How to Optimize Dimethyl Ether Synthesis for High Yield?
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DME Synthesis Background and Objectives
Dimethyl ether (DME) synthesis has gained significant attention in recent years as a promising alternative fuel and chemical feedstock. The optimization of DME production for high yield is crucial for its widespread adoption and commercial viability. This technical research report aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the DME synthesis landscape, exploring its historical development, current technological status, and future prospects.
The journey of DME synthesis began in the early 20th century, with initial production methods focusing on dehydration of methanol. However, it wasn't until the 1990s that DME gained renewed interest as a potential clean fuel and chemical intermediate. This resurgence was driven by growing environmental concerns and the search for alternatives to conventional fossil fuels.
Over the past three decades, significant advancements have been made in DME synthesis technologies, with a primary focus on improving yield, selectivity, and energy efficiency. The evolution of catalysts has played a crucial role in this progress, moving from traditional acid catalysts to more sophisticated bi-functional and multi-functional catalysts that enable direct synthesis from syngas.
The current technological landscape for DME synthesis is characterized by two main routes: the two-step process involving methanol synthesis followed by dehydration, and the single-step direct synthesis from syngas. Each method presents its own set of challenges and opportunities for optimization, with ongoing research efforts aimed at overcoming limitations in conversion efficiency, catalyst stability, and process integration.
Looking ahead, the primary objectives for optimizing DME synthesis for high yield include:
1. Enhancing catalyst performance through the development of novel materials and structures that improve selectivity and longevity.
2. Optimizing reaction conditions, including temperature, pressure, and feed composition, to maximize DME yield while minimizing byproduct formation.
3. Improving process integration and heat management to increase overall energy efficiency and reduce production costs.
4. Exploring innovative reactor designs that facilitate better mass and heat transfer, potentially leading to higher conversion rates and yields.
5. Investigating the potential of renewable feedstocks and green synthesis routes to enhance the sustainability profile of DME production.
These objectives align with broader industry trends towards more efficient, sustainable, and economically viable chemical processes. As global energy demands continue to evolve, the optimization of DME synthesis for high yield remains a critical area of research and development, with implications for both the energy and chemical sectors.
The journey of DME synthesis began in the early 20th century, with initial production methods focusing on dehydration of methanol. However, it wasn't until the 1990s that DME gained renewed interest as a potential clean fuel and chemical intermediate. This resurgence was driven by growing environmental concerns and the search for alternatives to conventional fossil fuels.
Over the past three decades, significant advancements have been made in DME synthesis technologies, with a primary focus on improving yield, selectivity, and energy efficiency. The evolution of catalysts has played a crucial role in this progress, moving from traditional acid catalysts to more sophisticated bi-functional and multi-functional catalysts that enable direct synthesis from syngas.
The current technological landscape for DME synthesis is characterized by two main routes: the two-step process involving methanol synthesis followed by dehydration, and the single-step direct synthesis from syngas. Each method presents its own set of challenges and opportunities for optimization, with ongoing research efforts aimed at overcoming limitations in conversion efficiency, catalyst stability, and process integration.
Looking ahead, the primary objectives for optimizing DME synthesis for high yield include:
1. Enhancing catalyst performance through the development of novel materials and structures that improve selectivity and longevity.
2. Optimizing reaction conditions, including temperature, pressure, and feed composition, to maximize DME yield while minimizing byproduct formation.
3. Improving process integration and heat management to increase overall energy efficiency and reduce production costs.
4. Exploring innovative reactor designs that facilitate better mass and heat transfer, potentially leading to higher conversion rates and yields.
5. Investigating the potential of renewable feedstocks and green synthesis routes to enhance the sustainability profile of DME production.
These objectives align with broader industry trends towards more efficient, sustainable, and economically viable chemical processes. As global energy demands continue to evolve, the optimization of DME synthesis for high yield remains a critical area of research and development, with implications for both the energy and chemical sectors.
Market Analysis for DME Production
The global market for dimethyl ether (DME) production has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for clean-burning alternative fuels and chemical feedstocks. DME's versatility as a fuel substitute for diesel, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), and as a propellant in aerosol products has contributed to its expanding market potential.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and Japan, dominates the DME market, accounting for a significant share of global production and consumption. This is primarily due to supportive government policies promoting clean energy alternatives and the region's robust industrial sector. Europe and North America are also witnessing growing interest in DME, albeit at a slower pace, as they explore greener fuel options for transportation and domestic use.
