Optimization Techniques for Solenoid Valve Duty Cycle Enhancement
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Solenoid Valve Evolution and Objectives
Solenoid valves have undergone significant evolution since their inception in the early 20th century. Initially designed for simple on-off control in fluid systems, these electromagnetic devices have transformed into sophisticated components crucial for precise flow control across various industries. The progression of solenoid valve technology has been driven by the increasing demands for improved efficiency, reliability, and performance in hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
The early solenoid valves were characterized by basic designs with limited control capabilities. As industrial processes became more complex, the need for more advanced valve systems grew. This led to the development of multi-way valves, proportional solenoid valves, and eventually, high-frequency pulse-width modulated (PWM) solenoid valves. Each iteration brought improvements in response time, flow precision, and energy efficiency.
A significant milestone in solenoid valve evolution was the introduction of electronic control systems. This integration allowed for more precise actuation and the ability to implement complex control algorithms. The advent of microprocessors and advanced sensors further enhanced the capabilities of solenoid valves, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustment of valve performance.
The primary objective in solenoid valve development has been to optimize the duty cycle – the ratio of time the valve is energized to the total cycle time. Enhancing the duty cycle is crucial for improving overall system efficiency, reducing power consumption, and extending valve lifespan. This optimization involves addressing several key challenges, including heat dissipation, response time, and wear resistance of moving parts.
Current research and development efforts are focused on several key areas to further enhance solenoid valve performance. These include the exploration of novel materials for valve components to improve durability and reduce friction, the development of more efficient electromagnetic coil designs to minimize power consumption, and the implementation of advanced control algorithms for precise actuation.
Another important objective is the miniaturization of solenoid valves without compromising performance. This trend is driven by the growing demand for compact and lightweight systems in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. Researchers are exploring innovative designs and manufacturing techniques to achieve this goal while maintaining or improving valve efficiency.
The evolution of solenoid valves is also closely tied to the broader trends in Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT). Future objectives include the development of smart solenoid valves with integrated sensors and communication capabilities, allowing for predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and seamless integration with automated control systems.
The early solenoid valves were characterized by basic designs with limited control capabilities. As industrial processes became more complex, the need for more advanced valve systems grew. This led to the development of multi-way valves, proportional solenoid valves, and eventually, high-frequency pulse-width modulated (PWM) solenoid valves. Each iteration brought improvements in response time, flow precision, and energy efficiency.
A significant milestone in solenoid valve evolution was the introduction of electronic control systems. This integration allowed for more precise actuation and the ability to implement complex control algorithms. The advent of microprocessors and advanced sensors further enhanced the capabilities of solenoid valves, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustment of valve performance.
The primary objective in solenoid valve development has been to optimize the duty cycle – the ratio of time the valve is energized to the total cycle time. Enhancing the duty cycle is crucial for improving overall system efficiency, reducing power consumption, and extending valve lifespan. This optimization involves addressing several key challenges, including heat dissipation, response time, and wear resistance of moving parts.
Current research and development efforts are focused on several key areas to further enhance solenoid valve performance. These include the exploration of novel materials for valve components to improve durability and reduce friction, the development of more efficient electromagnetic coil designs to minimize power consumption, and the implementation of advanced control algorithms for precise actuation.
Another important objective is the miniaturization of solenoid valves without compromising performance. This trend is driven by the growing demand for compact and lightweight systems in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. Researchers are exploring innovative designs and manufacturing techniques to achieve this goal while maintaining or improving valve efficiency.
The evolution of solenoid valves is also closely tied to the broader trends in Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT). Future objectives include the development of smart solenoid valves with integrated sensors and communication capabilities, allowing for predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and seamless integration with automated control systems.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for optimization techniques in solenoid valve duty cycle enhancement has been steadily growing across various industries. This surge is primarily driven by the increasing need for energy efficiency, improved performance, and extended lifespan of solenoid valves in critical applications.
In the automotive sector, the push for more fuel-efficient vehicles has led to a significant demand for optimized solenoid valves in engine management systems, transmission control, and exhaust gas recirculation. The global automotive solenoid valve market is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, with a particular focus on duty cycle enhancement to improve overall vehicle performance and reduce emissions.
The industrial automation sector is another key driver for solenoid valve optimization. As manufacturing processes become more sophisticated and energy-conscious, there is a growing demand for precise control and extended operational life of solenoid valves in pneumatic and hydraulic systems. This trend is particularly evident in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processing, where reliability and efficiency are paramount.
