LDPE in Electronics: Insulation and Protection Benefits
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE in Electronics: Overview and Objectives
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has emerged as a crucial material in the electronics industry, offering significant benefits in insulation and protection. This synthetic polymer, characterized by its low density and high flexibility, has been widely adopted in various electronic applications due to its unique properties and versatility.
The development of LDPE can be traced back to the 1930s when it was first synthesized by Imperial Chemical Industries. Since then, its use in electronics has grown exponentially, driven by the increasing demand for reliable insulation materials in the rapidly evolving technology sector. The primary objective of utilizing LDPE in electronics is to provide effective electrical insulation and physical protection to sensitive components, ensuring their optimal performance and longevity.
LDPE's excellent dielectric properties make it an ideal choice for insulating electrical wires and cables. Its low dielectric constant and high dielectric strength allow for efficient transmission of electrical signals while minimizing energy loss. This characteristic is particularly valuable in high-frequency applications and data transmission systems, where signal integrity is paramount.
In addition to its insulating properties, LDPE offers superior moisture resistance, which is crucial for protecting electronic components from environmental factors. This feature is especially important in outdoor or high-humidity applications, where moisture ingress can lead to corrosion and electrical failures. The material's ability to form a protective barrier against water and other liquids contributes significantly to the overall reliability and durability of electronic devices.
The flexibility and ease of processing of LDPE have led to its widespread use in the manufacturing of various electronic components. It can be easily molded into different shapes and forms, allowing for the creation of custom insulation solutions for specific electronic applications. This adaptability has made LDPE a preferred choice in the production of cable jackets, connector insulators, and protective casings for electronic devices.
As the electronics industry continues to evolve, with trends towards miniaturization and increased functionality, the role of LDPE in insulation and protection becomes even more critical. The ongoing research and development in LDPE technology aim to enhance its properties further, focusing on improving its thermal stability, mechanical strength, and resistance to environmental stressors. These advancements are expected to expand the application scope of LDPE in electronics, meeting the growing demands of emerging technologies such as 5G networks, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and advanced automotive electronics.
The development of LDPE can be traced back to the 1930s when it was first synthesized by Imperial Chemical Industries. Since then, its use in electronics has grown exponentially, driven by the increasing demand for reliable insulation materials in the rapidly evolving technology sector. The primary objective of utilizing LDPE in electronics is to provide effective electrical insulation and physical protection to sensitive components, ensuring their optimal performance and longevity.
LDPE's excellent dielectric properties make it an ideal choice for insulating electrical wires and cables. Its low dielectric constant and high dielectric strength allow for efficient transmission of electrical signals while minimizing energy loss. This characteristic is particularly valuable in high-frequency applications and data transmission systems, where signal integrity is paramount.
In addition to its insulating properties, LDPE offers superior moisture resistance, which is crucial for protecting electronic components from environmental factors. This feature is especially important in outdoor or high-humidity applications, where moisture ingress can lead to corrosion and electrical failures. The material's ability to form a protective barrier against water and other liquids contributes significantly to the overall reliability and durability of electronic devices.
The flexibility and ease of processing of LDPE have led to its widespread use in the manufacturing of various electronic components. It can be easily molded into different shapes and forms, allowing for the creation of custom insulation solutions for specific electronic applications. This adaptability has made LDPE a preferred choice in the production of cable jackets, connector insulators, and protective casings for electronic devices.
As the electronics industry continues to evolve, with trends towards miniaturization and increased functionality, the role of LDPE in insulation and protection becomes even more critical. The ongoing research and development in LDPE technology aim to enhance its properties further, focusing on improving its thermal stability, mechanical strength, and resistance to environmental stressors. These advancements are expected to expand the application scope of LDPE in electronics, meeting the growing demands of emerging technologies such as 5G networks, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and advanced automotive electronics.
Market Demand Analysis for LDPE in Electronics
The market demand for Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) in the electronics industry has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing need for reliable insulation and protection materials in electronic devices. As consumer electronics become more compact and sophisticated, the demand for high-performance insulating materials like LDPE has surged. This trend is particularly evident in the production of smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, where space constraints and performance requirements are pushing manufacturers to seek advanced insulation solutions.
The global LDPE market in the electronics sector is experiencing significant growth, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the material's excellent electrical insulation properties, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for various electronic applications. The automotive electronics segment is also contributing to this increased demand, as vehicles incorporate more advanced electronic systems requiring robust insulation.
