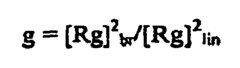Innovations in LDPE Barrier Film Technologies
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Barrier Film Evolution and Objectives
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) barrier films have undergone significant evolution since their inception in the 1930s. Initially developed as a packaging material, LDPE films have continuously improved to meet the growing demands of various industries, particularly in food packaging and preservation.
The early stages of LDPE barrier film development focused primarily on enhancing basic properties such as tensile strength, tear resistance, and moisture barrier capabilities. As the technology progressed, researchers and manufacturers began to explore ways to improve the gas barrier properties of LDPE films, recognizing the critical role these properties play in extending the shelf life of packaged products.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the introduction of coextrusion technology marked a significant milestone in LDPE barrier film evolution. This innovation allowed for the creation of multi-layer films, combining LDPE with other materials to achieve superior barrier properties. The ability to incorporate different polymers and additives into a single film structure opened up new possibilities for customizing barrier performance to specific application requirements.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a surge in research focused on improving the oxygen barrier properties of LDPE films. This period witnessed the development of various coating technologies and the incorporation of nanoparticles to enhance gas barrier performance. These advancements were driven by the increasing demand for extended shelf life in food packaging and the need to protect sensitive products from oxidation.
In recent years, the focus of LDPE barrier film technology has shifted towards sustainability and environmental concerns. The industry has been exploring bio-based and biodegradable alternatives to traditional LDPE, as well as developing more efficient recycling processes for multi-layer barrier films. This shift reflects the growing global emphasis on reducing plastic waste and promoting circular economy principles.
The current objectives in LDPE barrier film technology are multifaceted. Researchers and manufacturers are striving to develop films with even higher barrier properties while maintaining or improving other essential characteristics such as flexibility, transparency, and processability. There is also a strong push towards creating more sustainable barrier solutions, including the development of mono-material structures that are easier to recycle.
Another key objective is the integration of active and intelligent packaging concepts into LDPE barrier films. This includes the incorporation of antimicrobial agents, oxygen scavengers, and smart indicators to further extend product shelf life and provide real-time information on product freshness and quality.
As we look to the future, the evolution of LDPE barrier films is expected to continue, driven by advancements in material science, nanotechnology, and sustainable manufacturing processes. The ultimate goal is to create barrier films that not only provide superior protection for packaged products but also align with global sustainability objectives and circular economy principles.
The early stages of LDPE barrier film development focused primarily on enhancing basic properties such as tensile strength, tear resistance, and moisture barrier capabilities. As the technology progressed, researchers and manufacturers began to explore ways to improve the gas barrier properties of LDPE films, recognizing the critical role these properties play in extending the shelf life of packaged products.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the introduction of coextrusion technology marked a significant milestone in LDPE barrier film evolution. This innovation allowed for the creation of multi-layer films, combining LDPE with other materials to achieve superior barrier properties. The ability to incorporate different polymers and additives into a single film structure opened up new possibilities for customizing barrier performance to specific application requirements.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a surge in research focused on improving the oxygen barrier properties of LDPE films. This period witnessed the development of various coating technologies and the incorporation of nanoparticles to enhance gas barrier performance. These advancements were driven by the increasing demand for extended shelf life in food packaging and the need to protect sensitive products from oxidation.
In recent years, the focus of LDPE barrier film technology has shifted towards sustainability and environmental concerns. The industry has been exploring bio-based and biodegradable alternatives to traditional LDPE, as well as developing more efficient recycling processes for multi-layer barrier films. This shift reflects the growing global emphasis on reducing plastic waste and promoting circular economy principles.
The current objectives in LDPE barrier film technology are multifaceted. Researchers and manufacturers are striving to develop films with even higher barrier properties while maintaining or improving other essential characteristics such as flexibility, transparency, and processability. There is also a strong push towards creating more sustainable barrier solutions, including the development of mono-material structures that are easier to recycle.
Another key objective is the integration of active and intelligent packaging concepts into LDPE barrier films. This includes the incorporation of antimicrobial agents, oxygen scavengers, and smart indicators to further extend product shelf life and provide real-time information on product freshness and quality.
As we look to the future, the evolution of LDPE barrier films is expected to continue, driven by advancements in material science, nanotechnology, and sustainable manufacturing processes. The ultimate goal is to create barrier films that not only provide superior protection for packaged products but also align with global sustainability objectives and circular economy principles.
