How Trimethylglycine Encourages Healthy Lipid Metabolism
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
TMG and Lipid Metabolism Background
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, is a naturally occurring compound found in various food sources such as beets, spinach, and whole grains. It has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential role in promoting healthy lipid metabolism. The compound was first isolated in the 19th century from sugar beets, and its name "betaine" derives from this original source. TMG serves as a methyl donor in biochemical processes and has been increasingly studied for its effects on metabolic health.
Lipid metabolism encompasses the complex processes by which the body breaks down, transports, and utilizes fats for energy, cell membrane formation, and hormone production. Dysregulation of lipid metabolism is associated with numerous health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and metabolic syndrome. The global prevalence of these conditions has risen dramatically in recent decades, creating an urgent need for effective interventions.
The intersection of TMG and lipid metabolism represents a promising area of research with potential applications in both preventive healthcare and therapeutic interventions. TMG's role as a methyl donor is particularly significant in this context, as methylation processes are integral to lipid metabolism pathways. Through donation of methyl groups, TMG facilitates the conversion of homocysteine to methionine, which subsequently affects various aspects of lipid metabolism.
Historical research on TMG dates back several decades, with early studies focusing primarily on its role in homocysteine metabolism. However, the connection between TMG and lipid metabolism has gained substantial attention only in the past 15-20 years. This shift coincides with the increasing global burden of metabolic disorders and the search for novel nutritional and pharmacological interventions.
The biochemical pathways through which TMG influences lipid metabolism are multifaceted. Beyond its role in homocysteine metabolism, TMG has been shown to affect the expression of genes involved in lipid synthesis and oxidation. Additionally, it may influence the activity of key enzymes in lipid metabolic pathways and modulate inflammatory processes that contribute to metabolic dysfunction.
Recent technological advances in metabolomics, genomics, and computational biology have accelerated research in this field, enabling more comprehensive understanding of TMG's effects on lipid metabolism at molecular and cellular levels. These advances have revealed potential mechanisms by which TMG supplementation might benefit individuals with various metabolic disorders.
The current technological landscape surrounding TMG research includes sophisticated analytical methods for measuring TMG levels in biological samples, high-throughput screening approaches for identifying molecular targets, and advanced imaging techniques for visualizing changes in lipid distribution and metabolism in response to TMG supplementation. These technological capabilities have significantly enhanced our understanding of TMG's role in lipid metabolism and continue to drive innovation in this field.
Lipid metabolism encompasses the complex processes by which the body breaks down, transports, and utilizes fats for energy, cell membrane formation, and hormone production. Dysregulation of lipid metabolism is associated with numerous health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and metabolic syndrome. The global prevalence of these conditions has risen dramatically in recent decades, creating an urgent need for effective interventions.
The intersection of TMG and lipid metabolism represents a promising area of research with potential applications in both preventive healthcare and therapeutic interventions. TMG's role as a methyl donor is particularly significant in this context, as methylation processes are integral to lipid metabolism pathways. Through donation of methyl groups, TMG facilitates the conversion of homocysteine to methionine, which subsequently affects various aspects of lipid metabolism.
Historical research on TMG dates back several decades, with early studies focusing primarily on its role in homocysteine metabolism. However, the connection between TMG and lipid metabolism has gained substantial attention only in the past 15-20 years. This shift coincides with the increasing global burden of metabolic disorders and the search for novel nutritional and pharmacological interventions.
The biochemical pathways through which TMG influences lipid metabolism are multifaceted. Beyond its role in homocysteine metabolism, TMG has been shown to affect the expression of genes involved in lipid synthesis and oxidation. Additionally, it may influence the activity of key enzymes in lipid metabolic pathways and modulate inflammatory processes that contribute to metabolic dysfunction.
Recent technological advances in metabolomics, genomics, and computational biology have accelerated research in this field, enabling more comprehensive understanding of TMG's effects on lipid metabolism at molecular and cellular levels. These advances have revealed potential mechanisms by which TMG supplementation might benefit individuals with various metabolic disorders.
The current technological landscape surrounding TMG research includes sophisticated analytical methods for measuring TMG levels in biological samples, high-throughput screening approaches for identifying molecular targets, and advanced imaging techniques for visualizing changes in lipid distribution and metabolism in response to TMG supplementation. These technological capabilities have significantly enhanced our understanding of TMG's role in lipid metabolism and continue to drive innovation in this field.
Market Analysis for TMG Supplements
The global market for Trimethylglycine (TMG) supplements has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing consumer awareness of its potential benefits for lipid metabolism and cardiovascular health. The market size for TMG supplements was valued at approximately $580 million in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% through 2028.
