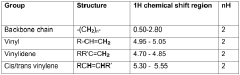
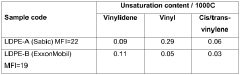
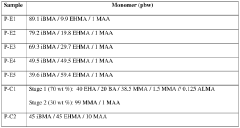
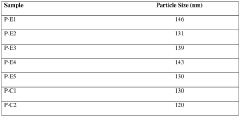
How to Improve LDPE Film Surface Properties?
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Film Evolution
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) film has undergone significant evolution since its introduction in the 1930s. Initially developed as a packaging material, LDPE film quickly gained popularity due to its flexibility, transparency, and moisture resistance. The early production methods focused on achieving consistent thickness and improving clarity, which were crucial for packaging applications.
In the 1950s and 1960s, advancements in extrusion technology led to more efficient production processes, allowing for thinner and wider films. This period also saw the introduction of blown film extrusion, which enabled the production of tubular films with enhanced mechanical properties. The improved strength and tear resistance expanded LDPE film applications beyond packaging into agricultural and construction sectors.
The 1970s marked a turning point in LDPE film evolution with the introduction of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE). While not a direct replacement, LLDPE complemented LDPE in many applications, offering improved tensile strength and puncture resistance. This development prompted research into blending LDPE with other polyethylenes to enhance overall film performance.
Surface modification techniques emerged in the 1980s as a key focus area. Corona treatment became widely adopted to improve the film's printability and adhesion properties. This period also saw increased attention to additives and masterbatches, which allowed manufacturers to tailor LDPE film properties for specific applications, such as UV resistance for agricultural films or anti-static properties for electronics packaging.
The 1990s and early 2000s witnessed a shift towards environmental considerations. Efforts to reduce film thickness without compromising strength became paramount, driven by both cost reduction and sustainability goals. This era also saw advancements in multilayer film technology, allowing for the combination of LDPE with other materials to create films with superior barrier properties.
Recent developments have focused on enhancing LDPE film's recyclability and biodegradability. Research into compatibilizers has improved the recycling process for mixed polyethylene waste streams. Additionally, the incorporation of bio-based additives and the development of oxo-degradable LDPE films have addressed growing environmental concerns.
Today, the evolution of LDPE film continues with a strong emphasis on surface properties. Advanced surface treatments, such as plasma modification and nanocoatings, are being explored to impart novel functionalities like antimicrobial properties or improved gas barrier characteristics. The ongoing research in this field aims to expand LDPE film applications in high-value sectors such as medical packaging and flexible electronics.
In the 1950s and 1960s, advancements in extrusion technology led to more efficient production processes, allowing for thinner and wider films. This period also saw the introduction of blown film extrusion, which enabled the production of tubular films with enhanced mechanical properties. The improved strength and tear resistance expanded LDPE film applications beyond packaging into agricultural and construction sectors.
The 1970s marked a turning point in LDPE film evolution with the introduction of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE). While not a direct replacement, LLDPE complemented LDPE in many applications, offering improved tensile strength and puncture resistance. This development prompted research into blending LDPE with other polyethylenes to enhance overall film performance.
Surface modification techniques emerged in the 1980s as a key focus area. Corona treatment became widely adopted to improve the film's printability and adhesion properties. This period also saw increased attention to additives and masterbatches, which allowed manufacturers to tailor LDPE film properties for specific applications, such as UV resistance for agricultural films or anti-static properties for electronics packaging.
The 1990s and early 2000s witnessed a shift towards environmental considerations. Efforts to reduce film thickness without compromising strength became paramount, driven by both cost reduction and sustainability goals. This era also saw advancements in multilayer film technology, allowing for the combination of LDPE with other materials to create films with superior barrier properties.
Recent developments have focused on enhancing LDPE film's recyclability and biodegradability. Research into compatibilizers has improved the recycling process for mixed polyethylene waste streams. Additionally, the incorporation of bio-based additives and the development of oxo-degradable LDPE films have addressed growing environmental concerns.
