delivery technologies, such as nanoparticle-based systems and site-specific targeting, are expected to enhance muscimol's therapeutic potential while minimizing systemic effects.
As the understanding of GABAergic synapses and their role in various neurological processes deepens, the muscimol market is poised for further expansion. The convergence of neuropharmacology, precision medicine, and advanced drug delivery technologies is likely to drive innovation in muscimol-based therapies. This evolving landscape presents opportunities for both established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms to develop novel treatments and diagnostic tools leveraging muscimol's unique properties.
Current Understanding of Muscimol-GABA Interaction
Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, has been extensively studied for its impact on GABAergic synapses. Current understanding of the Muscimol-GABA interaction reveals a complex interplay between this compound and the inhibitory neurotransmitter system in the central nervous system.
Muscimol acts primarily as a selective agonist for GABA-A receptors, mimicking the effects of GABA itself. When bound to these receptors, it enhances chloride ion influx into neurons, leading to hyperpolarization and decreased neuronal excitability. This mechanism underlies its potent inhibitory effects on neural activity, making it a valuable tool in neuroscience research and potential therapeutic applications.
Recent studies have elucidated the specific binding properties of Muscimol to GABA-A receptors. It has been found to exhibit high affinity for these receptors, with binding characteristics that differ slightly from endogenous GABA. This unique binding profile contributes to its prolonged and potent effects on GABAergic transmission.
The interaction between Muscimol and GABA-A receptors has been shown to induce conformational changes in the receptor complex, affecting not only ion channel opening but also receptor trafficking and synaptic localization. These findings highlight the multifaceted nature of Muscimol's impact on GABAergic synapses, extending beyond simple agonist activity.
Furthermore, research has revealed that Muscimol's effects on GABAergic synapses are not uniform across all brain regions. Differential expression of GABA-A receptor subunits in various neural circuits results in region-specific responses to Muscimol. This heterogeneity in action has important implications for both its experimental use and potential therapeutic applications.
Electrophysiological studies have demonstrated that Muscimol application leads to an increase in the frequency and amplitude of inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) in GABAergic synapses. This enhancement of inhibitory neurotransmission is thought to underlie many of the observed behavioral and physiological effects of Muscimol administration.
Recent advances in imaging techniques have allowed for real-time visualization of Muscimol's effects on GABAergic synapses. These studies have revealed rapid changes in synaptic structure and function following Muscimol exposure, providing new insights into the dynamic nature of inhibitory synapse modulation.
The current understanding of Muscimol-GABA interaction also encompasses its effects on synaptic plasticity. Long-term exposure to Muscimol has been shown to induce adaptive changes in GABAergic synapses, including alterations in receptor expression and synaptic strength. These findings have important implications for the use of Muscimol in chronic treatment paradigms and its potential long-term effects on neural circuits.
Muscimol acts primarily as a selective agonist for GABA-A receptors, mimicking the effects of GABA itself. When bound to these receptors, it enhances chloride ion influx into neurons, leading to hyperpolarization and decreased neuronal excitability. This mechanism underlies its potent inhibitory effects on neural activity, making it a valuable tool in neuroscience research and potential therapeutic applications.
Recent studies have elucidated the specific binding properties of Muscimol to GABA-A receptors. It has been found to exhibit high affinity for these receptors, with binding characteristics that differ slightly from endogenous GABA. This unique binding profile contributes to its prolonged and potent effects on GABAergic transmission.
The interaction between Muscimol and GABA-A receptors has been shown to induce conformational changes in the receptor complex, affecting not only ion channel opening but also receptor trafficking and synaptic localization. These findings highlight the multifaceted nature of Muscimol's impact on GABAergic synapses, extending beyond simple agonist activity.
Furthermore, research has revealed that Muscimol's effects on GABAergic synapses are not uniform across all brain regions. Differential expression of GABA-A receptor subunits in various neural circuits results in region-specific responses to Muscimol. This heterogeneity in action has important implications for both its experimental use and potential therapeutic applications.
Electrophysiological studies have demonstrated that Muscimol application leads to an increase in the frequency and amplitude of inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) in GABAergic synapses. This enhancement of inhibitory neurotransmission is thought to underlie many of the observed behavioral and physiological effects of Muscimol administration.
Recent advances in imaging techniques have allowed for real-time visualization of Muscimol's effects on GABAergic synapses. These studies have revealed rapid changes in synaptic structure and function following Muscimol exposure, providing new insights into the dynamic nature of inhibitory synapse modulation.
The current understanding of Muscimol-GABA interaction also encompasses its effects on synaptic plasticity. Long-term exposure to Muscimol has been shown to induce adaptive changes in GABAergic synapses, including alterations in receptor expression and synaptic strength. These findings have important implications for the use of Muscimol in chronic treatment paradigms and its potential long-term effects on neural circuits.
