How Solenoid Valves Improve Flow Calibration for Industrial Standards
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Solenoid Valve Technology Evolution and Objectives
Solenoid valves have played a pivotal role in industrial flow control systems for decades, evolving from simple on-off mechanisms to sophisticated, precision-controlled devices. The technology's journey began in the early 20th century with basic electromagnetic actuators, progressing through various stages of refinement to meet increasingly demanding industrial standards.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the advent of electronic control systems marked a significant leap in solenoid valve technology. This integration allowed for more precise control over fluid flow, laying the groundwork for modern calibration techniques. The subsequent decades saw rapid advancements in materials science, miniaturization, and digital control systems, further enhancing the capabilities of solenoid valves.
The primary objective of solenoid valve technology in flow calibration has been to achieve greater accuracy, reliability, and repeatability in fluid control processes. This goal has driven continuous innovation in valve design, materials, and control mechanisms. Modern solenoid valves incorporate advanced features such as proportional control, fast response times, and self-diagnostic capabilities, all of which contribute to improved flow calibration.
One of the key technological trends in recent years has been the development of "smart" solenoid valves. These valves integrate sensors and microprocessors, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustment of flow parameters. This advancement has significantly enhanced the precision of flow calibration, allowing for dynamic responses to changing process conditions.
Another important objective in the evolution of solenoid valve technology has been the reduction of energy consumption and environmental impact. This has led to the development of low-power solenoid valves and the use of more environmentally friendly materials in valve construction.
The integration of solenoid valves with Industry 4.0 technologies represents the latest frontier in their evolution. Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity and artificial intelligence are being leveraged to create predictive maintenance systems and optimize valve performance in complex industrial processes. These advancements are crucial for maintaining and improving calibration standards in increasingly automated industrial environments.
Looking ahead, the objectives for solenoid valve technology in flow calibration are focused on achieving even greater precision, expanding the range of operating conditions, and further integrating with digital control systems. Research is ongoing into novel actuation methods, such as piezoelectric systems, which promise even faster response times and finer control over fluid flow.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the advent of electronic control systems marked a significant leap in solenoid valve technology. This integration allowed for more precise control over fluid flow, laying the groundwork for modern calibration techniques. The subsequent decades saw rapid advancements in materials science, miniaturization, and digital control systems, further enhancing the capabilities of solenoid valves.
The primary objective of solenoid valve technology in flow calibration has been to achieve greater accuracy, reliability, and repeatability in fluid control processes. This goal has driven continuous innovation in valve design, materials, and control mechanisms. Modern solenoid valves incorporate advanced features such as proportional control, fast response times, and self-diagnostic capabilities, all of which contribute to improved flow calibration.
One of the key technological trends in recent years has been the development of "smart" solenoid valves. These valves integrate sensors and microprocessors, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustment of flow parameters. This advancement has significantly enhanced the precision of flow calibration, allowing for dynamic responses to changing process conditions.
Another important objective in the evolution of solenoid valve technology has been the reduction of energy consumption and environmental impact. This has led to the development of low-power solenoid valves and the use of more environmentally friendly materials in valve construction.
The integration of solenoid valves with Industry 4.0 technologies represents the latest frontier in their evolution. Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity and artificial intelligence are being leveraged to create predictive maintenance systems and optimize valve performance in complex industrial processes. These advancements are crucial for maintaining and improving calibration standards in increasingly automated industrial environments.
Looking ahead, the objectives for solenoid valve technology in flow calibration are focused on achieving even greater precision, expanding the range of operating conditions, and further integrating with digital control systems. Research is ongoing into novel actuation methods, such as piezoelectric systems, which promise even faster response times and finer control over fluid flow.
Industrial Demand for Precise Flow Calibration
The industrial sector's demand for precise flow calibration has been steadily increasing due to the growing complexity of manufacturing processes and the need for higher quality control standards. Accurate flow measurement and control are critical in various industries, including chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage production, and oil and gas refining. These industries require precise flow calibration to ensure product quality, maintain safety standards, and optimize production efficiency.