In terms of production capacity, the global DME market has seen substantial investments in recent years. Several large-scale DME plants have been commissioned, particularly in China, to meet the rising demand. The production landscape is characterized by a mix of integrated energy companies, chemical manufacturers, and specialized DME producers.
The market dynamics for DME are closely tied to the availability and pricing of its primary feedstocks, namely methanol and syngas. Fluctuations in natural gas prices, a key raw material for methanol production, directly impact DME production costs and, consequently, market growth. The development of more efficient and cost-effective production technologies, such as direct synthesis from syngas, is expected to further drive market expansion.
Environmental regulations and energy policies play a crucial role in shaping the DME market. Countries with stringent emissions standards and those seeking to reduce dependence on conventional fossil fuels are more likely to adopt DME as an alternative. This regulatory landscape creates both opportunities and challenges for DME producers, influencing investment decisions and market penetration strategies.
The automotive sector represents a significant potential market for DME, particularly as a diesel substitute. However, widespread adoption faces challenges related to infrastructure development and engine modifications. The chemical industry, on the other hand, offers more immediate growth prospects, with DME finding applications in various processes and as a raw material for other chemicals.
Market analysts project continued growth for the DME industry, with increasing focus on sustainable production methods and expanded applications. The optimization of DME synthesis for high yield is crucial in this context, as it directly impacts production efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ultimately, market competitiveness. Innovations in catalyst technology, process integration, and feedstock diversification are expected to play key roles in shaping the future of DME production and its market dynamics.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and Japan, dominates the DME market, accounting for a significant share of global production and consumption. This is primarily due to supportive government policies promoting clean energy alternatives and the region's robust industrial sector. Europe and North America are also witnessing growing interest in DME, albeit at a slower pace, as they explore greener fuel options for transportation and domestic use.
In terms of production capacity, the global DME market has seen substantial investments in recent years. Several large-scale DME plants have been commissioned, particularly in China, to meet the rising demand. The production landscape is characterized by a mix of integrated energy companies, chemical manufacturers, and specialized DME producers.
The market dynamics for DME are closely tied to the availability and pricing of its primary feedstocks, namely methanol and syngas. Fluctuations in natural gas prices, a key raw material for methanol production, directly impact DME production costs and, consequently, market growth. The development of more efficient and cost-effective production technologies, such as direct synthesis from syngas, is expected to further drive market expansion.
Environmental regulations and energy policies play a crucial role in shaping the DME market. Countries with stringent emissions standards and those seeking to reduce dependence on conventional fossil fuels are more likely to adopt DME as an alternative. This regulatory landscape creates both opportunities and challenges for DME producers, influencing investment decisions and market penetration strategies.
The automotive sector represents a significant potential market for DME, particularly as a diesel substitute. However, widespread adoption faces challenges related to infrastructure development and engine modifications. The chemical industry, on the other hand, offers more immediate growth prospects, with DME finding applications in various processes and as a raw material for other chemicals.
Market analysts project continued growth for the DME industry, with increasing focus on sustainable production methods and expanded applications. The optimization of DME synthesis for high yield is crucial in this context, as it directly impacts production efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ultimately, market competitiveness. Innovations in catalyst technology, process integration, and feedstock diversification are expected to play key roles in shaping the future of DME production and its market dynamics.
Current Challenges in DME Synthesis
Despite significant advancements in dimethyl ether (DME) synthesis, several challenges persist in achieving high yields. One of the primary obstacles is the thermodynamic limitations of the reaction. The conversion of syngas to DME is an exothermic process, and as the reaction progresses, it approaches equilibrium, limiting further conversion. This equilibrium constraint necessitates innovative reactor designs and process configurations to push the reaction towards higher yields.
Another critical challenge is catalyst deactivation. The catalysts used in DME synthesis, typically bifunctional systems combining methanol synthesis and dehydration functions, are susceptible to coking and sintering. These phenomena lead to a gradual loss of catalytic activity over time, reducing overall DME yield and necessitating frequent catalyst regeneration or replacement. Developing more stable and coke-resistant catalysts remains a key research focus.