In the oil and gas industry, the need for enhanced solenoid valve performance is critical for safety and operational efficiency. Optimized duty cycles can significantly improve the reliability of emergency shutdown systems and process control applications, leading to increased demand for advanced solenoid valve technologies in this sector.
The HVAC industry is also experiencing a surge in demand for optimized solenoid valves. As building energy management becomes increasingly important, there is a growing need for more efficient heating, cooling, and ventilation systems. Solenoid valves with enhanced duty cycles play a crucial role in improving the overall energy efficiency of HVAC systems, driving market growth in this sector.
The medical device industry is another area where the demand for optimized solenoid valves is on the rise. In applications such as respiratory equipment, diagnostic devices, and fluid control systems, precise and reliable valve operation is essential. The ongoing development of advanced medical technologies is expected to further boost the demand for high-performance solenoid valves with optimized duty cycles.
As environmental regulations become more stringent worldwide, there is an increasing focus on reducing energy consumption and improving the efficiency of industrial processes. This trend is driving the adoption of optimized solenoid valves across various industries, as they offer significant potential for energy savings and improved operational efficiency.
The market for solenoid valve optimization techniques is also being influenced by the growing adoption of Industry 4.0 and IoT technologies. Smart, connected solenoid valves with enhanced duty cycles are becoming increasingly popular, as they offer improved monitoring, predictive maintenance capabilities, and integration with broader industrial control systems.
In the automotive sector, the push for more fuel-efficient vehicles has led to a significant demand for optimized solenoid valves in engine management systems, transmission control, and exhaust gas recirculation. The global automotive solenoid valve market is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, with a particular focus on duty cycle enhancement to improve overall vehicle performance and reduce emissions.
The industrial automation sector is another key driver for solenoid valve optimization. As manufacturing processes become more sophisticated and energy-conscious, there is a growing demand for precise control and extended operational life of solenoid valves in pneumatic and hydraulic systems. This trend is particularly evident in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processing, where reliability and efficiency are paramount.
In the oil and gas industry, the need for enhanced solenoid valve performance is critical for safety and operational efficiency. Optimized duty cycles can significantly improve the reliability of emergency shutdown systems and process control applications, leading to increased demand for advanced solenoid valve technologies in this sector.
The HVAC industry is also experiencing a surge in demand for optimized solenoid valves. As building energy management becomes increasingly important, there is a growing need for more efficient heating, cooling, and ventilation systems. Solenoid valves with enhanced duty cycles play a crucial role in improving the overall energy efficiency of HVAC systems, driving market growth in this sector.
The medical device industry is another area where the demand for optimized solenoid valves is on the rise. In applications such as respiratory equipment, diagnostic devices, and fluid control systems, precise and reliable valve operation is essential. The ongoing development of advanced medical technologies is expected to further boost the demand for high-performance solenoid valves with optimized duty cycles.
As environmental regulations become more stringent worldwide, there is an increasing focus on reducing energy consumption and improving the efficiency of industrial processes. This trend is driving the adoption of optimized solenoid valves across various industries, as they offer significant potential for energy savings and improved operational efficiency.
The market for solenoid valve optimization techniques is also being influenced by the growing adoption of Industry 4.0 and IoT technologies. Smart, connected solenoid valves with enhanced duty cycles are becoming increasingly popular, as they offer improved monitoring, predictive maintenance capabilities, and integration with broader industrial control systems.
Technical Challenges
The optimization of solenoid valve duty cycles presents several significant technical challenges that researchers and engineers must address. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent trade-off between valve response time and power consumption. Achieving faster response times typically requires higher power input, which can lead to increased energy consumption and heat generation. This balance becomes particularly critical in applications where energy efficiency is paramount.
Another major challenge lies in the precise control of valve opening and closing times. The non-linear behavior of solenoid valves, influenced by factors such as magnetic hysteresis and mechanical inertia, makes it difficult to achieve consistent and accurate timing across different operating conditions. This variability can result in suboptimal performance and reduced overall system efficiency.
Material limitations also pose significant hurdles in enhancing duty cycle performance. The magnetic core materials used in solenoid valves are subject to saturation and eddy current losses, which can limit the maximum operating frequency and efficiency of the valve. Additionally, the mechanical components of the valve, such as springs and seals, are prone to wear and fatigue, potentially leading to reduced performance and reliability over time.
