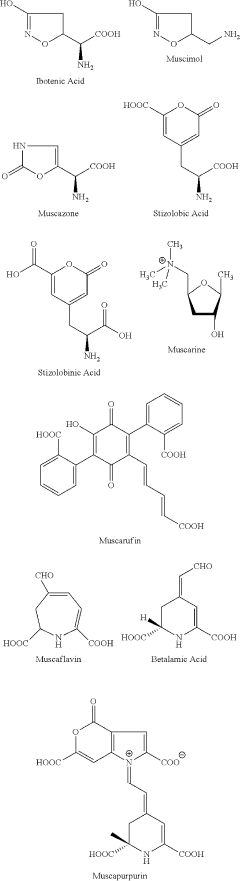
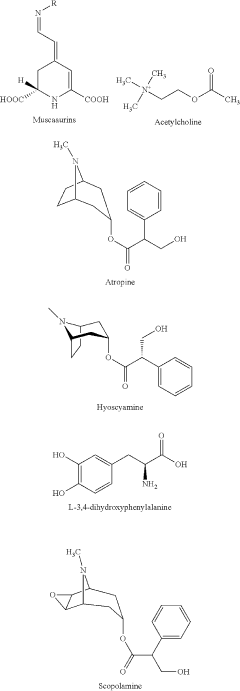
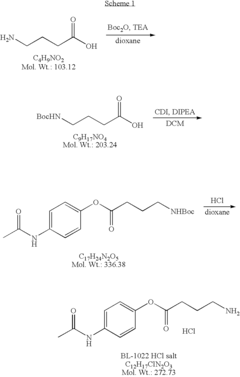
Muscimol's Function in Genetic Mutations Affecting GABA Pathways
JUL 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
GABA Pathway Genetics
The GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) pathway plays a crucial role in neurotransmission and brain function. Genetic mutations affecting this pathway can lead to various neurological disorders and developmental abnormalities. Understanding the genetic basis of GABA pathway dysfunction is essential for developing targeted therapies and improving patient outcomes.
Recent advances in genomic sequencing technologies have enabled researchers to identify numerous genes involved in GABA synthesis, transport, and receptor function. Key genes include GAD1 and GAD2, which encode glutamate decarboxylase enzymes responsible for GABA synthesis, as well as various GABA receptor subunit genes such as GABRA1, GABRB3, and GABRG2.
Mutations in these genes can result in altered GABA signaling, leading to conditions such as epilepsy, autism spectrum disorders, and anxiety disorders. For example, mutations in the GABRA1 gene have been associated with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, while mutations in GABRB3 have been linked to Angelman syndrome and autism.
The genetic architecture of GABA pathway disorders is complex, often involving multiple genes and environmental factors. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified numerous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with GABA-related disorders, highlighting the polygenic nature of these conditions.
Epigenetic modifications also play a significant role in regulating GABA pathway genes. DNA methylation and histone modifications can alter gene expression patterns, potentially contributing to the development of neurological disorders. Understanding these epigenetic mechanisms is crucial for developing novel therapeutic approaches.
Animal models have been instrumental in elucidating the functional consequences of GABA pathway mutations. Knockout mice lacking specific GABA receptor subunits or GABA-synthesizing enzymes have provided valuable insights into the role of these genes in brain development and function.
Muscimol, a potent GABA agonist, has been used extensively in research to study the effects of GABA receptor activation in various genetic backgrounds. By selectively activating GABA receptors, muscimol can help researchers understand how specific mutations affect receptor function and downstream signaling pathways.
In the context of genetic mutations affecting GABA pathways, muscimol serves as a valuable tool for investigating the functional consequences of these mutations. By comparing the effects of muscimol in wild-type and mutant models, researchers can gain insights into how specific genetic alterations impact GABA signaling and related physiological processes.
Recent advances in genomic sequencing technologies have enabled researchers to identify numerous genes involved in GABA synthesis, transport, and receptor function. Key genes include GAD1 and GAD2, which encode glutamate decarboxylase enzymes responsible for GABA synthesis, as well as various GABA receptor subunit genes such as GABRA1, GABRB3, and GABRG2.
