LDPE in Healthcare: Safe and Flexible Solutions
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Healthcare Evolution
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has undergone a remarkable evolution in healthcare applications since its introduction in the 1930s. Initially developed as an insulation material, LDPE's unique properties quickly caught the attention of medical professionals seeking safe and flexible solutions for various healthcare needs.
In the 1950s, LDPE made its debut in the medical field as a packaging material for sterile medical devices and pharmaceuticals. Its excellent barrier properties against moisture and contaminants, coupled with its flexibility and durability, made it an ideal choice for maintaining the integrity of sensitive medical products.
The 1960s and 1970s saw a significant expansion of LDPE's role in healthcare. Researchers and manufacturers began exploring its potential for direct patient contact applications. This period marked the development of LDPE-based disposable medical devices, such as gloves, syringes, and IV bags. The material's biocompatibility and resistance to chemicals made it particularly suitable for these applications.
As healthcare practices evolved in the 1980s and 1990s, so did the use of LDPE. The material found its way into more sophisticated medical devices, including catheters, tubing, and prosthetic components. Advancements in polymer science led to the development of specialized LDPE formulations with enhanced properties, such as improved clarity and increased strength, further expanding its utility in healthcare settings.
The turn of the millennium brought about a renewed focus on infection control and patient safety. LDPE's role in healthcare continued to grow, with innovations in antimicrobial and antithrombogenic coatings applied to LDPE surfaces. These advancements significantly reduced the risk of hospital-acquired infections and improved the overall safety of medical devices.
In recent years, the healthcare industry has placed increasing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility. This shift has driven research into biodegradable and recyclable LDPE alternatives for healthcare applications. While traditional LDPE remains widely used, efforts are underway to develop more eco-friendly versions that maintain the material's desirable properties while reducing its environmental impact.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDPE in healthcare is likely to continue, with a focus on smart materials and nanotechnology. Researchers are exploring ways to incorporate sensors and drug-delivery mechanisms into LDPE-based medical devices, paving the way for more personalized and efficient healthcare solutions. As the industry moves towards precision medicine and advanced therapies, LDPE's versatility and adaptability position it as a key material in shaping the future of healthcare technology.
In the 1950s, LDPE made its debut in the medical field as a packaging material for sterile medical devices and pharmaceuticals. Its excellent barrier properties against moisture and contaminants, coupled with its flexibility and durability, made it an ideal choice for maintaining the integrity of sensitive medical products.
The 1960s and 1970s saw a significant expansion of LDPE's role in healthcare. Researchers and manufacturers began exploring its potential for direct patient contact applications. This period marked the development of LDPE-based disposable medical devices, such as gloves, syringes, and IV bags. The material's biocompatibility and resistance to chemicals made it particularly suitable for these applications.
As healthcare practices evolved in the 1980s and 1990s, so did the use of LDPE. The material found its way into more sophisticated medical devices, including catheters, tubing, and prosthetic components. Advancements in polymer science led to the development of specialized LDPE formulations with enhanced properties, such as improved clarity and increased strength, further expanding its utility in healthcare settings.
The turn of the millennium brought about a renewed focus on infection control and patient safety. LDPE's role in healthcare continued to grow, with innovations in antimicrobial and antithrombogenic coatings applied to LDPE surfaces. These advancements significantly reduced the risk of hospital-acquired infections and improved the overall safety of medical devices.
In recent years, the healthcare industry has placed increasing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility. This shift has driven research into biodegradable and recyclable LDPE alternatives for healthcare applications. While traditional LDPE remains widely used, efforts are underway to develop more eco-friendly versions that maintain the material's desirable properties while reducing its environmental impact.
Looking ahead, the evolution of LDPE in healthcare is likely to continue, with a focus on smart materials and nanotechnology. Researchers are exploring ways to incorporate sensors and drug-delivery mechanisms into LDPE-based medical devices, paving the way for more personalized and efficient healthcare solutions. As the industry moves towards precision medicine and advanced therapies, LDPE's versatility and adaptability position it as a key material in shaping the future of healthcare technology.
Market Demand Analysis
The healthcare industry has witnessed a growing demand for Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) solutions, driven by the material's unique properties and versatility in medical applications. LDPE's flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance make it an ideal choice for various healthcare products, contributing to its increasing market presence.