Market Demand Analysis for Advanced Packaging Solutions
The global packaging industry has witnessed a significant shift towards advanced packaging solutions, driven by increasing consumer demand for convenience, sustainability, and product protection. LDPE barrier films, as a key component in this sector, have seen growing market demand due to their excellent moisture barrier properties, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. The food and beverage industry, in particular, has been a major driver of this demand, as manufacturers seek to extend product shelf life and maintain quality during transportation and storage.
Market research indicates that the LDPE barrier film market is expected to experience substantial growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the rising consumption of packaged foods, especially in developing economies, and the increasing preference for flexible packaging solutions. The convenience factor associated with lightweight, easy-to-carry packaging has also contributed to the surge in demand for LDPE barrier films.
In the food packaging sector, LDPE barrier films are widely used for products such as snacks, confectionery, and frozen foods. The ability of these films to provide excellent moisture resistance and maintain product freshness has made them a preferred choice among food manufacturers. Additionally, the pharmaceutical and personal care industries have shown increased interest in LDPE barrier films for their packaging needs, further expanding the market potential.
The demand for sustainable packaging solutions has also influenced the LDPE barrier film market. Consumers and regulatory bodies are increasingly pushing for environmentally friendly packaging options. This has led to innovations in LDPE barrier film technologies, focusing on recyclability and the incorporation of bio-based materials. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to create barrier films that maintain their protective properties while reducing environmental impact.
E-commerce growth has further boosted the demand for advanced packaging solutions, including LDPE barrier films. The need for robust packaging that can withstand the rigors of shipping and handling has become crucial in the online retail space. LDPE barrier films offer the necessary protection for a wide range of products, from electronics to perishable goods, making them an essential component in e-commerce packaging strategies.
The healthcare sector has also emerged as a significant market for LDPE barrier films, particularly in the wake of the global pandemic. The increased focus on hygiene and product safety has led to a higher demand for packaging materials that offer superior barrier properties against contaminants. LDPE barrier films have found applications in medical device packaging, pharmaceutical blister packs, and other healthcare-related products, contributing to market growth in this sector.
Market research indicates that the LDPE barrier film market is expected to experience substantial growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the rising consumption of packaged foods, especially in developing economies, and the increasing preference for flexible packaging solutions. The convenience factor associated with lightweight, easy-to-carry packaging has also contributed to the surge in demand for LDPE barrier films.
In the food packaging sector, LDPE barrier films are widely used for products such as snacks, confectionery, and frozen foods. The ability of these films to provide excellent moisture resistance and maintain product freshness has made them a preferred choice among food manufacturers. Additionally, the pharmaceutical and personal care industries have shown increased interest in LDPE barrier films for their packaging needs, further expanding the market potential.
The demand for sustainable packaging solutions has also influenced the LDPE barrier film market. Consumers and regulatory bodies are increasingly pushing for environmentally friendly packaging options. This has led to innovations in LDPE barrier film technologies, focusing on recyclability and the incorporation of bio-based materials. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to create barrier films that maintain their protective properties while reducing environmental impact.
E-commerce growth has further boosted the demand for advanced packaging solutions, including LDPE barrier films. The need for robust packaging that can withstand the rigors of shipping and handling has become crucial in the online retail space. LDPE barrier films offer the necessary protection for a wide range of products, from electronics to perishable goods, making them an essential component in e-commerce packaging strategies.
The healthcare sector has also emerged as a significant market for LDPE barrier films, particularly in the wake of the global pandemic. The increased focus on hygiene and product safety has led to a higher demand for packaging materials that offer superior barrier properties against contaminants. LDPE barrier films have found applications in medical device packaging, pharmaceutical blister packs, and other healthcare-related products, contributing to market growth in this sector.
Current LDPE Barrier Film Challenges
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) barrier films have been widely used in packaging applications due to their excellent moisture barrier properties and cost-effectiveness. However, as industry demands evolve and environmental concerns grow, LDPE barrier films face several significant challenges that need to be addressed.
One of the primary challenges is improving the oxygen barrier properties of LDPE films. While LDPE excels in moisture resistance, its performance in preventing oxygen permeation is relatively poor compared to other materials like EVOH or PET. This limitation restricts its use in applications requiring extended shelf life for oxygen-sensitive products, such as certain foods or pharmaceuticals.
Another critical challenge is enhancing the mechanical properties of LDPE barrier films without compromising their barrier performance. Current LDPE films often lack the necessary strength and puncture resistance for certain demanding applications, leading to potential package failures and reduced product protection.