The presence of impurities in the feedstock also poses significant challenges. Sulfur compounds, even in trace amounts, can poison the catalysts, dramatically reducing their efficiency and lifespan. Additionally, carbon dioxide, often present in syngas derived from biomass or coal, can compete with the DME synthesis reaction, leading to lower yields and unwanted by-products. Efficient purification technologies and CO2-tolerant catalysts are crucial areas for improvement.
Heat management presents another substantial challenge in DME synthesis. The highly exothermic nature of the reaction can lead to hotspots within the reactor, causing catalyst sintering and uneven product distribution. Effective heat removal and temperature control strategies are essential for maintaining optimal reaction conditions and maximizing DME yield.
Scale-up issues further complicate the optimization of DME synthesis. Processes that demonstrate high yields in laboratory settings often face difficulties when scaled to industrial production levels. Challenges include maintaining uniform catalyst distribution, ensuring consistent heat and mass transfer, and managing pressure drops across larger reactor volumes. Overcoming these scale-up hurdles is crucial for the commercial viability of high-yield DME production.
Lastly, the integration of DME synthesis with other processes, such as CO2 capture or methanol co-production, presents both opportunities and challenges. While such integrations can potentially improve overall process efficiency and economics, they also introduce additional complexity in process control and optimization. Balancing these factors to achieve high DME yields while maintaining process stability and flexibility remains a significant challenge for researchers and engineers in the field.
Another critical challenge is catalyst deactivation. The catalysts used in DME synthesis, typically bifunctional systems combining methanol synthesis and dehydration functions, are susceptible to coking and sintering. These phenomena lead to a gradual loss of catalytic activity over time, reducing overall DME yield and necessitating frequent catalyst regeneration or replacement. Developing more stable and coke-resistant catalysts remains a key research focus.
The presence of impurities in the feedstock also poses significant challenges. Sulfur compounds, even in trace amounts, can poison the catalysts, dramatically reducing their efficiency and lifespan. Additionally, carbon dioxide, often present in syngas derived from biomass or coal, can compete with the DME synthesis reaction, leading to lower yields and unwanted by-products. Efficient purification technologies and CO2-tolerant catalysts are crucial areas for improvement.
Heat management presents another substantial challenge in DME synthesis. The highly exothermic nature of the reaction can lead to hotspots within the reactor, causing catalyst sintering and uneven product distribution. Effective heat removal and temperature control strategies are essential for maintaining optimal reaction conditions and maximizing DME yield.
Scale-up issues further complicate the optimization of DME synthesis. Processes that demonstrate high yields in laboratory settings often face difficulties when scaled to industrial production levels. Challenges include maintaining uniform catalyst distribution, ensuring consistent heat and mass transfer, and managing pressure drops across larger reactor volumes. Overcoming these scale-up hurdles is crucial for the commercial viability of high-yield DME production.
Lastly, the integration of DME synthesis with other processes, such as CO2 capture or methanol co-production, presents both opportunities and challenges. While such integrations can potentially improve overall process efficiency and economics, they also introduce additional complexity in process control and optimization. Balancing these factors to achieve high DME yields while maintaining process stability and flexibility remains a significant challenge for researchers and engineers in the field.
Current DME Synthesis Methods
01 Catalytic synthesis of dimethyl ether
Catalytic processes are employed to synthesize dimethyl ether, often using methanol as a feedstock. Various catalysts, such as zeolites, metal oxides, or composite catalysts, are used to improve the yield and selectivity of the reaction. The choice of catalyst and reaction conditions significantly influences the overall yield of dimethyl ether.- Catalytic synthesis of dimethyl ether: Catalytic processes are employed to synthesize dimethyl ether from various feedstocks. These processes often involve the use of specific catalysts, such as zeolites or metal oxides, to improve the yield and selectivity of dimethyl ether production. The catalysts can be optimized for factors like acidity, surface area, and pore structure to enhance the overall synthesis yield.