In recent years, the global healthcare LDPE market has experienced significant growth, with projections indicating continued expansion. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising demand for disposable medical devices, packaging materials, and pharmaceutical containers. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, as the need for personal protective equipment (PPE) and medical supplies surged worldwide.
One of the key drivers of LDPE demand in healthcare is the growing emphasis on infection control and prevention. LDPE's non-reactive nature and ability to maintain sterility make it an excellent choice for medical packaging, disposable gloves, and protective covers. As healthcare facilities worldwide prioritize patient safety and hygiene, the demand for LDPE-based products is expected to increase.
The pharmaceutical sector also contributes significantly to the market demand for LDPE. The material's chemical resistance and barrier properties make it suitable for drug packaging, ensuring the integrity and shelf life of medications. With the pharmaceutical industry experiencing steady growth and the rise of personalized medicine, the demand for LDPE in this sector is projected to expand further.
Another factor driving market demand is the aging population in many developed countries. As the elderly population grows, there is an increased need for medical devices, mobility aids, and healthcare products that incorporate LDPE components. This demographic shift is expected to sustain long-term demand for LDPE in healthcare applications.
The trend towards home healthcare and telemedicine has also created new opportunities for LDPE products. Portable medical devices, remote monitoring equipment, and at-home diagnostic kits often utilize LDPE components, driving demand in this emerging market segment.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives are influencing market dynamics as well. While LDPE is not biodegradable, efforts are being made to improve recycling processes and develop more eco-friendly alternatives. This has led to increased research and development in sustainable LDPE formulations for healthcare applications, potentially opening new market opportunities.
In conclusion, the market demand for LDPE in healthcare is robust and multifaceted, driven by factors such as infection control, pharmaceutical packaging, aging populations, and emerging healthcare trends. As the industry continues to evolve, LDPE is expected to play a crucial role in meeting the diverse needs of healthcare providers and patients alike.
In recent years, the global healthcare LDPE market has experienced significant growth, with projections indicating continued expansion. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising demand for disposable medical devices, packaging materials, and pharmaceutical containers. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, as the need for personal protective equipment (PPE) and medical supplies surged worldwide.
One of the key drivers of LDPE demand in healthcare is the growing emphasis on infection control and prevention. LDPE's non-reactive nature and ability to maintain sterility make it an excellent choice for medical packaging, disposable gloves, and protective covers. As healthcare facilities worldwide prioritize patient safety and hygiene, the demand for LDPE-based products is expected to increase.
The pharmaceutical sector also contributes significantly to the market demand for LDPE. The material's chemical resistance and barrier properties make it suitable for drug packaging, ensuring the integrity and shelf life of medications. With the pharmaceutical industry experiencing steady growth and the rise of personalized medicine, the demand for LDPE in this sector is projected to expand further.
Another factor driving market demand is the aging population in many developed countries. As the elderly population grows, there is an increased need for medical devices, mobility aids, and healthcare products that incorporate LDPE components. This demographic shift is expected to sustain long-term demand for LDPE in healthcare applications.
The trend towards home healthcare and telemedicine has also created new opportunities for LDPE products. Portable medical devices, remote monitoring equipment, and at-home diagnostic kits often utilize LDPE components, driving demand in this emerging market segment.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives are influencing market dynamics as well. While LDPE is not biodegradable, efforts are being made to improve recycling processes and develop more eco-friendly alternatives. This has led to increased research and development in sustainable LDPE formulations for healthcare applications, potentially opening new market opportunities.
In conclusion, the market demand for LDPE in healthcare is robust and multifaceted, driven by factors such as infection control, pharmaceutical packaging, aging populations, and emerging healthcare trends. As the industry continues to evolve, LDPE is expected to play a crucial role in meeting the diverse needs of healthcare providers and patients alike.
Technical Challenges
The use of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) in healthcare applications presents several technical challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its safe and effective implementation. One of the primary concerns is the material's susceptibility to degradation when exposed to certain sterilization methods commonly used in medical settings. Traditional sterilization techniques such as high-temperature autoclaving or gamma radiation can potentially compromise the structural integrity of LDPE, leading to changes in its physical and chemical properties.
Another significant challenge lies in achieving the optimal balance between flexibility and strength. While LDPE's flexibility is a desirable trait for many healthcare applications, it can sometimes come at the cost of reduced tensile strength and puncture resistance. This trade-off becomes particularly critical in applications where the material needs to withstand mechanical stress or protect against contamination.