In chemical processing, for instance, the exact measurement of reactants and catalysts is essential for producing consistent, high-quality products. Even minor deviations in flow rates can lead to significant variations in product composition, potentially resulting in off-spec batches and substantial financial losses. Similarly, in the pharmaceutical industry, precise flow calibration is crucial for maintaining the correct ratios of active ingredients and excipients in drug formulations, directly impacting patient safety and regulatory compliance.
The food and beverage industry also heavily relies on accurate flow calibration for maintaining product consistency and meeting stringent quality standards. Whether it's controlling the flow of ingredients in a beverage production line or managing the precise dispensing of flavorings and additives, flow accuracy directly affects taste, texture, and overall product quality. In the oil and gas sector, precise flow measurement is vital for custody transfer operations, where even small inaccuracies can translate to significant financial implications.
Environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives have further intensified the need for precise flow calibration. Industries are under increasing pressure to minimize waste, reduce emissions, and optimize resource utilization. Accurate flow measurement plays a crucial role in achieving these objectives by enabling better process control and resource management.
The demand for precise flow calibration has also been driven by the advent of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT). As industrial processes become more interconnected and data-driven, the accuracy of flow measurements becomes even more critical. Real-time flow data is often integrated into broader process control systems, making precision essential for effective decision-making and process optimization.
Moreover, the trend towards miniaturization in many industries has created a need for accurate measurement and control of increasingly smaller flow rates. This has pushed the boundaries of flow calibration technology, driving innovations in sensor design and calibration methods to achieve higher levels of precision at lower flow rates.
As industries continue to evolve and face new challenges, the demand for precise flow calibration is expected to grow further. This trend is likely to drive ongoing innovations in flow measurement technologies, calibration methods, and the integration of advanced control systems to meet the ever-increasing standards of accuracy and reliability in industrial processes.
In chemical processing, for instance, the exact measurement of reactants and catalysts is essential for producing consistent, high-quality products. Even minor deviations in flow rates can lead to significant variations in product composition, potentially resulting in off-spec batches and substantial financial losses. Similarly, in the pharmaceutical industry, precise flow calibration is crucial for maintaining the correct ratios of active ingredients and excipients in drug formulations, directly impacting patient safety and regulatory compliance.
The food and beverage industry also heavily relies on accurate flow calibration for maintaining product consistency and meeting stringent quality standards. Whether it's controlling the flow of ingredients in a beverage production line or managing the precise dispensing of flavorings and additives, flow accuracy directly affects taste, texture, and overall product quality. In the oil and gas sector, precise flow measurement is vital for custody transfer operations, where even small inaccuracies can translate to significant financial implications.
Environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives have further intensified the need for precise flow calibration. Industries are under increasing pressure to minimize waste, reduce emissions, and optimize resource utilization. Accurate flow measurement plays a crucial role in achieving these objectives by enabling better process control and resource management.
The demand for precise flow calibration has also been driven by the advent of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT). As industrial processes become more interconnected and data-driven, the accuracy of flow measurements becomes even more critical. Real-time flow data is often integrated into broader process control systems, making precision essential for effective decision-making and process optimization.
Moreover, the trend towards miniaturization in many industries has created a need for accurate measurement and control of increasingly smaller flow rates. This has pushed the boundaries of flow calibration technology, driving innovations in sensor design and calibration methods to achieve higher levels of precision at lower flow rates.
As industries continue to evolve and face new challenges, the demand for precise flow calibration is expected to grow further. This trend is likely to drive ongoing innovations in flow measurement technologies, calibration methods, and the integration of advanced control systems to meet the ever-increasing standards of accuracy and reliability in industrial processes.
