LDPE and Food Safety: Ensuring Compliance and Quality
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Food Packaging Evolution and Objectives
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone in food packaging since its introduction in the 1930s. The evolution of LDPE in food packaging has been driven by the need for safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly packaging solutions. Initially, LDPE was primarily used for its excellent moisture barrier properties and flexibility, making it ideal for wrapping and preserving food products.
As consumer awareness and regulatory standards regarding food safety increased, the focus shifted towards developing LDPE formulations that minimized potential chemical migration into food. This led to the introduction of food-grade LDPE, specifically designed to meet stringent food contact regulations. The development of multi-layer packaging structures incorporating LDPE as a key component further enhanced its functionality, allowing for improved barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and other contaminants.
In recent years, the objectives for LDPE in food packaging have expanded beyond basic preservation. There is a growing emphasis on sustainability, with research focused on creating recyclable and biodegradable LDPE variants. Additionally, the integration of smart packaging technologies, such as indicators for freshness or temperature abuse, has become a key area of innovation in LDPE food packaging.
The current technological landscape for LDPE in food packaging is characterized by a balance between safety, functionality, and sustainability. Manufacturers are exploring advanced production techniques to enhance the material's properties while reducing its environmental footprint. This includes the development of thinner films that maintain strength and barrier properties, as well as the incorporation of nanocomposites to improve mechanical and barrier characteristics.
Looking forward, the objectives for LDPE in food packaging are multifaceted. There is a strong push towards developing fully recyclable LDPE packaging solutions that align with circular economy principles. Researchers are also exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional LDPE, aiming to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Furthermore, there is ongoing work to enhance the material's ability to extend shelf life and reduce food waste, a critical global concern.
The evolution of LDPE in food packaging reflects a continuous journey of innovation, driven by changing consumer demands, regulatory requirements, and environmental considerations. As the industry moves forward, the focus remains on creating packaging solutions that not only ensure food safety and quality but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
As consumer awareness and regulatory standards regarding food safety increased, the focus shifted towards developing LDPE formulations that minimized potential chemical migration into food. This led to the introduction of food-grade LDPE, specifically designed to meet stringent food contact regulations. The development of multi-layer packaging structures incorporating LDPE as a key component further enhanced its functionality, allowing for improved barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and other contaminants.
In recent years, the objectives for LDPE in food packaging have expanded beyond basic preservation. There is a growing emphasis on sustainability, with research focused on creating recyclable and biodegradable LDPE variants. Additionally, the integration of smart packaging technologies, such as indicators for freshness or temperature abuse, has become a key area of innovation in LDPE food packaging.
The current technological landscape for LDPE in food packaging is characterized by a balance between safety, functionality, and sustainability. Manufacturers are exploring advanced production techniques to enhance the material's properties while reducing its environmental footprint. This includes the development of thinner films that maintain strength and barrier properties, as well as the incorporation of nanocomposites to improve mechanical and barrier characteristics.
Looking forward, the objectives for LDPE in food packaging are multifaceted. There is a strong push towards developing fully recyclable LDPE packaging solutions that align with circular economy principles. Researchers are also exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional LDPE, aiming to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Furthermore, there is ongoing work to enhance the material's ability to extend shelf life and reduce food waste, a critical global concern.
The evolution of LDPE in food packaging reflects a continuous journey of innovation, driven by changing consumer demands, regulatory requirements, and environmental considerations. As the industry moves forward, the focus remains on creating packaging solutions that not only ensure food safety and quality but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
Market Demand for Safe LDPE Food Packaging
The demand for safe LDPE food packaging has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing consumer awareness of food safety issues and stringent regulatory requirements. The global market for LDPE food packaging is projected to reach significant growth, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding industry averages.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards packaging materials that ensure food safety while maintaining product quality and freshness. LDPE, known for its flexibility, durability, and barrier properties, has become a popular choice for food packaging applications. The material's ability to protect against moisture, oxygen, and contaminants makes it particularly suitable for preserving perishable goods and extending shelf life.