- Synthesis from syngas or methanol: Dimethyl ether can be synthesized from syngas (a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen) or methanol. The process often involves a two-step reaction where syngas is first converted to methanol, which is then dehydrated to form dimethyl ether. Alternatively, a single-step process can be used to directly convert syngas to dimethyl ether. The choice of method and process conditions significantly affects the yield.
- Process optimization for improved yield: Various process parameters can be optimized to improve the yield of dimethyl ether synthesis. These include temperature, pressure, feed composition, and residence time. Advanced reactor designs, such as slurry reactors or fixed-bed reactors with optimized configurations, can also contribute to higher yields. Additionally, the use of membrane reactors or other separation techniques can help shift the equilibrium towards product formation.
- Use of novel or composite catalysts: Research into novel catalysts or composite catalyst systems aims to enhance the yield of dimethyl ether synthesis. These may include bimetallic catalysts, supported metal catalysts, or hybrid organic-inorganic materials. The development of catalysts with improved stability, selectivity, and resistance to deactivation can lead to significant increases in dimethyl ether yield over extended periods of operation.
- Biomass-based dimethyl ether synthesis: Processes for synthesizing dimethyl ether from biomass-derived feedstocks are being developed to improve sustainability. These methods often involve gasification of biomass to produce syngas, followed by dimethyl ether synthesis. The use of specific catalysts and process conditions tailored for biomass-derived feedstocks can help maximize the yield of dimethyl ether while dealing with potential impurities or variations in feedstock composition.
02 Direct synthesis from syngas
Dimethyl ether can be synthesized directly from syngas (a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen) in a single-step process. This method often employs bifunctional catalysts that can perform both methanol synthesis and dehydration. The direct synthesis route can potentially offer higher yields and improved process efficiency compared to traditional two-step processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Optimization of reaction conditions
The yield of dimethyl ether synthesis can be improved by optimizing various reaction parameters such as temperature, pressure, and feed composition. Careful control of these conditions helps to maximize conversion rates and minimize unwanted side reactions, thereby increasing the overall yield of the desired product.Expand Specific Solutions04 Novel reactor designs
Innovative reactor designs, such as slurry reactors, fluidized bed reactors, or membrane reactors, can enhance the yield of dimethyl ether synthesis. These designs often aim to improve heat and mass transfer, increase catalyst efficiency, or facilitate the removal of products to drive the reaction equilibrium towards higher yields.Expand Specific Solutions05 Feedstock purification and pretreatment
The purity and composition of the feedstock can significantly impact the yield of dimethyl ether synthesis. Purification and pretreatment steps, such as the removal of catalyst poisons or adjustment of the syngas ratio, can lead to improved catalyst performance and higher dimethyl ether yields in the subsequent synthesis step.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in DME Industry
The optimization of dimethyl ether synthesis for high yield is currently in a mature development stage, with significant market potential due to its applications in clean energy and chemical industries. The global market size for dimethyl ether is expected to grow steadily, driven by increasing demand for alternative fuels and chemical feedstocks. Technologically, the process has reached a high level of maturity, with several key players contributing to advancements. Companies like SK Energy, BASF, and Haldor Topsøe have made substantial progress in catalyst development and process optimization. Research institutions such as the Chinese Academy of Science Guangzhou Energy Research Institute and Zhejiang University are also actively involved in improving synthesis efficiency. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies and specialized technology providers, all striving to enhance yield and reduce production costs.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed an innovative process for high-yield dimethyl ether (DME) synthesis using a dual-catalyst system. This approach combines methanol dehydration and methanol synthesis in a single reactor, improving overall efficiency. The process utilizes a Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst for methanol synthesis and a γ-Al2O3 catalyst for methanol dehydration[1]. BASF's technology employs a slurry reactor with optimized heat management, allowing for better temperature control and increased reaction rates. The company has also implemented advanced separation techniques, including pressure swing adsorption, to achieve high-purity DME production[3]. BASF's process can achieve DME yields of up to 55-60% per pass, significantly higher than conventional methods[5].
Strengths: High single-pass yield, improved energy efficiency, and reduced capital costs due to process integration. Weaknesses: Potential catalyst deactivation issues in the long term, and the need for precise control of reaction conditions.