The potential for leaching of additives and plasticizers from LDPE into medical solutions or biological samples is a concern that requires careful consideration. Although LDPE is generally considered inert, the presence of certain additives used to enhance its properties could potentially interact with drugs or biological materials, affecting their efficacy or purity.
Ensuring long-term stability and durability of LDPE in various healthcare environments poses another technical hurdle. The material must maintain its properties and performance over extended periods, even when exposed to diverse conditions such as varying temperatures, humidity levels, and chemical environments encountered in medical settings.
The challenge of enhancing LDPE's barrier properties is crucial for certain healthcare applications. While LDPE offers good moisture resistance, its permeability to gases and some organic compounds may limit its use in applications requiring high barrier performance, such as packaging for sensitive medical devices or pharmaceuticals.
Addressing the issue of biocompatibility and potential allergenic responses is vital for LDPE's widespread adoption in healthcare. Although LDPE is generally considered biocompatible, ensuring consistent purity and eliminating any potential for adverse reactions across a diverse patient population remains a technical challenge.
The recyclability and environmental impact of LDPE in healthcare applications present additional technical obstacles. Developing effective methods for recycling LDPE medical waste without compromising safety or increasing the risk of contamination is an ongoing challenge that requires innovative solutions.
Another significant challenge lies in achieving the optimal balance between flexibility and strength. While LDPE's flexibility is a desirable trait for many healthcare applications, it can sometimes come at the cost of reduced tensile strength and puncture resistance. This trade-off becomes particularly critical in applications where the material needs to withstand mechanical stress or protect against contamination.
The potential for leaching of additives and plasticizers from LDPE into medical solutions or biological samples is a concern that requires careful consideration. Although LDPE is generally considered inert, the presence of certain additives used to enhance its properties could potentially interact with drugs or biological materials, affecting their efficacy or purity.
Ensuring long-term stability and durability of LDPE in various healthcare environments poses another technical hurdle. The material must maintain its properties and performance over extended periods, even when exposed to diverse conditions such as varying temperatures, humidity levels, and chemical environments encountered in medical settings.
The challenge of enhancing LDPE's barrier properties is crucial for certain healthcare applications. While LDPE offers good moisture resistance, its permeability to gases and some organic compounds may limit its use in applications requiring high barrier performance, such as packaging for sensitive medical devices or pharmaceuticals.
Addressing the issue of biocompatibility and potential allergenic responses is vital for LDPE's widespread adoption in healthcare. Although LDPE is generally considered biocompatible, ensuring consistent purity and eliminating any potential for adverse reactions across a diverse patient population remains a technical challenge.
The recyclability and environmental impact of LDPE in healthcare applications present additional technical obstacles. Developing effective methods for recycling LDPE medical waste without compromising safety or increasing the risk of contamination is an ongoing challenge that requires innovative solutions.
Current LDPE Solutions
01 Safety features of LDPE
LDPE is generally considered safe for various applications due to its chemical inertness and low toxicity. It is often used in food packaging and medical devices. The material does not leach harmful substances under normal conditions, making it suitable for products that come into direct contact with food or skin.- Safety features of LDPE: LDPE is generally considered safe for various applications due to its chemical inertness and low toxicity. It is often used in food packaging and medical devices. The material does not leach harmful substances under normal conditions, making it suitable for contact with food and pharmaceuticals. Its safety profile is further enhanced by its resistance to chemical reactions and degradation.
- Flexibility characteristics of LDPE: LDPE is known for its high flexibility and elasticity. This property makes it ideal for applications requiring bendable or stretchable materials. The flexibility of LDPE is attributed to its branched molecular structure, which allows for easy deformation without breaking. This characteristic is particularly useful in the production of films, bags, and flexible packaging materials.
- LDPE in medical and pharmaceutical applications: The safety and flexibility of LDPE make it suitable for various medical and pharmaceutical applications. It is used in the production of medical devices, drug delivery systems, and packaging for medical supplies. The material's inertness ensures that it does not interact with drugs or biological substances, while its flexibility allows for the creation of adaptable medical products.