Current Challenges in Flow Calibration Systems
Flow calibration systems in industrial settings face several significant challenges that impact their accuracy, reliability, and efficiency. One of the primary issues is the inherent variability in fluid dynamics, which can lead to inconsistencies in flow measurements. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, pressure changes, and fluid viscosity variations can all contribute to measurement errors, making it difficult to maintain precise calibration standards across different operating conditions.
Another major challenge is the presence of turbulence and non-uniform flow patterns within pipelines and calibration equipment. These disturbances can create localized pressure differentials and velocity variations, leading to inaccurate readings and reduced repeatability in calibration processes. The complexity of fluid behavior in real-world industrial applications often exceeds the capabilities of traditional calibration methods, necessitating more sophisticated approaches to flow measurement and control.
The issue of scale is also a significant concern in flow calibration systems. Industrial processes often involve a wide range of flow rates, from very low to extremely high volumes. Calibrating instruments accurately across this entire spectrum presents technical difficulties, as different measurement principles and technologies may be required for various flow regimes. This challenge is further compounded by the need for calibration equipment that can handle diverse fluid types, including gases, liquids, and multiphase flows.
Contamination and wear of calibration equipment pose additional challenges to maintaining accurate flow measurements. Particulates, chemical reactions, and erosion can alter the internal geometry of flow meters and valves over time, leading to drift in calibration accuracy. This necessitates regular maintenance and recalibration, which can be time-consuming and costly for industrial operations.
The integration of calibration systems with existing industrial infrastructure presents its own set of challenges. Legacy systems may not be compatible with modern calibration technologies, requiring significant upgrades or custom solutions. Additionally, the need for real-time monitoring and adjustment of flow rates in dynamic industrial processes puts strain on calibration systems to provide rapid, accurate responses to changing conditions.
Lastly, the increasing demand for higher precision in industrial processes is pushing the limits of current calibration technologies. As manufacturing tolerances tighten and quality control standards become more stringent, there is a growing need for flow calibration systems that can deliver unprecedented levels of accuracy and repeatability. This challenge is driving research into advanced sensor technologies, improved data analysis techniques, and more sophisticated control algorithms to enhance the performance of flow calibration systems.
Another major challenge is the presence of turbulence and non-uniform flow patterns within pipelines and calibration equipment. These disturbances can create localized pressure differentials and velocity variations, leading to inaccurate readings and reduced repeatability in calibration processes. The complexity of fluid behavior in real-world industrial applications often exceeds the capabilities of traditional calibration methods, necessitating more sophisticated approaches to flow measurement and control.
The issue of scale is also a significant concern in flow calibration systems. Industrial processes often involve a wide range of flow rates, from very low to extremely high volumes. Calibrating instruments accurately across this entire spectrum presents technical difficulties, as different measurement principles and technologies may be required for various flow regimes. This challenge is further compounded by the need for calibration equipment that can handle diverse fluid types, including gases, liquids, and multiphase flows.
Contamination and wear of calibration equipment pose additional challenges to maintaining accurate flow measurements. Particulates, chemical reactions, and erosion can alter the internal geometry of flow meters and valves over time, leading to drift in calibration accuracy. This necessitates regular maintenance and recalibration, which can be time-consuming and costly for industrial operations.
The integration of calibration systems with existing industrial infrastructure presents its own set of challenges. Legacy systems may not be compatible with modern calibration technologies, requiring significant upgrades or custom solutions. Additionally, the need for real-time monitoring and adjustment of flow rates in dynamic industrial processes puts strain on calibration systems to provide rapid, accurate responses to changing conditions.
Lastly, the increasing demand for higher precision in industrial processes is pushing the limits of current calibration technologies. As manufacturing tolerances tighten and quality control standards become more stringent, there is a growing need for flow calibration systems that can deliver unprecedented levels of accuracy and repeatability. This challenge is driving research into advanced sensor technologies, improved data analysis techniques, and more sophisticated control algorithms to enhance the performance of flow calibration systems.
