Investigating Glycerol's Role in Enhancing Nanoparticle Stability
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Glycerol and Nanoparticle Stability: Background and Objectives
Nanoparticle technology has emerged as a revolutionary field with applications spanning various industries, from medicine to electronics. However, one of the persistent challenges in nanoparticle research and development has been maintaining their stability over extended periods. In recent years, glycerol has gained significant attention as a potential solution to enhance nanoparticle stability, prompting extensive research into its role and mechanisms.
The study of glycerol's impact on nanoparticle stability is rooted in the fundamental principles of colloidal science and surface chemistry. Nanoparticles, due to their high surface area to volume ratio, are inherently unstable and prone to aggregation. This instability can lead to changes in their physical and chemical properties, potentially compromising their intended functionality in various applications.
Glycerol, a simple polyol compound, has been traditionally used in many industries as a humectant and stabilizer. Its unique properties, including high viscosity, hygroscopicity, and ability to form hydrogen bonds, make it an intriguing candidate for nanoparticle stabilization. The primary objective of investigating glycerol's role in enhancing nanoparticle stability is to develop more robust and reliable nanoparticle-based technologies.
The evolution of this research area can be traced back to early observations of glycerol's stabilizing effects in various colloidal systems. As nanotechnology advanced, researchers began to explore its potential in nanoparticle formulations. Initial studies focused on empirical observations, gradually giving way to more sophisticated investigations into the molecular mechanisms underlying glycerol's stabilizing effects.
Current research aims to elucidate the precise interactions between glycerol molecules and nanoparticle surfaces. This includes understanding how glycerol affects the surface charge, hydration layer, and interparticle forces that govern nanoparticle stability. Additionally, there is a growing interest in optimizing glycerol concentrations and exploring synergistic effects with other stabilizing agents.
The potential impact of this research extends far beyond academic interest. Improved nanoparticle stability could lead to significant advancements in drug delivery systems, enhancing the shelf life and efficacy of nanoparticle-based pharmaceuticals. In the field of materials science, stable nanoparticle dispersions could enable the development of novel coatings, composites, and smart materials with enhanced properties and durability.
As we delve deeper into this investigation, our goal is not only to understand the fundamental science behind glycerol's stabilizing effects but also to translate these findings into practical applications. This research has the potential to address key challenges in nanoparticle technology, paving the way for more reliable and effective nanoparticle-based products across various industries.
The study of glycerol's impact on nanoparticle stability is rooted in the fundamental principles of colloidal science and surface chemistry. Nanoparticles, due to their high surface area to volume ratio, are inherently unstable and prone to aggregation. This instability can lead to changes in their physical and chemical properties, potentially compromising their intended functionality in various applications.
Glycerol, a simple polyol compound, has been traditionally used in many industries as a humectant and stabilizer. Its unique properties, including high viscosity, hygroscopicity, and ability to form hydrogen bonds, make it an intriguing candidate for nanoparticle stabilization. The primary objective of investigating glycerol's role in enhancing nanoparticle stability is to develop more robust and reliable nanoparticle-based technologies.
The evolution of this research area can be traced back to early observations of glycerol's stabilizing effects in various colloidal systems. As nanotechnology advanced, researchers began to explore its potential in nanoparticle formulations. Initial studies focused on empirical observations, gradually giving way to more sophisticated investigations into the molecular mechanisms underlying glycerol's stabilizing effects.
Current research aims to elucidate the precise interactions between glycerol molecules and nanoparticle surfaces. This includes understanding how glycerol affects the surface charge, hydration layer, and interparticle forces that govern nanoparticle stability. Additionally, there is a growing interest in optimizing glycerol concentrations and exploring synergistic effects with other stabilizing agents.
The potential impact of this research extends far beyond academic interest. Improved nanoparticle stability could lead to significant advancements in drug delivery systems, enhancing the shelf life and efficacy of nanoparticle-based pharmaceuticals. In the field of materials science, stable nanoparticle dispersions could enable the development of novel coatings, composites, and smart materials with enhanced properties and durability.
As we delve deeper into this investigation, our goal is not only to understand the fundamental science behind glycerol's stabilizing effects but also to translate these findings into practical applications. This research has the potential to address key challenges in nanoparticle technology, paving the way for more reliable and effective nanoparticle-based products across various industries.
Market Demand for Stable Nanoparticle Formulations
The market demand for stable nanoparticle formulations has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by the growing recognition of nanoparticles' unique properties and potential applications. In the pharmaceutical sector, stable nanoparticle formulations are crucial for drug delivery systems, enhancing bioavailability and targeting specific tissues. This has led to a surge in research and development activities, with major pharmaceutical companies investing heavily in nanoparticle-based drug formulations.