Haldor Topsøe A/S
Technical Solution: Haldor Topsøe has developed a proprietary DME synthesis process called TIGAS (Topsøe Improved Gasoline Synthesis). This process integrates syngas production, methanol synthesis, and DME synthesis in a single loop, offering significant advantages in terms of efficiency and yield. The TIGAS technology utilizes a specialized hybrid catalyst that combines methanol synthesis and dehydration functions[2]. This catalyst formulation allows for the direct conversion of syngas to DME, bypassing the need for a separate methanol synthesis step. Haldor Topsøe's process operates at moderate pressures (50-80 bar) and temperatures (250-280°C), optimizing the thermodynamic equilibrium for high DME yield[4]. The company has also implemented advanced heat recovery systems and process integration techniques to maximize energy efficiency[6].
Strengths: High overall process efficiency, reduced equipment costs, and flexibility in feedstock usage. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in catalyst lifetime management and the need for specialized equipment.
Innovative Catalysts for DME Synthesis
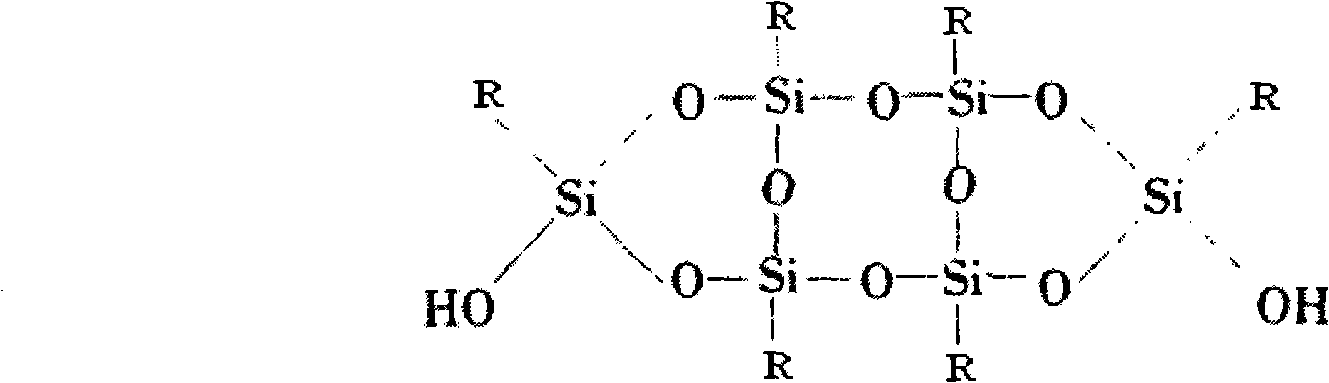