In the consumer electronics market, LDPE is widely used in cable insulation, connectors, and protective casings. The material's ability to withstand high temperatures and provide effective moisture barrier properties makes it particularly valuable in these applications. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, the demand for LDPE in smart home devices and industrial sensors is expected to rise, further driving market growth.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly countries like China, Japan, and South Korea, dominates the market demand for LDPE in electronics due to their strong electronics manufacturing base. However, emerging markets in Southeast Asia and India are showing rapid growth potential as they expand their electronics production capabilities.
Environmental concerns and regulations are influencing market dynamics, with a growing emphasis on recyclable and sustainable materials. This has led to increased research and development efforts to improve the recyclability of LDPE used in electronics, potentially opening new market opportunities for eco-friendly variants of the material.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the LDPE market in electronics. While it initially disrupted supply chains and manufacturing processes, the subsequent increase in remote work and digital communication has boosted demand for electronic devices, indirectly benefiting the LDPE market. As economies recover and 5G technology rolls out globally, the demand for LDPE in electronics is expected to see further growth, particularly in high-frequency applications where its insulation properties are crucial.
The global LDPE market in the electronics sector is experiencing significant growth, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the material's excellent electrical insulation properties, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for various electronic applications. The automotive electronics segment is also contributing to this increased demand, as vehicles incorporate more advanced electronic systems requiring robust insulation.
In the consumer electronics market, LDPE is widely used in cable insulation, connectors, and protective casings. The material's ability to withstand high temperatures and provide effective moisture barrier properties makes it particularly valuable in these applications. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, the demand for LDPE in smart home devices and industrial sensors is expected to rise, further driving market growth.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly countries like China, Japan, and South Korea, dominates the market demand for LDPE in electronics due to their strong electronics manufacturing base. However, emerging markets in Southeast Asia and India are showing rapid growth potential as they expand their electronics production capabilities.
Environmental concerns and regulations are influencing market dynamics, with a growing emphasis on recyclable and sustainable materials. This has led to increased research and development efforts to improve the recyclability of LDPE used in electronics, potentially opening new market opportunities for eco-friendly variants of the material.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the LDPE market in electronics. While it initially disrupted supply chains and manufacturing processes, the subsequent increase in remote work and digital communication has boosted demand for electronic devices, indirectly benefiting the LDPE market. As economies recover and 5G technology rolls out globally, the demand for LDPE in electronics is expected to see further growth, particularly in high-frequency applications where its insulation properties are crucial.
Current LDPE Applications and Challenges
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has become an integral component in the electronics industry, primarily due to its excellent insulation and protection properties. Currently, LDPE finds widespread applications in various electronic components and devices, serving as a crucial material for insulation, packaging, and protection against environmental factors.
In the field of wire and cable insulation, LDPE is extensively used due to its superior dielectric strength and flexibility. It provides effective electrical insulation for power cables, communication cables, and other wiring systems in electronic devices. The material's low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor make it particularly suitable for high-frequency applications, such as in coaxial cables used in telecommunications and data transmission.
LDPE is also widely employed in the packaging of electronic components and devices. Its moisture-resistant properties and chemical inertness make it an ideal choice for protecting sensitive electronic parts from humidity, dust, and other contaminants. LDPE films and bags are commonly used for wrapping circuit boards, semiconductors, and other delicate components during storage and transportation.
In the realm of electronic enclosures and housings, LDPE is utilized for its impact resistance and durability. It provides a protective barrier against physical damage and environmental factors for various electronic devices, including consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and automotive electronics.
Despite its widespread use, LDPE faces several challenges in the electronics industry. One significant challenge is its limited temperature resistance compared to other polymers. LDPE's relatively low melting point restricts its use in high-temperature applications, which can be a limitation in certain electronic systems that generate substantial heat during operation.
Another challenge is the material's susceptibility to stress cracking under certain conditions. This can potentially compromise the integrity of LDPE-based insulation or packaging in electronic applications, especially in environments with exposure to certain chemicals or mechanical stresses.
The growing demand for miniaturization and higher performance in electronic devices also poses challenges for LDPE. As electronic components become smaller and more densely packed, there is a need for insulation materials with improved dielectric properties and thermal management capabilities. This has led to the development of modified LDPE formulations and alternative materials that aim to address these limitations.
Environmental concerns and sustainability issues present additional challenges for LDPE in electronics. The industry is increasingly focusing on recyclable and biodegradable materials, which has prompted research into more eco-friendly alternatives to traditional LDPE in certain applications.
In the field of wire and cable insulation, LDPE is extensively used due to its superior dielectric strength and flexibility. It provides effective electrical insulation for power cables, communication cables, and other wiring systems in electronic devices. The material's low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor make it particularly suitable for high-frequency applications, such as in coaxial cables used in telecommunications and data transmission.