Thermal management presents another critical challenge in duty cycle optimization. High-frequency operation can lead to excessive heat generation within the solenoid coil and surrounding components. This heat buildup not only affects the electrical properties of the coil but can also cause thermal expansion, potentially altering the valve's mechanical characteristics and compromising its performance.
The complexity of fluid dynamics within the valve system adds another layer of difficulty to optimization efforts. Factors such as flow turbulence, pressure drops, and cavitation can significantly impact valve performance and must be carefully considered in the design and control strategies. Modeling and predicting these fluid behaviors accurately, especially under varying operating conditions, remains a challenging task.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced control algorithms and sensing technologies presents both opportunities and challenges. While these technologies offer the potential for more precise and adaptive duty cycle control, they also introduce complexity in terms of system design, implementation, and maintenance. Ensuring the reliability and robustness of these advanced control systems in diverse operating environments is a significant technical hurdle.
Lastly, the need for standardization and compatibility across different industries and applications poses a challenge in developing universally applicable optimization techniques. The diverse requirements of various sectors, ranging from automotive to process industries, necessitate flexible and adaptable solutions that can be tailored to specific operational needs while maintaining overall performance and efficiency.
Another major challenge lies in the precise control of valve opening and closing times. The non-linear behavior of solenoid valves, influenced by factors such as magnetic hysteresis and mechanical inertia, makes it difficult to achieve consistent and accurate timing across different operating conditions. This variability can result in suboptimal performance and reduced overall system efficiency.
Material limitations also pose significant hurdles in enhancing duty cycle performance. The magnetic core materials used in solenoid valves are subject to saturation and eddy current losses, which can limit the maximum operating frequency and efficiency of the valve. Additionally, the mechanical components of the valve, such as springs and seals, are prone to wear and fatigue, potentially leading to reduced performance and reliability over time.
Thermal management presents another critical challenge in duty cycle optimization. High-frequency operation can lead to excessive heat generation within the solenoid coil and surrounding components. This heat buildup not only affects the electrical properties of the coil but can also cause thermal expansion, potentially altering the valve's mechanical characteristics and compromising its performance.
The complexity of fluid dynamics within the valve system adds another layer of difficulty to optimization efforts. Factors such as flow turbulence, pressure drops, and cavitation can significantly impact valve performance and must be carefully considered in the design and control strategies. Modeling and predicting these fluid behaviors accurately, especially under varying operating conditions, remains a challenging task.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced control algorithms and sensing technologies presents both opportunities and challenges. While these technologies offer the potential for more precise and adaptive duty cycle control, they also introduce complexity in terms of system design, implementation, and maintenance. Ensuring the reliability and robustness of these advanced control systems in diverse operating environments is a significant technical hurdle.
Lastly, the need for standardization and compatibility across different industries and applications poses a challenge in developing universally applicable optimization techniques. The diverse requirements of various sectors, ranging from automotive to process industries, necessitate flexible and adaptable solutions that can be tailored to specific operational needs while maintaining overall performance and efficiency.
Current Optimization Solutions
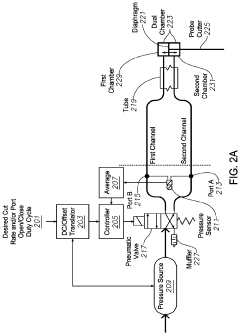
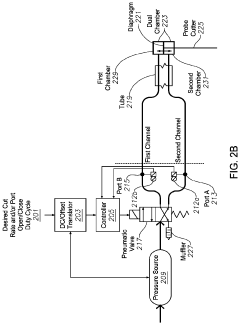
01 Duty cycle control for solenoid valves
Controlling the duty cycle of solenoid valves is crucial for optimizing their performance and efficiency. By adjusting the on-off time ratio, the valve's operation can be fine-tuned to meet specific requirements. This method allows for precise control of fluid flow, pressure regulation, and energy consumption in various applications.- Duty cycle control for solenoid valves: Controlling the duty cycle of solenoid valves is crucial for optimizing their performance and efficiency. By adjusting the on-time and off-time ratio, the valve's operation can be fine-tuned for specific applications. This control method allows for precise regulation of fluid flow and pressure, reducing energy consumption and wear on the valve components.
- Pulse width modulation in solenoid valve control: Pulse width modulation (PWM) is a technique used to control solenoid valves by rapidly switching the valve on and off. This method allows for precise control of the valve's opening and closing, enabling fine adjustment of fluid flow. PWM can help reduce power consumption and improve the overall efficiency of systems using solenoid valves.