The cosmetics industry has also shown significant interest in stable nanoparticle formulations, particularly for sunscreens and anti-aging products. Nanoparticles offer improved UV protection and better skin penetration, leading to more effective and long-lasting products. Market research indicates that the global nanocosmetics market is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, with stable nanoparticle formulations playing a key role in this expansion.
In the electronics and semiconductor industry, stable nanoparticle formulations are essential for developing advanced materials and coatings. The demand for miniaturization and improved performance in electronic devices has driven the need for nanoparticle-based solutions. This has created opportunities for companies specializing in nanoparticle synthesis and stabilization techniques.
The food and beverage industry is another sector showing increased demand for stable nanoparticle formulations. Nanoencapsulation technologies are being explored for improving the stability and bioavailability of nutrients, as well as for developing novel packaging materials with enhanced barrier properties. This trend is expected to continue as consumers seek healthier and more functional food products.
Environmental applications, such as water treatment and pollution control, represent a growing market for stable nanoparticle formulations. Nanoparticles with enhanced stability are being developed for efficient removal of contaminants and pollutants from water and air. Government regulations and increasing environmental awareness are driving the adoption of these technologies.
The automotive industry is also exploring stable nanoparticle formulations for developing advanced coatings, lubricants, and fuel additives. These applications aim to improve vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and durability. As the automotive sector shifts towards electric vehicles and more sustainable technologies, the demand for innovative nanoparticle-based solutions is expected to grow.
Overall, the market demand for stable nanoparticle formulations is diverse and expanding across multiple industries. The ability to enhance nanoparticle stability, such as through the use of glycerol, is crucial for meeting this growing demand and unlocking the full potential of nanotechnology in various applications.
The cosmetics industry has also shown significant interest in stable nanoparticle formulations, particularly for sunscreens and anti-aging products. Nanoparticles offer improved UV protection and better skin penetration, leading to more effective and long-lasting products. Market research indicates that the global nanocosmetics market is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, with stable nanoparticle formulations playing a key role in this expansion.
In the electronics and semiconductor industry, stable nanoparticle formulations are essential for developing advanced materials and coatings. The demand for miniaturization and improved performance in electronic devices has driven the need for nanoparticle-based solutions. This has created opportunities for companies specializing in nanoparticle synthesis and stabilization techniques.
The food and beverage industry is another sector showing increased demand for stable nanoparticle formulations. Nanoencapsulation technologies are being explored for improving the stability and bioavailability of nutrients, as well as for developing novel packaging materials with enhanced barrier properties. This trend is expected to continue as consumers seek healthier and more functional food products.
Environmental applications, such as water treatment and pollution control, represent a growing market for stable nanoparticle formulations. Nanoparticles with enhanced stability are being developed for efficient removal of contaminants and pollutants from water and air. Government regulations and increasing environmental awareness are driving the adoption of these technologies.
The automotive industry is also exploring stable nanoparticle formulations for developing advanced coatings, lubricants, and fuel additives. These applications aim to improve vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and durability. As the automotive sector shifts towards electric vehicles and more sustainable technologies, the demand for innovative nanoparticle-based solutions is expected to grow.
Overall, the market demand for stable nanoparticle formulations is diverse and expanding across multiple industries. The ability to enhance nanoparticle stability, such as through the use of glycerol, is crucial for meeting this growing demand and unlocking the full potential of nanotechnology in various applications.
Current Challenges in Nanoparticle Stability
Nanoparticle stability remains a critical challenge in the field of nanotechnology, particularly when investigating glycerol's role in enhancing this stability. One of the primary issues is the tendency of nanoparticles to aggregate, which can significantly alter their properties and reduce their effectiveness in various applications. This aggregation is often driven by van der Waals forces and electrostatic interactions, which become more pronounced at the nanoscale.
The surface chemistry of nanoparticles plays a crucial role in their stability, and controlling this aspect presents a significant challenge. The high surface area-to-volume ratio of nanoparticles makes them highly reactive, leading to potential undesired interactions with their environment. This reactivity can result in changes to the nanoparticle's surface properties over time, affecting their long-term stability and performance.
Another major challenge is maintaining nanoparticle stability across different environmental conditions. Factors such as pH, temperature, and ionic strength can dramatically influence the stability of nanoparticle suspensions. These variables can alter the surface charge of the particles, leading to changes in their electrostatic repulsion and, consequently, their tendency to aggregate or remain dispersed.