The food and beverage industry, a major consumer of LDPE packaging, has been experiencing robust growth, further fueling the demand for safe packaging solutions. Convenience foods, ready-to-eat meals, and on-the-go snacks have gained popularity, necessitating packaging that can withstand various temperature conditions and maintain food integrity.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented stricter guidelines for food contact materials, emphasizing the importance of safety and compliance. This has led to increased scrutiny of packaging materials, including LDPE, and a growing demand for products that meet or exceed these standards. Manufacturers are under pressure to ensure their LDPE packaging complies with regulations such as FDA requirements in the United States and EU directives in Europe.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for safe food packaging. Consumers have become more conscious of hygiene and food safety, leading to a preference for packaged foods over loose items. This trend has boosted the demand for LDPE packaging in various food sectors, including fresh produce, dairy, and bakery products.
Sustainability concerns have also influenced the market for LDPE food packaging. While LDPE is recyclable, there is a growing demand for eco-friendly alternatives and improved recycling infrastructure. This has prompted innovation in LDPE formulations and recycling technologies to address environmental concerns while maintaining food safety standards.
The e-commerce boom has created new opportunities for LDPE food packaging, as online food delivery services require reliable and safe packaging solutions. This has led to the development of specialized LDPE packaging designs that can withstand the rigors of transportation while ensuring food safety and quality upon delivery.
In conclusion, the market demand for safe LDPE food packaging is robust and multifaceted, driven by consumer preferences, regulatory requirements, industry growth, and evolving market dynamics. As food safety remains a top priority for consumers and regulators alike, the demand for innovative, compliant, and high-quality LDPE packaging solutions is expected to continue its upward trajectory in the foreseeable future.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards packaging materials that ensure food safety while maintaining product quality and freshness. LDPE, known for its flexibility, durability, and barrier properties, has become a popular choice for food packaging applications. The material's ability to protect against moisture, oxygen, and contaminants makes it particularly suitable for preserving perishable goods and extending shelf life.
The food and beverage industry, a major consumer of LDPE packaging, has been experiencing robust growth, further fueling the demand for safe packaging solutions. Convenience foods, ready-to-eat meals, and on-the-go snacks have gained popularity, necessitating packaging that can withstand various temperature conditions and maintain food integrity.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented stricter guidelines for food contact materials, emphasizing the importance of safety and compliance. This has led to increased scrutiny of packaging materials, including LDPE, and a growing demand for products that meet or exceed these standards. Manufacturers are under pressure to ensure their LDPE packaging complies with regulations such as FDA requirements in the United States and EU directives in Europe.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for safe food packaging. Consumers have become more conscious of hygiene and food safety, leading to a preference for packaged foods over loose items. This trend has boosted the demand for LDPE packaging in various food sectors, including fresh produce, dairy, and bakery products.
Sustainability concerns have also influenced the market for LDPE food packaging. While LDPE is recyclable, there is a growing demand for eco-friendly alternatives and improved recycling infrastructure. This has prompted innovation in LDPE formulations and recycling technologies to address environmental concerns while maintaining food safety standards.
The e-commerce boom has created new opportunities for LDPE food packaging, as online food delivery services require reliable and safe packaging solutions. This has led to the development of specialized LDPE packaging designs that can withstand the rigors of transportation while ensuring food safety and quality upon delivery.
In conclusion, the market demand for safe LDPE food packaging is robust and multifaceted, driven by consumer preferences, regulatory requirements, industry growth, and evolving market dynamics. As food safety remains a top priority for consumers and regulators alike, the demand for innovative, compliant, and high-quality LDPE packaging solutions is expected to continue its upward trajectory in the foreseeable future.
LDPE Food Safety Challenges and Limitations
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been widely used in food packaging due to its excellent barrier properties, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, as food safety regulations become increasingly stringent, LDPE faces several challenges and limitations in ensuring compliance and quality.
One of the primary concerns is the potential migration of chemical substances from LDPE packaging into food. While LDPE is generally considered safe, it can contain various additives and residual monomers that may leach into food products over time. This migration can be influenced by factors such as temperature, storage duration, and the nature of the food in contact with the packaging. Regulatory bodies worldwide have established strict limits on the migration of these substances, requiring manufacturers to conduct extensive testing and documentation to demonstrate compliance.
Another challenge lies in the recyclability and sustainability of LDPE packaging. As environmental concerns grow, there is increasing pressure to develop more eco-friendly packaging solutions. LDPE, being a petroleum-based plastic, faces scrutiny for its environmental impact. While it is technically recyclable, the recycling process for LDPE can be complex and often results in downcycling, where the recycled material is of lower quality than the original. This limitation poses challenges for companies aiming to improve their sustainability profiles and meet consumer demands for more environmentally friendly packaging options.
