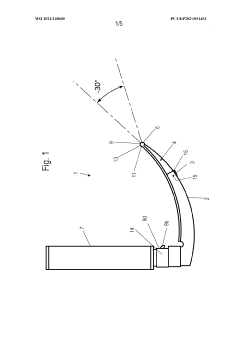
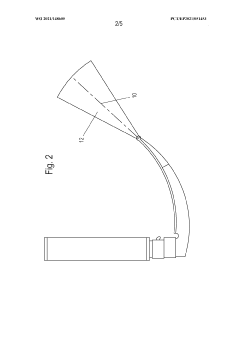
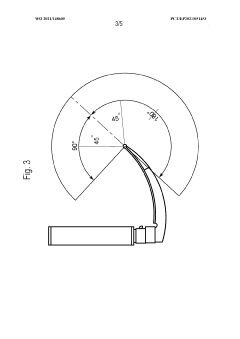
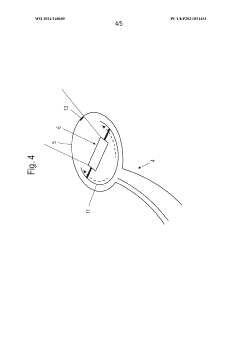
Laryngoscope innovations: Bridging clinical needs and technology.
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Laryngoscope Evolution
The evolution of the laryngoscope represents a fascinating journey through medical innovation, driven by the need for improved visualization and patient safety during intubation procedures. The first laryngoscope, developed in the early 19th century, was a simple mirror used to reflect light into the throat. This rudimentary device laid the foundation for subsequent advancements in laryngoscopy.
The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw significant progress with the introduction of electric illumination. In 1895, Alfred Kirstein developed the first direct laryngoscope, which allowed for a more straightforward view of the larynx. This was followed by Chevalier Jackson's refinements in the early 1900s, which standardized the design and technique of direct laryngoscopy.
The mid-20th century brought about the development of the Macintosh laryngoscope in 1943, which revolutionized the field with its curved blade design. This innovation significantly improved the ease of intubation and became the gold standard for decades. Parallel to this, the Miller blade, with its straight design, was introduced in 1941, offering an alternative approach for certain anatomical variations.
As medical understanding and technology advanced, so did laryngoscope design. The late 20th century saw the introduction of disposable blades and handles, addressing concerns about cross-contamination and infection control. This period also marked the beginning of ergonomic improvements, with handles and blades designed for better grip and maneuverability.
The turn of the 21st century heralded a new era in laryngoscopy with the advent of video laryngoscopes. These devices incorporate miniature cameras and LED lights, providing a clear, magnified view of the larynx on an external screen. This technology has dramatically improved the success rate of difficult intubations and has become an essential tool in emergency and critical care settings.
Recent years have seen further refinements in video laryngoscopy, including the development of portable and wireless devices. These innovations have enhanced mobility and ease of use in various clinical environments. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and augmented reality technologies is beginning to emerge, promising to provide real-time guidance and assistance during intubation procedures.
The ongoing evolution of laryngoscopes continues to focus on improving visualization, reducing trauma, and enhancing ease of use. Current research is exploring materials science for more flexible and durable blades, as well as incorporating advanced imaging technologies for even clearer views of the airway. As we look to the future, the convergence of miniaturization, digital technology, and biomechanics promises to further transform this critical medical tool, continually bridging clinical needs with cutting-edge technology.
The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw significant progress with the introduction of electric illumination. In 1895, Alfred Kirstein developed the first direct laryngoscope, which allowed for a more straightforward view of the larynx. This was followed by Chevalier Jackson's refinements in the early 1900s, which standardized the design and technique of direct laryngoscopy.
The mid-20th century brought about the development of the Macintosh laryngoscope in 1943, which revolutionized the field with its curved blade design. This innovation significantly improved the ease of intubation and became the gold standard for decades. Parallel to this, the Miller blade, with its straight design, was introduced in 1941, offering an alternative approach for certain anatomical variations.
As medical understanding and technology advanced, so did laryngoscope design. The late 20th century saw the introduction of disposable blades and handles, addressing concerns about cross-contamination and infection control. This period also marked the beginning of ergonomic improvements, with handles and blades designed for better grip and maneuverability.