Muscimol Mechanisms at GABAergic Synapses
01 Muscimol's effect on GABAergic synapses
Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, influences GABAergic synaptic transmission by binding to GABA-A receptors. This interaction enhances inhibitory neurotransmission in the central nervous system, leading to various neurophysiological effects. Research focuses on understanding the mechanisms of muscimol's action and its potential therapeutic applications in neurological disorders.- Muscimol as a GABA receptor agonist: Muscimol is a potent GABA receptor agonist that acts on GABAergic synapses. It binds to GABA-A receptors, enhancing inhibitory neurotransmission in the central nervous system. This compound is often used in research to study GABAergic signaling and its effects on neural activity.
- GABAergic synapse modulation for therapeutic applications: Modulation of GABAergic synapses, including the use of muscimol-like compounds, has potential therapeutic applications in various neurological and psychiatric disorders. Research focuses on developing novel compounds that target GABAergic synapses to treat conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disorders.
- Imaging and detection of GABAergic synapses: Advanced imaging techniques and detection methods are being developed to study GABAergic synapses and their function. These include fluorescent probes, electrophysiological recordings, and computational models that help visualize and analyze the dynamics of GABAergic neurotransmission.
- Artificial neural networks inspired by GABAergic synapses: The functioning of GABAergic synapses has inspired the development of artificial neural network models. These models incorporate inhibitory connections and dynamics similar to those observed in biological GABAergic synapses, potentially improving the performance and biological plausibility of artificial intelligence systems.
- Pharmacological manipulation of GABAergic synapses: Research into pharmacological agents that target GABAergic synapses, including muscimol derivatives and related compounds, aims to develop new treatments for neurological disorders. This includes the design of novel molecules that can selectively modulate GABAergic neurotransmission with improved efficacy and reduced side effects.
02 Neuroimaging techniques for studying GABAergic synapses
Advanced neuroimaging methods are employed to investigate GABAergic synaptic activity and the effects of compounds like muscimol. These techniques include functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and optical imaging, which allow researchers to visualize and quantify GABAergic neurotransmission in real-time, providing insights into synaptic plasticity and network dynamics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Genetic and molecular approaches to GABAergic synapse modulation
Researchers utilize genetic and molecular techniques to manipulate GABAergic synapses and study the effects of muscimol. This includes gene editing, optogenetics, and chemogenetics to selectively target and modulate GABAergic neurons and receptors. These approaches help elucidate the role of specific genes and proteins in GABAergic neurotransmission and their interaction with muscimol.Expand Specific Solutions04 Computational modeling of muscimol-GABAergic interactions
Computational models and simulations are developed to predict and analyze the complex interactions between muscimol and GABAergic synapses. These models incorporate neurophysiological data, receptor kinetics, and network dynamics to simulate the effects of muscimol on neural circuits. Machine learning algorithms are also employed to process and interpret large-scale data sets related to GABAergic synaptic function.Expand Specific Solutions05 Therapeutic applications of muscimol in GABAergic disorders
The potential therapeutic uses of muscimol in treating disorders associated with GABAergic dysfunction are explored. This includes research into epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and sleep disturbances. Studies focus on developing novel drug delivery methods, optimizing dosage regimens, and investigating combination therapies to enhance the efficacy of muscimol-based treatments while minimizing side effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in GABAergic Research and Drug Development
The field of GABAergic synapses and muscimol's impact is in a mature research phase, with significant market potential in neuropharmacology. The global neuroscience market, valued at $30.8 billion in 2020, is expected to grow substantially. Key players like SAGE Therapeutics and Janssen Pharmaceutica are leading in drug development, while academic institutions such as Northwestern University and Fudan University contribute crucial research. Companies like BioLineRx and CaaMTech are exploring innovative approaches, indicating a competitive landscape with diverse stakeholders from both industry and academia. The technology's maturity is evident in the advanced research conducted by established pharmaceutical companies and specialized neuroscience firms.
SAGE Therapeutics, Inc.
Technical Solution: SAGE Therapeutics has developed a novel approach to modulating GABAergic synapses using synthetic neurosteroids that act as positive allosteric modulators of GABA-A receptors. Their lead compound, brexanolone, is structurally similar to allopregnanolone and has been shown to enhance the effect of GABA at synapses[1]. This approach differs from muscimol's direct agonist action, potentially offering a more nuanced modulation of GABAergic transmission. The company has also explored other GABA-A receptor modulators, including SAGE-217, which has shown promise in treating major depressive disorder and other CNS disorders[2].
Strengths: Targeted approach to GABAergic modulation with potentially fewer side effects than direct agonists. Weaknesses: May not be as potent as direct GABA-A agonists like muscimol for certain applications.
