How to Enhance LDAC Audio Compression Algorithms?
JUL 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDAC Evolution and Objectives
LDAC, developed by Sony in 2015, represents a significant milestone in high-quality audio compression technology. This codec aims to deliver near-lossless audio transmission over Bluetooth connections, addressing the growing demand for superior audio quality in wireless devices. LDAC's evolution has been driven by the increasing consumer expectations for high-fidelity audio experiences in portable and wireless audio systems.
The primary objective of LDAC is to maximize audio quality while maintaining efficient data transmission over Bluetooth. It achieves this by employing adaptive bit rate technology, allowing for transmission rates of up to 990 kbps, which is significantly higher than standard Bluetooth codecs. This capability enables LDAC to support high-resolution audio formats, preserving more audio information compared to conventional compression methods.
Throughout its development, LDAC has undergone several iterations to improve its performance and compatibility. Initially exclusive to Sony devices, it has since been integrated into the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) in 2017, broadening its accessibility across various Android devices. This expansion has been crucial in establishing LDAC as a widely recognized standard for high-quality Bluetooth audio transmission.
The evolution of LDAC has been closely tied to advancements in Bluetooth technology, particularly the introduction of Bluetooth 5.0 and subsequent versions. These improvements in Bluetooth standards have allowed for increased data transfer rates and more stable connections, directly benefiting LDAC's performance and reliability.
Looking forward, the objectives for enhancing LDAC audio compression algorithms are multifaceted. One key goal is to further reduce latency while maintaining high audio quality, which is crucial for applications such as gaming and virtual reality. Another objective is to improve energy efficiency, addressing the power consumption concerns in portable devices.
Additionally, there is a push to enhance LDAC's adaptability to varying network conditions, ensuring consistent high-quality audio even in challenging wireless environments. This includes developing more sophisticated algorithms for dynamic bit rate adjustment and error concealment.
As the audio industry continues to evolve, LDAC aims to support emerging audio formats and technologies, such as 3D audio and object-based audio. This requires ongoing research and development to expand LDAC's capabilities while maintaining backward compatibility with existing devices and systems.
The primary objective of LDAC is to maximize audio quality while maintaining efficient data transmission over Bluetooth. It achieves this by employing adaptive bit rate technology, allowing for transmission rates of up to 990 kbps, which is significantly higher than standard Bluetooth codecs. This capability enables LDAC to support high-resolution audio formats, preserving more audio information compared to conventional compression methods.
Throughout its development, LDAC has undergone several iterations to improve its performance and compatibility. Initially exclusive to Sony devices, it has since been integrated into the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) in 2017, broadening its accessibility across various Android devices. This expansion has been crucial in establishing LDAC as a widely recognized standard for high-quality Bluetooth audio transmission.
The evolution of LDAC has been closely tied to advancements in Bluetooth technology, particularly the introduction of Bluetooth 5.0 and subsequent versions. These improvements in Bluetooth standards have allowed for increased data transfer rates and more stable connections, directly benefiting LDAC's performance and reliability.
Looking forward, the objectives for enhancing LDAC audio compression algorithms are multifaceted. One key goal is to further reduce latency while maintaining high audio quality, which is crucial for applications such as gaming and virtual reality. Another objective is to improve energy efficiency, addressing the power consumption concerns in portable devices.
Additionally, there is a push to enhance LDAC's adaptability to varying network conditions, ensuring consistent high-quality audio even in challenging wireless environments. This includes developing more sophisticated algorithms for dynamic bit rate adjustment and error concealment.
As the audio industry continues to evolve, LDAC aims to support emerging audio formats and technologies, such as 3D audio and object-based audio. This requires ongoing research and development to expand LDAC's capabilities while maintaining backward compatibility with existing devices and systems.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for enhanced LDAC audio compression algorithms is driven by the growing consumer appetite for high-quality wireless audio experiences. As more users adopt wireless headphones, earbuds, and speakers, there's an increasing expectation for audio quality that matches or surpasses traditional wired solutions. LDAC, developed by Sony, has positioned itself as a premium codec for high-resolution audio transmission over Bluetooth, but there's still room for improvement to meet evolving market needs.