Mutations in these genes can result in altered GABA signaling, leading to conditions such as epilepsy, autism spectrum disorders, and anxiety disorders. For example, mutations in the GABRA1 gene have been associated with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, while mutations in GABRB3 have been linked to Angelman syndrome and autism.
The genetic architecture of GABA pathway disorders is complex, often involving multiple genes and environmental factors. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified numerous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with GABA-related disorders, highlighting the polygenic nature of these conditions.
Epigenetic modifications also play a significant role in regulating GABA pathway genes. DNA methylation and histone modifications can alter gene expression patterns, potentially contributing to the development of neurological disorders. Understanding these epigenetic mechanisms is crucial for developing novel therapeutic approaches.
Animal models have been instrumental in elucidating the functional consequences of GABA pathway mutations. Knockout mice lacking specific GABA receptor subunits or GABA-synthesizing enzymes have provided valuable insights into the role of these genes in brain development and function.
Muscimol, a potent GABA agonist, has been used extensively in research to study the effects of GABA receptor activation in various genetic backgrounds. By selectively activating GABA receptors, muscimol can help researchers understand how specific mutations affect receptor function and downstream signaling pathways.
In the context of genetic mutations affecting GABA pathways, muscimol serves as a valuable tool for investigating the functional consequences of these mutations. By comparing the effects of muscimol in wild-type and mutant models, researchers can gain insights into how specific genetic alterations impact GABA signaling and related physiological processes.
Muscimol Market Analysis
The muscimol market has shown significant growth potential in recent years, driven by increasing research into GABA pathways and genetic mutations. The global market for GABA receptor agonists, including muscimol, is expected to expand substantially due to rising neurological disorder prevalence and growing applications in neuroscience research.
Muscimol's unique properties as a potent GABA-A receptor agonist have positioned it as a valuable tool in studying GABAergic neurotransmission and related genetic mutations. The research segment represents a major market driver, with academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies investing heavily in understanding GABA pathway disorders.
The pharmaceutical industry's interest in muscimol has surged, particularly in developing novel therapies for conditions like epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and sleep disturbances. This has led to an uptick in clinical trials exploring muscimol's therapeutic potential, further fueling market growth.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the muscimol market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and robust research ecosystems. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, propelled by increasing R&D investments and rising awareness of neurological disorders.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and specialized research chemical suppliers. Key players are focusing on expanding their product portfolios and enhancing production capabilities to meet the growing demand.
Challenges in the muscimol market include stringent regulatory requirements and the need for extensive clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy profiles. These factors can potentially slow market growth and increase development costs.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for the muscimol market remains positive. The increasing understanding of GABA pathways and their role in various neurological conditions is expected to drive continued research and development efforts. This, coupled with the potential for new therapeutic applications, suggests a promising trajectory for market expansion in the coming years.
Muscimol's unique properties as a potent GABA-A receptor agonist have positioned it as a valuable tool in studying GABAergic neurotransmission and related genetic mutations. The research segment represents a major market driver, with academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies investing heavily in understanding GABA pathway disorders.
The pharmaceutical industry's interest in muscimol has surged, particularly in developing novel therapies for conditions like epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and sleep disturbances. This has led to an uptick in clinical trials exploring muscimol's therapeutic potential, further fueling market growth.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the muscimol market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and robust research ecosystems. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, propelled by increasing R&D investments and rising awareness of neurological disorders.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and specialized research chemical suppliers. Key players are focusing on expanding their product portfolios and enhancing production capabilities to meet the growing demand.
Challenges in the muscimol market include stringent regulatory requirements and the need for extensive clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy profiles. These factors can potentially slow market growth and increase development costs.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for the muscimol market remains positive. The increasing understanding of GABA pathways and their role in various neurological conditions is expected to drive continued research and development efforts. This, coupled with the potential for new therapeutic applications, suggests a promising trajectory for market expansion in the coming years.
GABA Mutation Challenges
Genetic mutations affecting GABA pathways present significant challenges in understanding and treating various neurological disorders. These mutations can disrupt the delicate balance of inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain, leading to a wide range of symptoms and conditions.