LDPE also faces limitations in its barrier properties, particularly when it comes to oxygen and moisture transmission. While it provides good moisture resistance, its oxygen barrier properties are not as effective as some alternative materials. This can be a significant concern for food products that are sensitive to oxidation, potentially leading to reduced shelf life or compromised food quality. To address this, manufacturers often need to incorporate additional barrier layers or use modified LDPE formulations, which can increase production costs and complexity.
The use of LDPE in high-temperature applications presents another set of challenges. When exposed to elevated temperatures, such as in microwave heating or hot-filling processes, LDPE can soften and potentially deform. This limitation restricts its use in certain food packaging applications and necessitates the development of heat-resistant formulations or alternative packaging solutions for high-temperature scenarios.
Lastly, the growing concern over microplastics and their potential impact on human health and the environment poses a challenge for LDPE packaging. While LDPE itself is not typically considered a significant source of microplastics, the fragmentation of LDPE packaging waste in the environment can contribute to the overall microplastic pollution problem. This has led to increased scrutiny and calls for alternative packaging materials or improved end-of-life management strategies for LDPE products.
One of the primary concerns is the potential migration of chemical substances from LDPE packaging into food. While LDPE is generally considered safe, it can contain various additives and residual monomers that may leach into food products over time. This migration can be influenced by factors such as temperature, storage duration, and the nature of the food in contact with the packaging. Regulatory bodies worldwide have established strict limits on the migration of these substances, requiring manufacturers to conduct extensive testing and documentation to demonstrate compliance.
Another challenge lies in the recyclability and sustainability of LDPE packaging. As environmental concerns grow, there is increasing pressure to develop more eco-friendly packaging solutions. LDPE, being a petroleum-based plastic, faces scrutiny for its environmental impact. While it is technically recyclable, the recycling process for LDPE can be complex and often results in downcycling, where the recycled material is of lower quality than the original. This limitation poses challenges for companies aiming to improve their sustainability profiles and meet consumer demands for more environmentally friendly packaging options.
LDPE also faces limitations in its barrier properties, particularly when it comes to oxygen and moisture transmission. While it provides good moisture resistance, its oxygen barrier properties are not as effective as some alternative materials. This can be a significant concern for food products that are sensitive to oxidation, potentially leading to reduced shelf life or compromised food quality. To address this, manufacturers often need to incorporate additional barrier layers or use modified LDPE formulations, which can increase production costs and complexity.
The use of LDPE in high-temperature applications presents another set of challenges. When exposed to elevated temperatures, such as in microwave heating or hot-filling processes, LDPE can soften and potentially deform. This limitation restricts its use in certain food packaging applications and necessitates the development of heat-resistant formulations or alternative packaging solutions for high-temperature scenarios.
Lastly, the growing concern over microplastics and their potential impact on human health and the environment poses a challenge for LDPE packaging. While LDPE itself is not typically considered a significant source of microplastics, the fragmentation of LDPE packaging waste in the environment can contribute to the overall microplastic pollution problem. This has led to increased scrutiny and calls for alternative packaging materials or improved end-of-life management strategies for LDPE products.
Current LDPE Food Safety Compliance Solutions
01 Quality control methods for LDPE production
Various quality control methods are employed in LDPE production to ensure compliance with industry standards. These methods include monitoring and controlling key parameters such as melt flow index, density, and molecular weight distribution. Advanced analytical techniques and in-line monitoring systems are used to maintain consistent product quality throughout the manufacturing process.- Quality control methods for LDPE production: Various quality control methods are employed in LDPE production to ensure compliance with industry standards. These methods include monitoring and controlling process parameters, implementing advanced testing techniques, and utilizing specialized equipment for quality assurance. Such measures help maintain consistent product quality and meet regulatory requirements.
- Improved LDPE formulations for enhanced properties: Researchers have developed improved LDPE formulations to enhance specific properties such as strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance. These advancements involve the incorporation of additives, modification of molecular structure, or blending with other polymers. The resulting LDPE materials offer superior performance in various applications while maintaining compliance with industry standards.