The Regents of the University of California
Technical Solution: Researchers at the University of California have conducted extensive studies on the impact of muscimol on GABAergic synapses. They have utilized advanced imaging techniques, including two-photon microscopy, to visualize the effects of muscimol on individual synapses in real-time[3]. Their research has revealed that muscimol not only activates GABA-A receptors but also influences the clustering and distribution of these receptors at synapses. Additionally, they have investigated the role of muscimol in modulating synaptic plasticity and its potential neuroprotective effects in models of neurological disorders[4].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research techniques providing detailed insights into muscimol's synaptic effects. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on basic research, which may require additional steps for clinical translation.
Innovative Studies on Muscimol-GABA Receptor Binding
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentPendingUS20240050502A1
Innovation
- Development of purified Amanita muscaria compound compositions and formulations comprising specific ratios of ibotenic acid, muscimol, and other compounds, which are structurally distinct and free from other Amanita muscaria compounds, combined with excipients and serotonergic drugs, psilocybin derivatives, or cannabinoids to create pharmaceutical formulations for therapeutic use.
Conjugates comprising a GABA- or glycine compound, pharmaceutical compositions and combinations thereof and their use in treating CNS disorders
PatentInactiveUS8222296B2
Innovation
- Conjugating GABA or glycine with analgesic drugs, such as acetaminophen, to form novel conjugates that can cross the blood-brain barrier, allowing for the release of these compounds in brain tissues and enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of psychotropic drugs while reducing side effects.
Regulatory Framework for GABAergic Drug Development
The regulatory framework for GABAergic drug development is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in shaping the research, development, and commercialization of drugs targeting GABAergic synapses. This framework encompasses various regulatory bodies, guidelines, and processes that ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of GABAergic drugs throughout their lifecycle.
At the forefront of this regulatory framework is the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which oversees the approval process for new GABAergic drugs in the United States. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of these drugs through rigorous clinical trials and comprehensive data analysis. The agency has established specific guidelines for the development of drugs targeting the central nervous system, including those affecting GABAergic synapses.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) plays a similar role in regulating GABAergic drug development. The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) is responsible for evaluating marketing authorization applications for new drugs, including those targeting GABAergic synapses. The agency has also developed guidelines specific to the development of drugs for neurological disorders, which are relevant to GABAergic drug research.
The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) provides a platform for harmonizing regulatory requirements across different regions. The ICH guidelines, particularly those related to safety pharmacology studies and clinical trial design, are essential for GABAergic drug developers aiming for global market access.
Regulatory agencies require extensive preclinical and clinical data to support the safety and efficacy of GABAergic drugs. This includes in vitro and in vivo studies to elucidate the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, and potential side effects. Clinical trials must adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and typically involve multiple phases to assess safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing regimens.
The regulatory framework also addresses the manufacturing and quality control aspects of GABAergic drug development. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines ensure that drugs are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. These guidelines are particularly important for GABAergic drugs, given the precision required in their formulation and the potential for serious side effects if not properly manufactured.
Post-marketing surveillance is another critical component of the regulatory framework. Regulatory agencies require ongoing monitoring of GABAergic drugs after approval to identify any long-term safety concerns or rare adverse events that may not have been detected during clinical trials. This process involves pharmacovigilance systems and periodic safety update reports submitted by drug manufacturers.
As research into GABAergic synapses and related drugs continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are adapting to accommodate new technologies and approaches. This includes the development of guidelines for novel drug delivery systems, combination therapies, and personalized medicine approaches that may be particularly relevant to GABAergic drug development.
At the forefront of this regulatory framework is the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which oversees the approval process for new GABAergic drugs in the United States. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of these drugs through rigorous clinical trials and comprehensive data analysis. The agency has established specific guidelines for the development of drugs targeting the central nervous system, including those affecting GABAergic synapses.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) plays a similar role in regulating GABAergic drug development. The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) is responsible for evaluating marketing authorization applications for new drugs, including those targeting GABAergic synapses. The agency has also developed guidelines specific to the development of drugs for neurological disorders, which are relevant to GABAergic drug research.
The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) provides a platform for harmonizing regulatory requirements across different regions. The ICH guidelines, particularly those related to safety pharmacology studies and clinical trial design, are essential for GABAergic drug developers aiming for global market access.
Regulatory agencies require extensive preclinical and clinical data to support the safety and efficacy of GABAergic drugs. This includes in vitro and in vivo studies to elucidate the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, and potential side effects. Clinical trials must adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and typically involve multiple phases to assess safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing regimens.
