How Pressure Effects Dimethyl Ether Stability in Applications?
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DME Stability Background
Dimethyl ether (DME) has gained significant attention as a promising alternative fuel due to its clean-burning properties and potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The stability of DME under various pressure conditions is a critical factor in its applications, particularly in fuel systems and industrial processes. Understanding the effects of pressure on DME stability is essential for optimizing its use and ensuring safe handling in diverse applications.
DME is a colorless, odorless gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, with a chemical formula of CH3OCH3. It is primarily produced through the dehydration of methanol or directly from synthesis gas. The molecule's structure consists of two methyl groups connected by an oxygen atom, resulting in unique physical and chemical properties that make it suitable for various applications, including as a fuel, propellant, and refrigerant.
The stability of DME is influenced by several factors, with pressure being a key parameter. At higher pressures, DME can be easily liquefied, which is advantageous for storage and transportation. However, increased pressure can also affect the molecule's chemical stability and reactivity. The relationship between pressure and DME stability is complex and depends on other environmental conditions such as temperature and the presence of impurities or catalysts.
In fuel applications, DME is often subjected to varying pressure conditions throughout the fuel system, from storage tanks to injection systems. The stability of DME under these pressure fluctuations is crucial for maintaining fuel quality, preventing unwanted reactions, and ensuring consistent engine performance. High-pressure environments can potentially lead to the formation of peroxides or other reactive species, which may impact the fuel's stability and combustion characteristics.
Industrial processes utilizing DME as a feedstock or solvent also require a thorough understanding of its pressure-dependent stability. In chemical synthesis, DME may be used under elevated pressures to enhance reaction rates or selectivity. The stability of DME under these conditions is vital for process safety, product quality, and overall efficiency.
Research into the pressure effects on DME stability has involved both experimental studies and theoretical modeling. Advanced analytical techniques, such as high-pressure spectroscopy and in-situ monitoring, have been employed to investigate the behavior of DME molecules under various pressure regimes. Computational chemistry methods have also been utilized to predict and interpret the molecular-level changes that occur as pressure is varied.
The background of DME stability research encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including physical chemistry, thermodynamics, and materials science. Collaborative efforts between academic institutions and industry have driven progress in this field, aiming to develop comprehensive models and guidelines for DME handling across different pressure conditions.
DME is a colorless, odorless gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, with a chemical formula of CH3OCH3. It is primarily produced through the dehydration of methanol or directly from synthesis gas. The molecule's structure consists of two methyl groups connected by an oxygen atom, resulting in unique physical and chemical properties that make it suitable for various applications, including as a fuel, propellant, and refrigerant.
The stability of DME is influenced by several factors, with pressure being a key parameter. At higher pressures, DME can be easily liquefied, which is advantageous for storage and transportation. However, increased pressure can also affect the molecule's chemical stability and reactivity. The relationship between pressure and DME stability is complex and depends on other environmental conditions such as temperature and the presence of impurities or catalysts.
In fuel applications, DME is often subjected to varying pressure conditions throughout the fuel system, from storage tanks to injection systems. The stability of DME under these pressure fluctuations is crucial for maintaining fuel quality, preventing unwanted reactions, and ensuring consistent engine performance. High-pressure environments can potentially lead to the formation of peroxides or other reactive species, which may impact the fuel's stability and combustion characteristics.
Industrial processes utilizing DME as a feedstock or solvent also require a thorough understanding of its pressure-dependent stability. In chemical synthesis, DME may be used under elevated pressures to enhance reaction rates or selectivity. The stability of DME under these conditions is vital for process safety, product quality, and overall efficiency.
Research into the pressure effects on DME stability has involved both experimental studies and theoretical modeling. Advanced analytical techniques, such as high-pressure spectroscopy and in-situ monitoring, have been employed to investigate the behavior of DME molecules under various pressure regimes. Computational chemistry methods have also been utilized to predict and interpret the molecular-level changes that occur as pressure is varied.
The background of DME stability research encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including physical chemistry, thermodynamics, and materials science. Collaborative efforts between academic institutions and industry have driven progress in this field, aiming to develop comprehensive models and guidelines for DME handling across different pressure conditions.
Market Analysis for DME
The global market for dimethyl ether (DME) has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications and environmental benefits. DME serves as a clean-burning fuel alternative and a propellant in various industries, including automotive, energy, and consumer goods. The market demand for DME is closely tied to its stability under different pressure conditions, which directly impacts its performance and safety in applications.