Today, the evolution of LDPE film continues with a strong emphasis on surface properties. Advanced surface treatments, such as plasma modification and nanocoatings, are being explored to impart novel functionalities like antimicrobial properties or improved gas barrier characteristics. The ongoing research in this field aims to expand LDPE film applications in high-value sectors such as medical packaging and flexible electronics.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for improved LDPE film surface properties has been steadily increasing across various industries. This growth is primarily driven by the expanding packaging sector, which relies heavily on LDPE films for their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and recyclability. The global LDPE film market is experiencing robust growth, with a particular emphasis on enhanced surface properties to meet evolving consumer and industry needs.
In the food packaging industry, there is a significant demand for LDPE films with improved barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and other gases. This demand stems from the need to extend shelf life and maintain food quality. Additionally, the pharmaceutical and medical sectors require LDPE films with enhanced surface properties to ensure better protection and sterility of medical devices and drug packaging.
The agriculture sector is another key driver of market demand for improved LDPE film surface properties. Greenhouse films and mulch films with enhanced UV resistance, anti-fog properties, and better light transmission are in high demand to improve crop yields and reduce environmental impact. These advanced surface properties contribute to more efficient farming practices and sustainable agriculture.
In the consumer goods sector, there is a growing trend towards premium packaging solutions. This has led to increased demand for LDPE films with improved printability, gloss, and tactile properties. Manufacturers are seeking films that can provide a high-quality appearance and feel, enhancing brand perception and product appeal on store shelves.
The automotive industry is also contributing to the market demand for LDPE films with improved surface properties. These films are used in various applications, including interior components and protective coverings. The industry requires films with enhanced scratch resistance, UV stability, and anti-static properties to meet stringent quality and safety standards.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives are shaping market demand as well. There is a growing interest in LDPE films with improved recyclability and biodegradability. This trend is driven by both consumer preferences and regulatory pressures, pushing manufacturers to develop films with surface properties that facilitate easier recycling or decomposition without compromising performance.
The e-commerce boom has further fueled the demand for LDPE films with enhanced surface properties. As online shopping continues to grow, there is an increased need for packaging materials that can withstand the rigors of shipping while maintaining product integrity. This has led to a demand for films with improved puncture resistance, tear strength, and sealability.
Overall, the market demand for improved LDPE film surface properties is diverse and expanding. Industries across the board are seeking films that can offer better protection, enhanced aesthetics, improved functionality, and increased sustainability. This trend is expected to continue as technological advancements and innovative solutions emerge to address these evolving market needs.
In the food packaging industry, there is a significant demand for LDPE films with improved barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and other gases. This demand stems from the need to extend shelf life and maintain food quality. Additionally, the pharmaceutical and medical sectors require LDPE films with enhanced surface properties to ensure better protection and sterility of medical devices and drug packaging.
The agriculture sector is another key driver of market demand for improved LDPE film surface properties. Greenhouse films and mulch films with enhanced UV resistance, anti-fog properties, and better light transmission are in high demand to improve crop yields and reduce environmental impact. These advanced surface properties contribute to more efficient farming practices and sustainable agriculture.
In the consumer goods sector, there is a growing trend towards premium packaging solutions. This has led to increased demand for LDPE films with improved printability, gloss, and tactile properties. Manufacturers are seeking films that can provide a high-quality appearance and feel, enhancing brand perception and product appeal on store shelves.
The automotive industry is also contributing to the market demand for LDPE films with improved surface properties. These films are used in various applications, including interior components and protective coverings. The industry requires films with enhanced scratch resistance, UV stability, and anti-static properties to meet stringent quality and safety standards.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives are shaping market demand as well. There is a growing interest in LDPE films with improved recyclability and biodegradability. This trend is driven by both consumer preferences and regulatory pressures, pushing manufacturers to develop films with surface properties that facilitate easier recycling or decomposition without compromising performance.
The e-commerce boom has further fueled the demand for LDPE films with enhanced surface properties. As online shopping continues to grow, there is an increased need for packaging materials that can withstand the rigors of shipping while maintaining product integrity. This has led to a demand for films with improved puncture resistance, tear strength, and sealability.
Overall, the market demand for improved LDPE film surface properties is diverse and expanding. Industries across the board are seeking films that can offer better protection, enhanced aesthetics, improved functionality, and increased sustainability. This trend is expected to continue as technological advancements and innovative solutions emerge to address these evolving market needs.
Surface Challenges
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) films are widely used in packaging and other applications due to their excellent flexibility, transparency, and moisture barrier properties. However, the surface properties of LDPE films often present significant challenges that can limit their performance and applicability in various industries.