The recyclability of LDPE barrier films presents a significant hurdle in the current sustainability-focused market. Many LDPE barrier films incorporate multiple layers or additives to achieve desired properties, making them difficult to recycle through conventional methods. This challenge is particularly pressing as regulations and consumer preferences increasingly favor easily recyclable packaging materials.
Heat resistance is another area where LDPE barrier films face limitations. The relatively low melting point of LDPE restricts its use in hot-fill applications or products that may be exposed to high temperatures during processing or use. Improving the thermal stability of LDPE barrier films without sacrificing their flexibility and barrier properties remains a significant technical challenge.
The scalability and cost-effectiveness of producing high-performance LDPE barrier films also pose challenges. While various methods to enhance LDPE properties exist, many are not economically viable for large-scale production or significantly increase the overall cost of the packaging material.
Lastly, the industry faces the challenge of reducing the overall thickness of LDPE barrier films while maintaining or improving their performance. Thinner films are desirable for reducing material usage and improving flexibility, but achieving this without compromising barrier properties or mechanical strength remains a significant technical hurdle.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches in polymer science, material engineering, and processing technologies. The development of new additives, novel blending techniques, and advanced surface treatments are among the areas being explored to overcome these limitations and expand the capabilities of LDPE barrier films.
One of the primary challenges is improving the oxygen barrier properties of LDPE films. While LDPE excels in moisture resistance, its performance in preventing oxygen permeation is relatively poor compared to other materials like EVOH or PET. This limitation restricts its use in applications requiring extended shelf life for oxygen-sensitive products, such as certain foods or pharmaceuticals.
Another critical challenge is enhancing the mechanical properties of LDPE barrier films without compromising their barrier performance. Current LDPE films often lack the necessary strength and puncture resistance for certain demanding applications, leading to potential package failures and reduced product protection.
The recyclability of LDPE barrier films presents a significant hurdle in the current sustainability-focused market. Many LDPE barrier films incorporate multiple layers or additives to achieve desired properties, making them difficult to recycle through conventional methods. This challenge is particularly pressing as regulations and consumer preferences increasingly favor easily recyclable packaging materials.
Heat resistance is another area where LDPE barrier films face limitations. The relatively low melting point of LDPE restricts its use in hot-fill applications or products that may be exposed to high temperatures during processing or use. Improving the thermal stability of LDPE barrier films without sacrificing their flexibility and barrier properties remains a significant technical challenge.
The scalability and cost-effectiveness of producing high-performance LDPE barrier films also pose challenges. While various methods to enhance LDPE properties exist, many are not economically viable for large-scale production or significantly increase the overall cost of the packaging material.
Lastly, the industry faces the challenge of reducing the overall thickness of LDPE barrier films while maintaining or improving their performance. Thinner films are desirable for reducing material usage and improving flexibility, but achieving this without compromising barrier properties or mechanical strength remains a significant technical hurdle.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches in polymer science, material engineering, and processing technologies. The development of new additives, novel blending techniques, and advanced surface treatments are among the areas being explored to overcome these limitations and expand the capabilities of LDPE barrier films.
Existing LDPE Barrier Film Solutions
01 Composition of LDPE barrier films
LDPE barrier films can be enhanced by incorporating various additives and modifiers. These may include nanoparticles, compatibilizers, or other polymers to improve barrier properties against gases, moisture, and other substances. The specific composition can be tailored to meet the desired barrier requirements for different applications.- LDPE blends for improved barrier properties: Blending LDPE with other polymers or additives can enhance barrier properties. These blends may include combinations with HDPE, LLDPE, or various nanocomposites to create films with improved gas and moisture barrier characteristics. The resulting films often exhibit better mechanical properties and increased resistance to permeation.
- Multilayer LDPE barrier films: Multilayer structures incorporating LDPE layers can significantly improve barrier properties. These films often include layers of different materials, such as EVOH or nylon, sandwiched between LDPE layers. The combination of materials allows for customization of barrier properties against specific gases or moisture while maintaining the desirable characteristics of LDPE.
- Surface treatment of LDPE films: Various surface treatments can be applied to LDPE films to enhance their barrier properties. These may include plasma treatment, corona discharge, or the application of coatings. Such treatments can modify the surface energy of the film, improving its ability to resist permeation of gases and moisture.