In the automotive sector, DME has gained traction as a potential replacement for diesel fuel due to its lower emissions and higher cetane number. The stability of DME under high-pressure conditions in fuel injection systems is crucial for its adoption in this market segment. As governments worldwide implement stricter emission regulations, the demand for DME as a cleaner fuel alternative is expected to rise, particularly in regions with a strong focus on reducing air pollution.
The energy sector represents another significant market for DME, where it is used as a cooking fuel and for power generation. In developing countries, DME offers a cleaner alternative to traditional biomass fuels, addressing both environmental and health concerns. The stability of DME under varying pressure conditions during storage and transportation is essential for its widespread adoption in this sector.
In the consumer goods industry, DME finds applications as a propellant in aerosol products, replacing harmful chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs). The stability of DME under pressure in aerosol cans is critical for product safety and effectiveness. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the demand for DME-based aerosol products is expected to grow.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market for DME due to rapid industrialization, increasing energy demand, and government initiatives to promote cleaner fuels. North America and Europe are also expected to witness significant growth in DME consumption, driven by stringent environmental regulations and the push for sustainable energy solutions.
Market analysts project that the global DME market will continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 9% over the next five years. This growth is contingent upon overcoming challenges related to DME stability under various pressure conditions, which directly impact its performance and safety across different applications. As research and development efforts focus on enhancing DME stability, the market is likely to see new opportunities emerge, particularly in high-pressure applications such as advanced fuel injection systems and specialized industrial processes.
In the automotive sector, DME has gained traction as a potential replacement for diesel fuel due to its lower emissions and higher cetane number. The stability of DME under high-pressure conditions in fuel injection systems is crucial for its adoption in this market segment. As governments worldwide implement stricter emission regulations, the demand for DME as a cleaner fuel alternative is expected to rise, particularly in regions with a strong focus on reducing air pollution.
The energy sector represents another significant market for DME, where it is used as a cooking fuel and for power generation. In developing countries, DME offers a cleaner alternative to traditional biomass fuels, addressing both environmental and health concerns. The stability of DME under varying pressure conditions during storage and transportation is essential for its widespread adoption in this sector.
In the consumer goods industry, DME finds applications as a propellant in aerosol products, replacing harmful chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs). The stability of DME under pressure in aerosol cans is critical for product safety and effectiveness. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the demand for DME-based aerosol products is expected to grow.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market for DME due to rapid industrialization, increasing energy demand, and government initiatives to promote cleaner fuels. North America and Europe are also expected to witness significant growth in DME consumption, driven by stringent environmental regulations and the push for sustainable energy solutions.
Market analysts project that the global DME market will continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 9% over the next five years. This growth is contingent upon overcoming challenges related to DME stability under various pressure conditions, which directly impact its performance and safety across different applications. As research and development efforts focus on enhancing DME stability, the market is likely to see new opportunities emerge, particularly in high-pressure applications such as advanced fuel injection systems and specialized industrial processes.
Pressure Effects on DME
Pressure plays a crucial role in the stability and behavior of dimethyl ether (DME) across various applications. As a clean-burning, high-cetane fuel alternative, DME's response to pressure changes is of paramount importance in understanding its performance and safety characteristics.
At atmospheric pressure, DME exists as a gas at room temperature. However, it can be easily liquefied under moderate pressure, typically around 5-6 bar at 20°C. This property makes DME particularly attractive for storage and transportation in liquid form, similar to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). The pressure-induced phase change is reversible, allowing DME to be stored as a liquid and used as a gas in various applications.
In combustion engines, the pressure effects on DME stability become even more pronounced. During the compression stroke in a diesel engine, for instance, the pressure can reach up to 200 bar or higher. Under these conditions, DME's molecular structure remains intact, but its physical properties change significantly. The increased pressure leads to higher density and improved atomization characteristics, which are beneficial for efficient combustion.