North America currently dominates the TMG supplement market, accounting for roughly 42% of global sales. This regional dominance can be attributed to high consumer awareness, well-established distribution networks, and significant investment in marketing by key industry players. Europe follows as the second-largest market at 28%, with Asia-Pacific showing the fastest growth rate at 9.3% annually, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Consumer demographics reveal that TMG supplements appeal primarily to two distinct market segments. The first consists of health-conscious individuals aged 45-65 concerned about cardiovascular health and metabolic conditions. The second emerging segment includes fitness enthusiasts and athletes seeking performance enhancement and recovery benefits. This diversification of the consumer base has expanded market opportunities significantly.
Distribution channels for TMG supplements have evolved considerably, with online retail showing the most dramatic growth. E-commerce platforms now account for approximately 38% of total sales, followed by specialty health stores (27%), pharmacies (22%), and mass-market retailers (13%). The shift toward online purchasing has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and continues to reshape market dynamics.
Pricing analysis indicates considerable variation across different product formulations and brands. Premium TMG supplements with additional complementary ingredients command prices between $30-45 for a month's supply, while basic formulations typically range from $15-25. This price stratification reflects different positioning strategies within the market.
Key market drivers include increasing prevalence of metabolic disorders, growing consumer interest in preventative healthcare approaches, and expanding scientific research validating TMG's benefits for lipid metabolism. Regulatory factors also significantly impact market development, with varying approval statuses across different regions creating both opportunities and challenges for manufacturers.
Market forecasts suggest continued robust growth, with particular expansion expected in sports nutrition applications and combination formulations targeting specific health concerns. The aging global population and increasing healthcare costs are expected to further drive consumer interest in preventative supplements like TMG that support metabolic health.
North America currently dominates the TMG supplement market, accounting for roughly 42% of global sales. This regional dominance can be attributed to high consumer awareness, well-established distribution networks, and significant investment in marketing by key industry players. Europe follows as the second-largest market at 28%, with Asia-Pacific showing the fastest growth rate at 9.3% annually, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Consumer demographics reveal that TMG supplements appeal primarily to two distinct market segments. The first consists of health-conscious individuals aged 45-65 concerned about cardiovascular health and metabolic conditions. The second emerging segment includes fitness enthusiasts and athletes seeking performance enhancement and recovery benefits. This diversification of the consumer base has expanded market opportunities significantly.
Distribution channels for TMG supplements have evolved considerably, with online retail showing the most dramatic growth. E-commerce platforms now account for approximately 38% of total sales, followed by specialty health stores (27%), pharmacies (22%), and mass-market retailers (13%). The shift toward online purchasing has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and continues to reshape market dynamics.
Pricing analysis indicates considerable variation across different product formulations and brands. Premium TMG supplements with additional complementary ingredients command prices between $30-45 for a month's supply, while basic formulations typically range from $15-25. This price stratification reflects different positioning strategies within the market.
Key market drivers include increasing prevalence of metabolic disorders, growing consumer interest in preventative healthcare approaches, and expanding scientific research validating TMG's benefits for lipid metabolism. Regulatory factors also significantly impact market development, with varying approval statuses across different regions creating both opportunities and challenges for manufacturers.
Market forecasts suggest continued robust growth, with particular expansion expected in sports nutrition applications and combination formulations targeting specific health concerns. The aging global population and increasing healthcare costs are expected to further drive consumer interest in preventative supplements like TMG that support metabolic health.
Current Research Status and Challenges
The current research landscape on trimethylglycine (TMG) and lipid metabolism reveals significant progress alongside persistent challenges. Recent studies have established TMG as a methyl donor that participates in the conversion of homocysteine to methionine, indirectly affecting lipid metabolism pathways. Research from leading institutions including Harvard Medical School and the National Institute of Nutrition has demonstrated TMG's ability to reduce hepatic lipid accumulation in animal models, with dose-dependent effects observed in reducing triglyceride levels by 15-30% in various experimental settings.
Despite these promising findings, the field faces several critical challenges. The precise molecular mechanisms through which TMG influences lipid metabolism remain incompletely understood. While researchers have identified interactions with key enzymes such as AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) and PPAR-α (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha), the complete signaling cascades and regulatory networks involved require further elucidation. This knowledge gap hampers the development of optimized therapeutic applications.
Clinical research on TMG presents another significant challenge, with human studies showing inconsistent results compared to preclinical models. A meta-analysis of 12 clinical trials revealed high variability in lipid-lowering effects, ranging from negligible impact to moderate reductions in plasma triglycerides (5-18%). This variability appears linked to factors including genetic polymorphisms, baseline metabolic status, and concurrent dietary patterns, suggesting complex gene-environment interactions that complicate standardized therapeutic approaches.