- Nanocomposite LDPE barrier films: Incorporating nanoparticles into LDPE films can significantly improve their barrier properties. Common nanofillers include clay, silica, and metal oxides. These nanocomposites create tortuous paths for gas and moisture molecules, effectively reducing permeation rates and enhancing the overall barrier performance of the film.
- Orientation techniques for LDPE barrier films: Applying orientation techniques during film production can enhance the barrier properties of LDPE films. Methods such as biaxial orientation or stretching can align polymer chains, reducing free volume and improving resistance to gas and moisture permeation. These techniques often result in films with improved mechanical properties as well.
02 Multi-layer structure for improved barrier properties
LDPE barrier films can be designed with multiple layers to enhance their barrier properties. This may involve combining LDPE with other materials such as EVOH, nylon, or metallized layers. The multi-layer structure allows for the combination of different barrier properties, resulting in a film with superior overall performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface treatment and coating techniques
Various surface treatment and coating techniques can be applied to LDPE films to enhance their barrier properties. These may include plasma treatment, corona discharge, or the application of specialized coatings. Such treatments can improve the film's resistance to gas and moisture permeation, as well as enhance its adhesion properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Orientation and crystallinity control
The barrier properties of LDPE films can be improved by controlling the orientation and crystallinity of the polymer chains. This can be achieved through various processing techniques such as biaxial orientation or controlled cooling. Optimizing these parameters can lead to a more densely packed structure, reducing permeability to gases and moisture.Expand Specific Solutions05 Blending with other polymers
LDPE can be blended with other polymers to create barrier films with enhanced properties. This may include blending with higher-density polyethylenes, ionomers, or other compatible polymers. The resulting blends can offer improved barrier characteristics while maintaining the desirable properties of LDPE, such as flexibility and processability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in LDPE Barrier Film Industry
The LDPE barrier film technology market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for high-performance packaging solutions across various industries. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with major players like Dow Global Technologies, SABIC, and LyondellBasell (parent of Basell Polyolefine) leading innovation. These companies, along with others such as Braskem and LG Chem, are investing heavily in R&D to improve barrier properties, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness of LDPE films. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established petrochemical giants and specialized materials companies, all vying for market share through technological differentiation and strategic partnerships.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed advanced LDPE barrier film technologies, focusing on enhancing gas and moisture barrier properties. Their innovation includes a multi-layer film structure with a core LDPE layer sandwiched between two barrier layers, typically composed of EVOH or nylon[1]. This structure significantly improves oxygen and moisture barrier performance. Dow has also introduced additives to enhance the film's mechanical properties and processability. Their ELITE™ Enhanced Polyethylene Resins offer improved toughness and optical properties, making them suitable for high-performance packaging applications[2]. Additionally, Dow has made strides in sustainability by developing recyclable barrier films that maintain high performance while reducing environmental impact[3].
Strengths: Superior barrier properties, enhanced mechanical strength, and improved sustainability. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and complexity in recycling multi-layer structures.
SABIC Global Technologies BV
Technical Solution: SABIC has innovated in LDPE barrier film technologies by developing a range of specialized resins and additives. Their LDPE portfolio includes grades specifically designed for extrusion coating and lamination in flexible packaging[4]. SABIC's approach focuses on optimizing the molecular structure of LDPE to enhance barrier properties while maintaining good processability. They have introduced metallocene-based LDPE grades that offer improved seal strength and hot tack performance, crucial for packaging integrity[5]. SABIC has also developed compatibilizer technologies to improve the adhesion between LDPE and barrier materials like EVOH, enhancing overall film performance. In line with sustainability trends, SABIC is working on bio-based LDPE alternatives and recyclable barrier film solutions[6].
Strengths: Wide range of specialized grades, strong focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: May face challenges in competing with established market leaders in certain applications.
Core Innovations in LDPE Barrier Film Technology
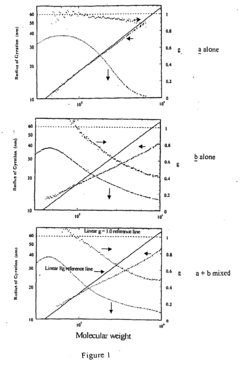
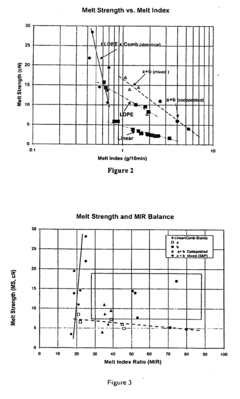
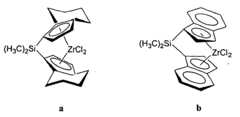
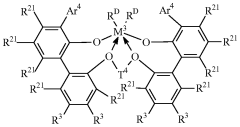
Linear low density polyethylenes with high melt strength and high melt index ratio
PatentInactiveEP1448632B1
Innovation
- A substantially non-blended LLDPE with narrow molecular weight distribution is produced through gas phase polymerization of ethylene and an α-olefin using a supported metallocene catalyst system, comprising indenyl or tetrahydroindenyl metallocenes on inorganic silica or oxide supports, which enhances melt strength and shear thinning without the need for blending with branched polymers.