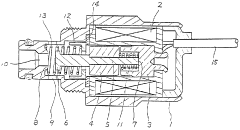
Existing Solenoid Valve Solutions for Flow Calibration
01 Flow measurement and calibration techniques
Various methods and devices are used for measuring and calibrating flow in solenoid valves. These include using flow meters, pressure sensors, and specialized calibration equipment to accurately determine and adjust the flow rate through the valve. Calibration processes may involve comparing measured flow rates to predetermined standards or using software-assisted calibration procedures.- Flow measurement and calibration techniques: Various methods and devices are used for measuring and calibrating flow in solenoid valves. These include using flow sensors, pressure sensors, and specialized calibration equipment to accurately determine and adjust the flow rate through the valve. Calibration procedures may involve comparing measured flow rates to reference standards and making necessary adjustments to ensure precise control.
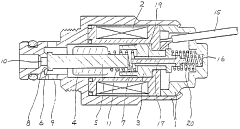
- Electronic control systems for solenoid valves: Advanced electronic control systems are implemented to improve the accuracy and responsiveness of solenoid valve operation. These systems may include microprocessors, digital signal processors, and feedback loops that continuously monitor and adjust valve performance. Such control systems can compensate for variations in temperature, pressure, and other environmental factors to maintain consistent flow rates.
- Mechanical design improvements for flow control: Innovations in the mechanical design of solenoid valves contribute to better flow control and calibration. These may include optimized valve seat geometries, improved sealing mechanisms, and novel actuator designs. Such improvements can enhance the valve's ability to maintain consistent flow rates across a wide range of operating conditions and reduce the need for frequent recalibration.
- Integration of solenoid valves in fluid systems: Solenoid valves are integrated into complex fluid systems, requiring careful calibration to ensure proper system performance. This integration may involve incorporating the valves into fuel injection systems, hydraulic circuits, or pneumatic control systems. Calibration techniques are developed to account for the interactions between the valve and other system components, ensuring optimal overall performance.
- Automated calibration and self-diagnostic systems: Advanced solenoid valve systems incorporate automated calibration and self-diagnostic features. These systems can perform regular self-checks, detect deviations from expected performance, and automatically adjust valve parameters to maintain accurate flow control. Such features reduce the need for manual intervention and improve the long-term reliability and precision of the valve operation.
02 Electronic control systems for solenoid valve calibration
Advanced electronic control systems are employed to automate and improve the accuracy of solenoid valve flow calibration. These systems may include microprocessors, digital signal processors, and specialized software algorithms to analyze flow data, adjust valve parameters, and maintain precise flow control. Some systems incorporate machine learning or adaptive control techniques for continuous calibration and optimization.Expand Specific Solutions03 Mechanical design improvements for flow calibration
Innovations in the mechanical design of solenoid valves contribute to improved flow calibration capabilities. These may include adjustable valve seats, precision-machined components, and novel sealing mechanisms that allow for fine-tuning of flow characteristics. Some designs incorporate built-in calibration ports or features that facilitate easier and more accurate flow adjustment.Expand Specific Solutions04 Temperature compensation in flow calibration
Temperature effects on solenoid valve performance are addressed through various compensation techniques during flow calibration. This may involve using temperature sensors, implementing temperature-dependent calibration curves, or employing materials with specific thermal properties to maintain consistent flow characteristics across a range of operating temperatures.Expand Specific Solutions05 In-situ and real-time calibration methods
Techniques for calibrating solenoid valve flow without removing the valve from the system are developed. These in-situ methods may use integrated sensors, bypass flow paths, or external calibration devices to perform real-time flow measurements and adjustments. Some approaches allow for continuous calibration during normal operation, ensuring optimal performance over time.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Solenoid Valve Manufacturing
The solenoid valve market for flow calibration in industrial standards is in a mature growth phase, with a significant market size driven by increasing automation across industries. The technology has reached a high level of maturity, with established players like Robert Bosch GmbH, Eaton Corp., and Mitsubishi Electric Corp. leading innovation. These companies leverage their extensive experience in industrial automation to offer advanced solenoid valve solutions. Emerging players such as MKS, Inc. and Eagle Industry Co. Ltd. are also contributing to market competitiveness by focusing on niche applications and technological advancements, further driving the industry's evolution and expanding its applications in precision flow control.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has developed advanced solenoid valve technology for precise flow calibration in industrial applications. Their system utilizes electromagnetic actuation combined with high-precision sensors to achieve accurate and repeatable flow control. The valves incorporate a microprocessor-controlled driver that adjusts the magnetic field strength in real-time, allowing for dynamic flow regulation[1]. This technology enables flow rates to be calibrated within ±0.5% accuracy across a wide operating range[2]. Bosch's solenoid valves also feature self-diagnostic capabilities and can compensate for wear and environmental factors to maintain long-term calibration stability[3].