The global wireless audio market is experiencing robust growth, with a particular emphasis on high-fidelity solutions. This trend is fueled by the proliferation of streaming services offering lossless audio tiers and the rising popularity of high-resolution audio formats. Consumers are becoming more discerning about audio quality, creating a demand for advanced compression algorithms that can deliver near-lossless audio over bandwidth-constrained Bluetooth connections.
In the professional audio sector, there's a growing need for improved wireless audio solutions in live performance, studio recording, and broadcast applications. These industries require ultra-low latency, high bit-rate, and stable connections, presenting an opportunity for enhanced LDAC algorithms to penetrate new market segments beyond consumer electronics.
The automotive industry is another significant market driver for advanced audio compression technologies. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, the in-car audio experience is gaining importance. Enhanced LDAC algorithms could play a crucial role in delivering premium audio experiences in next-generation vehicles, especially as wireless connectivity becomes more prevalent in automotive infotainment systems.
The gaming industry also presents a substantial market opportunity for improved audio compression. With the rise of mobile and cloud gaming, there's an increasing demand for high-quality, low-latency audio that can enhance immersive gaming experiences. Enhanced LDAC algorithms could address this need, potentially opening up new partnerships with gaming hardware manufacturers and streaming platforms.
As smart home ecosystems continue to expand, there's a growing market for high-quality wireless audio solutions that can seamlessly integrate with various devices and platforms. Improved LDAC algorithms could facilitate better audio experiences across a range of smart home applications, from multi-room audio systems to voice-controlled assistants.
The healthcare and accessibility sectors also present unique market opportunities for enhanced audio compression technologies. Improved algorithms could benefit hearing aid technologies, telemedicine applications, and assistive devices, where clear and accurate audio transmission is critical.
The global wireless audio market is experiencing robust growth, with a particular emphasis on high-fidelity solutions. This trend is fueled by the proliferation of streaming services offering lossless audio tiers and the rising popularity of high-resolution audio formats. Consumers are becoming more discerning about audio quality, creating a demand for advanced compression algorithms that can deliver near-lossless audio over bandwidth-constrained Bluetooth connections.
In the professional audio sector, there's a growing need for improved wireless audio solutions in live performance, studio recording, and broadcast applications. These industries require ultra-low latency, high bit-rate, and stable connections, presenting an opportunity for enhanced LDAC algorithms to penetrate new market segments beyond consumer electronics.
The automotive industry is another significant market driver for advanced audio compression technologies. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, the in-car audio experience is gaining importance. Enhanced LDAC algorithms could play a crucial role in delivering premium audio experiences in next-generation vehicles, especially as wireless connectivity becomes more prevalent in automotive infotainment systems.
The gaming industry also presents a substantial market opportunity for improved audio compression. With the rise of mobile and cloud gaming, there's an increasing demand for high-quality, low-latency audio that can enhance immersive gaming experiences. Enhanced LDAC algorithms could address this need, potentially opening up new partnerships with gaming hardware manufacturers and streaming platforms.
As smart home ecosystems continue to expand, there's a growing market for high-quality wireless audio solutions that can seamlessly integrate with various devices and platforms. Improved LDAC algorithms could facilitate better audio experiences across a range of smart home applications, from multi-room audio systems to voice-controlled assistants.
The healthcare and accessibility sectors also present unique market opportunities for enhanced audio compression technologies. Improved algorithms could benefit hearing aid technologies, telemedicine applications, and assistive devices, where clear and accurate audio transmission is critical.
Technical Challenges
LDAC, developed by Sony, is a high-resolution audio codec that has gained significant traction in the wireless audio market. However, as with any technology, it faces several technical challenges that need to be addressed to enhance its performance and maintain its competitive edge.
One of the primary challenges in enhancing LDAC audio compression algorithms is the trade-off between audio quality and bitrate efficiency. While LDAC already offers impressive audio quality at high bitrates, there is a constant demand for improved efficiency, especially in bandwidth-constrained environments. Achieving higher compression ratios without compromising audio fidelity remains a significant hurdle.
Another challenge lies in the computational complexity of the LDAC algorithm. As the codec aims to deliver high-quality audio in real-time, it requires substantial processing power. This can lead to increased power consumption in portable devices, potentially impacting battery life. Optimizing the algorithm for lower computational complexity while maintaining audio quality is a critical area for improvement.