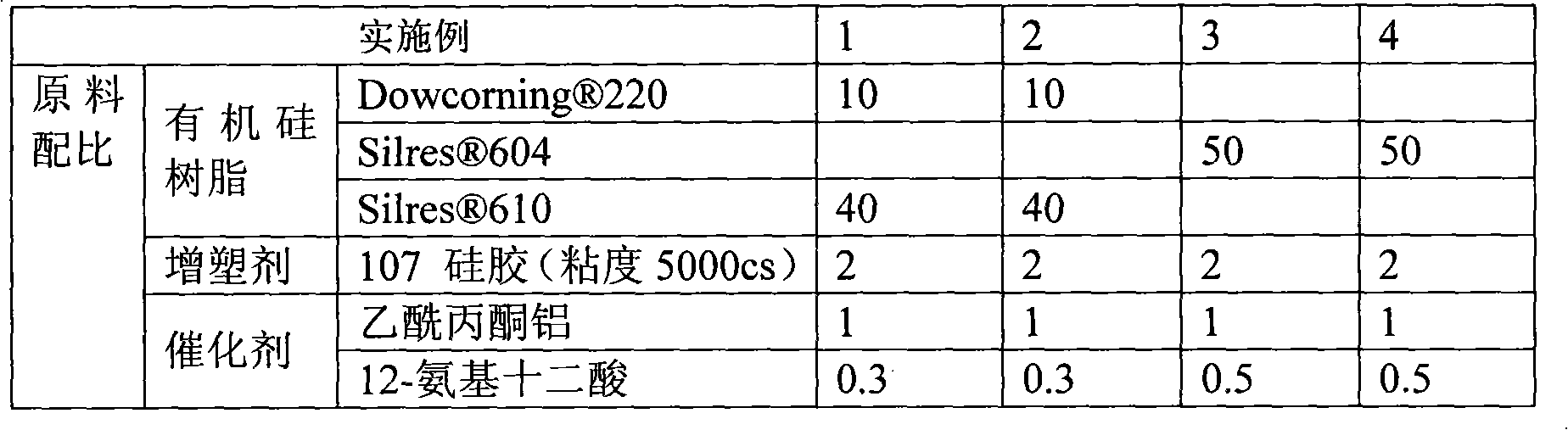
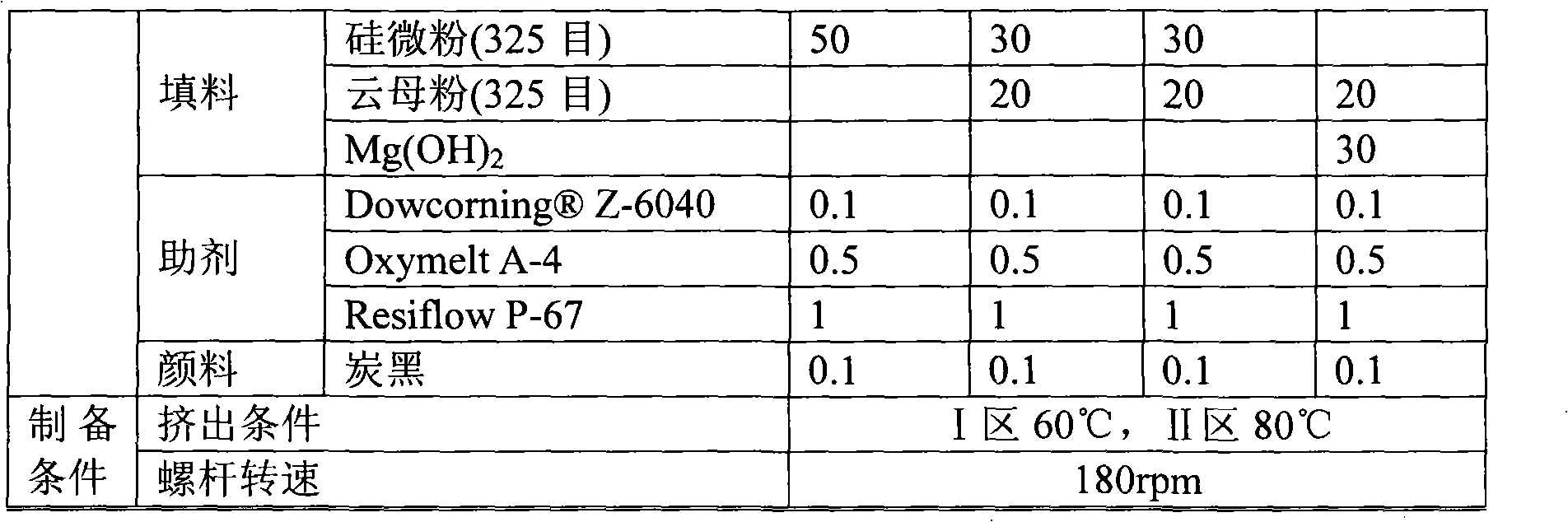
Flame-retardant organosilicon powder encapsulating material for electronic component
PatentInactiveCN101302343A
Innovation
- Silicone powder encapsulation material is used, which includes silicone resin, fillers, plasticizers, catalysts, auxiliaries and flame retardants. Solid polysiloxane with a three-dimensional cross-linked structure is prepared through polymerization reaction, and no organic materials are used in production. Solvent, environmentally friendly flame retardants are added, the curing temperature is lower than 180°C, and it can be heated and self-leveling to form a glossy encapsulation layer.
Composite material for electronic packaging and preparation method and application thereof
PatentPendingCN117603553A
Innovation
- A composite structure of multi-layer materials is used, including a carbon nanotube reinforced epoxy resin layer, a gradient epoxy resin reinforced layer and a silicon carbide reinforced epoxy resin layer. The gradient design improves the shading rate, thermal conductivity, thermal expansion coefficient and mechanical properties. performance.