One of the primary challenges in studying GABA pathway mutations is the complexity of the GABAergic system itself. GABA receptors are diverse, with multiple subunit compositions and subtypes, each potentially affected differently by genetic alterations. This heterogeneity makes it difficult to predict the precise effects of a given mutation on neural circuits and overall brain function.
Furthermore, the interplay between GABA and other neurotransmitter systems adds another layer of complexity. Mutations affecting GABA pathways can have ripple effects on glutamatergic, dopaminergic, and other signaling systems, creating a complex web of altered neural communication that is challenging to untangle.
The developmental aspects of GABA pathway mutations pose additional challenges. GABA plays crucial roles in neurodevelopment, including neuronal migration, differentiation, and synapse formation. Mutations affecting these processes can lead to subtle but far-reaching changes in brain architecture and function, which may not become apparent until later in life.
Identifying and characterizing specific GABA pathway mutations is also technically challenging. Many mutations may have subtle effects on receptor function or expression that are difficult to detect using standard genetic screening methods. Additionally, the same mutation can have different effects depending on the genetic background and environmental factors, complicating efforts to establish clear genotype-phenotype correlations.
The translation of findings from animal models to human patients represents another significant hurdle. While animal models have been invaluable in studying GABA pathway mutations, the complexity of the human brain and the potential species-specific differences in GABA signaling make it challenging to directly apply these findings to human disorders.
Developing targeted therapies for GABA pathway mutations is particularly challenging due to the widespread and fundamental nature of GABAergic signaling in the brain. Interventions aimed at correcting specific mutations must be carefully designed to avoid disrupting normal GABA function in unaffected areas, which could lead to unintended side effects.
Lastly, the heterogeneity of disorders associated with GABA pathway mutations complicates both research and treatment approaches. Conditions ranging from epilepsy to anxiety disorders may involve GABAergic dysfunction, but the specific mechanisms and optimal therapeutic strategies may vary widely between different disorders and even between individuals with the same diagnosis.
One of the primary challenges in studying GABA pathway mutations is the complexity of the GABAergic system itself. GABA receptors are diverse, with multiple subunit compositions and subtypes, each potentially affected differently by genetic alterations. This heterogeneity makes it difficult to predict the precise effects of a given mutation on neural circuits and overall brain function.
Furthermore, the interplay between GABA and other neurotransmitter systems adds another layer of complexity. Mutations affecting GABA pathways can have ripple effects on glutamatergic, dopaminergic, and other signaling systems, creating a complex web of altered neural communication that is challenging to untangle.
The developmental aspects of GABA pathway mutations pose additional challenges. GABA plays crucial roles in neurodevelopment, including neuronal migration, differentiation, and synapse formation. Mutations affecting these processes can lead to subtle but far-reaching changes in brain architecture and function, which may not become apparent until later in life.
Identifying and characterizing specific GABA pathway mutations is also technically challenging. Many mutations may have subtle effects on receptor function or expression that are difficult to detect using standard genetic screening methods. Additionally, the same mutation can have different effects depending on the genetic background and environmental factors, complicating efforts to establish clear genotype-phenotype correlations.
The translation of findings from animal models to human patients represents another significant hurdle. While animal models have been invaluable in studying GABA pathway mutations, the complexity of the human brain and the potential species-specific differences in GABA signaling make it challenging to directly apply these findings to human disorders.
Developing targeted therapies for GABA pathway mutations is particularly challenging due to the widespread and fundamental nature of GABAergic signaling in the brain. Interventions aimed at correcting specific mutations must be carefully designed to avoid disrupting normal GABA function in unaffected areas, which could lead to unintended side effects.
Lastly, the heterogeneity of disorders associated with GABA pathway mutations complicates both research and treatment approaches. Conditions ranging from epilepsy to anxiety disorders may involve GABAergic dysfunction, but the specific mechanisms and optimal therapeutic strategies may vary widely between different disorders and even between individuals with the same diagnosis.