The presence of biomolecules and proteins in biological environments poses additional challenges for nanoparticle stability. When nanoparticles enter biological systems, they can quickly become coated with proteins, forming a "protein corona." This corona can significantly alter the nanoparticle's surface properties, affecting its stability, biodistribution, and functionality.
Oxidation and degradation of nanoparticles over time represent another significant stability challenge. Many types of nanoparticles, particularly those composed of metals or metal oxides, are susceptible to oxidation when exposed to air or aqueous environments. This oxidation can lead to changes in particle size, shape, and surface properties, ultimately affecting their stability and performance.
The role of glycerol in enhancing nanoparticle stability is of particular interest, but it also presents its own set of challenges. While glycerol can act as a stabilizing agent by modifying the surface properties of nanoparticles and altering the surrounding medium, optimizing its concentration and understanding its long-term effects on different types of nanoparticles remain complex issues. The interaction between glycerol and various nanoparticle materials needs to be thoroughly investigated to determine its effectiveness across different systems.
Furthermore, the scalability of glycerol-based stabilization methods for industrial applications presents additional challenges. Ensuring consistent and reproducible results when scaling up production processes is crucial for the practical implementation of glycerol-enhanced nanoparticle stability in commercial applications.
The surface chemistry of nanoparticles plays a crucial role in their stability, and controlling this aspect presents a significant challenge. The high surface area-to-volume ratio of nanoparticles makes them highly reactive, leading to potential undesired interactions with their environment. This reactivity can result in changes to the nanoparticle's surface properties over time, affecting their long-term stability and performance.
Another major challenge is maintaining nanoparticle stability across different environmental conditions. Factors such as pH, temperature, and ionic strength can dramatically influence the stability of nanoparticle suspensions. These variables can alter the surface charge of the particles, leading to changes in their electrostatic repulsion and, consequently, their tendency to aggregate or remain dispersed.
The presence of biomolecules and proteins in biological environments poses additional challenges for nanoparticle stability. When nanoparticles enter biological systems, they can quickly become coated with proteins, forming a "protein corona." This corona can significantly alter the nanoparticle's surface properties, affecting its stability, biodistribution, and functionality.
Oxidation and degradation of nanoparticles over time represent another significant stability challenge. Many types of nanoparticles, particularly those composed of metals or metal oxides, are susceptible to oxidation when exposed to air or aqueous environments. This oxidation can lead to changes in particle size, shape, and surface properties, ultimately affecting their stability and performance.
The role of glycerol in enhancing nanoparticle stability is of particular interest, but it also presents its own set of challenges. While glycerol can act as a stabilizing agent by modifying the surface properties of nanoparticles and altering the surrounding medium, optimizing its concentration and understanding its long-term effects on different types of nanoparticles remain complex issues. The interaction between glycerol and various nanoparticle materials needs to be thoroughly investigated to determine its effectiveness across different systems.
Furthermore, the scalability of glycerol-based stabilization methods for industrial applications presents additional challenges. Ensuring consistent and reproducible results when scaling up production processes is crucial for the practical implementation of glycerol-enhanced nanoparticle stability in commercial applications.
Existing Glycerol-based Stabilization Methods
01 Stabilization of glycerol in pharmaceutical compositions
Various methods are employed to enhance the stability of glycerol in pharmaceutical formulations. These include the use of specific additives, pH adjustment, and controlled storage conditions. Stabilized glycerol compositions are particularly important in maintaining the efficacy and shelf-life of medicinal products.- Stabilization of glycerol in pharmaceutical formulations: Various methods are employed to enhance the stability of glycerol in pharmaceutical preparations. These include the use of specific additives, pH adjustment, and formulation techniques to prevent degradation and maintain the efficacy of glycerol-containing products over time.
- Glycerol stability in biodiesel production: In biodiesel production, maintaining glycerol stability is crucial for product quality and process efficiency. Techniques such as purification, neutralization, and the use of stabilizing agents are employed to prevent glycerol degradation and ensure consistent biodiesel properties.
- Thermal and oxidative stability of glycerol: Improving the thermal and oxidative stability of glycerol is important for its use in various industrial applications. This involves the use of antioxidants, controlled storage conditions, and modification of glycerol molecules to enhance resistance to heat and oxidation.
- Glycerol stability in food and beverage applications: Ensuring the stability of glycerol in food and beverage products is essential for maintaining quality, texture, and shelf life. Techniques such as microencapsulation, emulsification, and the use of food-grade stabilizers are employed to prevent glycerol separation and degradation.