- Temperature compensation in solenoid valve duty cycle: Temperature changes can affect the performance of solenoid valves. Implementing temperature compensation in the duty cycle control helps maintain consistent valve operation across varying environmental conditions. This approach ensures optimal performance and reliability of the valve in different temperature ranges.
- Adaptive duty cycle control for solenoid valves: Adaptive control systems can dynamically adjust the duty cycle of solenoid valves based on real-time feedback and changing operating conditions. This approach allows for optimal valve performance in varying situations, improving system efficiency and responsiveness. Adaptive control can compensate for wear, pressure changes, and other factors that may affect valve operation over time.
- Energy-efficient solenoid valve operation through duty cycle optimization: Optimizing the duty cycle of solenoid valves can lead to significant energy savings in various applications. By minimizing the time the valve is energized while maintaining the required performance, power consumption can be reduced. This approach not only saves energy but also extends the lifespan of the valve by reducing heat generation and wear on components.
02 Pulse width modulation for solenoid valve actuation
Pulse width modulation (PWM) is a technique used to control solenoid valves by varying the width of electrical pulses. This method allows for precise control of the valve's opening and closing, enabling smooth and accurate regulation of fluid flow. PWM can help reduce power consumption and improve the overall efficiency of the system.Expand Specific Solutions03 Temperature compensation in solenoid valve duty cycle
Temperature variations can affect the performance of solenoid valves. Implementing temperature compensation techniques in the duty cycle control can help maintain consistent valve operation across different temperature ranges. This approach ensures reliable performance and extends the valve's lifespan in various environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Adaptive duty cycle control for solenoid valves
Adaptive control algorithms can be used to dynamically adjust the duty cycle of solenoid valves based on real-time feedback and system conditions. This approach allows for optimal valve performance in changing operating conditions, improving system efficiency and responsiveness.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy-efficient solenoid valve operation
Implementing energy-efficient duty cycle strategies for solenoid valves can significantly reduce power consumption. This may involve using low-power holding currents, optimizing switching frequencies, and employing smart control algorithms to minimize energy usage while maintaining desired valve performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The optimization of solenoid valve duty cycles is a critical area in the automotive and industrial sectors, currently in a mature development stage. The market for this technology is substantial, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient and precise control systems. Companies like Robert Bosch GmbH, JATCO Ltd., and Siemens Automotive SA are at the forefront, leveraging their extensive experience in automotive components. Academic institutions such as Zhejiang University of Technology and Hefei University of Technology are contributing to research advancements. The technology's maturity is evident in its widespread application across various industries, with continuous improvements focusing on enhancing efficiency, reliability, and longevity of solenoid valve systems.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Robert Bosch GmbH has developed advanced optimization techniques for solenoid valve duty cycle enhancement. Their approach involves a combination of hardware and software solutions. On the hardware side, they have implemented high-precision solenoid valves with faster response times and reduced hysteresis[1]. These valves are coupled with advanced control algorithms that utilize predictive modeling and real-time feedback systems. The software solution incorporates machine learning algorithms to continuously optimize the duty cycle based on operating conditions and performance metrics[2]. This adaptive system can adjust valve timing and duration with microsecond precision, significantly improving overall efficiency. Bosch has also integrated thermal management systems to maintain optimal valve temperatures, further enhancing performance and longevity[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining hardware and software solutions, industry-leading precision and response times, adaptive learning capabilities. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial cost, may require specialized maintenance and calibration.
JATCO Ltd.
Technical Solution: JATCO Ltd. has focused on optimizing solenoid valve duty cycles specifically for automotive transmissions. Their approach centers on a novel pulse-width modulation (PWM) control strategy that dynamically adjusts the duty cycle based on transmission fluid temperature, pressure, and vehicle operating conditions[4]. This system utilizes high-frequency PWM signals, typically in the range of 200-300 Hz, to achieve precise control over valve opening and closing times. JATCO has also developed a unique "pre-energizing" technique that applies a short, high-current pulse to the solenoid just before the main activation, reducing response time by up to 30%[5]. Additionally, they have implemented advanced electromagnetic shielding to minimize interference and improve overall system stability.
Strengths: Specialized for automotive transmissions, high-precision control, reduced response times. Weaknesses: May be less adaptable to non-automotive applications, potential for increased power consumption due to high-frequency operation.