- Environmental considerations of LDPE: While LDPE offers many benefits in terms of safety and flexibility, its environmental impact is a concern. Efforts are being made to improve the recyclability and biodegradability of LDPE products. Research is ongoing to develop more eco-friendly versions of LDPE or alternative materials that maintain similar safety and flexibility properties while reducing environmental impact.
- Innovations in LDPE formulations: Ongoing research focuses on enhancing the properties of LDPE through various formulations and additives. These innovations aim to improve the material's strength, barrier properties, and heat resistance while maintaining its inherent safety and flexibility. New formulations also explore ways to enhance the material's compatibility with other polymers and improve its processing characteristics.
02 Flexibility and mechanical properties of LDPE
LDPE is known for its excellent flexibility and impact resistance. It has a low crystallinity, which contributes to its softness and pliability. This flexibility makes it ideal for applications such as flexible packaging, films, and squeeze bottles. LDPE also exhibits good tear resistance and elongation properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 LDPE blends and composites for enhanced properties
Blending LDPE with other polymers or additives can improve its properties. For example, combining LDPE with higher-density polyethylene or other materials can enhance its strength, barrier properties, or specific performance characteristics while maintaining flexibility. These blends are used in various industries to meet specific application requirements.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental considerations and recyclability of LDPE
While LDPE is recyclable, its widespread use in single-use plastics has raised environmental concerns. Efforts are being made to improve the recyclability of LDPE products and develop more sustainable alternatives. Some innovations focus on incorporating biodegradable additives or creating LDPE blends that are more environmentally friendly.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications leveraging LDPE safety and flexibility
The combination of safety and flexibility makes LDPE suitable for a wide range of applications. It is commonly used in the production of plastic bags, food packaging, medical tubing, wire and cable insulation, and various consumer products. Its flexibility allows for the creation of thin films and membranes, while its safety profile makes it appropriate for products that require direct contact with food or medical applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The LDPE healthcare market is in a mature growth stage, with a significant global market size driven by increasing demand for safe and flexible medical solutions. The technology has reached a high level of maturity, with established players like Dow Global Technologies, ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, and SABIC dominating the market. These companies have extensive R&D capabilities and production facilities, allowing them to offer a wide range of LDPE products tailored for healthcare applications. Emerging players such as Basell Polyolefine and Braskem are also making strides in this sector, focusing on innovative formulations and sustainable solutions to gain market share in this competitive landscape.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed advanced LDPE resins specifically for healthcare applications. Their ENGAGE™ polyolefin elastomers offer excellent flexibility and durability for medical devices and packaging. Dow's LDPE solutions incorporate antimicrobial properties, enhancing safety in healthcare settings[1]. They have also introduced DOWLEX™ polyethylene resins, which provide improved chemical resistance and sterilization compatibility for medical containers and tubing[2]. Dow's focus on sustainability has led to the development of bio-based LDPE alternatives, reducing the carbon footprint of healthcare products while maintaining performance[3].
Strengths: Wide range of specialized LDPE products for healthcare, strong R&D capabilities, focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to standard LDPE, potential regulatory hurdles for new materials.
Saudi Basic Industries Corp.
Technical Solution: SABIC has developed a range of LDPE resins tailored for healthcare applications under their SABIC® LDPE healthcare portfolio. These materials offer excellent processability and are suitable for various medical devices and packaging solutions. SABIC's healthcare-grade LDPE meets stringent regulatory requirements, including USP Class VI and ISO 10993 biocompatibility standards[4]. The company has also introduced SABIC® PCR LDPE compounds, incorporating post-consumer recycled content without compromising performance or safety, addressing sustainability concerns in healthcare[5]. SABIC's LDPE solutions feature enhanced clarity and chemical resistance, making them ideal for IV bags, tubing, and other critical medical applications[6].
Strengths: Comprehensive healthcare-specific LDPE portfolio, strong focus on regulatory compliance, innovative recycled content solutions. Weaknesses: Limited presence in some regional markets, potential supply chain challenges.