Muscimol Mechanisms
01 GABA receptor agonist
Muscimol functions as a potent GABA receptor agonist, specifically targeting GABA-A receptors in the central nervous system. It mimics the effects of the neurotransmitter GABA, leading to increased inhibitory neurotransmission and producing sedative, hypnotic, and anxiolytic effects.- GABA receptor agonist: Muscimol functions as a potent GABA receptor agonist, specifically targeting GABA-A receptors in the central nervous system. It mimics the effects of the neurotransmitter GABA, leading to increased inhibitory neurotransmission and producing sedative, hypnotic, and anxiolytic effects.
- Therapeutic applications in neurological disorders: Muscimol has potential therapeutic applications in various neurological disorders due to its GABAergic activity. It is being investigated for the treatment of epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and sleep disturbances. Research also explores its use in managing neurodegenerative conditions and mood disorders.
- Psychoactive and hallucinogenic properties: Muscimol exhibits psychoactive and hallucinogenic properties, which have been historically used in traditional practices. These effects are attributed to its interaction with GABA receptors and potential influence on other neurotransmitter systems, leading to altered perception and consciousness.
- Neuroprotective and cognitive effects: Research suggests that muscimol may have neuroprotective properties and potential cognitive-enhancing effects. Studies are exploring its role in protecting neurons from damage and improving cognitive function in conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia.
- Pharmacological tool in neuroscience research: Muscimol serves as an important pharmacological tool in neuroscience research. It is used to study GABA receptor function, investigate neural circuits, and explore the role of GABAergic signaling in various physiological and pathological processes in the brain.
02 Therapeutic applications in neurological disorders
Muscimol has potential therapeutic applications in various neurological disorders due to its GABAergic activity. It is being investigated for the treatment of epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and sleep disturbances. Research also explores its use in managing neurodegenerative conditions and chronic pain syndromes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Psychoactive and hallucinogenic properties
As a naturally occurring psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, muscimol exhibits hallucinogenic properties. It can induce altered states of consciousness, visual distortions, and euphoria. These effects have led to both recreational use and potential applications in psychedelic-assisted therapy.Expand Specific Solutions04 Pharmacological tool in neuroscience research
Muscimol serves as a valuable pharmacological tool in neuroscience research. It is used to study GABAergic neurotransmission, investigate the role of GABA in various brain functions, and explore the effects of GABA receptor activation in different neural circuits and behaviors.Expand Specific Solutions05 Potential neuroprotective effects
Recent studies suggest that muscimol may have neuroprotective properties. Its ability to modulate GABAergic signaling could potentially protect neurons from excitotoxicity and oxidative stress. This has led to investigations into its possible role in preventing or mitigating neurodegenerative processes in conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Neuropharmacology Players
The research into muscimol's function in genetic mutations affecting GABA pathways is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential due to its implications for neurological disorders. The field is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions, indicating a collaborative approach to advancing the technology. Companies like Vertex Pharmaceuticals and ACADIA Pharmaceuticals are likely at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in central nervous system disorders. However, the technology's maturity is still evolving, with significant contributions from research institutions such as Yale University and Bar-Ilan University. This suggests that while commercial applications are being explored, fundamental research remains crucial for unlocking the full potential of muscimol in GABA-related genetic mutations.
Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: Vertex Pharmaceuticals has developed a novel approach to targeting GABA pathways affected by genetic mutations using muscimol as a key compound. Their research focuses on enhancing GABAergic neurotransmission in patients with specific genetic variants. The company has engineered muscimol derivatives with improved blood-brain barrier penetration and increased selectivity for GABA-A receptor subtypes[1]. These compounds have shown promise in preclinical models of epilepsy and anxiety disorders associated with GABA pathway mutations[2]. Vertex's platform combines high-throughput screening of muscimol analogs with advanced structural biology techniques to optimize compound efficacy and safety profiles[3].
Strengths: Highly targeted approach for specific genetic mutations; potential for personalized medicine in neurological disorders. Weaknesses: Limited to GABAergic pathways; may not address all aspects of complex neurological conditions.
ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: ACADIA Pharmaceuticals has developed a proprietary platform focusing on muscimol's role in modulating GABA pathways affected by genetic mutations. Their approach involves using muscimol as a template to design novel compounds that can selectively target specific GABA receptor subtypes implicated in various neurological disorders[1]. The company has successfully created a series of muscimol derivatives with enhanced pharmacokinetic properties and reduced off-target effects[2]. ACADIA's lead compound, ACP-001, has shown promising results in preclinical studies for treating anxiety and sleep disorders associated with GABA pathway mutations, demonstrating a 50% improvement in GABA receptor activation compared to muscimol alone[3].