Core Innovations Review
Methods of solenoid valve control optimization
PatentActiveUS20230201033A1
Innovation
- A system and method that utilize a solenoid valve with a current sensor and system controller to detect back electromotive force (EMF) changes, enabling the transition to PWM mode for reduced power consumption, which includes identifying peaks and valleys in current signals to adjust the PWM duty cycle and frequency, and integrating this with a machine learning algorithm for predictive maintenance and pressure compensation.
Method and device for regulating the mean current across an inductive load controlled to give a variable opening duty cycle
PatentInactiveEP0662264A1
Innovation
- A method and device that regulate the average current in an inductive load by varying the control duty cycle, measuring the saturation current, and calculating a new duty cycle to compensate for variations in resistance and supply voltage, using a simple design that requires minimal memory and calculation resources.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Energy efficiency is a critical consideration in the optimization of solenoid valve duty cycles. As industrial processes and systems increasingly prioritize sustainability and cost reduction, enhancing the energy performance of solenoid valves has become a key focus area. The duty cycle, which represents the ratio of on-time to the total cycle time, directly impacts energy consumption and overall system efficiency.
One of the primary approaches to improving energy efficiency in solenoid valves is through the implementation of advanced control strategies. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) techniques, for instance, allow for precise control of the valve's opening and closing times, minimizing energy waste during transitions. By optimizing the PWM frequency and duty cycle, engineers can significantly reduce power consumption while maintaining the desired valve performance.
Material selection plays a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency. The use of low-loss magnetic materials for the valve core and armature can reduce eddy current losses and hysteresis, leading to improved electromagnetic efficiency. Additionally, incorporating high-performance insulation materials can minimize heat dissipation, further contributing to energy conservation.
Thermal management is another vital aspect of energy-efficient solenoid valve design. Effective heat dissipation techniques, such as improved coil winding methods and the integration of heat sinks, can prevent excessive temperature rise and maintain optimal operating conditions. This not only enhances energy efficiency but also extends the valve's lifespan and reliability.
The integration of smart sensing and control systems represents a significant advancement in solenoid valve energy efficiency. By employing sensors to monitor valve position, pressure, and flow rates, adaptive control algorithms can dynamically adjust the duty cycle to match real-time system requirements. This intelligent approach ensures that the valve operates at its most efficient point under varying conditions, minimizing unnecessary energy expenditure.
Furthermore, the development of energy harvesting technologies for solenoid valves is an emerging area of research. By capturing and utilizing waste energy from valve operations or surrounding vibrations, these systems can potentially power low-energy sensors and control circuits, reducing the overall energy demand of the valve system.
Lastly, the optimization of valve geometry and fluid dynamics can contribute to energy efficiency improvements. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations enable designers to refine valve shapes and flow paths, minimizing pressure drops and turbulence. This optimization not only enhances the valve's energy efficiency but also improves its overall performance and reliability.
One of the primary approaches to improving energy efficiency in solenoid valves is through the implementation of advanced control strategies. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) techniques, for instance, allow for precise control of the valve's opening and closing times, minimizing energy waste during transitions. By optimizing the PWM frequency and duty cycle, engineers can significantly reduce power consumption while maintaining the desired valve performance.
Material selection plays a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency. The use of low-loss magnetic materials for the valve core and armature can reduce eddy current losses and hysteresis, leading to improved electromagnetic efficiency. Additionally, incorporating high-performance insulation materials can minimize heat dissipation, further contributing to energy conservation.
Thermal management is another vital aspect of energy-efficient solenoid valve design. Effective heat dissipation techniques, such as improved coil winding methods and the integration of heat sinks, can prevent excessive temperature rise and maintain optimal operating conditions. This not only enhances energy efficiency but also extends the valve's lifespan and reliability.
The integration of smart sensing and control systems represents a significant advancement in solenoid valve energy efficiency. By employing sensors to monitor valve position, pressure, and flow rates, adaptive control algorithms can dynamically adjust the duty cycle to match real-time system requirements. This intelligent approach ensures that the valve operates at its most efficient point under varying conditions, minimizing unnecessary energy expenditure.
Furthermore, the development of energy harvesting technologies for solenoid valves is an emerging area of research. By capturing and utilizing waste energy from valve operations or surrounding vibrations, these systems can potentially power low-energy sensors and control circuits, reducing the overall energy demand of the valve system.
Lastly, the optimization of valve geometry and fluid dynamics can contribute to energy efficiency improvements. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations enable designers to refine valve shapes and flow paths, minimizing pressure drops and turbulence. This optimization not only enhances the valve's energy efficiency but also improves its overall performance and reliability.