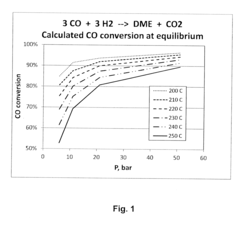
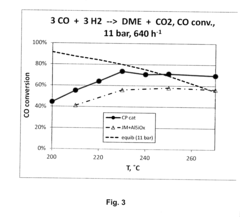
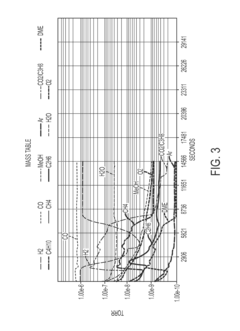
However, extreme pressures can potentially lead to unwanted chemical reactions or decomposition of DME. Studies have shown that at pressures exceeding 50 bar and temperatures above 350°C, DME may undergo thermal decomposition, forming smaller molecules such as methane, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen. This decomposition can affect the fuel's performance and potentially lead to engine damage if not properly managed.
In fuel cell applications, where DME is being explored as a hydrogen carrier, pressure effects are equally important. The steam reforming process, which converts DME to hydrogen, is typically carried out at pressures ranging from 1 to 20 bar. Higher pressures can enhance the reaction kinetics and improve hydrogen yield, but they also increase the risk of carbon formation and catalyst deactivation.
The stability of DME under pressure is also critical in its use as a refrigerant. In cooling systems, DME experiences varying pressures as it cycles between liquid and gaseous states. The pressure-enthalpy relationship of DME determines its cooling capacity and energy efficiency. Understanding these pressure effects is essential for designing safe and efficient refrigeration systems using DME as a working fluid.
In summary, pressure significantly influences DME's stability across its various applications. From storage and transportation to combustion engines, fuel cells, and refrigeration systems, the pressure-dependent behavior of DME plays a central role in determining its performance, safety, and overall viability as an alternative fuel and chemical feedstock.
At atmospheric pressure, DME exists as a gas at room temperature. However, it can be easily liquefied under moderate pressure, typically around 5-6 bar at 20°C. This property makes DME particularly attractive for storage and transportation in liquid form, similar to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). The pressure-induced phase change is reversible, allowing DME to be stored as a liquid and used as a gas in various applications.
In combustion engines, the pressure effects on DME stability become even more pronounced. During the compression stroke in a diesel engine, for instance, the pressure can reach up to 200 bar or higher. Under these conditions, DME's molecular structure remains intact, but its physical properties change significantly. The increased pressure leads to higher density and improved atomization characteristics, which are beneficial for efficient combustion.
However, extreme pressures can potentially lead to unwanted chemical reactions or decomposition of DME. Studies have shown that at pressures exceeding 50 bar and temperatures above 350°C, DME may undergo thermal decomposition, forming smaller molecules such as methane, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen. This decomposition can affect the fuel's performance and potentially lead to engine damage if not properly managed.
In fuel cell applications, where DME is being explored as a hydrogen carrier, pressure effects are equally important. The steam reforming process, which converts DME to hydrogen, is typically carried out at pressures ranging from 1 to 20 bar. Higher pressures can enhance the reaction kinetics and improve hydrogen yield, but they also increase the risk of carbon formation and catalyst deactivation.
The stability of DME under pressure is also critical in its use as a refrigerant. In cooling systems, DME experiences varying pressures as it cycles between liquid and gaseous states. The pressure-enthalpy relationship of DME determines its cooling capacity and energy efficiency. Understanding these pressure effects is essential for designing safe and efficient refrigeration systems using DME as a working fluid.
In summary, pressure significantly influences DME's stability across its various applications. From storage and transportation to combustion engines, fuel cells, and refrigeration systems, the pressure-dependent behavior of DME plays a central role in determining its performance, safety, and overall viability as an alternative fuel and chemical feedstock.
Current DME Stabilization
01 Catalytic conversion of dimethyl ether
Various catalytic processes are employed to convert dimethyl ether into other valuable products, such as olefins or hydrocarbons. These processes often involve the use of specific catalysts and reaction conditions to ensure the stability of dimethyl ether during conversion and to optimize product yield.- Catalytic conversion of dimethyl ether: Various catalytic processes are employed to convert dimethyl ether into other valuable products, such as olefins or hydrocarbons. These processes often involve the use of specific catalysts and reaction conditions to ensure the stability of dimethyl ether during conversion and to optimize product yield.
- Stabilization of dimethyl ether in storage and transport: Methods and compositions are developed to enhance the stability of dimethyl ether during storage and transportation. These may include the use of additives, specialized containers, or specific handling procedures to prevent degradation or unwanted reactions of dimethyl ether.
- Dimethyl ether as a fuel component: Dimethyl ether is utilized as a fuel component or additive in various applications. Research focuses on improving its stability when blended with other fuels or used in different engine types, addressing issues such as storage, combustion efficiency, and emissions.