Latency is another crucial factor that needs attention. While LDAC performs well in terms of audio quality, its latency can be a concern in certain applications, particularly in gaming or live performances where minimal delay is crucial. Reducing encoding and decoding times without sacrificing audio quality presents a significant technical challenge.
The variability in wireless transmission conditions poses another hurdle. LDAC needs to adapt to changing network conditions to maintain consistent audio quality. Developing robust error correction and concealment techniques that can handle packet loss and interference in various wireless environments is an ongoing challenge.
Compatibility and interoperability with a wide range of devices and platforms is another area that requires continuous improvement. As the audio ecosystem becomes more diverse, ensuring seamless integration and optimal performance across different hardware and software configurations becomes increasingly complex.
Furthermore, the challenge of supporting multi-channel audio formats while maintaining high compression efficiency is becoming more relevant as immersive audio experiences gain popularity. Adapting LDAC to efficiently handle spatial audio and object-based audio formats without significantly increasing bandwidth requirements is a complex task.
Lastly, as the audio industry moves towards more personalized experiences, incorporating adaptive audio processing techniques into LDAC presents both an opportunity and a challenge. Developing algorithms that can dynamically adjust to individual listening preferences or environmental conditions while maintaining the core benefits of LDAC is an area ripe for innovation.
One of the primary challenges in enhancing LDAC audio compression algorithms is the trade-off between audio quality and bitrate efficiency. While LDAC already offers impressive audio quality at high bitrates, there is a constant demand for improved efficiency, especially in bandwidth-constrained environments. Achieving higher compression ratios without compromising audio fidelity remains a significant hurdle.
Another challenge lies in the computational complexity of the LDAC algorithm. As the codec aims to deliver high-quality audio in real-time, it requires substantial processing power. This can lead to increased power consumption in portable devices, potentially impacting battery life. Optimizing the algorithm for lower computational complexity while maintaining audio quality is a critical area for improvement.
Latency is another crucial factor that needs attention. While LDAC performs well in terms of audio quality, its latency can be a concern in certain applications, particularly in gaming or live performances where minimal delay is crucial. Reducing encoding and decoding times without sacrificing audio quality presents a significant technical challenge.
The variability in wireless transmission conditions poses another hurdle. LDAC needs to adapt to changing network conditions to maintain consistent audio quality. Developing robust error correction and concealment techniques that can handle packet loss and interference in various wireless environments is an ongoing challenge.
Compatibility and interoperability with a wide range of devices and platforms is another area that requires continuous improvement. As the audio ecosystem becomes more diverse, ensuring seamless integration and optimal performance across different hardware and software configurations becomes increasingly complex.
Furthermore, the challenge of supporting multi-channel audio formats while maintaining high compression efficiency is becoming more relevant as immersive audio experiences gain popularity. Adapting LDAC to efficiently handle spatial audio and object-based audio formats without significantly increasing bandwidth requirements is a complex task.
Lastly, as the audio industry moves towards more personalized experiences, incorporating adaptive audio processing techniques into LDAC presents both an opportunity and a challenge. Developing algorithms that can dynamically adjust to individual listening preferences or environmental conditions while maintaining the core benefits of LDAC is an area ripe for innovation.
Current LDAC Solutions
01 Improved encoding efficiency for LDAC
Enhancements to LDAC audio compression algorithms focus on improving encoding efficiency. This involves optimizing the bit allocation process, refining quantization techniques, and implementing advanced psychoacoustic models to achieve higher quality audio at lower bitrates.- Improved encoding efficiency for LDAC: Enhancements to LDAC audio compression algorithms focus on improving encoding efficiency. This involves optimizing bit allocation, refining quantization techniques, and implementing advanced psychoacoustic models to achieve higher quality audio at lower bitrates. These improvements allow for better preservation of audio fidelity while maintaining the benefits of compressed audio transmission.
- Adaptive bitrate control for LDAC: LDAC compression algorithms are enhanced with adaptive bitrate control mechanisms. These systems dynamically adjust the compression parameters based on network conditions, device capabilities, and audio content complexity. This ensures optimal audio quality and stability across various transmission scenarios, improving the overall user experience in wireless audio applications.
- Multi-channel audio processing in LDAC: Advancements in LDAC algorithms focus on improving multi-channel audio processing. This includes enhanced spatial audio encoding, better channel separation, and more efficient representation of surround sound information. These improvements allow for more immersive audio experiences while maintaining the high compression efficiency that LDAC is known for.