- Environmental compliance and sustainability in LDPE production: LDPE manufacturers are focusing on environmental compliance and sustainability by implementing eco-friendly production processes, reducing waste, and developing recyclable or biodegradable LDPE variants. These efforts aim to minimize the environmental impact of LDPE production and usage while meeting regulatory requirements and consumer demands for sustainable materials.
- Testing and certification procedures for LDPE compliance: Standardized testing and certification procedures are crucial for ensuring LDPE compliance with industry regulations and quality standards. These procedures involve various physical, chemical, and mechanical tests to evaluate properties such as density, melt flow index, tensile strength, and thermal stability. Certification processes help validate the quality and performance of LDPE products for different applications.
- Advanced manufacturing techniques for high-quality LDPE: Innovative manufacturing techniques have been developed to produce high-quality LDPE with improved consistency and performance. These techniques may include advanced reactor designs, precise control of polymerization conditions, or novel catalytic systems. By optimizing the production process, manufacturers can achieve better control over LDPE properties and ensure compliance with stringent quality standards.
02 LDPE compliance with food contact regulations
LDPE materials used in food packaging applications must comply with specific regulations to ensure safety. This involves testing for migration of substances, adherence to composition limits, and obtaining necessary certifications. Manufacturers implement rigorous quality control measures and documentation processes to meet these regulatory requirements.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental compliance and sustainability of LDPE
To address environmental concerns, LDPE manufacturers are focusing on improving the sustainability of their products. This includes developing biodegradable or recyclable LDPE formulations, implementing energy-efficient production processes, and reducing waste. Compliance with environmental regulations and obtaining relevant certifications are crucial aspects of LDPE quality management.Expand Specific Solutions04 LDPE quality enhancement through additives and blending
The quality and performance of LDPE can be enhanced through the use of additives and blending with other polymers. This approach allows for customization of properties such as strength, flexibility, and barrier characteristics. Careful selection and incorporation of additives, as well as precise blending techniques, are essential for maintaining compliance while improving product quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Testing and characterization methods for LDPE quality assurance
Advanced testing and characterization methods are crucial for ensuring LDPE quality and compliance. These include thermal analysis, spectroscopic techniques, mechanical property testing, and morphological studies. Implementing standardized testing protocols and utilizing state-of-the-art analytical instruments help manufacturers maintain consistent product quality and meet regulatory requirements.Expand Specific Solutions
Key LDPE Food Packaging Industry Players
The LDPE food safety market is in a mature stage, characterized by established regulations and widespread adoption across the food packaging industry. The global market size for food-grade LDPE is substantial, driven by increasing demand for safe and compliant packaging solutions. Technologically, the field is well-developed, with major players like Dow Global Technologies, SABIC, and ExxonMobil Chemical Patents leading innovation. These companies, along with others such as Braskem and BASF, are continually refining their LDPE formulations to enhance food safety compliance and quality. The competitive landscape is marked by a focus on developing advanced LDPE materials that meet stringent regulatory requirements while improving performance and sustainability.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies LLC has developed advanced LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) formulations specifically designed for food packaging applications. Their technology focuses on enhancing the barrier properties of LDPE films, which is crucial for maintaining food freshness and safety. They have implemented a multi-layer film structure that incorporates nanocomposites, improving oxygen and moisture barrier properties by up to 40% compared to standard LDPE films[1]. Additionally, Dow has developed a proprietary additive package that enhances the material's resistance to migration and leaching, ensuring compliance with FDA and EU food contact regulations[2]. The company has also introduced a novel crosslinking process that improves the heat resistance of LDPE, allowing for a wider range of food processing applications, including hot-fill and retort packaging[3].
Strengths: Superior barrier properties, enhanced regulatory compliance, and improved heat resistance. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and more complex manufacturing processes compared to standard LDPE.
Tetra Laval Holdings & Finance SA
Technical Solution: Tetra Laval, through its Tetra Pak division, has pioneered innovative LDPE-based packaging solutions for the food industry. Their approach focuses on aseptic packaging technology, which utilizes a thin LDPE layer as a key component in their multi-layer packaging structure. The company has developed a proprietary LDPE formulation that provides excellent sealing properties while minimizing the risk of chemical migration[4]. Tetra Pak's LDPE layer is combined with paperboard and aluminum foil to create a robust barrier against light, oxygen, and microorganisms. Their latest innovation includes the incorporation of plant-based LDPE, derived from sugarcane, which reduces the carbon footprint of the packaging while maintaining food safety standards[5]. The company has also implemented advanced sterilization techniques that work in conjunction with their LDPE-based packaging to ensure extended shelf life for liquid foods without the need for preservatives or refrigeration[6].