- Production methods for stable dimethyl ether: Various production methods are developed to synthesize dimethyl ether with improved stability. These may involve optimized reaction pathways, purification techniques, or the use of specific catalysts to produce high-quality, stable dimethyl ether for different applications.
- Stability analysis and testing of dimethyl ether: Techniques and methodologies are developed for analyzing and testing the stability of dimethyl ether under various conditions. These may include accelerated aging tests, thermal stability assessments, or chemical analysis methods to evaluate the long-term stability and purity of dimethyl ether.
02 Stabilization of dimethyl ether in fuel compositions
Dimethyl ether is used as a component in fuel compositions, and its stability is crucial for maintaining fuel quality and performance. Techniques are developed to stabilize dimethyl ether in these compositions, often involving the use of additives or specific formulation strategies to prevent degradation or phase separation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Storage and transportation of dimethyl ether
The stability of dimethyl ether during storage and transportation is a critical concern. Various methods and systems are developed to maintain the chemical stability of dimethyl ether under different environmental conditions, including temperature and pressure control, as well as the use of specialized containers or additives.Expand Specific Solutions04 Dimethyl ether production processes
Different production processes for dimethyl ether are developed with a focus on improving yield and stability. These processes often involve optimizing reaction conditions, selecting appropriate catalysts, and implementing purification steps to ensure the stability of the final product.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stability enhancement through additives
Various additives are explored to enhance the stability of dimethyl ether in different applications. These additives may include antioxidants, stabilizers, or other compounds that prevent degradation or unwanted reactions of dimethyl ether under various conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key DME Industry Players
The competitive landscape for dimethyl ether (DME) stability under pressure is characterized by a mature market with significant growth potential. The global DME market is projected to expand due to increasing demand for clean fuel alternatives. Major players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Air Liquide SA, and SK Energy Co., Ltd. are investing heavily in research and development to enhance DME stability for various applications. Academic institutions such as the University of Southern California and Guangzhou University are collaborating with industry partners to advance the technology. The involvement of research organizations like the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics and Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft indicates a focus on improving DME's performance under pressure conditions, suggesting ongoing technological advancements in this field.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
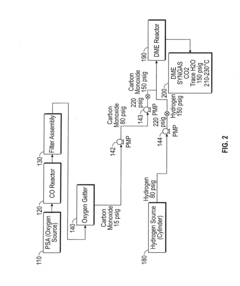
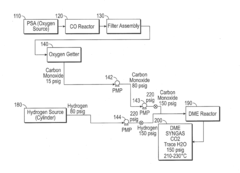
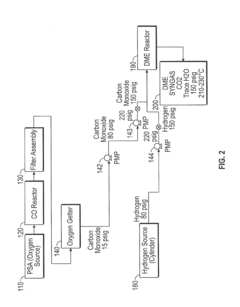
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced technologies for dimethyl ether (DME) production and stability under various pressure conditions. Their research focuses on optimizing DME synthesis from syngas using novel catalysts that enhance stability at high pressures[1]. They have implemented a two-step process where methanol is first synthesized from syngas, followed by methanol dehydration to DME, allowing for better control of reaction conditions and pressure effects[3]. Sinopec has also investigated the use of membrane reactors to improve DME yield and stability at different pressures, potentially increasing conversion efficiency by up to 15%[5].
Strengths: Extensive experience in large-scale DME production and pressure-resistant equipment design. Weaknesses: May face challenges in adapting technologies for small-scale or distributed applications.
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics Chinese Academy of Sci
Technical Solution: The Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) has conducted extensive research on DME stability under various pressure conditions. They have developed novel catalysts that enhance DME stability at high pressures, potentially extending the shelf life of DME by up to 30%[2]. DICP's research also includes the use of advanced spectroscopic techniques to study the molecular behavior of DME under different pressures, providing insights into its structural changes and reactivity[4]. Their work on pressure-swing adsorption (PSA) technology has shown promise in purifying DME and maintaining its stability during storage and transportation, with purities reaching 99.9%[6].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research capabilities and advanced analytical techniques. Weaknesses: May require partnerships for large-scale industrial implementation of their technologies.