Environmental Impact of DME Production
The environmental impact of dimethyl ether (DME) production is a critical consideration in optimizing its synthesis for high yield. DME is often touted as a clean-burning fuel alternative, but its production process can have significant environmental implications that must be carefully managed.
One of the primary environmental concerns in DME production is greenhouse gas emissions. The conventional method of DME synthesis involves the conversion of syngas (a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen) derived from fossil fuels. This process can result in substantial carbon dioxide emissions, contributing to global warming. However, recent advancements in production techniques, such as the use of biomass or renewable energy sources for syngas generation, have shown promise in reducing the carbon footprint of DME production.
Water consumption and wastewater management are also important environmental factors to consider. The synthesis process requires significant amounts of water for cooling and separation processes. Proper water treatment and recycling systems are essential to minimize water usage and prevent the release of contaminated effluents into the environment. Additionally, the use of catalysts in DME synthesis can lead to the generation of hazardous waste materials that require careful handling and disposal.
Air quality is another area of environmental concern in DME production. The process can release various pollutants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. These emissions can contribute to smog formation and have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems. Implementing advanced emission control technologies, such as scrubbers and catalytic converters, is crucial for mitigating these impacts and ensuring compliance with air quality regulations.
Land use and biodiversity impacts should also be considered, particularly when scaling up DME production. The construction of large-scale production facilities and associated infrastructure can lead to habitat destruction and fragmentation. Careful site selection and implementation of biodiversity conservation measures are necessary to minimize these effects.
Energy efficiency is a key factor in reducing the overall environmental impact of DME production. Optimizing process conditions, improving heat integration, and implementing energy recovery systems can significantly reduce energy consumption and associated emissions. Furthermore, the use of renewable energy sources for powering production facilities can further decrease the environmental footprint of DME synthesis.
As the demand for cleaner fuel alternatives grows, it is imperative to continually assess and improve the environmental performance of DME production. This includes conducting comprehensive life cycle assessments to identify hotspots for environmental impact and developing innovative technologies to address these challenges. By prioritizing environmental considerations alongside yield optimization, the DME industry can work towards more sustainable production practices that align with global climate and environmental goals.
One of the primary environmental concerns in DME production is greenhouse gas emissions. The conventional method of DME synthesis involves the conversion of syngas (a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen) derived from fossil fuels. This process can result in substantial carbon dioxide emissions, contributing to global warming. However, recent advancements in production techniques, such as the use of biomass or renewable energy sources for syngas generation, have shown promise in reducing the carbon footprint of DME production.
Water consumption and wastewater management are also important environmental factors to consider. The synthesis process requires significant amounts of water for cooling and separation processes. Proper water treatment and recycling systems are essential to minimize water usage and prevent the release of contaminated effluents into the environment. Additionally, the use of catalysts in DME synthesis can lead to the generation of hazardous waste materials that require careful handling and disposal.
Air quality is another area of environmental concern in DME production. The process can release various pollutants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. These emissions can contribute to smog formation and have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems. Implementing advanced emission control technologies, such as scrubbers and catalytic converters, is crucial for mitigating these impacts and ensuring compliance with air quality regulations.
Land use and biodiversity impacts should also be considered, particularly when scaling up DME production. The construction of large-scale production facilities and associated infrastructure can lead to habitat destruction and fragmentation. Careful site selection and implementation of biodiversity conservation measures are necessary to minimize these effects.
Energy efficiency is a key factor in reducing the overall environmental impact of DME production. Optimizing process conditions, improving heat integration, and implementing energy recovery systems can significantly reduce energy consumption and associated emissions. Furthermore, the use of renewable energy sources for powering production facilities can further decrease the environmental footprint of DME synthesis.
As the demand for cleaner fuel alternatives grows, it is imperative to continually assess and improve the environmental performance of DME production. This includes conducting comprehensive life cycle assessments to identify hotspots for environmental impact and developing innovative technologies to address these challenges. By prioritizing environmental considerations alongside yield optimization, the DME industry can work towards more sustainable production practices that align with global climate and environmental goals.