- Error resilience and packet loss concealment: LDAC compression algorithms are enhanced with improved error resilience and packet loss concealment techniques. These advancements help maintain audio quality in challenging wireless environments by implementing robust error correction codes, intelligent packet interleaving, and advanced interpolation methods for lost audio frames.
- Integration with other audio codecs and standards: Enhancements to LDAC focus on improving interoperability and integration with other audio codecs and standards. This includes developing seamless transcoding mechanisms, supporting a wider range of audio formats, and ensuring compatibility with emerging audio technologies. These improvements allow for greater flexibility in audio ecosystem integration and broader adoption of LDAC technology.
02 Adaptive bitrate control for LDAC
LDAC compression algorithms are enhanced with adaptive bitrate control mechanisms. These systems dynamically adjust the compression parameters based on network conditions, device capabilities, and audio content complexity to maintain optimal audio quality and transmission stability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Multi-channel audio processing in LDAC
Improvements in LDAC algorithms for multi-channel audio processing include enhanced spatial coding techniques, efficient channel coupling methods, and optimized downmixing/upmixing processes to preserve spatial information while maintaining compression efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Error resilience and concealment in LDAC
LDAC compression algorithms are enhanced with improved error resilience and concealment techniques. These include robust frame structure designs, advanced error detection and correction methods, and intelligent packet loss concealment algorithms to maintain audio quality in challenging transmission environments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Low-latency LDAC compression
Enhancements to LDAC algorithms focus on reducing encoding and decoding latency while maintaining high audio quality. This involves optimizing the frame size, implementing efficient buffer management techniques, and developing streamlined processing pipelines for real-time applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The LDAC audio compression algorithm market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand for high-quality wireless audio solutions. The market size is expanding as more devices adopt LDAC technology, driven by the growing popularity of wireless headphones and speakers. Technologically, LDAC is relatively mature but still evolving, with companies like Sony, Samsung, and Huawei leading innovation. Microsoft, Fraunhofer, and STMicroelectronics are also contributing to advancements in audio compression. As consumer expectations for audio quality rise, competition among these players is intensifying, spurring further improvements in LDAC and related technologies.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei has developed its own high-resolution audio codec called HWA (Hi-Res Wireless Audio), which competes with LDAC. While not directly enhancing LDAC, Huawei's approach to audio compression offers insights into potential improvements. HWA utilizes advanced signal processing algorithms to achieve high bitrates up to 990 kbps[4]. The codec employs adaptive bit rate technology, dynamically adjusting compression levels based on wireless connection quality and device capabilities[5]. Huawei has also implemented sophisticated error correction mechanisms to maintain audio integrity in challenging wireless environments. These techniques could be applied to enhance LDAC's performance and reliability.
Strengths: High bitrate capabilities, adaptive compression, and robust error correction. Weaknesses: Limited ecosystem support compared to more established codecs like LDAC.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung, while not the creator of LDAC, has been actively supporting and implementing the codec in its devices. Their approach to enhancing audio compression algorithms focuses on optimizing the integration of LDAC with their hardware and software ecosystems. Samsung has developed advanced digital signal processing (DSP) techniques to improve the real-time encoding and decoding of LDAC streams on their mobile devices[10]. They have also implemented adaptive power management strategies to balance audio quality and battery life when using LDAC. Samsung's research into AI-enhanced audio processing, particularly in noise reduction and audio upscaling, could potentially be applied to further improve LDAC's performance[11]. Additionally, their work on seamless audio switching between devices in their ecosystem could inform enhancements to LDAC's connection stability and user experience.
Strengths: Wide device ecosystem for implementation, advanced DSP capabilities, and AI-enhanced audio processing. Weaknesses: Improvements may be limited to Samsung's ecosystem, potentially reducing broader impact on LDAC standard.