Strengths: High precision, wide operating range, self-diagnostic capabilities. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost, may require specialized maintenance.
Eaton Corp.
Technical Solution: Eaton has innovated in solenoid valve technology for flow calibration with their AxisPro™ proportional valves. These valves utilize closed-loop control and advanced spool designs to provide precise flow regulation. The system incorporates onboard electronics and embedded sensors for real-time flow monitoring and adjustment[4]. Eaton's valves can achieve flow linearity within ±3% of the command signal, enabling accurate calibration for various industrial processes[5]. The AxisPro™ series also features adaptive control algorithms that can compensate for changes in fluid viscosity and temperature, ensuring consistent performance across different operating conditions[6].
Strengths: Adaptive control, onboard electronics for precise regulation. Weaknesses: May have higher initial cost, potential complexity in setup and integration.
Innovative Solenoid Valve Designs for Calibration
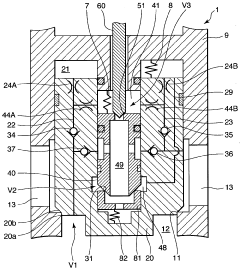
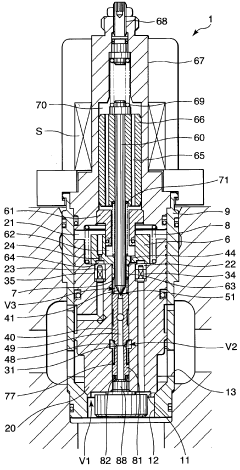
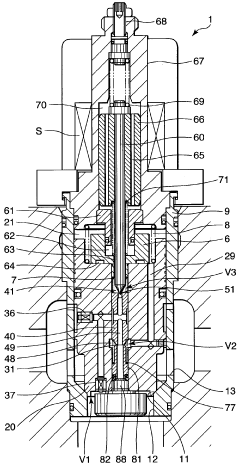
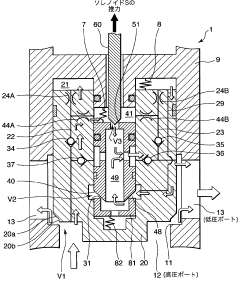
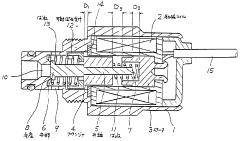
Solenoid-driven flow rate control valve
PatentWO2010067853A1
Innovation
- The solenoid-driven flow control valve design incorporates a main valve, auxiliary valve, and pilot valve configuration, with specific orifice and chamber connections, and a solenoid-driven pilot pin, allowing for controlled fluid flow between ports by adjusting the lift of the pilot pin to manage flow rates effectively.
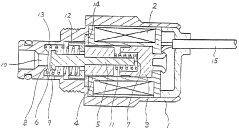
Solenoid valve for flow rate regulating
PatentInactiveJP1988076971A
Innovation
- The design incorporates multiple springs with initial loads set to zero, allowing for gentle axial movement of the valve shaft, where the electromagnetic force controls the valve opening and closing, ensuring consistent flow rates by adjusting the spring loads in response to current changes, thereby maintaining stable fluid flow characteristics.