Strengths: Aseptic packaging expertise, sustainable LDPE options, and extended shelf life capabilities. Weaknesses: Limited to liquid food applications and potentially higher costs compared to simpler packaging solutions.
Innovations in LDPE Food Safety Technologies
Laminated packaging material for paper container
PatentWO2000044632A1
Innovation
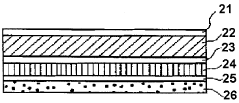
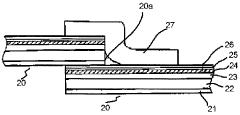
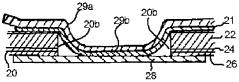
- A packaging material comprising a thermoplastic layer, a paper layer, and a barrier layer, with an innermost thermoplastic layer made of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) having specific molecular weight distribution and melting properties, enhancing sealability and preventing leakage while maintaining quality.
Multilayer composite film and use thereof
PatentInactiveEP1137538A1
Innovation
- A multilayer composite film with outer layers of Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) and a middle layer comprising a blend of polypropylene, thermoplastic polyolefin, and a slip agent, designed to provide elasticity, temperature resistance, and compatibility, with specific density and melt index ranges ensuring co-extrusion and food safety.
Regulatory Framework for LDPE Food Packaging
The regulatory framework for LDPE food packaging is a complex and evolving landscape designed to ensure the safety and quality of food products. At the global level, organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) provide guidelines and standards that influence national regulations. These international bodies work to harmonize food safety practices and packaging requirements across borders.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in regulating food contact materials, including LDPE. The FDA's Code of Federal Regulations Title 21, specifically Part 177, outlines the requirements for polymers used in food packaging. This includes specifications for the composition, manufacturing processes, and intended use of LDPE in food contact applications. The FDA also employs a system of Food Contact Notifications (FCNs) to evaluate and approve new food contact substances.
The European Union has established a comprehensive regulatory framework through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the European Commission. Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 serves as the cornerstone for food contact materials in the EU, setting out general principles of safety and inertness. For plastic materials specifically, Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 provides detailed rules on composition, migration limits, and testing requirements for LDPE and other polymers used in food packaging.
In Asia, countries like Japan and China have their own regulatory systems. Japan's Food Sanitation Law and the associated standards set by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare govern food packaging materials. China's GB standards, particularly GB 4806.1-2016 and GB 9685-2016, outline the requirements for food contact materials and additives, including those used in LDPE packaging.
These regulatory frameworks typically address several key aspects of LDPE food packaging. They establish limits for the migration of substances from the packaging into food, set standards for overall migration and specific migration of certain compounds, and define testing methodologies to ensure compliance. Additionally, they often include positive lists of approved substances that can be used in the manufacture of food contact materials.
Compliance with these regulations requires manufacturers to implement rigorous quality control measures, conduct regular testing, and maintain detailed documentation of their processes and materials. As scientific understanding of food safety evolves and new potential risks are identified, regulatory bodies continually update their frameworks, necessitating ongoing vigilance and adaptation from the food packaging industry.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in regulating food contact materials, including LDPE. The FDA's Code of Federal Regulations Title 21, specifically Part 177, outlines the requirements for polymers used in food packaging. This includes specifications for the composition, manufacturing processes, and intended use of LDPE in food contact applications. The FDA also employs a system of Food Contact Notifications (FCNs) to evaluate and approve new food contact substances.
The European Union has established a comprehensive regulatory framework through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the European Commission. Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 serves as the cornerstone for food contact materials in the EU, setting out general principles of safety and inertness. For plastic materials specifically, Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 provides detailed rules on composition, migration limits, and testing requirements for LDPE and other polymers used in food packaging.
In Asia, countries like Japan and China have their own regulatory systems. Japan's Food Sanitation Law and the associated standards set by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare govern food packaging materials. China's GB standards, particularly GB 4806.1-2016 and GB 9685-2016, outline the requirements for food contact materials and additives, including those used in LDPE packaging.