Core LDAC Innovations
Method for compression and expansion of digital audio data
PatentInactiveUS20060271374A1
Innovation
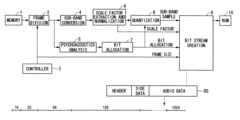
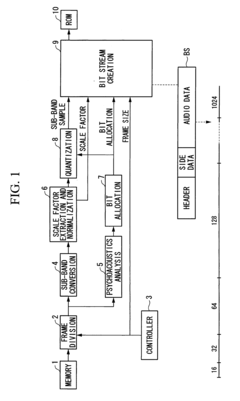
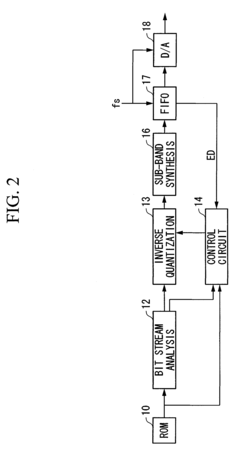
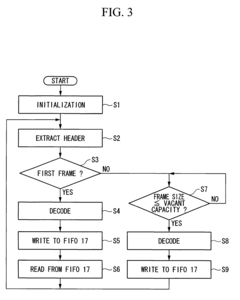
- The method involves dividing digital audio data into frames with gradually increasing sample sizes from 16 to 1024, applying psychoacoustic analysis and quantization, and decoding in units of frames with memory management to control decoding based on available capacity, allowing for efficient compression and expansion with minimal latency.
Method for compression and expansion of digital audio data
PatentInactiveUS7711555B2
Innovation
- The method involves dividing digital audio data into frames with gradually increasing sample sizes from 16 to 1024, applying psychoacoustic analysis and quantization, and decoding in units of frames with memory management to control decoding based on available capacity, allowing for efficient compression and expansion with minimal latency.
Codec Standardization
The standardization of audio codecs plays a crucial role in ensuring interoperability and widespread adoption of audio compression technologies. In the context of enhancing LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) audio compression algorithms, codec standardization efforts are essential for establishing a common framework and promoting industry-wide acceptance.
LDAC, developed by Sony, is a proprietary audio coding technology designed for high-quality wireless audio transmission. While it offers superior audio quality compared to many existing codecs, its proprietary nature limits its widespread adoption. To enhance LDAC and promote its broader use, standardization efforts are necessary.
One potential avenue for standardization is through organizations such as the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These bodies can facilitate the development of open standards that incorporate LDAC's advanced features while ensuring compatibility with existing audio systems.
Standardization efforts should focus on defining key parameters and performance metrics for high-quality audio compression. This includes specifying bit rates, frequency response, latency, and other critical factors that impact audio quality and transmission efficiency. By establishing these standards, manufacturers and developers can create compatible products that leverage LDAC's enhanced algorithms.
Furthermore, codec standardization should address the integration of LDAC with existing audio ecosystems. This involves defining protocols for device discovery, connection establishment, and seamless switching between different audio sources. Such standardization efforts can enhance the user experience and promote wider adoption of LDAC-based technologies.
Another important aspect of codec standardization is the development of reference implementations and testing methodologies. These tools enable manufacturers to validate their implementations and ensure compliance with the established standards. This process helps maintain consistency and quality across different devices and platforms.
Standardization efforts should also consider the evolving landscape of audio technologies, including emerging trends such as spatial audio and object-based audio. By incorporating provisions for these advanced features, the standardized codec can remain relevant and adaptable to future audio innovations.
Collaboration between industry stakeholders, including hardware manufacturers, software developers, and content providers, is crucial for successful codec standardization. This collaborative approach ensures that the standardized codec meets the diverse needs of the audio industry while promoting innovation and competition.
LDAC, developed by Sony, is a proprietary audio coding technology designed for high-quality wireless audio transmission. While it offers superior audio quality compared to many existing codecs, its proprietary nature limits its widespread adoption. To enhance LDAC and promote its broader use, standardization efforts are necessary.
One potential avenue for standardization is through organizations such as the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These bodies can facilitate the development of open standards that incorporate LDAC's advanced features while ensuring compatibility with existing audio systems.
Standardization efforts should focus on defining key parameters and performance metrics for high-quality audio compression. This includes specifying bit rates, frequency response, latency, and other critical factors that impact audio quality and transmission efficiency. By establishing these standards, manufacturers and developers can create compatible products that leverage LDAC's enhanced algorithms.
Furthermore, codec standardization should address the integration of LDAC with existing audio ecosystems. This involves defining protocols for device discovery, connection establishment, and seamless switching between different audio sources. Such standardization efforts can enhance the user experience and promote wider adoption of LDAC-based technologies.