The turn of the 21st century heralded a new era in laryngoscopy with the advent of video laryngoscopes. These devices incorporate miniature cameras and LED lights, providing a clear, magnified view of the larynx on an external screen. This technology has dramatically improved the success rate of difficult intubations and has become an essential tool in emergency and critical care settings.
Recent years have seen further refinements in video laryngoscopy, including the development of portable and wireless devices. These innovations have enhanced mobility and ease of use in various clinical environments. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and augmented reality technologies is beginning to emerge, promising to provide real-time guidance and assistance during intubation procedures.
The ongoing evolution of laryngoscopes continues to focus on improving visualization, reducing trauma, and enhancing ease of use. Current research is exploring materials science for more flexible and durable blades, as well as incorporating advanced imaging technologies for even clearer views of the airway. As we look to the future, the convergence of miniaturization, digital technology, and biomechanics promises to further transform this critical medical tool, continually bridging clinical needs with cutting-edge technology.
Clinical Demand Analysis
The demand for innovative laryngoscopes stems from the critical need to improve airway management in various clinical settings. Anesthesiologists, emergency physicians, and critical care specialists frequently encounter challenges during intubation procedures, particularly in difficult airway scenarios. These challenges can lead to complications, increased procedure time, and potential patient harm.
Market analysis reveals a growing demand for advanced laryngoscopes that address these clinical needs. The global laryngoscope market is experiencing steady growth, driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic respiratory diseases, the rising number of surgical procedures, and the growing geriatric population. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of efficient and safe intubation techniques, further boosting the demand for innovative laryngoscope solutions.
Healthcare providers are seeking laryngoscopes that offer improved visualization, easier maneuverability, and enhanced patient safety. There is a particular emphasis on devices that can handle difficult airways, such as those encountered in obese patients, patients with limited neck mobility, or those with anatomical abnormalities. The market shows a strong preference for video laryngoscopes, which provide better glottic views and facilitate easier intubation compared to traditional direct laryngoscopes.
Another significant trend in the clinical demand for laryngoscopes is the need for devices that reduce the risk of cross-contamination and healthcare-associated infections. This has led to an increased interest in single-use laryngoscopes or those with easily sterilizable components. Healthcare facilities are also looking for cost-effective solutions that balance performance with economic considerations, especially in resource-limited settings.
The demand for laryngoscopes extends beyond hospital settings. There is a growing need for portable and robust devices suitable for use in pre-hospital emergency care, military field operations, and remote healthcare facilities. These environments require laryngoscopes that are durable, easy to transport, and capable of functioning in challenging conditions.
Training and education represent another aspect of clinical demand. Medical institutions are seeking laryngoscopes that can be integrated into simulation-based training programs, allowing healthcare professionals to practice and improve their intubation skills in a safe environment. This has created a market for laryngoscopes with built-in recording and feedback capabilities, enabling detailed analysis of intubation techniques and performance.
In conclusion, the clinical demand for laryngoscope innovations is driven by the need for improved patient outcomes, enhanced safety, and increased efficiency in airway management procedures. The market seeks solutions that bridge the gap between advanced technology and practical clinical application, addressing the diverse challenges faced by healthcare providers across various medical specialties and settings.
Market analysis reveals a growing demand for advanced laryngoscopes that address these clinical needs. The global laryngoscope market is experiencing steady growth, driven by factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic respiratory diseases, the rising number of surgical procedures, and the growing geriatric population. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of efficient and safe intubation techniques, further boosting the demand for innovative laryngoscope solutions.
Healthcare providers are seeking laryngoscopes that offer improved visualization, easier maneuverability, and enhanced patient safety. There is a particular emphasis on devices that can handle difficult airways, such as those encountered in obese patients, patients with limited neck mobility, or those with anatomical abnormalities. The market shows a strong preference for video laryngoscopes, which provide better glottic views and facilitate easier intubation compared to traditional direct laryngoscopes.
Another significant trend in the clinical demand for laryngoscopes is the need for devices that reduce the risk of cross-contamination and healthcare-associated infections. This has led to an increased interest in single-use laryngoscopes or those with easily sterilizable components. Healthcare facilities are also looking for cost-effective solutions that balance performance with economic considerations, especially in resource-limited settings.