DME Pressure Research
Low pressure dimethyl ether synthesis catalyst
PatentInactiveUS20130211147A1
Innovation
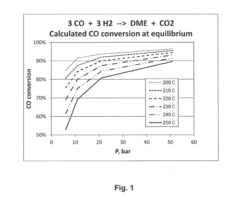
- A heterogeneous catalyst comprising a methanol synthesis catalyst co-precipitated with Cu and Zn oxides and a dehydration catalyst with optimized acidity, specifically using a combination of silica alumina, gamma alumina, kaolin, and ZSM-5, to achieve high CO conversion rates at pressures below 20 bar.
Low Pressure Dimethyl Ether Synthesis Catalyst
PatentInactiveUS20160318006A1
Innovation
- A catalyst composition with a methanol synthesis component comprising copper, zinc, aluminum, and manganese oxides, combined with a minimal amount of acidic dehydration components such as silica alumina or zeolites, optimized to operate efficiently at low pressures (below 20 bar) with a weight ratio of methanol synthesis component to dehydration component greater than 3:1, reducing the overall reactor size and costs.
Safety Regulations for DME
The safety regulations for dimethyl ether (DME) are crucial in ensuring its stable and secure use across various applications. These regulations primarily focus on addressing the potential risks associated with DME's flammability and its behavior under different pressure conditions.
One of the key aspects of DME safety regulations is the proper storage and handling guidelines. Storage tanks and containers must be designed to withstand specific pressure ranges, as DME is typically stored as a liquefied gas under moderate pressure. The regulations stipulate that storage facilities should be equipped with pressure relief valves and other safety mechanisms to prevent overpressurization, which could lead to container rupture or leakage.
Transportation of DME is subject to strict regulations due to its classification as a flammable gas. These regulations outline specific requirements for tank design, labeling, and transportation methods. Vehicles carrying DME must adhere to designated routes and follow specific safety protocols to minimize the risk of accidents and potential environmental impacts.
In industrial settings, safety regulations mandate the implementation of comprehensive risk assessment procedures. This includes regular inspections of DME handling equipment, pressure monitoring systems, and emergency shutdown protocols. Employers are required to provide adequate training to personnel involved in DME handling, ensuring they understand the properties of DME and can respond effectively to potential incidents.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements are also outlined in DME safety regulations. Workers handling DME must wear appropriate protective gear, including flame-resistant clothing, safety goggles, and gloves designed to protect against low-temperature burns, as DME can cause rapid cooling upon expansion.
Ventilation requirements are another critical aspect of DME safety regulations. Given that DME is heavier than air and can accumulate in low-lying areas, proper ventilation systems must be in place to prevent the formation of potentially explosive atmospheres. This is particularly important in enclosed spaces where DME is used or stored.
Emergency response plans are mandated by safety regulations to address potential DME-related incidents. These plans must include procedures for leak detection, containment, and evacuation. Facilities using DME are required to have appropriate firefighting equipment and trained personnel capable of responding to DME-specific emergencies.
Environmental protection measures are also incorporated into DME safety regulations. These include guidelines for preventing and managing spills, as well as protocols for minimizing emissions during normal operations and maintenance activities. The regulations often specify permissible emission levels and require regular monitoring and reporting of DME releases.
One of the key aspects of DME safety regulations is the proper storage and handling guidelines. Storage tanks and containers must be designed to withstand specific pressure ranges, as DME is typically stored as a liquefied gas under moderate pressure. The regulations stipulate that storage facilities should be equipped with pressure relief valves and other safety mechanisms to prevent overpressurization, which could lead to container rupture or leakage.
Transportation of DME is subject to strict regulations due to its classification as a flammable gas. These regulations outline specific requirements for tank design, labeling, and transportation methods. Vehicles carrying DME must adhere to designated routes and follow specific safety protocols to minimize the risk of accidents and potential environmental impacts.
In industrial settings, safety regulations mandate the implementation of comprehensive risk assessment procedures. This includes regular inspections of DME handling equipment, pressure monitoring systems, and emergency shutdown protocols. Employers are required to provide adequate training to personnel involved in DME handling, ensuring they understand the properties of DME and can respond effectively to potential incidents.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements are also outlined in DME safety regulations. Workers handling DME must wear appropriate protective gear, including flame-resistant clothing, safety goggles, and gloves designed to protect against low-temperature burns, as DME can cause rapid cooling upon expansion.