One of the primary surface challenges faced by LDPE films is their inherently low surface energy. This characteristic results in poor wettability and adhesion, making it difficult to print, coat, or bond the films effectively. The low surface energy also contributes to issues with ink adhesion and the formation of stable coatings, which can lead to reduced product quality and increased production costs.
Another critical challenge is the tendency of LDPE films to develop static charges on their surface. This electrostatic buildup can attract dust and other contaminants, compromising the film's appearance and potentially interfering with downstream processing or end-use applications. The static charge can also pose safety hazards in certain manufacturing environments.
Surface roughness and uniformity present additional challenges for LDPE films. Inconsistencies in surface texture can lead to variations in optical properties, affecting the film's clarity and gloss. These irregularities can also impact the film's barrier properties and its ability to form consistent seals in packaging applications.
The migration of additives and low molecular weight components to the film surface over time is another significant issue. This phenomenon, known as blooming, can alter the surface properties of the film, potentially affecting its appearance, adhesion characteristics, and overall performance. Blooming can be particularly problematic in food packaging applications, where it may lead to undesirable interactions with the packaged contents.
LDPE films are also susceptible to surface degradation when exposed to environmental factors such as UV radiation, heat, and moisture. This degradation can manifest as yellowing, loss of mechanical properties, and changes in surface chemistry, all of which can significantly impact the film's longevity and functionality.
The hydrophobic nature of LDPE film surfaces poses challenges in applications requiring improved moisture management or enhanced printability. This characteristic limits the film's ability to absorb or retain water-based coatings and inks, necessitating specialized surface treatments or the use of solvent-based alternatives, which may have environmental implications.
Addressing these surface challenges is crucial for expanding the utility and performance of LDPE films across various industries. Improving surface properties can lead to enhanced printability, better adhesion characteristics, reduced static buildup, and improved barrier properties. These enhancements can open up new applications for LDPE films and improve their competitiveness against alternative materials.
One of the primary surface challenges faced by LDPE films is their inherently low surface energy. This characteristic results in poor wettability and adhesion, making it difficult to print, coat, or bond the films effectively. The low surface energy also contributes to issues with ink adhesion and the formation of stable coatings, which can lead to reduced product quality and increased production costs.
Another critical challenge is the tendency of LDPE films to develop static charges on their surface. This electrostatic buildup can attract dust and other contaminants, compromising the film's appearance and potentially interfering with downstream processing or end-use applications. The static charge can also pose safety hazards in certain manufacturing environments.
Surface roughness and uniformity present additional challenges for LDPE films. Inconsistencies in surface texture can lead to variations in optical properties, affecting the film's clarity and gloss. These irregularities can also impact the film's barrier properties and its ability to form consistent seals in packaging applications.
The migration of additives and low molecular weight components to the film surface over time is another significant issue. This phenomenon, known as blooming, can alter the surface properties of the film, potentially affecting its appearance, adhesion characteristics, and overall performance. Blooming can be particularly problematic in food packaging applications, where it may lead to undesirable interactions with the packaged contents.
LDPE films are also susceptible to surface degradation when exposed to environmental factors such as UV radiation, heat, and moisture. This degradation can manifest as yellowing, loss of mechanical properties, and changes in surface chemistry, all of which can significantly impact the film's longevity and functionality.
The hydrophobic nature of LDPE film surfaces poses challenges in applications requiring improved moisture management or enhanced printability. This characteristic limits the film's ability to absorb or retain water-based coatings and inks, necessitating specialized surface treatments or the use of solvent-based alternatives, which may have environmental implications.
Addressing these surface challenges is crucial for expanding the utility and performance of LDPE films across various industries. Improving surface properties can lead to enhanced printability, better adhesion characteristics, reduced static buildup, and improved barrier properties. These enhancements can open up new applications for LDPE films and improve their competitiveness against alternative materials.
Current Solutions
01 Surface modification techniques for LDPE films
Various surface modification techniques can be applied to LDPE films to enhance their properties. These methods include plasma treatment, corona discharge, and chemical treatments. Such modifications can improve adhesion, printability, and wettability of the film surface, making it suitable for a wider range of applications.- Surface modification techniques for LDPE films: Various surface modification techniques can be applied to LDPE films to enhance their properties. These methods include plasma treatment, corona discharge, and chemical treatments. Such modifications can improve adhesion, printability, and wettability of the film surface, making it suitable for a wider range of applications.