The demand for laryngoscopes extends beyond hospital settings. There is a growing need for portable and robust devices suitable for use in pre-hospital emergency care, military field operations, and remote healthcare facilities. These environments require laryngoscopes that are durable, easy to transport, and capable of functioning in challenging conditions.
Training and education represent another aspect of clinical demand. Medical institutions are seeking laryngoscopes that can be integrated into simulation-based training programs, allowing healthcare professionals to practice and improve their intubation skills in a safe environment. This has created a market for laryngoscopes with built-in recording and feedback capabilities, enabling detailed analysis of intubation techniques and performance.
In conclusion, the clinical demand for laryngoscope innovations is driven by the need for improved patient outcomes, enhanced safety, and increased efficiency in airway management procedures. The market seeks solutions that bridge the gap between advanced technology and practical clinical application, addressing the diverse challenges faced by healthcare providers across various medical specialties and settings.
Technical Challenges
The current state of laryngoscope technology presents several significant challenges that hinder optimal performance in clinical settings. One primary issue is the limited field of view offered by traditional laryngoscopes, which can impede the visualization of critical anatomical structures during intubation procedures. This constraint often leads to increased procedure time and potential complications, especially in patients with difficult airways.
Another major challenge lies in the ergonomics of existing laryngoscope designs. Many healthcare professionals report discomfort and strain during prolonged use, which can affect the precision and efficiency of intubation procedures. The need for improved ergonomics is particularly crucial in emergency situations where rapid and accurate intubation is essential.
The integration of advanced imaging technologies into laryngoscopes presents both opportunities and challenges. While video laryngoscopes offer enhanced visualization, they often come with a steep learning curve for practitioners accustomed to traditional direct laryngoscopy. Additionally, the cost and maintenance of these sophisticated devices can be prohibitive for some healthcare facilities, limiting widespread adoption.
Infection control remains a persistent concern in laryngoscope design and usage. The complex structures of modern laryngoscopes can make thorough cleaning and sterilization challenging, potentially increasing the risk of cross-contamination between patients. Developing materials and designs that facilitate effective sterilization without compromising functionality is an ongoing technical hurdle.
Power management and battery life pose significant challenges, particularly for portable and wireless laryngoscope models. Ensuring consistent performance throughout extended procedures while maintaining a compact and lightweight design is a delicate balance that engineers continue to grapple with.
The need for real-time data integration and analysis during intubation procedures presents another frontier for innovation. Developing systems that can provide immediate feedback on intubation depth, tube placement, and vital signs while maintaining simplicity of use is a complex technical challenge.
Lastly, the variability in patient anatomy and clinical scenarios necessitates the development of adaptable laryngoscope designs. Creating devices that can effectively accommodate a wide range of patient sizes, from pediatric to bariatric cases, while maintaining optimal performance across various clinical settings remains a significant technical obstacle in the field of laryngoscope innovation.
Another major challenge lies in the ergonomics of existing laryngoscope designs. Many healthcare professionals report discomfort and strain during prolonged use, which can affect the precision and efficiency of intubation procedures. The need for improved ergonomics is particularly crucial in emergency situations where rapid and accurate intubation is essential.
The integration of advanced imaging technologies into laryngoscopes presents both opportunities and challenges. While video laryngoscopes offer enhanced visualization, they often come with a steep learning curve for practitioners accustomed to traditional direct laryngoscopy. Additionally, the cost and maintenance of these sophisticated devices can be prohibitive for some healthcare facilities, limiting widespread adoption.
Infection control remains a persistent concern in laryngoscope design and usage. The complex structures of modern laryngoscopes can make thorough cleaning and sterilization challenging, potentially increasing the risk of cross-contamination between patients. Developing materials and designs that facilitate effective sterilization without compromising functionality is an ongoing technical hurdle.
Power management and battery life pose significant challenges, particularly for portable and wireless laryngoscope models. Ensuring consistent performance throughout extended procedures while maintaining a compact and lightweight design is a delicate balance that engineers continue to grapple with.
The need for real-time data integration and analysis during intubation procedures presents another frontier for innovation. Developing systems that can provide immediate feedback on intubation depth, tube placement, and vital signs while maintaining simplicity of use is a complex technical challenge.