LDPE is also widely employed in the packaging of electronic components and devices. Its moisture-resistant properties and chemical inertness make it an ideal choice for protecting sensitive electronic parts from humidity, dust, and other contaminants. LDPE films and bags are commonly used for wrapping circuit boards, semiconductors, and other delicate components during storage and transportation.
In the realm of electronic enclosures and housings, LDPE is utilized for its impact resistance and durability. It provides a protective barrier against physical damage and environmental factors for various electronic devices, including consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and automotive electronics.
Despite its widespread use, LDPE faces several challenges in the electronics industry. One significant challenge is its limited temperature resistance compared to other polymers. LDPE's relatively low melting point restricts its use in high-temperature applications, which can be a limitation in certain electronic systems that generate substantial heat during operation.
Another challenge is the material's susceptibility to stress cracking under certain conditions. This can potentially compromise the integrity of LDPE-based insulation or packaging in electronic applications, especially in environments with exposure to certain chemicals or mechanical stresses.
The growing demand for miniaturization and higher performance in electronic devices also poses challenges for LDPE. As electronic components become smaller and more densely packed, there is a need for insulation materials with improved dielectric properties and thermal management capabilities. This has led to the development of modified LDPE formulations and alternative materials that aim to address these limitations.
Environmental concerns and sustainability issues present additional challenges for LDPE in electronics. The industry is increasingly focusing on recyclable and biodegradable materials, which has prompted research into more eco-friendly alternatives to traditional LDPE in certain applications.
Existing LDPE Insulation Solutions
01 LDPE insulation for electrical applications
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is widely used as an insulation material in electrical applications due to its excellent dielectric properties, flexibility, and durability. It is commonly used in cable and wire insulation, providing protection against electrical current and environmental factors.- LDPE insulation for electrical applications: Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is widely used as an insulation material in electrical applications due to its excellent dielectric properties, flexibility, and durability. It is commonly used in cable and wire insulation, providing effective protection against electrical current and environmental factors.
- LDPE protective packaging: LDPE is utilized in protective packaging applications due to its lightweight nature, impact resistance, and moisture barrier properties. It is used to create protective films, bubble wrap, and cushioning materials for various products during storage and transportation.
- LDPE in thermal insulation: LDPE is employed in thermal insulation applications, particularly in the construction industry. Its low thermal conductivity makes it an effective material for insulating buildings, pipes, and other structures, helping to maintain temperature control and energy efficiency.
- LDPE composites for enhanced properties: Researchers are developing LDPE composites by incorporating various additives or fillers to enhance its properties. These composites aim to improve mechanical strength, flame retardancy, or specific insulation characteristics while maintaining the benefits of LDPE.
- LDPE in agricultural applications: LDPE is used in agricultural applications for protection and insulation purposes. It is employed in greenhouse coverings, mulch films, and crop protection materials, providing a barrier against adverse weather conditions and helping to maintain optimal growing environments.
02 LDPE protective packaging and films
LDPE is utilized in the production of protective packaging materials and films. Its properties, such as flexibility, moisture resistance, and impact strength, make it suitable for creating protective layers for various products during storage and transportation.Expand Specific Solutions03 LDPE in thermal insulation applications
LDPE is employed in thermal insulation applications due to its low thermal conductivity. It can be used in the form of foam or as a component in composite insulation materials, providing effective heat retention or reflection in various industries and construction.Expand Specific Solutions04 LDPE blends and composites for enhanced protection
LDPE is often blended with other materials or used in composites to enhance its protective properties. These blends and composites can offer improved mechanical strength, chemical resistance, or specific functional characteristics tailored for particular protection requirements.Expand Specific Solutions05 LDPE in agricultural and horticultural protection
LDPE is used in agricultural and horticultural applications for protection against environmental factors. It is commonly used in greenhouse films, mulch films, and protective covers, offering benefits such as moisture retention, temperature control, and pest protection for crops and plants.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in LDPE and Electronics Industry
The LDPE in electronics market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for insulation and protection in electronic devices. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating continued growth due to the rising production of consumer electronics and automotive applications. Technologically, LDPE for electronics is relatively mature, but ongoing innovations focus on enhancing performance and sustainability. Key players like Borealis AG, Dow Global Technologies LLC, and ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc. are investing in R&D to develop advanced LDPE formulations with improved electrical and thermal properties. Emerging companies such as Far East Smarter Energy Co., Ltd. and Jiangyin Jiangtai New Polymers Co., Ltd. are also contributing to market competitiveness through specialized product offerings.