Regulatory Standards for Industrial Flow Calibration
Regulatory standards for industrial flow calibration play a crucial role in ensuring accuracy, consistency, and reliability across various industries. These standards are established and maintained by national and international organizations to provide a framework for precise measurement and control of fluid flow in industrial processes.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several key standards related to flow measurement and calibration. ISO 5167 is a comprehensive standard that covers the measurement of fluid flow by means of pressure differential devices inserted in circular cross-section conduits running full. This standard provides guidelines for the design, installation, and use of orifice plates, nozzles, and Venturi tubes.
In the United States, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides traceability for flow measurements and calibrations. NIST maintains primary flow standards and offers calibration services to ensure that secondary standards used in industry are accurate and reliable. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) has also developed standards for flow measurement, such as the ASME MFC series, which covers various flow measurement techniques and devices.
The European Union has implemented the Measuring Instruments Directive (MID) to harmonize regulations for measuring instruments across member states. This directive includes specific requirements for flow meters used in various applications, ensuring consistency and accuracy in measurements throughout the EU.
For the oil and gas industry, the American Petroleum Institute (API) has established standards such as API MPMS Chapter 4, which focuses on proving systems for liquid hydrocarbons. These standards are critical for ensuring accurate measurement and calibration of flow in petroleum production and distribution.
In the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors, regulatory bodies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe have stringent requirements for flow calibration. These regulations are part of broader Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, ensuring the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products.
The increasing adoption of digital technologies in industrial processes has led to the development of standards for smart flow meters and calibration systems. The NAMUR (User Association of Automation Technology in Process Industries) recommendations, particularly NE 107, provide guidelines for self-monitoring and diagnosis of field devices, including flow meters.
Compliance with these regulatory standards is essential for industries to maintain quality control, ensure product safety, and meet legal requirements. Regular calibration and verification of flow measurement devices, in accordance with these standards, help minimize measurement uncertainties and improve overall process efficiency.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed several key standards related to flow measurement and calibration. ISO 5167 is a comprehensive standard that covers the measurement of fluid flow by means of pressure differential devices inserted in circular cross-section conduits running full. This standard provides guidelines for the design, installation, and use of orifice plates, nozzles, and Venturi tubes.
In the United States, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides traceability for flow measurements and calibrations. NIST maintains primary flow standards and offers calibration services to ensure that secondary standards used in industry are accurate and reliable. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) has also developed standards for flow measurement, such as the ASME MFC series, which covers various flow measurement techniques and devices.
The European Union has implemented the Measuring Instruments Directive (MID) to harmonize regulations for measuring instruments across member states. This directive includes specific requirements for flow meters used in various applications, ensuring consistency and accuracy in measurements throughout the EU.
For the oil and gas industry, the American Petroleum Institute (API) has established standards such as API MPMS Chapter 4, which focuses on proving systems for liquid hydrocarbons. These standards are critical for ensuring accurate measurement and calibration of flow in petroleum production and distribution.
In the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors, regulatory bodies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe have stringent requirements for flow calibration. These regulations are part of broader Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, ensuring the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products.
The increasing adoption of digital technologies in industrial processes has led to the development of standards for smart flow meters and calibration systems. The NAMUR (User Association of Automation Technology in Process Industries) recommendations, particularly NE 107, provide guidelines for self-monitoring and diagnosis of field devices, including flow meters.
Compliance with these regulatory standards is essential for industries to maintain quality control, ensure product safety, and meet legal requirements. Regular calibration and verification of flow measurement devices, in accordance with these standards, help minimize measurement uncertainties and improve overall process efficiency.
Economic Impact of Improved Flow Calibration
The economic impact of improved flow calibration through the use of solenoid valves in industrial standards is significant and far-reaching. This technological advancement has the potential to transform various sectors of the economy, leading to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced product quality.