Lastly, the variability in patient anatomy and clinical scenarios necessitates the development of adaptable laryngoscope designs. Creating devices that can effectively accommodate a wide range of patient sizes, from pediatric to bariatric cases, while maintaining optimal performance across various clinical settings remains a significant technical obstacle in the field of laryngoscope innovation.
Current Solutions
01 Improved visualization and illumination
Modern laryngoscopes incorporate advanced lighting systems and imaging technologies to enhance visibility during intubation procedures. These improvements may include LED lights, fiber optic systems, or integrated cameras to provide clearer views of the larynx and surrounding structures.- Illumination systems for laryngoscopes: Advanced illumination systems are integrated into laryngoscopes to improve visibility during intubation procedures. These systems may include LED lights, fiber optic cables, or other innovative lighting technologies to provide clear and adjustable illumination of the airway.
- Video laryngoscope designs: Video laryngoscopes incorporate miniature cameras and display screens to provide real-time imaging of the larynx during intubation. These designs may feature adjustable viewing angles, high-resolution displays, and ergonomic handles for improved operator control and patient comfort.
- Disposable laryngoscope blades: Single-use, disposable laryngoscope blades are designed to reduce the risk of cross-contamination between patients. These blades may be made from lightweight, durable materials and can be easily attached and detached from reusable handles.
- Articulating laryngoscope blades: Laryngoscopes with articulating or flexible blades allow for easier navigation of difficult airways. These designs may incorporate mechanisms for adjusting the blade angle or curvature during the intubation process, improving the success rate of challenging procedures.
- Integration of additional medical devices: Advanced laryngoscopes may incorporate or interface with other medical devices to enhance functionality. This can include integrated suction systems, oxygen delivery mechanisms, or compatibility with endotracheal tube guidance systems for more comprehensive airway management.
02 Ergonomic design and handle modifications
Laryngoscopes are being designed with improved ergonomics to enhance user comfort and control during procedures. This includes modifications to handle shapes, grip materials, and weight distribution to reduce hand fatigue and improve maneuverability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of video and display technologies
Video laryngoscopes incorporate small cameras and display screens to provide real-time visual feedback during intubation. These devices can improve success rates and facilitate teaching and documentation of procedures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Disposable and sterile components
To reduce the risk of cross-contamination and simplify sterilization processes, laryngoscopes are being designed with disposable blades or sheaths. Some models feature fully disposable units for single-use applications in emergency or field settings.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advanced blade designs and materials
Innovative blade designs are being developed to improve intubation success and patient comfort. This includes the use of new materials, adjustable blade angles, and specialized shapes to accommodate different anatomical variations and challenging airway scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The laryngoscope innovation landscape is characterized by a competitive market in its growth phase, with significant potential for expansion. The global laryngoscope market size is projected to reach substantial figures, driven by increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures and technological advancements. Companies like Karl Storz SE & Co. KG, Verathon, Inc., and Teleflex Medical Inc. are at the forefront of technological maturity, offering advanced video laryngoscopes and digital imaging solutions. Emerging players such as Zhejiang Youyi Medical Equipment Co Ltd and Adroit Surgical LLC are introducing novel designs, while established medical device manufacturers like Covidien (part of Medtronic) continue to innovate. Research institutions and hospitals are also contributing to the field, indicating a collaborative ecosystem focused on bridging clinical needs with cutting-edge technology.
Covidien AG
Technical Solution: Covidien AG has developed advanced video laryngoscopes that integrate high-resolution cameras and LED lighting for improved visualization during intubation procedures. Their McGRATH MAC video laryngoscope features a unique single-use blade design with an integrated camera, providing a clear view of the airway on a portable display[1]. The device also incorporates anti-fog technology to maintain visibility in challenging conditions. Covidien's laryngoscopes are designed to be ergonomic and easy to use, with intuitive controls and a lightweight construction to reduce operator fatigue during prolonged procedures[2].
Strengths: High-quality imaging, disposable blades for infection control, ergonomic design. Weaknesses: Reliance on electronic components may increase cost and maintenance requirements.