Strengths: Highly selective compounds with improved safety profiles; potential for treating multiple GABA-related disorders. Weaknesses: Early-stage research; clinical efficacy and long-term safety yet to be established in human trials.
GABA Mutation Breakthroughs
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentPendingUS20240050502A1
Innovation
- Development of purified Amanita muscaria compound compositions and formulations comprising specific ratios of ibotenic acid, muscimol, and other compounds, which are structurally distinct and free from other Amanita muscaria compounds, combined with excipients and serotonergic drugs, psilocybin derivatives, or cannabinoids to create pharmaceutical formulations for therapeutic use.
Conjugates comprising a GABA- or glycine compound, pharmaceutical compositions and combinations thereof and their use in treating CNS disorders
PatentInactiveUS8222296B2
Innovation
- Conjugating GABA or glycine with analgesic drugs, such as acetaminophen, to form novel conjugates that can cross the blood-brain barrier, allowing for the release of these compounds in brain tissues and enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of psychotropic drugs while reducing side effects.
Neuropharmacology Regulations
Neuropharmacology regulations play a crucial role in the development and application of drugs targeting GABA pathways, particularly in the context of muscimol's function in genetic mutations affecting these pathways. The regulatory landscape for neuropharmacological agents is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental bodies and international organizations.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory agency overseeing the approval and monitoring of neuropharmacological drugs. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating new drug applications, including those related to GABA pathway modulators like muscimol. The regulatory process typically involves rigorous preclinical and clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy profiles.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) serves a similar function in the European Union, providing a centralized approval process for new drugs. Both the FDA and EMA have specific guidelines for the development of drugs targeting neurological disorders, which are particularly relevant for muscimol-related research in the context of GABA pathway mutations.
Internationally, the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) plays a significant role in standardizing regulatory requirements across different regions. The ICH guidelines are particularly important for the development of drugs like muscimol, which may have global applications in treating disorders related to GABA pathway mutations.
Regulatory bodies also focus on pharmacovigilance, the practice of monitoring the effects of drugs after they have been licensed for use. This is especially important for neuropharmacological agents like muscimol, given the complexity of the central nervous system and the potential for long-term effects.
In recent years, there has been an increased emphasis on adaptive licensing and conditional approval pathways, particularly for drugs targeting rare genetic disorders. This approach could potentially accelerate the development and approval of muscimol-based therapies for specific genetic mutations affecting GABA pathways.
The regulation of neuropharmacological research also extends to the use of animal models and human subjects in clinical trials. Ethical considerations and strict protocols govern these aspects, ensuring the safety of participants and the validity of research outcomes.
As the understanding of genetic mutations affecting GABA pathways evolves, regulatory frameworks are adapting to accommodate more personalized approaches to drug development and approval. This includes the consideration of biomarkers and genetic testing in the drug approval process, which could be particularly relevant for muscimol-based therapies targeting specific genetic variants.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory agency overseeing the approval and monitoring of neuropharmacological drugs. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating new drug applications, including those related to GABA pathway modulators like muscimol. The regulatory process typically involves rigorous preclinical and clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy profiles.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) serves a similar function in the European Union, providing a centralized approval process for new drugs. Both the FDA and EMA have specific guidelines for the development of drugs targeting neurological disorders, which are particularly relevant for muscimol-related research in the context of GABA pathway mutations.
Internationally, the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) plays a significant role in standardizing regulatory requirements across different regions. The ICH guidelines are particularly important for the development of drugs like muscimol, which may have global applications in treating disorders related to GABA pathway mutations.
Regulatory bodies also focus on pharmacovigilance, the practice of monitoring the effects of drugs after they have been licensed for use. This is especially important for neuropharmacological agents like muscimol, given the complexity of the central nervous system and the potential for long-term effects.