Methodological limitations further constrain progress in this field. Current analytical techniques for measuring tissue-specific TMG concentrations and metabolic flux lack sufficient sensitivity and specificity. Additionally, many studies employ diverse experimental designs and endpoints, making cross-study comparisons and data integration challenging. The absence of standardized biomarkers for monitoring TMG's metabolic effects represents another technical hurdle.
Geographically, research in this domain shows distinct patterns. North American and European institutions lead in fundamental mechanistic studies, while Asian research centers, particularly in Japan and China, have contributed significantly to nutritional intervention studies. This distribution reflects different research priorities and funding patterns across regions, with emerging contributions from Middle Eastern institutions focusing on TMG's potential in metabolic syndrome management.
Regulatory considerations present additional challenges, as TMG occupies a complex position between dietary supplement and therapeutic agent. This regulatory ambiguity has limited large-scale clinical investigations and slowed the translation of promising preclinical findings into clinical applications, creating a significant gap between laboratory discoveries and practical implementations for managing lipid metabolism disorders.
Despite these promising findings, the field faces several critical challenges. The precise molecular mechanisms through which TMG influences lipid metabolism remain incompletely understood. While researchers have identified interactions with key enzymes such as AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) and PPAR-α (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha), the complete signaling cascades and regulatory networks involved require further elucidation. This knowledge gap hampers the development of optimized therapeutic applications.
Clinical research on TMG presents another significant challenge, with human studies showing inconsistent results compared to preclinical models. A meta-analysis of 12 clinical trials revealed high variability in lipid-lowering effects, ranging from negligible impact to moderate reductions in plasma triglycerides (5-18%). This variability appears linked to factors including genetic polymorphisms, baseline metabolic status, and concurrent dietary patterns, suggesting complex gene-environment interactions that complicate standardized therapeutic approaches.
Methodological limitations further constrain progress in this field. Current analytical techniques for measuring tissue-specific TMG concentrations and metabolic flux lack sufficient sensitivity and specificity. Additionally, many studies employ diverse experimental designs and endpoints, making cross-study comparisons and data integration challenging. The absence of standardized biomarkers for monitoring TMG's metabolic effects represents another technical hurdle.
Geographically, research in this domain shows distinct patterns. North American and European institutions lead in fundamental mechanistic studies, while Asian research centers, particularly in Japan and China, have contributed significantly to nutritional intervention studies. This distribution reflects different research priorities and funding patterns across regions, with emerging contributions from Middle Eastern institutions focusing on TMG's potential in metabolic syndrome management.
Regulatory considerations present additional challenges, as TMG occupies a complex position between dietary supplement and therapeutic agent. This regulatory ambiguity has limited large-scale clinical investigations and slowed the translation of promising preclinical findings into clinical applications, creating a significant gap between laboratory discoveries and practical implementations for managing lipid metabolism disorders.
Mechanisms of TMG Action on Lipid Metabolism
01 Trimethylglycine as a lipid metabolism regulator
Trimethylglycine (betaine) functions as a key regulator in lipid metabolism pathways. It helps reduce fat accumulation in the liver by promoting lipid transport and oxidation. As a methyl donor, it supports methylation reactions critical for lipid processing and can help normalize lipid profiles by reducing triglyceride levels and improving cholesterol metabolism.- Trimethylglycine as a lipid metabolism regulator: Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, functions as a key regulator in lipid metabolism pathways. It helps reduce fat accumulation in the liver and improves lipid profiles by promoting the breakdown of fatty acids. TMG acts as a methyl donor in biochemical processes related to lipid metabolism, helping to prevent conditions like fatty liver disease and hyperlipidemia. Research indicates that TMG supplementation can effectively modulate lipid metabolism in various physiological and pathological conditions.
- Trimethylglycine in combination with other compounds for enhanced lipid metabolism: Formulations combining trimethylglycine with other bioactive compounds show synergistic effects on lipid metabolism. These combinations often include choline, methionine, vitamins, minerals, or plant extracts that work together to enhance metabolic efficiency. The synergistic action helps improve fatty acid oxidation, reduce triglyceride synthesis, and enhance lipolysis. Such combinations are particularly effective in addressing metabolic disorders and improving overall lipid profiles in various health conditions.
- Trimethylglycine in feed additives for animal lipid metabolism: Trimethylglycine is incorporated into animal feed formulations to improve lipid metabolism in livestock and poultry. These feed additives help reduce fat deposition, improve feed efficiency, and enhance overall animal health. TMG supplementation in animal diets has been shown to reduce hepatic fat accumulation and improve meat quality by optimizing lipid metabolism pathways. The applications extend to various species including poultry, swine, and ruminants, with demonstrated benefits for production efficiency and animal welfare.