Karl Storz SE & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Karl Storz has pioneered the development of flexible video laryngoscopes, such as the C-MAC S Video Laryngoscope. This device features a flexible tip that can be manipulated to navigate difficult airways, combined with high-resolution imaging technology. The C-MAC system offers interchangeable blades to suit different patient anatomies and clinical scenarios[3]. Karl Storz has also integrated advanced image processing algorithms to enhance contrast and clarity in low-light conditions. Their laryngoscopes often include features like recording capabilities and compatibility with hospital information systems for seamless documentation[4].
Strengths: Versatile blade options, advanced imaging technology, integration with hospital systems. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to traditional laryngoscopes, potential for more complex training requirements.
Key Technological Advancements
Tip light laryngoscope for trans-tissue illumination
PatentWO2021148605A1
Innovation
- A tip light laryngoscope with a distal light source positioned at the tip of the blade for trans-tissue illumination, combined with a secondary proximal light source for surrounding illumination, allowing for enhanced visualization of the laryngeal structures and improved guidance of the endotracheal tube insertion.
DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH CAPACITY AND LOW COST VIDEOLARYNGOSCOPE WITH NATIONAL TECHNOLOGY
PatentPendingBR102022005405A2
Innovation
- Development of a Videolaryngoscope using 3D printing with ABS filaments, featuring a 5.5 mm diameter endoscopic camera and five interchangeable blade sizes, designed for easy sterilization and varying patient anatomies, addressing the cost and usability issues.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding laryngoscope innovations plays a crucial role in ensuring patient safety, product efficacy, and market access. In the United States, laryngoscopes are classified as Class I medical devices by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), subject to general controls but exempt from premarket notification requirements. However, novel laryngoscope technologies may be classified differently based on their intended use and risk profile.
The European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) categorizes laryngoscopes under Class I or Class IIa, depending on their specific features and intended use. This classification determines the conformity assessment procedures and clinical evidence requirements for market approval.
Regulatory bodies worldwide emphasize the importance of quality management systems in the development and manufacturing of laryngoscopes. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and implement robust quality control measures to ensure consistent product performance and safety.
Clinical evaluation and post-market surveillance are integral components of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers are required to collect and analyze clinical data to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of their laryngoscope innovations. This includes conducting clinical trials, gathering user feedback, and monitoring adverse events.
Regulatory agencies also focus on the usability and human factors aspects of laryngoscope design. Manufacturers must conduct thorough usability studies to ensure that their devices can be used safely and effectively by healthcare professionals in various clinical settings.
As laryngoscope technologies continue to evolve, incorporating features such as video imaging and artificial intelligence, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address these advancements. Cybersecurity considerations have become increasingly important, particularly for connected devices that may transmit or store patient data.
International harmonization efforts, such as the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP), aim to streamline regulatory processes across different countries. This facilitates global market access for innovative laryngoscope technologies while maintaining high standards of safety and efficacy.
Regulatory compliance extends beyond initial market approval, encompassing ongoing requirements for device labeling, packaging, and instructions for use. Manufacturers must provide clear and comprehensive information to users, including proper cleaning and sterilization procedures, to ensure safe and effective device operation.
The European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) categorizes laryngoscopes under Class I or Class IIa, depending on their specific features and intended use. This classification determines the conformity assessment procedures and clinical evidence requirements for market approval.
Regulatory bodies worldwide emphasize the importance of quality management systems in the development and manufacturing of laryngoscopes. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and implement robust quality control measures to ensure consistent product performance and safety.
Clinical evaluation and post-market surveillance are integral components of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers are required to collect and analyze clinical data to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of their laryngoscope innovations. This includes conducting clinical trials, gathering user feedback, and monitoring adverse events.
Regulatory agencies also focus on the usability and human factors aspects of laryngoscope design. Manufacturers must conduct thorough usability studies to ensure that their devices can be used safely and effectively by healthcare professionals in various clinical settings.
As laryngoscope technologies continue to evolve, incorporating features such as video imaging and artificial intelligence, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address these advancements. Cybersecurity considerations have become increasingly important, particularly for connected devices that may transmit or store patient data.
International harmonization efforts, such as the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP), aim to streamline regulatory processes across different countries. This facilitates global market access for innovative laryngoscope technologies while maintaining high standards of safety and efficacy.