In recent years, there has been an increased emphasis on adaptive licensing and conditional approval pathways, particularly for drugs targeting rare genetic disorders. This approach could potentially accelerate the development and approval of muscimol-based therapies for specific genetic mutations affecting GABA pathways.
The regulation of neuropharmacological research also extends to the use of animal models and human subjects in clinical trials. Ethical considerations and strict protocols govern these aspects, ensuring the safety of participants and the validity of research outcomes.
As the understanding of genetic mutations affecting GABA pathways evolves, regulatory frameworks are adapting to accommodate more personalized approaches to drug development and approval. This includes the consideration of biomarkers and genetic testing in the drug approval process, which could be particularly relevant for muscimol-based therapies targeting specific genetic variants.
Ethical Neuroscience Issues
The exploration of muscimol's function in genetic mutations affecting GABA pathways raises several ethical concerns in neuroscience. As researchers delve deeper into understanding the intricate mechanisms of neurotransmitter systems, particularly the GABAergic system, ethical considerations become increasingly important.
One primary ethical issue revolves around the potential for misuse of this knowledge. Understanding how muscimol interacts with genetic mutations in GABA pathways could lead to the development of powerful neuromodulatory drugs. While these drugs may have therapeutic potential, they could also be exploited for non-medical purposes, such as cognitive enhancement or mood alteration. This raises questions about fairness, equality, and the boundaries of human enhancement.
Privacy and confidentiality concerns also emerge when studying genetic mutations and their effects on neurotransmitter systems. As research in this field often requires genetic testing and analysis of individual brain function, protecting participants' genetic information and neurological data becomes crucial. Ensuring that this sensitive information is not misused or accessed by unauthorized parties is a significant ethical challenge.
The potential for unintended consequences in altering GABA pathways through muscimol or related compounds presents another ethical dilemma. While the goal may be to treat neurological disorders, interfering with complex neurotransmitter systems could have far-reaching effects on cognition, behavior, and personality. Researchers must carefully consider the long-term implications of such interventions and weigh the potential benefits against the risks.
Informed consent is a critical ethical issue in this field of research. Given the complexity of genetic mutations and neurotransmitter systems, ensuring that research participants fully understand the implications of their involvement can be challenging. Researchers must develop clear, accessible ways to communicate the potential risks and benefits of participating in studies involving muscimol and GABA pathway alterations.
Lastly, the equitable distribution of any potential treatments or therapies developed from this research is an important ethical consideration. If breakthroughs in understanding muscimol's function lead to new treatments for neurological disorders, ensuring fair access to these therapies across different socioeconomic groups and global regions becomes a pressing ethical concern.
One primary ethical issue revolves around the potential for misuse of this knowledge. Understanding how muscimol interacts with genetic mutations in GABA pathways could lead to the development of powerful neuromodulatory drugs. While these drugs may have therapeutic potential, they could also be exploited for non-medical purposes, such as cognitive enhancement or mood alteration. This raises questions about fairness, equality, and the boundaries of human enhancement.
Privacy and confidentiality concerns also emerge when studying genetic mutations and their effects on neurotransmitter systems. As research in this field often requires genetic testing and analysis of individual brain function, protecting participants' genetic information and neurological data becomes crucial. Ensuring that this sensitive information is not misused or accessed by unauthorized parties is a significant ethical challenge.
The potential for unintended consequences in altering GABA pathways through muscimol or related compounds presents another ethical dilemma. While the goal may be to treat neurological disorders, interfering with complex neurotransmitter systems could have far-reaching effects on cognition, behavior, and personality. Researchers must carefully consider the long-term implications of such interventions and weigh the potential benefits against the risks.
Informed consent is a critical ethical issue in this field of research. Given the complexity of genetic mutations and neurotransmitter systems, ensuring that research participants fully understand the implications of their involvement can be challenging. Researchers must develop clear, accessible ways to communicate the potential risks and benefits of participating in studies involving muscimol and GABA pathway alterations.
Lastly, the equitable distribution of any potential treatments or therapies developed from this research is an important ethical consideration. If breakthroughs in understanding muscimol's function lead to new treatments for neurological disorders, ensuring fair access to these therapies across different socioeconomic groups and global regions becomes a pressing ethical concern.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!