Borealis AG
Technical Solution: Borealis AG has developed advanced LDPE formulations specifically tailored for electronics applications. Their LDPE compounds feature enhanced dielectric properties and thermal stability, making them ideal for insulation in high-frequency electronic devices[1]. The company's proprietary crosslinking technology improves the material's resistance to heat and chemicals, extending the lifespan of electronic components[3]. Borealis has also introduced LDPE grades with reduced carbon footprint, addressing sustainability concerns in the electronics industry[5].
Strengths: Superior insulation properties, enhanced thermal stability, and eco-friendly options. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to standard LDPE grades, limited availability in some regions.
Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Furukawa Electric has pioneered the development of ultra-thin LDPE films for flexible electronics and displays. Their proprietary extrusion process allows for the production of LDPE films as thin as 10 microns while maintaining excellent dielectric properties[2]. The company has also developed LDPE-based composite materials that combine the insulation benefits of LDPE with enhanced mechanical strength, suitable for wearable electronics and IoT devices[4]. Furukawa's LDPE solutions incorporate antistatic additives to prevent dust accumulation and improve device reliability[6].
Strengths: Expertise in ultra-thin film production, innovative composite materials, and antistatic properties. Weaknesses: May have limited applications outside of specific electronic niches, potential for higher production costs.
Core Innovations in LDPE for Electronics
Polymer composition
PatentPendingUS20230070748A1
Innovation
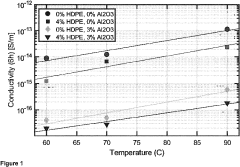
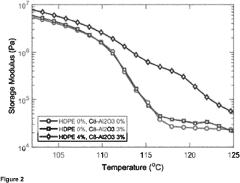
- A polymer composition comprising a blend of low-density polyethylene (LDPE), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and an aliphatic functional inorganic nanoparticle filler, which significantly reduces DC conductivity while maintaining or improving thermomechanical properties.
Cable insulation comprising a blend of LDPE and polypropylene
PatentWO2016200600A1
Innovation
- A blend of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) with a crystallinity greater than 40% and polypropylene, where the polypropylene content is between 1% and 14% with an upper melting point of at least 130°C, along with a peroxide content of at least 0.5%, is used to enhance extensional viscosity during cable extrusion.
Environmental Impact of LDPE in Electronics
The environmental impact of LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) in electronics is a complex issue that requires careful consideration. While LDPE offers significant benefits in terms of insulation and protection for electronic components, its widespread use also raises concerns about sustainability and ecological consequences.
One of the primary environmental challenges associated with LDPE in electronics is its persistence in the environment. As a petroleum-based plastic, LDPE does not biodegrade easily, potentially lasting for hundreds of years in landfills or natural ecosystems. This longevity contributes to the growing problem of plastic pollution, particularly in marine environments where discarded electronic waste can accumulate.
The production of LDPE for electronic applications also has environmental implications. The manufacturing process involves the use of fossil fuels and energy-intensive procedures, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Additionally, the extraction of raw materials for LDPE production can lead to habitat destruction and ecosystem disruption in oil-rich regions.
However, it is important to note that LDPE's use in electronics can have some positive environmental effects. Its excellent insulation properties help improve the energy efficiency of electronic devices, potentially reducing overall energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. Furthermore, LDPE's protective qualities can extend the lifespan of electronic products, reducing the frequency of replacements and thereby minimizing electronic waste generation.
Recycling presents both a challenge and an opportunity for mitigating the environmental impact of LDPE in electronics. While LDPE is theoretically recyclable, the presence of additives and contaminants in electronic applications can complicate the recycling process. Developing more efficient recycling technologies and implementing effective e-waste management systems are crucial steps in addressing this issue.
The electronics industry is increasingly exploring alternatives to traditional LDPE, such as bio-based plastics and recyclable polymers. These innovations aim to maintain the beneficial properties of LDPE while reducing its environmental footprint. However, the adoption of these alternatives faces challenges in terms of cost, performance, and scalability.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of LDPE in electronics is multifaceted, involving trade-offs between its functional benefits and ecological concerns. As the industry continues to evolve, balancing these factors will be crucial in developing sustainable solutions that meet both technological and environmental needs.
One of the primary environmental challenges associated with LDPE in electronics is its persistence in the environment. As a petroleum-based plastic, LDPE does not biodegrade easily, potentially lasting for hundreds of years in landfills or natural ecosystems. This longevity contributes to the growing problem of plastic pollution, particularly in marine environments where discarded electronic waste can accumulate.
The production of LDPE for electronic applications also has environmental implications. The manufacturing process involves the use of fossil fuels and energy-intensive procedures, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Additionally, the extraction of raw materials for LDPE production can lead to habitat destruction and ecosystem disruption in oil-rich regions.