The regulatory framework also addresses the manufacturing and quality control aspects of GABAergic drug development. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines ensure that drugs are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. These guidelines are particularly important for GABAergic drugs, given the precision required in their formulation and the potential for serious side effects if not properly manufactured.
Post-marketing surveillance is another critical component of the regulatory framework. Regulatory agencies require ongoing monitoring of GABAergic drugs after approval to identify any long-term safety concerns or rare adverse events that may not have been detected during clinical trials. This process involves pharmacovigilance systems and periodic safety update reports submitted by drug manufacturers.
As research into GABAergic synapses and related drugs continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are adapting to accommodate new technologies and approaches. This includes the development of guidelines for novel drug delivery systems, combination therapies, and personalized medicine approaches that may be particularly relevant to GABAergic drug development.
Ethical Considerations in Neuropharmacological Research
Ethical considerations in neuropharmacological research, particularly in studies involving muscimol and its impact on GABAergic synapses, are of paramount importance. The use of muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, raises several ethical concerns that researchers must address to ensure the responsible conduct of their studies.
One primary ethical consideration is the potential for unintended neurological effects in research subjects. Muscimol's powerful impact on GABAergic synapses can lead to significant alterations in brain function, potentially causing temporary or long-lasting changes in cognition, behavior, or emotional states. Researchers must carefully weigh the scientific benefits against the risks to participants' well-being and autonomy.
Informed consent is another crucial ethical aspect of such research. Given the complex nature of neuropharmacological interventions, it is essential to ensure that participants fully understand the potential risks and implications of their involvement. This includes providing clear, accessible information about the effects of muscimol on GABAergic synapses and the broader impact on brain function.
The ethical use of animal models in muscimol research also demands careful consideration. While animal studies are often necessary for advancing our understanding of GABAergic synapses, researchers must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to minimize suffering and ensure humane treatment. This includes using the minimum number of animals required for statistically significant results and employing alternative methods where possible.
Data privacy and confidentiality present additional ethical challenges in neuropharmacological research. The sensitive nature of brain-related data necessitates robust protocols for data protection, storage, and sharing. Researchers must ensure that participants' neurological information is safeguarded against unauthorized access or misuse.
Long-term follow-up and monitoring of research participants is an ethical imperative in studies involving muscimol. Given the potential for lasting effects on GABAergic synapses, researchers have a responsibility to track participants' neurological health over extended periods, providing necessary support and interventions if adverse effects are observed.
The ethical implications of potential therapeutic applications arising from muscimol research must also be considered. While discoveries may lead to new treatments for neurological disorders, researchers must be cautious about overpromising or prematurely promoting findings, ensuring that public communication is balanced and evidence-based.
Lastly, the ethical conduct of muscimol research requires transparency and peer review. Researchers should openly share their methodologies, findings, and ethical considerations with the scientific community, allowing for critical evaluation and replication of results. This openness is crucial for maintaining public trust and advancing the field responsibly.
One primary ethical consideration is the potential for unintended neurological effects in research subjects. Muscimol's powerful impact on GABAergic synapses can lead to significant alterations in brain function, potentially causing temporary or long-lasting changes in cognition, behavior, or emotional states. Researchers must carefully weigh the scientific benefits against the risks to participants' well-being and autonomy.
Informed consent is another crucial ethical aspect of such research. Given the complex nature of neuropharmacological interventions, it is essential to ensure that participants fully understand the potential risks and implications of their involvement. This includes providing clear, accessible information about the effects of muscimol on GABAergic synapses and the broader impact on brain function.
The ethical use of animal models in muscimol research also demands careful consideration. While animal studies are often necessary for advancing our understanding of GABAergic synapses, researchers must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to minimize suffering and ensure humane treatment. This includes using the minimum number of animals required for statistically significant results and employing alternative methods where possible.
Data privacy and confidentiality present additional ethical challenges in neuropharmacological research. The sensitive nature of brain-related data necessitates robust protocols for data protection, storage, and sharing. Researchers must ensure that participants' neurological information is safeguarded against unauthorized access or misuse.
Long-term follow-up and monitoring of research participants is an ethical imperative in studies involving muscimol. Given the potential for lasting effects on GABAergic synapses, researchers have a responsibility to track participants' neurological health over extended periods, providing necessary support and interventions if adverse effects are observed.
The ethical implications of potential therapeutic applications arising from muscimol research must also be considered. While discoveries may lead to new treatments for neurological disorders, researchers must be cautious about overpromising or prematurely promoting findings, ensuring that public communication is balanced and evidence-based.
Lastly, the ethical conduct of muscimol research requires transparency and peer review. Researchers should openly share their methodologies, findings, and ethical considerations with the scientific community, allowing for critical evaluation and replication of results. This openness is crucial for maintaining public trust and advancing the field responsibly.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!