Regulatory compliance extends beyond initial market approval, encompassing ongoing requirements for device labeling, packaging, and instructions for use. Manufacturers must provide clear and comprehensive information to users, including proper cleaning and sterilization procedures, to ensure safe and effective device operation.
Patient Safety Considerations
Patient safety is a paramount concern in the development and implementation of laryngoscope innovations. As these devices are used in critical airway management procedures, any technological advancements must prioritize patient well-being and minimize potential risks.
One of the primary safety considerations is the reduction of trauma during intubation. Traditional laryngoscopes can cause tissue damage and dental injuries if not used with proper technique. Innovative designs incorporating softer materials and improved blade shapes aim to minimize these risks. For instance, video laryngoscopes with curved blades allow for gentler insertion and reduced force application on the patient's oral structures.
Infection control is another crucial aspect of patient safety in laryngoscope use. Single-use disposable blades have gained popularity as they eliminate the risk of cross-contamination between patients. For reusable devices, advanced sterilization techniques and materials resistant to microbial growth are being developed to ensure thorough decontamination between uses.
The integration of real-time monitoring systems in laryngoscopes can significantly enhance patient safety. Sensors that detect excessive pressure or prolonged intubation attempts can alert clinicians to potential complications, allowing for immediate corrective action. Additionally, some innovative laryngoscopes incorporate temperature sensors to prevent thermal injuries to delicate airway tissues.
Ergonomic design improvements also contribute to patient safety by reducing the likelihood of operator errors. Laryngoscopes with enhanced grip and balance allow for more precise control, minimizing the risk of accidental trauma. Furthermore, intuitive user interfaces and clear visual displays on video laryngoscopes can improve decision-making during critical moments of the intubation process.
The development of smart laryngoscopes with artificial intelligence capabilities presents new opportunities for patient safety enhancement. These devices can provide real-time guidance to clinicians, suggesting optimal insertion angles and techniques based on patient-specific anatomical data. This technology has the potential to reduce complications, especially in challenging intubation scenarios.
As laryngoscope innovations continue to evolve, regulatory bodies play a crucial role in ensuring patient safety. Stringent testing and approval processes are necessary to validate the safety and efficacy of new devices before they enter clinical use. Ongoing post-market surveillance and reporting mechanisms are equally important to identify and address any unforeseen safety issues that may arise during widespread adoption.
One of the primary safety considerations is the reduction of trauma during intubation. Traditional laryngoscopes can cause tissue damage and dental injuries if not used with proper technique. Innovative designs incorporating softer materials and improved blade shapes aim to minimize these risks. For instance, video laryngoscopes with curved blades allow for gentler insertion and reduced force application on the patient's oral structures.
Infection control is another crucial aspect of patient safety in laryngoscope use. Single-use disposable blades have gained popularity as they eliminate the risk of cross-contamination between patients. For reusable devices, advanced sterilization techniques and materials resistant to microbial growth are being developed to ensure thorough decontamination between uses.
The integration of real-time monitoring systems in laryngoscopes can significantly enhance patient safety. Sensors that detect excessive pressure or prolonged intubation attempts can alert clinicians to potential complications, allowing for immediate corrective action. Additionally, some innovative laryngoscopes incorporate temperature sensors to prevent thermal injuries to delicate airway tissues.
Ergonomic design improvements also contribute to patient safety by reducing the likelihood of operator errors. Laryngoscopes with enhanced grip and balance allow for more precise control, minimizing the risk of accidental trauma. Furthermore, intuitive user interfaces and clear visual displays on video laryngoscopes can improve decision-making during critical moments of the intubation process.
The development of smart laryngoscopes with artificial intelligence capabilities presents new opportunities for patient safety enhancement. These devices can provide real-time guidance to clinicians, suggesting optimal insertion angles and techniques based on patient-specific anatomical data. This technology has the potential to reduce complications, especially in challenging intubation scenarios.
As laryngoscope innovations continue to evolve, regulatory bodies play a crucial role in ensuring patient safety. Stringent testing and approval processes are necessary to validate the safety and efficacy of new devices before they enter clinical use. Ongoing post-market surveillance and reporting mechanisms are equally important to identify and address any unforeseen safety issues that may arise during widespread adoption.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!