In manufacturing industries, precise flow calibration enabled by solenoid valves can result in substantial cost savings. By ensuring accurate material dispensing and reducing waste, companies can optimize their production processes and minimize raw material expenses. This improved efficiency translates directly to increased profit margins and competitiveness in the global market.
The energy sector stands to benefit greatly from enhanced flow calibration. Power plants and refineries rely heavily on precise fluid control for optimal performance. With solenoid valves improving flow calibration, these facilities can achieve higher energy efficiency, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. This not only contributes to the bottom line of energy companies but also supports broader economic goals of sustainability and reduced carbon emissions.
In the pharmaceutical and chemical industries, accurate flow calibration is crucial for maintaining product quality and safety. Solenoid valves enable more precise control of ingredient mixing and dosing, leading to higher consistency in production. This improvement can significantly reduce the risk of product recalls and associated financial losses, while also enhancing consumer trust and brand reputation.
The agriculture sector can also experience economic benefits from improved flow calibration. Precision irrigation systems utilizing solenoid valves can optimize water usage, leading to increased crop yields and reduced water waste. This efficiency gain not only improves farm profitability but also contributes to sustainable resource management, which has long-term economic implications for regions facing water scarcity.
From a macroeconomic perspective, the widespread adoption of improved flow calibration technologies can drive innovation and create new job opportunities in valve manufacturing, system integration, and related technical services. This technological advancement may also spur the development of new industries and applications, further contributing to economic growth and diversification.
Moreover, the enhanced accuracy and reliability offered by solenoid valves in flow calibration can lead to improved compliance with regulatory standards across various industries. This reduction in compliance-related risks and potential fines represents a significant economic benefit for businesses operating in highly regulated environments.
In conclusion, the economic impact of improved flow calibration through solenoid valves extends beyond immediate cost savings, encompassing broader effects on industry competitiveness, resource efficiency, and innovation-driven growth. As this technology continues to evolve and find new applications, its positive influence on the global economy is likely to expand further.
In manufacturing industries, precise flow calibration enabled by solenoid valves can result in substantial cost savings. By ensuring accurate material dispensing and reducing waste, companies can optimize their production processes and minimize raw material expenses. This improved efficiency translates directly to increased profit margins and competitiveness in the global market.
The energy sector stands to benefit greatly from enhanced flow calibration. Power plants and refineries rely heavily on precise fluid control for optimal performance. With solenoid valves improving flow calibration, these facilities can achieve higher energy efficiency, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. This not only contributes to the bottom line of energy companies but also supports broader economic goals of sustainability and reduced carbon emissions.
In the pharmaceutical and chemical industries, accurate flow calibration is crucial for maintaining product quality and safety. Solenoid valves enable more precise control of ingredient mixing and dosing, leading to higher consistency in production. This improvement can significantly reduce the risk of product recalls and associated financial losses, while also enhancing consumer trust and brand reputation.
The agriculture sector can also experience economic benefits from improved flow calibration. Precision irrigation systems utilizing solenoid valves can optimize water usage, leading to increased crop yields and reduced water waste. This efficiency gain not only improves farm profitability but also contributes to sustainable resource management, which has long-term economic implications for regions facing water scarcity.
From a macroeconomic perspective, the widespread adoption of improved flow calibration technologies can drive innovation and create new job opportunities in valve manufacturing, system integration, and related technical services. This technological advancement may also spur the development of new industries and applications, further contributing to economic growth and diversification.
Moreover, the enhanced accuracy and reliability offered by solenoid valves in flow calibration can lead to improved compliance with regulatory standards across various industries. This reduction in compliance-related risks and potential fines represents a significant economic benefit for businesses operating in highly regulated environments.
In conclusion, the economic impact of improved flow calibration through solenoid valves extends beyond immediate cost savings, encompassing broader effects on industry competitiveness, resource efficiency, and innovation-driven growth. As this technology continues to evolve and find new applications, its positive influence on the global economy is likely to expand further.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!