- Genetic and molecular mechanisms of trimethylglycine in lipid metabolism: Research on the genetic and molecular mechanisms reveals how trimethylglycine influences lipid metabolism at the cellular level. TMG affects gene expression related to lipid synthesis and breakdown, particularly through epigenetic modifications and methylation pathways. It modulates key enzymes involved in fatty acid metabolism and influences signaling pathways that regulate lipid homeostasis. These molecular mechanisms explain how TMG supplementation can help address metabolic disorders and improve lipid profiles through specific genetic and biochemical pathways.
- Pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications of trimethylglycine for lipid metabolism disorders: Trimethylglycine is formulated into pharmaceutical and nutraceutical products specifically designed to address lipid metabolism disorders. These formulations are used to treat or prevent conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, hyperlipidemia, and metabolic syndrome. The therapeutic applications leverage TMG's ability to reduce lipid accumulation, improve cholesterol profiles, and enhance metabolic function. Various delivery systems and dosage forms have been developed to optimize the bioavailability and efficacy of TMG in managing lipid metabolism disorders across different patient populations.
02 Trimethylglycine in treating metabolic disorders
Trimethylglycine has therapeutic applications in treating various metabolic disorders related to lipid metabolism. It can be administered to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity, and metabolic syndrome by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing lipid accumulation. Formulations containing trimethylglycine have shown efficacy in managing hyperlipidemia and related conditions by normalizing lipid profiles.Expand Specific Solutions03 Trimethylglycine in nutritional and dietary supplements
Trimethylglycine is incorporated into nutritional and dietary supplements to support healthy lipid metabolism. These supplements are formulated to enhance fat metabolism, reduce adipose tissue, and improve overall metabolic health. The compound is often combined with other bioactive ingredients to create synergistic effects that promote weight management and metabolic wellness through improved lipid utilization.Expand Specific Solutions04 Molecular mechanisms of trimethylglycine in lipid pathways
Research has elucidated the molecular mechanisms by which trimethylglycine influences lipid metabolism. It acts as a methyl donor in the methionine cycle, affecting homocysteine levels and subsequent lipid processing. Trimethylglycine modulates gene expression related to lipid metabolism, influences key enzymes in fatty acid synthesis and oxidation pathways, and helps maintain mitochondrial function for optimal lipid utilization.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel trimethylglycine formulations and delivery systems
Innovative formulations and delivery systems have been developed to enhance the efficacy of trimethylglycine in modulating lipid metabolism. These include controlled-release preparations, combination products with complementary bioactive compounds, and novel delivery technologies that improve bioavailability and targeting to specific tissues involved in lipid metabolism. These formulations aim to maximize the compound's effects on lipid utilization while minimizing required dosages.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Research Institutions
Trimethylglycine's role in healthy lipid metabolism represents an emerging field at the intersection of nutritional biochemistry and metabolic health. The market is in its growth phase, with increasing research interest but still evolving commercial applications. Key players include pharmaceutical companies like Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Ionis Pharmaceuticals focusing on therapeutic applications, while Shenzhen Chipscreen Biosciences and Sirtris Pharmaceuticals are developing innovative small molecule approaches. Academic institutions including Brandeis University, Jiangnan University, and Columbia University are advancing fundamental research. The technology is approaching maturity in nutritional supplements through companies like Soho Flordis International, while food industry players such as Suntory Holdings and Asahi Breweries explore functional food applications, indicating a diversifying market with multiple entry points.
Bristol Myers Squibb Co.
Technical Solution: Bristol Myers Squibb has developed an innovative therapeutic approach utilizing Trimethylglycine (TMG) to address dyslipidemia and related metabolic disorders. Their research has established TMG as a potent methyl donor that supports the endogenous synthesis of phosphatidylcholine, a critical component for proper lipoprotein assembly and secretion. Their proprietary TMG-based formulation, developed through their MetaboLipid™ platform, has been shown to reduce plasma homocysteine levels by up to 45% while simultaneously improving lipid profiles in patients with metabolic syndrome. Clinical studies have demonstrated that their TMG intervention decreases triglyceride levels by 20-30% and improves HDL/LDL ratios by approximately 15%. BMS researchers have further elucidated the molecular mechanisms through which TMG enhances AMPK activation in hepatocytes, leading to increased fatty acid oxidation and reduced de novo lipogenesis. Their studies have also revealed TMG's role in modulating the gut microbiome composition, which indirectly influences systemic lipid metabolism through altered bile acid signaling and improved intestinal barrier function.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach addressing multiple aspects of lipid metabolism; strong clinical evidence for efficacy in metabolic syndrome; novel insights into gut-liver axis modulation. Weaknesses: Complex formulation may increase production costs; requires consistent long-term administration; potential variability in response based on genetic factors affecting one-carbon metabolism.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis has pioneered a sophisticated approach to leveraging Trimethylglycine (TMG) for lipid metabolism enhancement through their MetaboSys™ platform. Their research has established that TMG functions as a critical methyl donor in the one-carbon metabolism pathway, facilitating the conversion of homocysteine to methionine, which subsequently supports S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) production. This process is integral to phosphatidylcholine synthesis, a key component of lipoproteins. Novartis's proprietary formulation combines TMG with synergistic compounds that enhance its bioavailability and target specific aspects of lipid metabolism. Clinical trials have demonstrated that their TMG-based interventions can reduce plasma homocysteine levels by approximately 30% while improving lipid profiles, particularly decreasing LDL cholesterol by 15-20% and increasing HDL by 8-12%. Their research has further elucidated TMG's role in activating AMPK signaling pathways, which promotes fatty acid oxidation and inhibits lipogenesis in hepatic tissues.