Another important aspect of codec standardization is the development of reference implementations and testing methodologies. These tools enable manufacturers to validate their implementations and ensure compliance with the established standards. This process helps maintain consistency and quality across different devices and platforms.
Standardization efforts should also consider the evolving landscape of audio technologies, including emerging trends such as spatial audio and object-based audio. By incorporating provisions for these advanced features, the standardized codec can remain relevant and adaptable to future audio innovations.
Collaboration between industry stakeholders, including hardware manufacturers, software developers, and content providers, is crucial for successful codec standardization. This collaborative approach ensures that the standardized codec meets the diverse needs of the audio industry while promoting innovation and competition.
Power Efficiency Strategies
Power efficiency is a critical consideration in enhancing LDAC audio compression algorithms, particularly for mobile and battery-powered devices. The optimization of power consumption in LDAC encoding and decoding processes can significantly extend device battery life and improve overall user experience.
One key strategy for improving power efficiency in LDAC algorithms is the implementation of adaptive processing techniques. These techniques dynamically adjust the computational complexity of the algorithm based on the audio content and available system resources. For instance, during periods of low complexity audio, the algorithm can reduce its processing load, thereby conserving power.
Another approach involves the optimization of memory access patterns. LDAC algorithms typically require frequent memory operations, which can be power-intensive. By redesigning data structures and algorithms to minimize cache misses and improve data locality, the overall power consumption can be reduced. This may include techniques such as data prefetching and loop fusion to maximize the efficiency of memory accesses.
Hardware acceleration is another promising avenue for enhancing power efficiency. By offloading computationally intensive tasks to dedicated hardware units, such as digital signal processors (DSPs) or application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), the main processor can operate at lower clock speeds or enter low-power states more frequently. This can result in substantial power savings, especially for devices that process audio streams continuously.
The use of low-power modes and intelligent power management is also crucial. Implementing fine-grained power gating techniques allows unused portions of the processing pipeline to be powered down when not in use. Additionally, voltage and frequency scaling can be employed to match the processing requirements of the current audio stream, further optimizing power consumption.
Algorithmic optimizations specific to LDAC can also contribute to power efficiency. This may include refining the psychoacoustic model to reduce unnecessary processing of imperceptible audio components or improving the efficiency of the entropy coding stage. By reducing the overall computational complexity of the algorithm without compromising audio quality, significant power savings can be achieved.
Lastly, the integration of machine learning techniques can lead to more intelligent power management. By training models to predict optimal algorithm parameters based on audio characteristics and system state, the LDAC implementation can make more informed decisions about resource allocation and processing intensity, potentially leading to substantial improvements in power efficiency.
One key strategy for improving power efficiency in LDAC algorithms is the implementation of adaptive processing techniques. These techniques dynamically adjust the computational complexity of the algorithm based on the audio content and available system resources. For instance, during periods of low complexity audio, the algorithm can reduce its processing load, thereby conserving power.
Another approach involves the optimization of memory access patterns. LDAC algorithms typically require frequent memory operations, which can be power-intensive. By redesigning data structures and algorithms to minimize cache misses and improve data locality, the overall power consumption can be reduced. This may include techniques such as data prefetching and loop fusion to maximize the efficiency of memory accesses.
Hardware acceleration is another promising avenue for enhancing power efficiency. By offloading computationally intensive tasks to dedicated hardware units, such as digital signal processors (DSPs) or application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), the main processor can operate at lower clock speeds or enter low-power states more frequently. This can result in substantial power savings, especially for devices that process audio streams continuously.
The use of low-power modes and intelligent power management is also crucial. Implementing fine-grained power gating techniques allows unused portions of the processing pipeline to be powered down when not in use. Additionally, voltage and frequency scaling can be employed to match the processing requirements of the current audio stream, further optimizing power consumption.
Algorithmic optimizations specific to LDAC can also contribute to power efficiency. This may include refining the psychoacoustic model to reduce unnecessary processing of imperceptible audio components or improving the efficiency of the entropy coding stage. By reducing the overall computational complexity of the algorithm without compromising audio quality, significant power savings can be achieved.
Lastly, the integration of machine learning techniques can lead to more intelligent power management. By training models to predict optimal algorithm parameters based on audio characteristics and system state, the LDAC implementation can make more informed decisions about resource allocation and processing intensity, potentially leading to substantial improvements in power efficiency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!