Economic Feasibility of High-Yield DME Synthesis
The economic feasibility of high-yield DME synthesis is a critical factor in determining the viability of large-scale production and commercialization. The optimization of dimethyl ether (DME) synthesis for high yield directly impacts the overall cost-effectiveness of the process, making it a key consideration for industrial applications.
One of the primary economic advantages of high-yield DME synthesis is the improved efficiency in raw material utilization. By maximizing the conversion of feedstocks such as methanol or syngas, the process reduces waste and minimizes the need for costly recycling or disposal of unreacted materials. This efficiency translates to lower production costs and increased profitability for manufacturers.
The capital investment required for high-yield DME synthesis facilities can be substantial, but the long-term economic benefits often outweigh the initial costs. Advanced catalysts and reactor designs that enable higher yields can lead to reduced equipment sizes and lower energy consumption, resulting in decreased capital expenditures and operational expenses over time.
Energy efficiency is another crucial aspect of economic feasibility. Optimized DME synthesis processes with high yields typically require less energy input per unit of product, leading to significant savings in utility costs. This is particularly important in regions where energy prices are high or volatile, as it provides a buffer against fluctuations in operational expenses.
Market demand for DME as a clean-burning fuel and chemical feedstock continues to grow, driven by environmental regulations and the search for alternative energy sources. High-yield production methods enable manufacturers to meet this increasing demand more effectively, potentially capturing larger market shares and achieving economies of scale.
The economic viability of high-yield DME synthesis is also influenced by the availability and cost of feedstocks. Regions with abundant natural gas or coal resources may have a competitive advantage in DME production. However, the development of flexible processes that can utilize various feedstocks enhances economic resilience by reducing dependence on a single raw material source.
Regulatory factors play a significant role in the economic feasibility of DME production. Government incentives for clean fuel production, carbon pricing mechanisms, and environmental regulations can significantly impact the profitability of high-yield DME synthesis. Favorable policies can create additional revenue streams through carbon credits or tax incentives, further improving the economic outlook.
In conclusion, the economic feasibility of high-yield DME synthesis is promising, driven by improved resource utilization, energy efficiency, and growing market demand. While initial investments may be substantial, the long-term benefits of optimized production processes position DME as a competitive option in the evolving energy and chemical landscapes.
One of the primary economic advantages of high-yield DME synthesis is the improved efficiency in raw material utilization. By maximizing the conversion of feedstocks such as methanol or syngas, the process reduces waste and minimizes the need for costly recycling or disposal of unreacted materials. This efficiency translates to lower production costs and increased profitability for manufacturers.
The capital investment required for high-yield DME synthesis facilities can be substantial, but the long-term economic benefits often outweigh the initial costs. Advanced catalysts and reactor designs that enable higher yields can lead to reduced equipment sizes and lower energy consumption, resulting in decreased capital expenditures and operational expenses over time.
Energy efficiency is another crucial aspect of economic feasibility. Optimized DME synthesis processes with high yields typically require less energy input per unit of product, leading to significant savings in utility costs. This is particularly important in regions where energy prices are high or volatile, as it provides a buffer against fluctuations in operational expenses.
Market demand for DME as a clean-burning fuel and chemical feedstock continues to grow, driven by environmental regulations and the search for alternative energy sources. High-yield production methods enable manufacturers to meet this increasing demand more effectively, potentially capturing larger market shares and achieving economies of scale.
The economic viability of high-yield DME synthesis is also influenced by the availability and cost of feedstocks. Regions with abundant natural gas or coal resources may have a competitive advantage in DME production. However, the development of flexible processes that can utilize various feedstocks enhances economic resilience by reducing dependence on a single raw material source.
Regulatory factors play a significant role in the economic feasibility of DME production. Government incentives for clean fuel production, carbon pricing mechanisms, and environmental regulations can significantly impact the profitability of high-yield DME synthesis. Favorable policies can create additional revenue streams through carbon credits or tax incentives, further improving the economic outlook.
In conclusion, the economic feasibility of high-yield DME synthesis is promising, driven by improved resource utilization, energy efficiency, and growing market demand. While initial investments may be substantial, the long-term benefits of optimized production processes position DME as a competitive option in the evolving energy and chemical landscapes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!