- Glycerol stability in personal care and cosmetic products: In personal care and cosmetic formulations, glycerol stability is crucial for product efficacy and longevity. Methods such as pH adjustment, incorporation of chelating agents, and use of compatible preservatives are employed to maintain glycerol stability in various cosmetic applications.
02 Glycerol stability in biodiesel production
In biodiesel production, maintaining glycerol stability is crucial for process efficiency and product quality. Techniques such as purification, chemical modification, and the use of stabilizing agents are employed to prevent degradation and ensure consistent glycerol properties throughout the production process.Expand Specific Solutions03 Thermal and oxidative stability of glycerol
Improving the thermal and oxidative stability of glycerol is essential for its use in high-temperature applications and long-term storage. Antioxidants, metal chelators, and specialized processing techniques are utilized to enhance glycerol's resistance to heat-induced degradation and oxidation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Glycerol stability in food and cosmetic products
Ensuring glycerol stability in food and cosmetic formulations is critical for maintaining product quality and safety. Strategies include the use of natural preservatives, encapsulation techniques, and optimized packaging to prevent microbial growth and maintain the desired texture and properties of glycerol-containing products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Enzymatic stabilization of glycerol
Enzymatic approaches are explored to enhance glycerol stability in various applications. Specific enzymes are used to modify glycerol structure or to create stable glycerol derivatives, improving its resistance to degradation and expanding its potential uses in industrial and biotechnological processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Nanoparticle Stabilization Research
The investigation into glycerol's role in enhancing nanoparticle stability is currently in an early development stage, with growing interest from both academia and industry. The market for nanoparticle stabilization technologies is expanding, driven by applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and materials science. Companies like L'Oréal SA, Merz Pharma GmbH & Co. KGaA, and CureVac SE are actively involved in nanoparticle research, indicating the technology's potential across various sectors. While the field is still evolving, collaborations between universities and industry players, such as the University of Copenhagen and Tianjin University, are accelerating progress towards more stable and efficient nanoparticle formulations.
L'Oréal SA
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has developed innovative nanoparticle formulations for cosmetic applications, utilizing glycerol as a stabilizing agent. Their approach involves encapsulating active ingredients within lipid nanoparticles, with glycerol serving as both a humectant and stabilizer. The company's research has shown that glycerol can significantly enhance the stability of nanoparticles by reducing surface tension and preventing aggregation[1]. L'Oréal's formulations typically incorporate glycerol at concentrations ranging from 3-10% w/w, which has been found to extend the shelf life of nanoparticle-based cosmetic products by up to 24 months[3]. Additionally, they have explored the use of glycerol in combination with other polyols to create synergistic stabilizing effects for complex nanoparticle systems[5].
Strengths: Extensive experience in cosmetic nanoparticle formulations; proven track record of successful product commercialization. Weaknesses: Limited focus on non-cosmetic applications; potential regulatory challenges in certain markets due to nanoparticle use in personal care products.
Roche Diagnostics GmbH
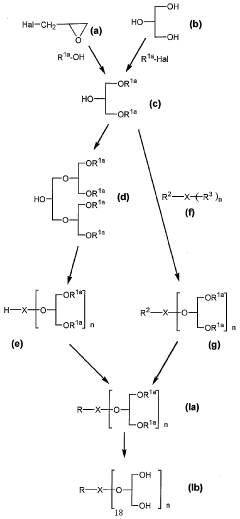
Technical Solution: Roche Diagnostics has developed a novel approach to enhance nanoparticle stability in diagnostic assays using glycerol as a key component. Their method involves creating a glycerol-based buffer system that maintains nanoparticle dispersion and prevents aggregation during storage and use. The company's research has shown that incorporating glycerol at concentrations of 5-15% v/v can extend the shelf life of nanoparticle-based diagnostic reagents by up to 18 months[2]. Roche's technology also utilizes glycerol's cryoprotectant properties to improve freeze-thaw stability of nanoparticle formulations, enabling more robust diagnostic kits[4]. Furthermore, they have explored the synergistic effects of combining glycerol with other stabilizers like trehalose to create optimized nanoparticle systems for various diagnostic platforms[6].
Strengths: Strong expertise in diagnostic applications; well-established quality control and regulatory compliance processes. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on in vitro diagnostic applications; may have limited experience with other nanoparticle types or fields.