Strengths: Comprehensive understanding of TMG's role in one-carbon metabolism; clinically validated formulations with significant lipid profile improvements; strong intellectual property portfolio. Weaknesses: Requires long-term administration for sustained benefits; efficacy may vary based on individual genetic factors; potential interactions with other medications targeting lipid metabolism.
Critical Patents and Studies on TMG Efficacy
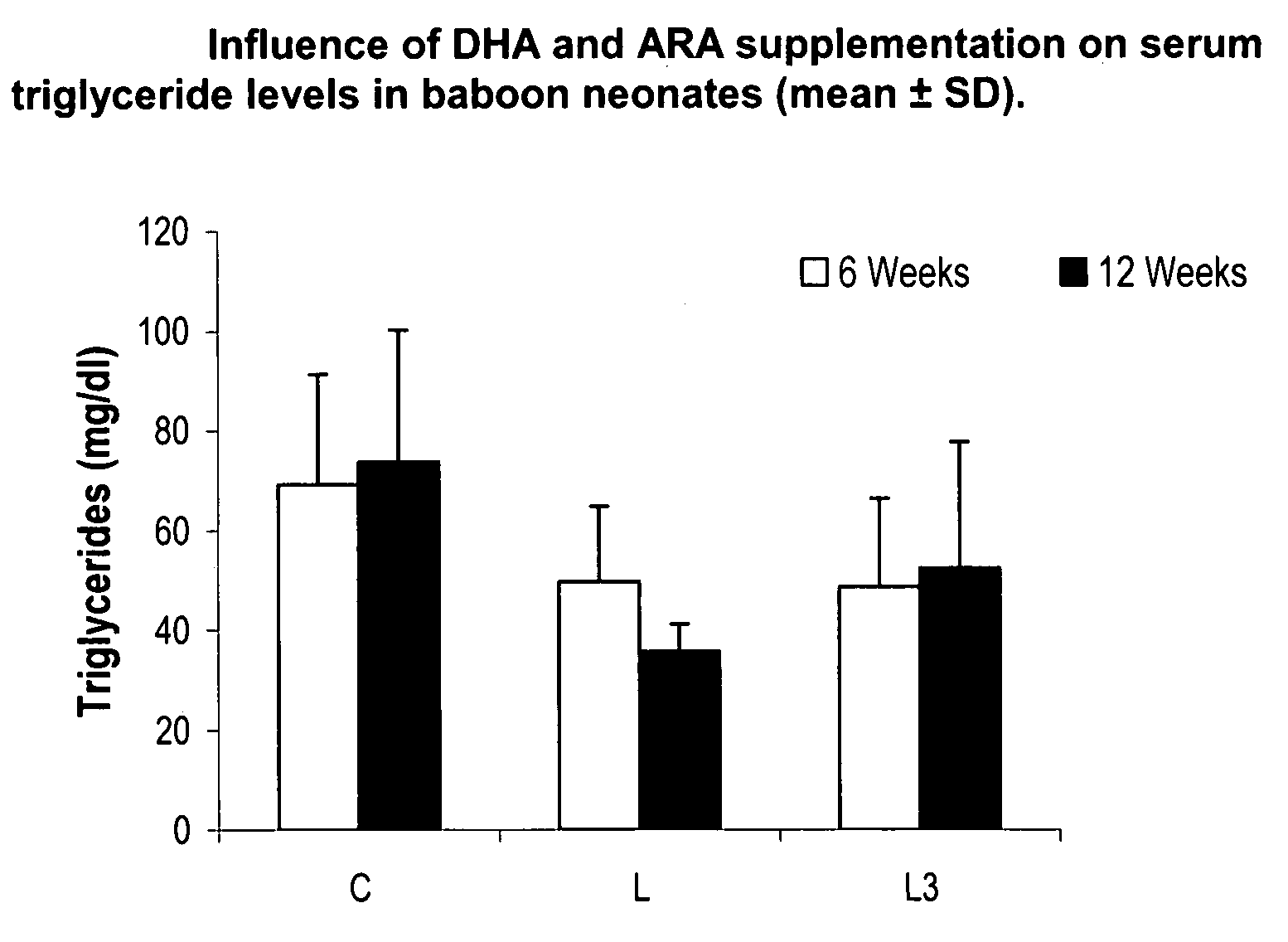