- Additives for improving LDPE film surface properties: Incorporating specific additives into LDPE films can significantly enhance their surface properties. These additives may include slip agents, anti-block agents, and antistatic agents. By carefully selecting and blending these additives, manufacturers can improve the film's coefficient of friction, reduce tackiness, and enhance its overall performance.
- Coatings and laminates for LDPE films: Applying coatings or creating laminates with other materials can enhance the surface properties of LDPE films. These techniques can improve barrier properties, increase chemical resistance, and provide additional functionality such as heat-sealability or UV protection. The choice of coating or laminate material depends on the specific requirements of the end application.
- Blending LDPE with other polymers: Blending LDPE with other polymers can result in films with improved surface properties. Common blend partners include LLDPE, HDPE, or specialty polymers. These blends can enhance tensile strength, tear resistance, and impact strength while maintaining the desirable properties of LDPE such as flexibility and clarity.
- Processing conditions affecting LDPE film surface properties: The processing conditions during LDPE film production can significantly impact its surface properties. Factors such as extrusion temperature, cooling rate, and draw ratio can influence crystallinity, orientation, and surface roughness. Optimizing these parameters can lead to improved optical properties, better printability, and enhanced mechanical characteristics of the film surface.
02 Additives for improving LDPE film surface properties
Incorporating specific additives into LDPE films can significantly alter their surface properties. These additives may include slip agents, anti-block agents, and antistatic agents. By carefully selecting and blending these additives, manufacturers can achieve desired surface characteristics such as reduced friction, improved clarity, and enhanced electrostatic dissipation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Coatings and laminates for LDPE films
Applying coatings or creating laminates with other materials can dramatically alter the surface properties of LDPE films. These techniques can impart new functionalities such as improved barrier properties, enhanced printability, or increased durability. The choice of coating material or laminate partner depends on the specific requirements of the end application.Expand Specific Solutions04 Heat treatment and annealing of LDPE films
Controlled heat treatment and annealing processes can be used to modify the surface properties of LDPE films. These thermal processes can affect crystallinity, orientation, and surface energy of the film, leading to changes in mechanical strength, optical properties, and chemical resistance. Careful control of temperature and cooling rates is crucial for achieving desired surface characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Blending LDPE with other polymers
Blending LDPE with other compatible polymers can result in films with unique surface properties. This approach allows for the combination of desirable characteristics from different polymers, potentially improving tensile strength, tear resistance, or barrier properties. The selection of blend components and their ratios is critical in achieving the desired surface properties for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The market for improving LDPE film surface properties is in a mature stage, with a significant global market size driven by packaging and agricultural applications. The technology is well-established, with ongoing incremental innovations. Key players like ExxonMobil Chemical, Dow Global Technologies, and SABIC Global Technologies dominate the market with advanced R&D capabilities. Emerging companies from China, such as PetroChina and Sinopec, are increasingly competitive. The focus is on developing cost-effective solutions for enhanced film properties, with a trend towards sustainable and bio-based alternatives. Collaboration between industry leaders and research institutions is driving further advancements in this field.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed innovative solutions for improving LDPE film surface properties. Their approach includes the use of metallocene catalysts to produce LDPE with more uniform molecular weight distribution, resulting in better optical properties and surface smoothness[5]. They have also introduced a range of specialty additives, such as slip agents and antiblock compounds, tailored for specific LDPE film applications[6]. ExxonMobil's Exceed™ XP performance polymers utilize a proprietary process to create LDPE films with exceptional toughness, optical properties, and processability[7]. Furthermore, they have developed advanced coextrusion techniques that allow for the creation of multi-layer films with optimized surface properties for each layer[8].