These regulatory frameworks typically address several key aspects of LDPE food packaging. They establish limits for the migration of substances from the packaging into food, set standards for overall migration and specific migration of certain compounds, and define testing methodologies to ensure compliance. Additionally, they often include positive lists of approved substances that can be used in the manufacture of food contact materials.
Compliance with these regulations requires manufacturers to implement rigorous quality control measures, conduct regular testing, and maintain detailed documentation of their processes and materials. As scientific understanding of food safety evolves and new potential risks are identified, regulatory bodies continually update their frameworks, necessitating ongoing vigilance and adaptation from the food packaging industry.
Environmental Impact of LDPE Food Packaging
The environmental impact of LDPE food packaging is a critical concern in the context of food safety and sustainability. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) is widely used in food packaging due to its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. However, its environmental footprint has become a subject of increasing scrutiny.
LDPE food packaging contributes significantly to plastic waste accumulation in landfills and oceans. Its non-biodegradable nature means that LDPE can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, leading to long-term ecological consequences. Marine ecosystems are particularly vulnerable, with LDPE fragments often mistaken for food by marine life, causing harm to wildlife and potentially entering the food chain.
The production of LDPE also raises environmental concerns. The manufacturing process relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Additionally, the extraction and processing of raw materials for LDPE production can lead to habitat destruction and pollution of local ecosystems.
Recycling LDPE food packaging presents challenges due to contamination from food residues and the mix of different plastic types often used in packaging. While LDPE is technically recyclable, the infrastructure and processes for effective recycling are not universally available, leading to low recycling rates globally.
Recent innovations aim to mitigate the environmental impact of LDPE food packaging. Biodegradable and compostable alternatives are being developed, although these often come with their own set of environmental trade-offs. Improved recycling technologies and infrastructure are also being implemented to increase the recycling rates of LDPE packaging.
The food industry is increasingly adopting eco-friendly packaging solutions, including reduced packaging, reusable containers, and packaging made from recycled LDPE. These initiatives aim to create a more circular economy for plastic packaging, reducing waste and environmental impact.
Regulatory measures are being implemented worldwide to address the environmental concerns associated with LDPE food packaging. These include bans on single-use plastics, extended producer responsibility schemes, and incentives for using recycled materials in packaging production.
As the food industry continues to prioritize safety and quality, balancing these requirements with environmental sustainability remains a significant challenge. The future of LDPE food packaging will likely involve a combination of improved recycling practices, innovative material alternatives, and a shift towards more sustainable packaging designs that maintain food safety standards while minimizing environmental impact.
LDPE food packaging contributes significantly to plastic waste accumulation in landfills and oceans. Its non-biodegradable nature means that LDPE can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, leading to long-term ecological consequences. Marine ecosystems are particularly vulnerable, with LDPE fragments often mistaken for food by marine life, causing harm to wildlife and potentially entering the food chain.
The production of LDPE also raises environmental concerns. The manufacturing process relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Additionally, the extraction and processing of raw materials for LDPE production can lead to habitat destruction and pollution of local ecosystems.
Recycling LDPE food packaging presents challenges due to contamination from food residues and the mix of different plastic types often used in packaging. While LDPE is technically recyclable, the infrastructure and processes for effective recycling are not universally available, leading to low recycling rates globally.
Recent innovations aim to mitigate the environmental impact of LDPE food packaging. Biodegradable and compostable alternatives are being developed, although these often come with their own set of environmental trade-offs. Improved recycling technologies and infrastructure are also being implemented to increase the recycling rates of LDPE packaging.
The food industry is increasingly adopting eco-friendly packaging solutions, including reduced packaging, reusable containers, and packaging made from recycled LDPE. These initiatives aim to create a more circular economy for plastic packaging, reducing waste and environmental impact.
Regulatory measures are being implemented worldwide to address the environmental concerns associated with LDPE food packaging. These include bans on single-use plastics, extended producer responsibility schemes, and incentives for using recycled materials in packaging production.
As the food industry continues to prioritize safety and quality, balancing these requirements with environmental sustainability remains a significant challenge. The future of LDPE food packaging will likely involve a combination of improved recycling practices, innovative material alternatives, and a shift towards more sustainable packaging designs that maintain food safety standards while minimizing environmental impact.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!