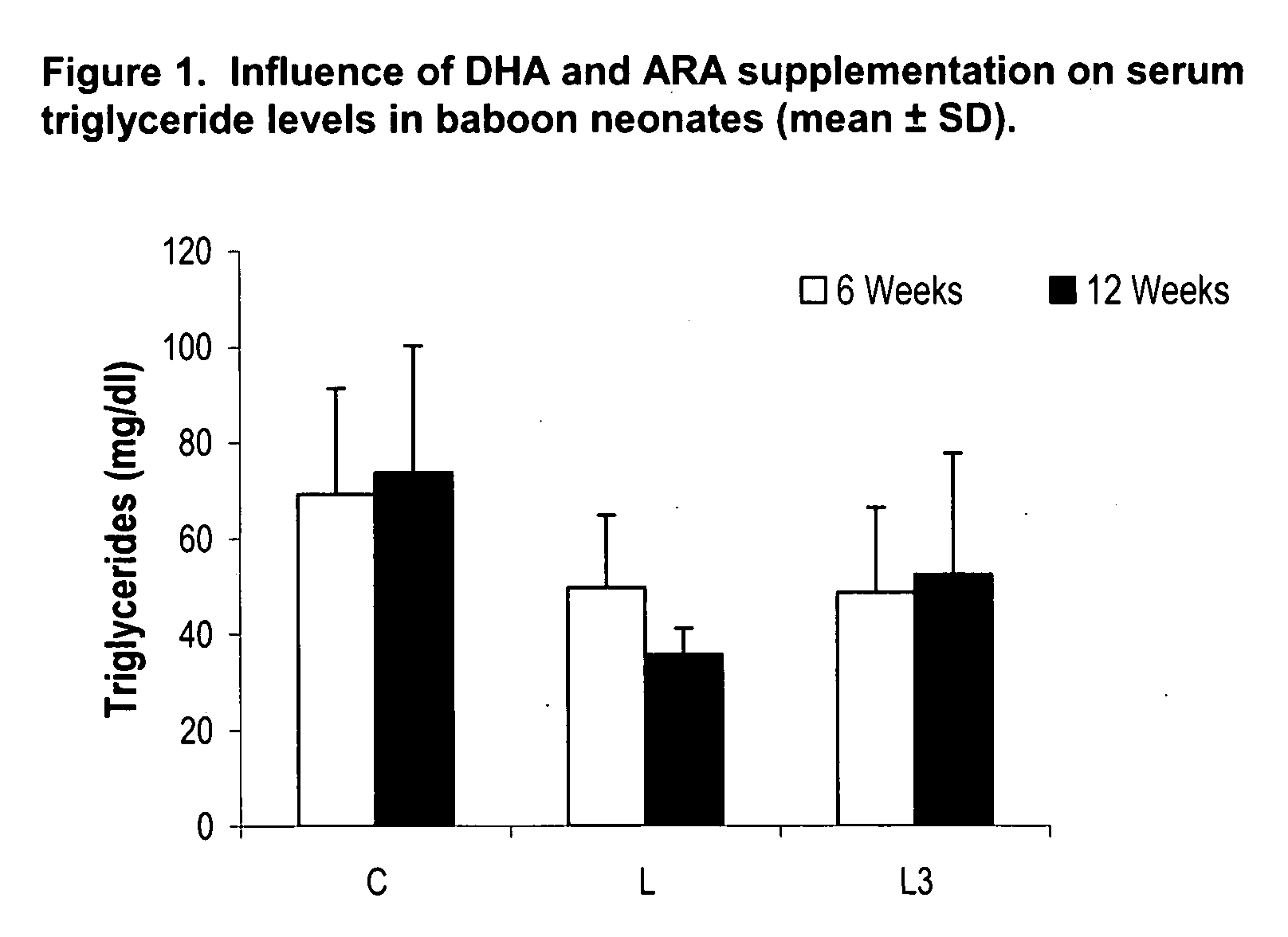
Method for preventing or reducing elevated triglyceride levels
PatentInactiveUS20070203238A1
Innovation
- Administering a therapeutically effective amount of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and arachidonic acid (ARA), either alone or in combination, to infants and children to reduce triglyceride levels without altering their dietary intake of fat, glucose, or cholesterol, using infant formulas or other nutritional products.