Strengths: Advanced catalyst technology; wide range of specialized additives for various applications. Weaknesses: Some solutions may be more suitable for high-end applications, potentially limiting cost-effectiveness for commodity films.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed advanced LDPE film technologies to improve surface properties. Their approach includes using specialty comonomer incorporation and controlled long-chain branching to enhance film clarity, gloss, and printability[1]. They have also implemented a proprietary extrusion coating process that allows for better adhesion and barrier properties[2]. Dow's ELITE™ Enhanced Polyethylene Resins utilize a unique catalyst and process technology to create LDPE films with improved toughness, optical properties, and processability[3]. Additionally, they have introduced additives and surface treatments that can significantly reduce film blocking and improve slip characteristics without compromising other film properties[4].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach addressing multiple surface properties simultaneously; proprietary technologies for enhanced performance. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment or processes, potentially increasing production costs.
Key Innovations
Process for modifying ldpe
PatentWO2019105851A1
Innovation
- Reactive extrusion of LDPE with a low number of unsaturations, specifically terminal vinyl groups, in the presence of an organic peroxide, optimizing temperature and residence time to minimize gel formation and enhance melt strength and homogeneity, achieving MFI of at least 4 g/10 min and melt strength of 8.0 cN.
Polyethylene cast films
PatentWO2019243348A1
Innovation
- A multi-layer polyethylene film structure comprising linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) layers with specific density and melt mass flow rate ranges, produced using cast extrusion, which includes layers derived from ethylene and 1-octene or 1-hexene, and utilizing single-site catalysts for enhanced properties.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of improving LDPE film surface properties is a critical consideration in the development and application of these materials. As the demand for enhanced LDPE films grows, it is essential to evaluate the ecological consequences of various surface modification techniques.
Surface treatments often involve chemical processes that may introduce additional substances into the environment. For instance, corona discharge treatment, a common method for improving LDPE film surface properties, generates ozone as a byproduct. While ozone in the upper atmosphere is beneficial, ground-level ozone can contribute to air pollution and pose health risks. Manufacturers must implement proper ventilation and filtration systems to mitigate these effects.
Chemical treatments, such as plasma or flame treatments, may utilize potentially harmful substances. The disposal of these chemicals and any waste products requires careful management to prevent soil and water contamination. Implementing closed-loop systems and recycling processes can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of these treatments.
The improved surface properties of LDPE films can lead to positive environmental outcomes. Enhanced barrier properties can extend the shelf life of packaged products, reducing food waste and the associated environmental impact. Additionally, improved printability and adhesion properties may reduce the need for additional packaging layers, potentially decreasing overall material usage and waste.
However, the modification of LDPE film surfaces may affect their recyclability. Some treatments can introduce contaminants or alter the chemical composition of the film, making it more challenging to recycle through conventional methods. This issue highlights the importance of developing surface modification techniques that maintain or improve the recyclability of LDPE films.
The energy consumption associated with surface modification processes is another environmental concern. Many treatments require significant energy inputs, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions if not sourced from renewable energy. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on optimizing these processes for energy efficiency and exploring the use of renewable energy sources to power surface treatment equipment.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is a growing emphasis on developing bio-based or biodegradable alternatives to traditional LDPE films. These materials may offer improved surface properties while reducing the long-term environmental impact associated with plastic waste. However, the production and end-of-life management of these alternatives must be carefully evaluated to ensure a net positive environmental effect.
Surface treatments often involve chemical processes that may introduce additional substances into the environment. For instance, corona discharge treatment, a common method for improving LDPE film surface properties, generates ozone as a byproduct. While ozone in the upper atmosphere is beneficial, ground-level ozone can contribute to air pollution and pose health risks. Manufacturers must implement proper ventilation and filtration systems to mitigate these effects.
Chemical treatments, such as plasma or flame treatments, may utilize potentially harmful substances. The disposal of these chemicals and any waste products requires careful management to prevent soil and water contamination. Implementing closed-loop systems and recycling processes can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of these treatments.
The improved surface properties of LDPE films can lead to positive environmental outcomes. Enhanced barrier properties can extend the shelf life of packaged products, reducing food waste and the associated environmental impact. Additionally, improved printability and adhesion properties may reduce the need for additional packaging layers, potentially decreasing overall material usage and waste.
However, the modification of LDPE film surfaces may affect their recyclability. Some treatments can introduce contaminants or alter the chemical composition of the film, making it more challenging to recycle through conventional methods. This issue highlights the importance of developing surface modification techniques that maintain or improve the recyclability of LDPE films.