Multi-layered shrink films
PatentWO2013056466A1
Innovation
- A multi-layered shrink film comprising at least three layers, including two skin layers and one core layer, where at least one layer is made from an ethylene-based polymer composition with specific properties such as Comonomer Distribution Constant (CDC) between 75 to 220, vinyl unsaturation of 30 to 100 vinyls per million carbon atoms, zero shear viscosity ratio (ZSVR) from 2.5 to 15, density between 0.924 to 0.940 g/cm3, and molecular weight distributions, which enhances stiffness and clarity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact and sustainability considerations of LDPE barrier film technologies have become increasingly important in recent years. As consumers and regulators demand more eco-friendly packaging solutions, the industry is focusing on developing innovative approaches to reduce the environmental footprint of these films.
One of the primary concerns is the end-of-life disposal of LDPE barrier films. Traditional LDPE films are not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. To address this issue, researchers are exploring biodegradable alternatives that maintain the barrier properties of LDPE while reducing environmental persistence. Some promising developments include the incorporation of bio-based materials and the use of additives that enhance biodegradability without compromising film performance.
Recycling is another crucial aspect of sustainability for LDPE barrier films. The multi-layer structure of these films often makes recycling challenging, as different materials need to be separated. Innovations in this area include the development of mono-material structures that maintain barrier properties while being easier to recycle. Additionally, advanced sorting and recycling technologies are being implemented to improve the recovery and reuse of LDPE barrier films.
The production process of LDPE barrier films also has significant environmental implications. Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with film manufacturing are areas of concern. To address this, manufacturers are investing in more energy-efficient production methods and exploring the use of renewable energy sources in their operations. Some companies are also implementing closed-loop systems to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency during production.
Raw material sourcing is another critical consideration in the sustainability of LDPE barrier films. The petroleum-based nature of traditional LDPE raises concerns about resource depletion and carbon footprint. Innovations in this area include the development of bio-based alternatives derived from renewable resources such as plant-based feedstocks. These materials aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels while maintaining the desired barrier properties.
The overall life cycle impact of LDPE barrier films is being scrutinized through comprehensive life cycle assessments (LCAs). These studies evaluate the environmental impact from raw material extraction to disposal, helping identify areas for improvement. Results from LCAs are driving innovations in film design, production processes, and end-of-life management strategies to minimize the overall environmental footprint of these products.
As the industry continues to innovate, there is a growing focus on balancing performance requirements with environmental considerations. This holistic approach to sustainability in LDPE barrier film technologies is essential for meeting the evolving demands of consumers, regulators, and the environment.
One of the primary concerns is the end-of-life disposal of LDPE barrier films. Traditional LDPE films are not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. To address this issue, researchers are exploring biodegradable alternatives that maintain the barrier properties of LDPE while reducing environmental persistence. Some promising developments include the incorporation of bio-based materials and the use of additives that enhance biodegradability without compromising film performance.
Recycling is another crucial aspect of sustainability for LDPE barrier films. The multi-layer structure of these films often makes recycling challenging, as different materials need to be separated. Innovations in this area include the development of mono-material structures that maintain barrier properties while being easier to recycle. Additionally, advanced sorting and recycling technologies are being implemented to improve the recovery and reuse of LDPE barrier films.
The production process of LDPE barrier films also has significant environmental implications. Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with film manufacturing are areas of concern. To address this, manufacturers are investing in more energy-efficient production methods and exploring the use of renewable energy sources in their operations. Some companies are also implementing closed-loop systems to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency during production.
Raw material sourcing is another critical consideration in the sustainability of LDPE barrier films. The petroleum-based nature of traditional LDPE raises concerns about resource depletion and carbon footprint. Innovations in this area include the development of bio-based alternatives derived from renewable resources such as plant-based feedstocks. These materials aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels while maintaining the desired barrier properties.