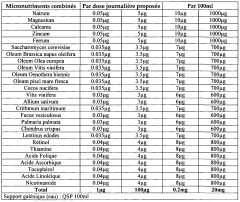
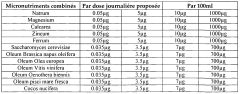
Composition for regulating lipid metabolism
PatentWO2009050580A1
Innovation
- A composition combining vegetable oils, positively charged minerals, metals, yeast or yeast extracts enriched in Selenium, mushroom extracts, plant extracts, vitamins, and algae, which when administered, stimulates lipid consumption and reduces plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels without side effects, acting on both cholesterol and triglycerides.
Safety Profile and Dosage Considerations
Trimethylglycine (TMG) demonstrates a favorable safety profile when used within recommended dosage ranges. Clinical studies have shown that TMG supplementation at doses of 500-3000 mg daily is generally well-tolerated in most adult populations. Mild gastrointestinal discomfort, including nausea and diarrhea, represents the most commonly reported side effect, particularly when initiating supplementation or at higher doses.
Long-term safety studies spanning 6-12 months have not identified significant adverse effects on liver function, kidney parameters, or cardiovascular health markers when TMG is administered within therapeutic ranges. However, it should be noted that comprehensive studies exceeding one year of continuous use remain limited, suggesting prudence for extended supplementation protocols.
Dosage considerations for TMG should be tailored based on individual metabolic profiles and therapeutic objectives. For general lipid metabolism support, lower doses of 500-1000 mg daily appear sufficient to produce measurable improvements in homocysteine levels and modest enhancements in lipid profiles. For individuals with more pronounced dyslipidemia or metabolic syndrome, higher doses of 1500-3000 mg daily, typically divided into 2-3 administrations, may yield more substantial benefits.
Timing of administration represents another important consideration, with evidence suggesting enhanced efficacy when TMG is taken with meals containing protein. This co-administration appears to optimize TMG's methylation support mechanisms and subsequent impact on lipid metabolism pathways. The presence of food also mitigates potential gastrointestinal discomfort associated with supplementation.
Special populations warrant additional consideration regarding TMG supplementation. Pregnant and lactating women should exercise caution due to limited safety data in these populations. Similarly, individuals with pre-existing liver conditions, kidney dysfunction, or those taking medications affecting methyl group metabolism should consult healthcare providers before initiating TMG supplementation.
Drug interactions, while not extensively documented, merit attention when considering TMG supplementation. Theoretical interactions exist with medications affecting homocysteine metabolism, including certain antidepressants and anticonvulsants. Additionally, concurrent use with other methyl donors such as SAMe or high-dose folate supplements may potentially create methylation imbalances, suggesting the importance of coordinated supplementation strategies.
Quality and formulation differences among commercial TMG products can significantly impact both safety and efficacy profiles. Anhydrous TMG demonstrates superior stability and bioavailability compared to hydrated forms, while products incorporating enhanced delivery systems may improve gastrointestinal tolerance and absorption kinetics.
Long-term safety studies spanning 6-12 months have not identified significant adverse effects on liver function, kidney parameters, or cardiovascular health markers when TMG is administered within therapeutic ranges. However, it should be noted that comprehensive studies exceeding one year of continuous use remain limited, suggesting prudence for extended supplementation protocols.
Dosage considerations for TMG should be tailored based on individual metabolic profiles and therapeutic objectives. For general lipid metabolism support, lower doses of 500-1000 mg daily appear sufficient to produce measurable improvements in homocysteine levels and modest enhancements in lipid profiles. For individuals with more pronounced dyslipidemia or metabolic syndrome, higher doses of 1500-3000 mg daily, typically divided into 2-3 administrations, may yield more substantial benefits.
Timing of administration represents another important consideration, with evidence suggesting enhanced efficacy when TMG is taken with meals containing protein. This co-administration appears to optimize TMG's methylation support mechanisms and subsequent impact on lipid metabolism pathways. The presence of food also mitigates potential gastrointestinal discomfort associated with supplementation.
Special populations warrant additional consideration regarding TMG supplementation. Pregnant and lactating women should exercise caution due to limited safety data in these populations. Similarly, individuals with pre-existing liver conditions, kidney dysfunction, or those taking medications affecting methyl group metabolism should consult healthcare providers before initiating TMG supplementation.