The energy consumption associated with surface modification processes is another environmental concern. Many treatments require significant energy inputs, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions if not sourced from renewable energy. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on optimizing these processes for energy efficiency and exploring the use of renewable energy sources to power surface treatment equipment.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is a growing emphasis on developing bio-based or biodegradable alternatives to traditional LDPE films. These materials may offer improved surface properties while reducing the long-term environmental impact associated with plastic waste. However, the production and end-of-life management of these alternatives must be carefully evaluated to ensure a net positive environmental effect.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in the improvement of LDPE film surface properties, as it ensures that the manufacturing processes and final products meet the necessary safety and quality standards. The regulatory landscape for LDPE films is complex and varies across different regions and applications, particularly in food packaging and medical devices.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates LDPE films used in food contact applications under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Manufacturers must ensure that their LDPE films comply with FDA regulations, including 21 CFR 177.1520, which specifies the permissible raw materials and additives for polyethylene films. Additionally, the FDA requires that any surface treatments or modifications to improve LDPE film properties must be safe for food contact and not alter the film's overall composition beyond acceptable limits.
The European Union has its own set of regulations governing LDPE films, particularly those used in food packaging. The EU Plastics Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 outlines specific migration limits for various substances used in plastic food contact materials, including LDPE films. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with these limits through rigorous testing and documentation.
Environmental regulations also impact the development of improved LDPE film surface properties. Many countries have implemented restrictions on certain chemicals and additives used in plastic production, such as bisphenol A (BPA) and certain phthalates. These regulations drive the need for alternative, environmentally friendly solutions to enhance LDPE film surface properties.
The medical device industry has its own set of regulatory requirements for LDPE films. In the United States, the FDA's Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) oversees medical devices, including those incorporating LDPE films. Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their products through appropriate testing and documentation.
Globally, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides standards that are often adopted or referenced by regulatory bodies. ISO 10993 series, for instance, is crucial for evaluating the biocompatibility of medical devices, including those using LDPE films. Adherence to these standards is often necessary for market approval in many countries.
As the focus on sustainability increases, new regulations are emerging that impact LDPE film production and surface modification. For example, the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive aims to reduce plastic waste, which may influence the development of more recyclable or biodegradable LDPE films with enhanced surface properties.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory requirements necessitates a comprehensive approach to improving LDPE film surface properties. Manufacturers must carefully consider the intended use of their films and ensure that any surface modifications or treatments align with applicable regulations. This often involves extensive testing, documentation, and sometimes pre-market approval processes, depending on the specific application and jurisdiction.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates LDPE films used in food contact applications under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Manufacturers must ensure that their LDPE films comply with FDA regulations, including 21 CFR 177.1520, which specifies the permissible raw materials and additives for polyethylene films. Additionally, the FDA requires that any surface treatments or modifications to improve LDPE film properties must be safe for food contact and not alter the film's overall composition beyond acceptable limits.
The European Union has its own set of regulations governing LDPE films, particularly those used in food packaging. The EU Plastics Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 outlines specific migration limits for various substances used in plastic food contact materials, including LDPE films. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with these limits through rigorous testing and documentation.
Environmental regulations also impact the development of improved LDPE film surface properties. Many countries have implemented restrictions on certain chemicals and additives used in plastic production, such as bisphenol A (BPA) and certain phthalates. These regulations drive the need for alternative, environmentally friendly solutions to enhance LDPE film surface properties.
The medical device industry has its own set of regulatory requirements for LDPE films. In the United States, the FDA's Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) oversees medical devices, including those incorporating LDPE films. Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their products through appropriate testing and documentation.
Globally, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides standards that are often adopted or referenced by regulatory bodies. ISO 10993 series, for instance, is crucial for evaluating the biocompatibility of medical devices, including those using LDPE films. Adherence to these standards is often necessary for market approval in many countries.
As the focus on sustainability increases, new regulations are emerging that impact LDPE film production and surface modification. For example, the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive aims to reduce plastic waste, which may influence the development of more recyclable or biodegradable LDPE films with enhanced surface properties.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory requirements necessitates a comprehensive approach to improving LDPE film surface properties. Manufacturers must carefully consider the intended use of their films and ensure that any surface modifications or treatments align with applicable regulations. This often involves extensive testing, documentation, and sometimes pre-market approval processes, depending on the specific application and jurisdiction.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!