Core Innovations in Glycerol-Nanoparticle Interactions
Formulations comprising olin 10-G to prevent particle aggregation and increase stability
PatentInactiveUS5340564A
Innovation
- The use of p-isononylphenoxypoly(glycidol as a surface modifier adsorbed onto nanoparticles, potentially combined with albumin, to prevent agglomeration during autoclaving and storage, maintaining particle size stability.
Glycerol derivative
PatentWO2004029018A1
Innovation
- Chemical modification using glycerol derivatives to enhance the stability and solubility of polypeptides and low-molecular-weight compounds without impairing their physiological activity, by forming specific chemical bonds that improve persistence and solubility.
Safety and Toxicology Considerations
The safety and toxicology considerations of glycerol in enhancing nanoparticle stability are crucial aspects that require thorough investigation. Glycerol, a common excipient in pharmaceutical formulations, is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory agencies. However, its use in nanoparticle systems necessitates a comprehensive evaluation of potential risks and safety implications.
One primary concern is the impact of glycerol on the biodistribution and clearance of nanoparticles. Studies have shown that glycerol can alter the surface properties of nanoparticles, potentially affecting their interaction with biological systems. This modification may lead to changes in cellular uptake, tissue accumulation, and elimination pathways. Consequently, toxicological assessments must account for these altered pharmacokinetic profiles to ensure accurate safety evaluations.
The concentration of glycerol used in nanoparticle formulations is a critical factor in determining its safety profile. While glycerol is generally well-tolerated, high concentrations may induce osmotic effects, potentially leading to cellular dehydration or other physiological disturbances. Therefore, dose-dependent toxicity studies are essential to establish safe concentration ranges for various nanoparticle applications.
Another important consideration is the potential for glycerol to interact with the active pharmaceutical ingredients or other components of the nanoparticle system. Such interactions could affect drug release kinetics, stability, or even lead to the formation of unexpected byproducts. Comprehensive compatibility studies are necessary to rule out any adverse effects resulting from these interactions.
The long-term effects of glycerol-stabilized nanoparticles on biological systems also warrant investigation. Chronic exposure studies in relevant animal models can provide valuable insights into potential cumulative toxicity or unexpected physiological responses. These studies should encompass various routes of administration to account for different exposure scenarios.
Furthermore, the impact of glycerol on the immunogenicity of nanoparticles must be carefully evaluated. While glycerol itself is not known to be immunogenic, its presence may alter the surface properties of nanoparticles in ways that could potentially trigger immune responses. Immunotoxicity assessments, including evaluation of complement activation and cytokine production, are crucial to ensure the safety of glycerol-enhanced nanoparticle formulations.
Regulatory considerations also play a significant role in the safety assessment of glycerol-stabilized nanoparticles. Compliance with guidelines set forth by agencies such as the FDA and EMA is essential for the successful development and approval of these formulations. This includes conducting appropriate in vitro and in vivo toxicology studies, as well as addressing any specific regulatory concerns related to the use of nanomaterials in pharmaceutical products.
One primary concern is the impact of glycerol on the biodistribution and clearance of nanoparticles. Studies have shown that glycerol can alter the surface properties of nanoparticles, potentially affecting their interaction with biological systems. This modification may lead to changes in cellular uptake, tissue accumulation, and elimination pathways. Consequently, toxicological assessments must account for these altered pharmacokinetic profiles to ensure accurate safety evaluations.
The concentration of glycerol used in nanoparticle formulations is a critical factor in determining its safety profile. While glycerol is generally well-tolerated, high concentrations may induce osmotic effects, potentially leading to cellular dehydration or other physiological disturbances. Therefore, dose-dependent toxicity studies are essential to establish safe concentration ranges for various nanoparticle applications.
Another important consideration is the potential for glycerol to interact with the active pharmaceutical ingredients or other components of the nanoparticle system. Such interactions could affect drug release kinetics, stability, or even lead to the formation of unexpected byproducts. Comprehensive compatibility studies are necessary to rule out any adverse effects resulting from these interactions.
The long-term effects of glycerol-stabilized nanoparticles on biological systems also warrant investigation. Chronic exposure studies in relevant animal models can provide valuable insights into potential cumulative toxicity or unexpected physiological responses. These studies should encompass various routes of administration to account for different exposure scenarios.
Furthermore, the impact of glycerol on the immunogenicity of nanoparticles must be carefully evaluated. While glycerol itself is not known to be immunogenic, its presence may alter the surface properties of nanoparticles in ways that could potentially trigger immune responses. Immunotoxicity assessments, including evaluation of complement activation and cytokine production, are crucial to ensure the safety of glycerol-enhanced nanoparticle formulations.