However, it is important to note that LDPE's use in electronics can have some positive environmental effects. Its excellent insulation properties help improve the energy efficiency of electronic devices, potentially reducing overall energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. Furthermore, LDPE's protective qualities can extend the lifespan of electronic products, reducing the frequency of replacements and thereby minimizing electronic waste generation.
Recycling presents both a challenge and an opportunity for mitigating the environmental impact of LDPE in electronics. While LDPE is theoretically recyclable, the presence of additives and contaminants in electronic applications can complicate the recycling process. Developing more efficient recycling technologies and implementing effective e-waste management systems are crucial steps in addressing this issue.
The electronics industry is increasingly exploring alternatives to traditional LDPE, such as bio-based plastics and recyclable polymers. These innovations aim to maintain the beneficial properties of LDPE while reducing its environmental footprint. However, the adoption of these alternatives faces challenges in terms of cost, performance, and scalability.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of LDPE in electronics is multifaceted, involving trade-offs between its functional benefits and ecological concerns. As the industry continues to evolve, balancing these factors will be crucial in developing sustainable solutions that meet both technological and environmental needs.
LDPE Recycling and Sustainability Strategies
As the electronics industry continues to evolve, the importance of sustainable practices in the production and disposal of electronic components becomes increasingly crucial. LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene), widely used for insulation and protection in electronics, presents both challenges and opportunities in terms of recycling and sustainability.
The recycling of LDPE from electronic waste requires specialized processes due to the presence of various additives and contaminants. Current recycling strategies focus on mechanical recycling, where LDPE is separated, cleaned, and reprocessed into new products. However, this method often results in downcycling, producing lower-quality materials suitable for less demanding applications.
To address this issue, advanced recycling technologies are being developed. Chemical recycling, which breaks down LDPE into its molecular components, shows promise in producing high-quality recycled materials suitable for use in new electronic applications. This process can potentially close the loop in LDPE recycling, allowing for true circular economy practices in the electronics industry.
Sustainability strategies for LDPE in electronics extend beyond recycling. Manufacturers are exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived LDPE, which could significantly reduce the carbon footprint of electronic insulation materials. These bio-based polymers offer similar insulation and protection properties while being more environmentally friendly throughout their lifecycle.
Design for recyclability is another key strategy being adopted by electronics manufacturers. This approach involves designing products with end-of-life considerations in mind, making it easier to separate and recycle LDPE components. Modular designs and easily detachable insulation materials are examples of this strategy in action.
Furthermore, extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs are being implemented in various regions, holding manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. These programs incentivize the development of more sustainable LDPE alternatives and improved recycling infrastructure.
Collaboration across the value chain is essential for implementing effective LDPE recycling and sustainability strategies. Electronics manufacturers, recycling facilities, and material scientists are working together to develop innovative solutions that balance performance requirements with environmental considerations. This collaborative approach is crucial for overcoming the technical and economic challenges associated with LDPE recycling in electronics.
The recycling of LDPE from electronic waste requires specialized processes due to the presence of various additives and contaminants. Current recycling strategies focus on mechanical recycling, where LDPE is separated, cleaned, and reprocessed into new products. However, this method often results in downcycling, producing lower-quality materials suitable for less demanding applications.
To address this issue, advanced recycling technologies are being developed. Chemical recycling, which breaks down LDPE into its molecular components, shows promise in producing high-quality recycled materials suitable for use in new electronic applications. This process can potentially close the loop in LDPE recycling, allowing for true circular economy practices in the electronics industry.
Sustainability strategies for LDPE in electronics extend beyond recycling. Manufacturers are exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived LDPE, which could significantly reduce the carbon footprint of electronic insulation materials. These bio-based polymers offer similar insulation and protection properties while being more environmentally friendly throughout their lifecycle.
Design for recyclability is another key strategy being adopted by electronics manufacturers. This approach involves designing products with end-of-life considerations in mind, making it easier to separate and recycle LDPE components. Modular designs and easily detachable insulation materials are examples of this strategy in action.
Furthermore, extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs are being implemented in various regions, holding manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. These programs incentivize the development of more sustainable LDPE alternatives and improved recycling infrastructure.
Collaboration across the value chain is essential for implementing effective LDPE recycling and sustainability strategies. Electronics manufacturers, recycling facilities, and material scientists are working together to develop innovative solutions that balance performance requirements with environmental considerations. This collaborative approach is crucial for overcoming the technical and economic challenges associated with LDPE recycling in electronics.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!