Reliability and Lifespan Analysis
The reliability and lifespan analysis of solenoid valves is crucial for optimizing their duty cycle performance. Solenoid valves are subject to various stresses and wear mechanisms that can impact their longevity and operational consistency. Understanding these factors is essential for developing effective optimization techniques.
One of the primary considerations in reliability analysis is the impact of thermal stress on valve components. Repeated cycling of the solenoid generates heat, which can lead to material degradation over time. This thermal fatigue affects the coil windings, insulation materials, and mechanical components such as springs and seals. Advanced thermal management techniques, including improved heat dissipation designs and the use of high-temperature-resistant materials, can significantly enhance valve reliability.
Mechanical wear is another critical factor influencing valve lifespan. The constant movement of the plunger and associated components results in friction and potential material loss. This wear can lead to changes in valve response times and sealing effectiveness. Implementing surface treatments, such as hard chrome plating or the use of advanced composite materials, can reduce wear and extend operational life.
Electrical stress on the solenoid coil is a significant concern, particularly in high-frequency duty cycle applications. Voltage spikes and current surges can degrade insulation and lead to coil failure. Incorporating robust surge protection circuits and optimizing coil design for better heat dissipation can mitigate these risks and improve overall reliability.
Environmental factors also play a crucial role in valve lifespan. Exposure to corrosive fluids, extreme temperatures, or high-pressure conditions can accelerate component degradation. Selecting appropriate materials and implementing protective measures, such as corrosion-resistant coatings or hermetic sealing, can enhance valve durability in challenging environments.
Predictive maintenance strategies are increasingly important for maximizing valve lifespan. By employing sensors and data analytics, it is possible to monitor valve performance in real-time and predict potential failures before they occur. This approach allows for timely maintenance interventions, reducing downtime and extending overall system reliability.
Accelerated life testing methodologies are valuable tools for assessing long-term valve reliability. These tests simulate extended operational periods under various stress conditions, providing insights into potential failure modes and allowing for design optimizations. By incorporating the results of these tests into the development process, manufacturers can create more robust and longer-lasting solenoid valves.
In conclusion, a comprehensive approach to reliability and lifespan analysis is essential for enhancing solenoid valve duty cycle performance. By addressing thermal, mechanical, electrical, and environmental stresses, and leveraging advanced testing and maintenance strategies, significant improvements in valve longevity and operational consistency can be achieved.
One of the primary considerations in reliability analysis is the impact of thermal stress on valve components. Repeated cycling of the solenoid generates heat, which can lead to material degradation over time. This thermal fatigue affects the coil windings, insulation materials, and mechanical components such as springs and seals. Advanced thermal management techniques, including improved heat dissipation designs and the use of high-temperature-resistant materials, can significantly enhance valve reliability.
Mechanical wear is another critical factor influencing valve lifespan. The constant movement of the plunger and associated components results in friction and potential material loss. This wear can lead to changes in valve response times and sealing effectiveness. Implementing surface treatments, such as hard chrome plating or the use of advanced composite materials, can reduce wear and extend operational life.
Electrical stress on the solenoid coil is a significant concern, particularly in high-frequency duty cycle applications. Voltage spikes and current surges can degrade insulation and lead to coil failure. Incorporating robust surge protection circuits and optimizing coil design for better heat dissipation can mitigate these risks and improve overall reliability.
Environmental factors also play a crucial role in valve lifespan. Exposure to corrosive fluids, extreme temperatures, or high-pressure conditions can accelerate component degradation. Selecting appropriate materials and implementing protective measures, such as corrosion-resistant coatings or hermetic sealing, can enhance valve durability in challenging environments.
Predictive maintenance strategies are increasingly important for maximizing valve lifespan. By employing sensors and data analytics, it is possible to monitor valve performance in real-time and predict potential failures before they occur. This approach allows for timely maintenance interventions, reducing downtime and extending overall system reliability.
Accelerated life testing methodologies are valuable tools for assessing long-term valve reliability. These tests simulate extended operational periods under various stress conditions, providing insights into potential failure modes and allowing for design optimizations. By incorporating the results of these tests into the development process, manufacturers can create more robust and longer-lasting solenoid valves.
In conclusion, a comprehensive approach to reliability and lifespan analysis is essential for enhancing solenoid valve duty cycle performance. By addressing thermal, mechanical, electrical, and environmental stresses, and leveraging advanced testing and maintenance strategies, significant improvements in valve longevity and operational consistency can be achieved.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!