Innovative LDPE Patents
High pressure LDPE for medical applications
PatentWO2011057764A1
Innovation
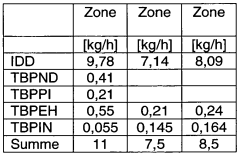
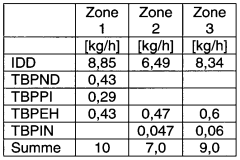
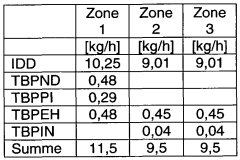
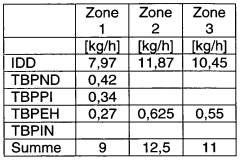
- A new LDPE material with a density of at least 0.932 g/cm3, higher crystallinity, and melting temperature, achieved through radical polymerization with specific peroxide initiators and chain transfer agents, allowing for faster and higher temperature sterilization while maintaining high processability for blow molding.
High pressure LDPE for medical applications
PatentActiveUS20120220738A1
Innovation
- Development of a new LDPE with higher density and crystallinity, achieved through radical polymerization, allowing for higher melting and softening temperatures while maintaining a high melt flow rate, enabling faster and more effective sterilization processes.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of LDPE usage in healthcare applications. The healthcare industry is subject to stringent regulations to ensure patient safety and product efficacy. For LDPE products, compliance with various regulatory bodies is essential to maintain market access and consumer trust.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of medical devices and materials used in healthcare. LDPE products must adhere to FDA guidelines, including those outlined in 21 CFR Part 177, which specifies the requirements for polymers in food contact applications. Additionally, manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent quality and safety in production processes.
The European Union employs the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) for healthcare products. These regulations set high standards for safety and performance, requiring manufacturers to conduct thorough risk assessments and maintain detailed technical documentation. LDPE products used in medical devices must meet these requirements to obtain CE marking and access the European market.
ISO 13485 is an international standard specifically designed for quality management systems in the medical device industry. Compliance with this standard demonstrates a commitment to quality and safety in the design, development, and manufacturing of LDPE healthcare products. It also facilitates regulatory compliance across different markets.
Biocompatibility testing is another crucial aspect of regulatory compliance for LDPE in healthcare. Standards such as ISO 10993 provide guidelines for evaluating the biological safety of medical devices and materials. LDPE products must undergo rigorous testing to ensure they do not cause adverse reactions when in contact with human tissues or bodily fluids.
Environmental regulations also play a role in LDPE compliance. With increasing focus on sustainability, manufacturers must consider regulations related to waste management, recycling, and the use of eco-friendly materials. This includes adherence to directives like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) in the EU.
Maintaining regulatory compliance is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring of changing regulations and standards. Manufacturers must stay informed about updates to existing regulations and the introduction of new ones. This may involve regular audits, documentation updates, and potentially product modifications to ensure continued compliance.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance for LDPE in healthcare encompasses a wide range of standards and regulations across different regions. Adherence to these requirements is essential for ensuring product safety, maintaining market access, and building consumer trust in LDPE healthcare solutions.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of medical devices and materials used in healthcare. LDPE products must adhere to FDA guidelines, including those outlined in 21 CFR Part 177, which specifies the requirements for polymers in food contact applications. Additionally, manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent quality and safety in production processes.
The European Union employs the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) for healthcare products. These regulations set high standards for safety and performance, requiring manufacturers to conduct thorough risk assessments and maintain detailed technical documentation. LDPE products used in medical devices must meet these requirements to obtain CE marking and access the European market.
ISO 13485 is an international standard specifically designed for quality management systems in the medical device industry. Compliance with this standard demonstrates a commitment to quality and safety in the design, development, and manufacturing of LDPE healthcare products. It also facilitates regulatory compliance across different markets.
Biocompatibility testing is another crucial aspect of regulatory compliance for LDPE in healthcare. Standards such as ISO 10993 provide guidelines for evaluating the biological safety of medical devices and materials. LDPE products must undergo rigorous testing to ensure they do not cause adverse reactions when in contact with human tissues or bodily fluids.
Environmental regulations also play a role in LDPE compliance. With increasing focus on sustainability, manufacturers must consider regulations related to waste management, recycling, and the use of eco-friendly materials. This includes adherence to directives like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) in the EU.
Maintaining regulatory compliance is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring of changing regulations and standards. Manufacturers must stay informed about updates to existing regulations and the introduction of new ones. This may involve regular audits, documentation updates, and potentially product modifications to ensure continued compliance.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance for LDPE in healthcare encompasses a wide range of standards and regulations across different regions. Adherence to these requirements is essential for ensuring product safety, maintaining market access, and building consumer trust in LDPE healthcare solutions.