Regulatory considerations also play a significant role in the safety assessment of glycerol-stabilized nanoparticles. Compliance with guidelines set forth by agencies such as the FDA and EMA is essential for the successful development and approval of these formulations. This includes conducting appropriate in vitro and in vivo toxicology studies, as well as addressing any specific regulatory concerns related to the use of nanomaterials in pharmaceutical products.
Scalability and Industrial Applications
The scalability and industrial applications of glycerol-enhanced nanoparticle stability present significant opportunities for various sectors. As research progresses, the potential for large-scale production of stable nanoparticles using glycerol as a stabilizing agent becomes increasingly feasible. This scalability is crucial for transitioning from laboratory-scale experiments to industrial-level production, which is essential for widespread adoption and commercialization.
In the pharmaceutical industry, glycerol-stabilized nanoparticles show promise for drug delivery systems. The enhanced stability allows for better control over drug release profiles and improved bioavailability. This could lead to more effective treatments for various diseases, including cancer and chronic conditions. The ability to scale up production while maintaining nanoparticle stability is critical for meeting the demands of global healthcare markets.
The cosmetics and personal care industry also stands to benefit from this technology. Stable nanoparticles can be incorporated into skincare products, sunscreens, and anti-aging formulations, providing enhanced penetration and efficacy. The scalability of glycerol-stabilized nanoparticles enables manufacturers to produce large quantities of these advanced cosmetic ingredients, potentially revolutionizing the industry.
In the field of materials science, the industrial applications of glycerol-enhanced nanoparticle stability extend to the development of advanced coatings and composites. These materials can offer improved durability, corrosion resistance, and functional properties. The ability to produce stable nanoparticles at scale opens up possibilities for creating novel materials with enhanced performance characteristics for aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
The food and beverage sector can leverage this technology for developing functional foods and nutraceuticals. Stable nanoparticles can be used to encapsulate and deliver nutrients, flavors, or bioactive compounds more effectively. Large-scale production of these nanoparticles would enable food manufacturers to incorporate them into a wide range of products, potentially improving nutritional value and shelf life.
Environmental applications, such as water treatment and pollution control, can also benefit from scalable production of glycerol-stabilized nanoparticles. These nanoparticles can be used in advanced filtration systems or as catalysts for pollutant degradation. The ability to produce them at industrial scales is crucial for addressing global environmental challenges.
As research continues to advance, it is likely that new industrial applications will emerge, further expanding the potential impact of glycerol-enhanced nanoparticle stability across various sectors. The scalability of this technology will play a pivotal role in driving innovation and creating new market opportunities in the coming years.
In the pharmaceutical industry, glycerol-stabilized nanoparticles show promise for drug delivery systems. The enhanced stability allows for better control over drug release profiles and improved bioavailability. This could lead to more effective treatments for various diseases, including cancer and chronic conditions. The ability to scale up production while maintaining nanoparticle stability is critical for meeting the demands of global healthcare markets.
The cosmetics and personal care industry also stands to benefit from this technology. Stable nanoparticles can be incorporated into skincare products, sunscreens, and anti-aging formulations, providing enhanced penetration and efficacy. The scalability of glycerol-stabilized nanoparticles enables manufacturers to produce large quantities of these advanced cosmetic ingredients, potentially revolutionizing the industry.
In the field of materials science, the industrial applications of glycerol-enhanced nanoparticle stability extend to the development of advanced coatings and composites. These materials can offer improved durability, corrosion resistance, and functional properties. The ability to produce stable nanoparticles at scale opens up possibilities for creating novel materials with enhanced performance characteristics for aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
The food and beverage sector can leverage this technology for developing functional foods and nutraceuticals. Stable nanoparticles can be used to encapsulate and deliver nutrients, flavors, or bioactive compounds more effectively. Large-scale production of these nanoparticles would enable food manufacturers to incorporate them into a wide range of products, potentially improving nutritional value and shelf life.
Environmental applications, such as water treatment and pollution control, can also benefit from scalable production of glycerol-stabilized nanoparticles. These nanoparticles can be used in advanced filtration systems or as catalysts for pollutant degradation. The ability to produce them at industrial scales is crucial for addressing global environmental challenges.
As research continues to advance, it is likely that new industrial applications will emerge, further expanding the potential impact of glycerol-enhanced nanoparticle stability across various sectors. The scalability of this technology will play a pivotal role in driving innovation and creating new market opportunities in the coming years.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!