The overall life cycle impact of LDPE barrier films is being scrutinized through comprehensive life cycle assessments (LCAs). These studies evaluate the environmental impact from raw material extraction to disposal, helping identify areas for improvement. Results from LCAs are driving innovations in film design, production processes, and end-of-life management strategies to minimize the overall environmental footprint of these products.
As the industry continues to innovate, there is a growing focus on balancing performance requirements with environmental considerations. This holistic approach to sustainability in LDPE barrier film technologies is essential for meeting the evolving demands of consumers, regulators, and the environment.
Regulatory Landscape for Food Packaging Materials
The regulatory landscape for food packaging materials, including LDPE barrier films, is complex and constantly evolving. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing food packaging materials. The FDA's regulations are outlined in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), specifically in 21 CFR 174-179, which covers indirect food additives and food contact substances.
For LDPE barrier films, manufacturers must ensure compliance with FDA regulations, particularly 21 CFR 177.1520, which pertains to olefin polymers. This regulation specifies the permissible raw materials, additives, and processing aids that can be used in the production of LDPE films intended for food contact. Additionally, any new additives or modifications to the film composition must undergo a Food Contact Notification (FCN) process or obtain approval through a Food Additive Petition.
In the European Union, the regulatory framework for food packaging materials is governed by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the European Commission. The primary regulation is EC 1935/2004, which establishes general principles for all food contact materials. Specific to plastic materials, including LDPE films, is EU Regulation 10/2011, which provides a positive list of authorized substances and sets migration limits for various components.
Japan's regulatory system for food packaging materials is administered by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW). The Food Sanitation Act and its associated regulations outline the requirements for food contact materials, including LDPE barrier films. Manufacturers must ensure compliance with the Positive List System for food contact materials, which specifies permitted substances and their usage limits.
Global harmonization efforts, such as those led by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI), aim to streamline regulatory requirements across different regions. However, significant differences in regulatory approaches and specific requirements still exist between countries, posing challenges for manufacturers operating in multiple markets.
Emerging regulations are focusing on sustainability and environmental concerns. For instance, the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive aims to reduce plastic waste, which may impact the use of certain types of LDPE barrier films in food packaging. Similarly, various countries are implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, which could influence the design and recyclability of LDPE barrier films.
As innovations in LDPE barrier film technologies continue to advance, regulatory bodies are likely to adapt their frameworks to address new materials and processes. This may include updated guidelines for novel barrier coatings, nanocomposites, or bio-based LDPE alternatives. Manufacturers and researchers in this field must stay informed about these regulatory developments to ensure compliance and market access for their innovative products.
For LDPE barrier films, manufacturers must ensure compliance with FDA regulations, particularly 21 CFR 177.1520, which pertains to olefin polymers. This regulation specifies the permissible raw materials, additives, and processing aids that can be used in the production of LDPE films intended for food contact. Additionally, any new additives or modifications to the film composition must undergo a Food Contact Notification (FCN) process or obtain approval through a Food Additive Petition.
In the European Union, the regulatory framework for food packaging materials is governed by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the European Commission. The primary regulation is EC 1935/2004, which establishes general principles for all food contact materials. Specific to plastic materials, including LDPE films, is EU Regulation 10/2011, which provides a positive list of authorized substances and sets migration limits for various components.
Japan's regulatory system for food packaging materials is administered by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW). The Food Sanitation Act and its associated regulations outline the requirements for food contact materials, including LDPE barrier films. Manufacturers must ensure compliance with the Positive List System for food contact materials, which specifies permitted substances and their usage limits.
Global harmonization efforts, such as those led by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI), aim to streamline regulatory requirements across different regions. However, significant differences in regulatory approaches and specific requirements still exist between countries, posing challenges for manufacturers operating in multiple markets.
Emerging regulations are focusing on sustainability and environmental concerns. For instance, the EU's Single-Use Plastics Directive aims to reduce plastic waste, which may impact the use of certain types of LDPE barrier films in food packaging. Similarly, various countries are implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, which could influence the design and recyclability of LDPE barrier films.
As innovations in LDPE barrier film technologies continue to advance, regulatory bodies are likely to adapt their frameworks to address new materials and processes. This may include updated guidelines for novel barrier coatings, nanocomposites, or bio-based LDPE alternatives. Manufacturers and researchers in this field must stay informed about these regulatory developments to ensure compliance and market access for their innovative products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!