Sustainability Aspects
Sustainability has become a crucial aspect in the healthcare industry, and LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) plays a significant role in addressing environmental concerns while maintaining the safety and flexibility required in medical applications. The use of LDPE in healthcare products offers several sustainability advantages that contribute to reducing the environmental impact of medical waste and promoting eco-friendly practices.
One of the primary sustainability benefits of LDPE in healthcare is its recyclability. LDPE can be easily recycled and repurposed, reducing the amount of plastic waste that ends up in landfills or oceans. Many healthcare facilities have implemented recycling programs specifically for LDPE products, such as packaging materials and disposable medical items. This circular approach to material usage helps conserve resources and minimize the environmental footprint of healthcare operations.
Furthermore, LDPE's lightweight nature contributes to sustainability by reducing transportation-related emissions. The lower weight of LDPE products compared to alternative materials results in decreased fuel consumption during shipping and distribution, thereby lowering the carbon footprint associated with healthcare supply chains. This aspect is particularly important given the global nature of medical supply networks and the increasing focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the healthcare sector.
LDPE also offers advantages in terms of energy efficiency during production. The manufacturing process for LDPE typically requires less energy compared to other plastics, resulting in lower carbon emissions. Additionally, advancements in LDPE production technologies have led to more sustainable manufacturing practices, including the use of renewable energy sources and the implementation of closed-loop systems that minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards the development of bio-based LDPE alternatives. These materials are derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, offering a more sustainable option that reduces dependence on fossil fuels. While still in the early stages of adoption in healthcare, bio-based LDPE shows promise in further enhancing the sustainability profile of medical products without compromising on safety or performance.
The durability and longevity of LDPE products also contribute to sustainability by reducing the need for frequent replacements. In healthcare settings, where sterility and reliability are paramount, LDPE's resistance to wear and tear ensures that products maintain their integrity over extended periods. This longevity translates to less frequent disposal and replacement, ultimately reducing waste generation and resource consumption.
As the healthcare industry continues to prioritize sustainability, LDPE remains a valuable material in balancing environmental concerns with the stringent requirements of medical applications. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on further improving the sustainability aspects of LDPE, including enhancing its biodegradability and exploring innovative recycling technologies. These advancements will likely solidify LDPE's position as a key player in the transition towards more sustainable healthcare practices.
One of the primary sustainability benefits of LDPE in healthcare is its recyclability. LDPE can be easily recycled and repurposed, reducing the amount of plastic waste that ends up in landfills or oceans. Many healthcare facilities have implemented recycling programs specifically for LDPE products, such as packaging materials and disposable medical items. This circular approach to material usage helps conserve resources and minimize the environmental footprint of healthcare operations.
Furthermore, LDPE's lightweight nature contributes to sustainability by reducing transportation-related emissions. The lower weight of LDPE products compared to alternative materials results in decreased fuel consumption during shipping and distribution, thereby lowering the carbon footprint associated with healthcare supply chains. This aspect is particularly important given the global nature of medical supply networks and the increasing focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the healthcare sector.
LDPE also offers advantages in terms of energy efficiency during production. The manufacturing process for LDPE typically requires less energy compared to other plastics, resulting in lower carbon emissions. Additionally, advancements in LDPE production technologies have led to more sustainable manufacturing practices, including the use of renewable energy sources and the implementation of closed-loop systems that minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards the development of bio-based LDPE alternatives. These materials are derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn, offering a more sustainable option that reduces dependence on fossil fuels. While still in the early stages of adoption in healthcare, bio-based LDPE shows promise in further enhancing the sustainability profile of medical products without compromising on safety or performance.
The durability and longevity of LDPE products also contribute to sustainability by reducing the need for frequent replacements. In healthcare settings, where sterility and reliability are paramount, LDPE's resistance to wear and tear ensures that products maintain their integrity over extended periods. This longevity translates to less frequent disposal and replacement, ultimately reducing waste generation and resource consumption.
As the healthcare industry continues to prioritize sustainability, LDPE remains a valuable material in balancing environmental concerns with the stringent requirements of medical applications. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on further improving the sustainability aspects of LDPE, including enhancing its biodegradability and exploring innovative recycling technologies. These advancements will likely solidify LDPE's position as a key player in the transition towards more sustainable healthcare practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!