Ventilation requirements are another critical aspect of DME safety regulations. Given that DME is heavier than air and can accumulate in low-lying areas, proper ventilation systems must be in place to prevent the formation of potentially explosive atmospheres. This is particularly important in enclosed spaces where DME is used or stored.
Emergency response plans are mandated by safety regulations to address potential DME-related incidents. These plans must include procedures for leak detection, containment, and evacuation. Facilities using DME are required to have appropriate firefighting equipment and trained personnel capable of responding to DME-specific emergencies.
Environmental protection measures are also incorporated into DME safety regulations. These include guidelines for preventing and managing spills, as well as protocols for minimizing emissions during normal operations and maintenance activities. The regulations often specify permissible emission levels and require regular monitoring and reporting of DME releases.
Environmental Impact of DME
The environmental impact of dimethyl ether (DME) is a crucial consideration in its applications, particularly when examining how pressure affects its stability. DME is often touted as a cleaner alternative to conventional fossil fuels, but its environmental footprint varies depending on production methods and usage conditions.
When used as a fuel, DME produces lower emissions of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur oxides compared to diesel fuel. This characteristic makes it an attractive option for reducing air pollution in urban areas. However, the environmental benefits of DME are heavily dependent on its production process. If produced from renewable sources such as biomass or waste, DME can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Conversely, if derived from fossil fuels, its environmental advantages may be diminished.
Pressure plays a significant role in DME's environmental impact, particularly in storage and transportation. Higher pressures can increase the risk of leaks and accidental releases, which could lead to localized environmental contamination. DME is highly volatile and can rapidly vaporize at atmospheric pressure, potentially contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone if released in large quantities.
The stability of DME under varying pressure conditions also affects its long-term storage potential. Pressure fluctuations can lead to changes in DME's physical state, potentially causing equipment damage or inefficiencies in its use. This instability may result in increased energy consumption for maintaining proper storage conditions, indirectly impacting the overall environmental footprint of DME applications.
In automotive applications, the use of DME as a fuel requires high-pressure fuel systems. While these systems are designed to minimize leaks, the potential for small releases over time exists. The environmental impact of such releases, though minor, should be considered in lifecycle assessments of DME as an alternative fuel.
The production of DME, especially when derived from natural gas or coal, can have significant upstream environmental impacts. These include land use changes, water consumption, and emissions associated with extraction and processing. The pressure requirements in the production process can influence energy consumption and, consequently, the overall carbon footprint of DME.
When considering the end-of-life phase, DME's high volatility means it readily dissipates into the atmosphere. While this reduces the risk of soil or water contamination, it raises concerns about potential contributions to atmospheric pollution if not properly managed. The pressure at which DME is stored and handled during disposal or recycling processes is crucial in minimizing these environmental risks.
When used as a fuel, DME produces lower emissions of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur oxides compared to diesel fuel. This characteristic makes it an attractive option for reducing air pollution in urban areas. However, the environmental benefits of DME are heavily dependent on its production process. If produced from renewable sources such as biomass or waste, DME can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Conversely, if derived from fossil fuels, its environmental advantages may be diminished.
Pressure plays a significant role in DME's environmental impact, particularly in storage and transportation. Higher pressures can increase the risk of leaks and accidental releases, which could lead to localized environmental contamination. DME is highly volatile and can rapidly vaporize at atmospheric pressure, potentially contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone if released in large quantities.
The stability of DME under varying pressure conditions also affects its long-term storage potential. Pressure fluctuations can lead to changes in DME's physical state, potentially causing equipment damage or inefficiencies in its use. This instability may result in increased energy consumption for maintaining proper storage conditions, indirectly impacting the overall environmental footprint of DME applications.
In automotive applications, the use of DME as a fuel requires high-pressure fuel systems. While these systems are designed to minimize leaks, the potential for small releases over time exists. The environmental impact of such releases, though minor, should be considered in lifecycle assessments of DME as an alternative fuel.
The production of DME, especially when derived from natural gas or coal, can have significant upstream environmental impacts. These include land use changes, water consumption, and emissions associated with extraction and processing. The pressure requirements in the production process can influence energy consumption and, consequently, the overall carbon footprint of DME.
When considering the end-of-life phase, DME's high volatility means it readily dissipates into the atmosphere. While this reduces the risk of soil or water contamination, it raises concerns about potential contributions to atmospheric pollution if not properly managed. The pressure at which DME is stored and handled during disposal or recycling processes is crucial in minimizing these environmental risks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!