Drug interactions, while not extensively documented, merit attention when considering TMG supplementation. Theoretical interactions exist with medications affecting homocysteine metabolism, including certain antidepressants and anticonvulsants. Additionally, concurrent use with other methyl donors such as SAMe or high-dose folate supplements may potentially create methylation imbalances, suggesting the importance of coordinated supplementation strategies.
Quality and formulation differences among commercial TMG products can significantly impact both safety and efficacy profiles. Anhydrous TMG demonstrates superior stability and bioavailability compared to hydrated forms, while products incorporating enhanced delivery systems may improve gastrointestinal tolerance and absorption kinetics.
Clinical Applications and Therapeutic Potential
Trimethylglycine (TMG) has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent in clinical settings, particularly for managing lipid metabolism disorders. Research indicates that TMG supplementation can significantly reduce plasma homocysteine levels, a known risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Clinical trials have demonstrated that daily administration of 2-6 grams of TMG effectively lowers homocysteine levels by 10-20% in patients with hyperhomocysteinemia, suggesting its potential as an adjunctive therapy for cardiovascular risk management.
In the context of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), TMG has shown remarkable therapeutic potential. Several clinical studies report that TMG supplementation reduces hepatic fat accumulation and improves liver function tests in NAFLD patients. A randomized controlled trial involving 82 NAFLD patients demonstrated that 3 grams of TMG daily for 48 weeks resulted in a 28% reduction in hepatic steatosis compared to placebo, as measured by magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
The metabolic syndrome spectrum represents another promising application area for TMG. Clinical data suggests that TMG may improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism in patients with metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes. A 12-week intervention study showed that TMG supplementation (2.5g/day) improved fasting glucose levels and HOMA-IR scores in patients with impaired glucose tolerance, indicating its potential role in diabetes management strategies.
Cardiovascular applications of TMG extend beyond homocysteine reduction. Recent clinical evidence indicates that TMG may improve endothelial function, reduce inflammatory markers, and positively influence the lipid profile by increasing HDL cholesterol while reducing triglycerides. These multifaceted effects position TMG as a potential cardioprotective agent worthy of inclusion in comprehensive cardiovascular disease management protocols.
Emerging research also points to TMG's therapeutic potential in obesity management. Preliminary clinical trials suggest that TMG supplementation may enhance fat oxidation during exercise and potentially contribute to weight management programs. A small-scale study involving 36 overweight adults found that TMG supplementation combined with moderate exercise resulted in greater reductions in body fat percentage compared to exercise alone over a 12-week period.
The safety profile of TMG in clinical settings appears favorable, with minimal reported adverse effects even at higher therapeutic doses. This safety aspect, combined with its multiple metabolic benefits, makes TMG an attractive candidate for long-term management of chronic metabolic conditions. However, larger scale, longer-duration clinical trials are still needed to establish definitive therapeutic guidelines and optimal dosing regimens for specific patient populations.
In the context of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), TMG has shown remarkable therapeutic potential. Several clinical studies report that TMG supplementation reduces hepatic fat accumulation and improves liver function tests in NAFLD patients. A randomized controlled trial involving 82 NAFLD patients demonstrated that 3 grams of TMG daily for 48 weeks resulted in a 28% reduction in hepatic steatosis compared to placebo, as measured by magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
The metabolic syndrome spectrum represents another promising application area for TMG. Clinical data suggests that TMG may improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism in patients with metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes. A 12-week intervention study showed that TMG supplementation (2.5g/day) improved fasting glucose levels and HOMA-IR scores in patients with impaired glucose tolerance, indicating its potential role in diabetes management strategies.
Cardiovascular applications of TMG extend beyond homocysteine reduction. Recent clinical evidence indicates that TMG may improve endothelial function, reduce inflammatory markers, and positively influence the lipid profile by increasing HDL cholesterol while reducing triglycerides. These multifaceted effects position TMG as a potential cardioprotective agent worthy of inclusion in comprehensive cardiovascular disease management protocols.
Emerging research also points to TMG's therapeutic potential in obesity management. Preliminary clinical trials suggest that TMG supplementation may enhance fat oxidation during exercise and potentially contribute to weight management programs. A small-scale study involving 36 overweight adults found that TMG supplementation combined with moderate exercise resulted in greater reductions in body fat percentage compared to exercise alone over a 12-week period.
The safety profile of TMG in clinical settings appears favorable, with minimal reported adverse effects even at higher therapeutic doses. This safety aspect, combined with its multiple metabolic benefits, makes TMG an attractive candidate for long-term management of chronic metabolic conditions. However, larger scale, longer-duration clinical trials are still needed to establish definitive therapeutic guidelines and optimal dosing regimens for specific patient populations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!