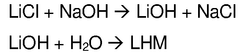Optimize Lithium Chloride Synthesis for Cost Efficiency
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LiCl Synthesis Background and Objectives
Lithium chloride (LiCl) has emerged as a critical compound in various industrial applications, particularly in battery technology, pharmaceuticals, and metallurgy. The synthesis of high-purity LiCl has traditionally followed several established routes, including the reaction of lithium carbonate with hydrochloric acid, direct reaction of lithium metal with chlorine gas, and extraction from lithium-rich brines. The historical development of these synthesis methods dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring during the 1950s and 1960s as demand for lithium compounds increased.
In recent years, the exponential growth of the electric vehicle market and renewable energy storage systems has dramatically escalated the demand for lithium compounds, including LiCl. This compound serves as a precursor for lithium metal production and as an intermediate in the manufacturing of other lithium chemicals. The global lithium market has experienced unprecedented growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate exceeding 14% through 2030.
Current synthesis methods face significant challenges related to energy consumption, reagent costs, and environmental impact. Traditional processes typically require high temperatures, expensive starting materials, or generate substantial waste streams. These factors contribute to the relatively high production cost of LiCl, which directly impacts downstream applications, particularly in cost-sensitive markets like grid-scale energy storage.
The technical evolution trajectory shows a gradual shift from energy-intensive thermal processes toward more environmentally sustainable approaches. Recent research has focused on developing ambient-temperature synthesis routes, recovery from secondary sources, and continuous flow processing techniques. These developments align with broader industry trends toward greener chemistry and circular economy principles.
The primary objective of this technical research is to identify and evaluate potential optimization pathways for LiCl synthesis that can significantly reduce production costs while maintaining product quality specifications. Specifically, we aim to achieve a minimum 30% reduction in overall production costs through innovations in reaction pathways, catalyst systems, energy integration, or process intensification.
Secondary objectives include minimizing environmental footprint through reduced waste generation and energy consumption, developing scalable processes suitable for industrial implementation, and ensuring compatibility with existing manufacturing infrastructure. The research will prioritize approaches that can be implemented within a 2-3 year timeframe to address immediate market pressures while positioning for longer-term technological advancements in the lithium value chain.
In recent years, the exponential growth of the electric vehicle market and renewable energy storage systems has dramatically escalated the demand for lithium compounds, including LiCl. This compound serves as a precursor for lithium metal production and as an intermediate in the manufacturing of other lithium chemicals. The global lithium market has experienced unprecedented growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate exceeding 14% through 2030.
Current synthesis methods face significant challenges related to energy consumption, reagent costs, and environmental impact. Traditional processes typically require high temperatures, expensive starting materials, or generate substantial waste streams. These factors contribute to the relatively high production cost of LiCl, which directly impacts downstream applications, particularly in cost-sensitive markets like grid-scale energy storage.
The technical evolution trajectory shows a gradual shift from energy-intensive thermal processes toward more environmentally sustainable approaches. Recent research has focused on developing ambient-temperature synthesis routes, recovery from secondary sources, and continuous flow processing techniques. These developments align with broader industry trends toward greener chemistry and circular economy principles.
The primary objective of this technical research is to identify and evaluate potential optimization pathways for LiCl synthesis that can significantly reduce production costs while maintaining product quality specifications. Specifically, we aim to achieve a minimum 30% reduction in overall production costs through innovations in reaction pathways, catalyst systems, energy integration, or process intensification.
Secondary objectives include minimizing environmental footprint through reduced waste generation and energy consumption, developing scalable processes suitable for industrial implementation, and ensuring compatibility with existing manufacturing infrastructure. The research will prioritize approaches that can be implemented within a 2-3 year timeframe to address immediate market pressures while positioning for longer-term technological advancements in the lithium value chain.
Market Demand Analysis for Lithium Chloride
The global lithium chloride market has been experiencing significant growth, driven primarily by the expanding lithium-ion battery industry. Market research indicates that the global lithium compounds market, including lithium chloride, is projected to reach $20 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate of 9.7% from 2023 to 2028. Lithium chloride specifically represents approximately 8% of this market, with steady growth anticipated as industrial applications diversify.
The demand for lithium chloride spans multiple sectors beyond battery production. In the pharmaceutical industry, lithium chloride serves as a precursor for lithium-based medications used in treating bipolar disorder and other psychiatric conditions. This segment has shown consistent annual growth of 5-6% globally, with particularly strong demand in North America and Europe.
Industrial applications constitute another significant market segment. Lithium chloride is extensively used in air conditioning systems and industrial dehumidification processes due to its hygroscopic properties. With increasing focus on energy-efficient climate control systems, this application segment is expected to grow at 7.8% annually through 2027.
The metallurgical industry represents a substantial consumer of lithium chloride, particularly in aluminum brazing and welding flux formulations. This sector's demand has increased by approximately 6.2% annually over the past five years, driven by construction and automotive manufacturing activities in emerging economies.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the lithium chloride market, accounting for approximately 45% of global consumption. China remains the largest consumer and producer, followed by Japan and South Korea. North America and Europe collectively represent about 38% of the market, with specialized applications in pharmaceutical and high-tech industries driving demand.
Supply chain considerations have become increasingly critical in the lithium chloride market. Recent geopolitical tensions and pandemic-related disruptions have highlighted vulnerabilities in the global supply chain, prompting many end-users to seek cost-efficient and reliable sourcing alternatives. This trend has accelerated interest in optimized synthesis methods that can reduce production costs and environmental impact.
Price sensitivity analysis indicates that a 15-20% reduction in lithium chloride production costs could potentially expand the market by capturing new application segments currently using alternative compounds. Industries particularly responsive to price reductions include water treatment, ceramics manufacturing, and certain consumer product categories where lithium chloride offers performance advantages but has been historically cost-prohibitive.
The demand for lithium chloride spans multiple sectors beyond battery production. In the pharmaceutical industry, lithium chloride serves as a precursor for lithium-based medications used in treating bipolar disorder and other psychiatric conditions. This segment has shown consistent annual growth of 5-6% globally, with particularly strong demand in North America and Europe.
Industrial applications constitute another significant market segment. Lithium chloride is extensively used in air conditioning systems and industrial dehumidification processes due to its hygroscopic properties. With increasing focus on energy-efficient climate control systems, this application segment is expected to grow at 7.8% annually through 2027.
The metallurgical industry represents a substantial consumer of lithium chloride, particularly in aluminum brazing and welding flux formulations. This sector's demand has increased by approximately 6.2% annually over the past five years, driven by construction and automotive manufacturing activities in emerging economies.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the lithium chloride market, accounting for approximately 45% of global consumption. China remains the largest consumer and producer, followed by Japan and South Korea. North America and Europe collectively represent about 38% of the market, with specialized applications in pharmaceutical and high-tech industries driving demand.
Supply chain considerations have become increasingly critical in the lithium chloride market. Recent geopolitical tensions and pandemic-related disruptions have highlighted vulnerabilities in the global supply chain, prompting many end-users to seek cost-efficient and reliable sourcing alternatives. This trend has accelerated interest in optimized synthesis methods that can reduce production costs and environmental impact.
Price sensitivity analysis indicates that a 15-20% reduction in lithium chloride production costs could potentially expand the market by capturing new application segments currently using alternative compounds. Industries particularly responsive to price reductions include water treatment, ceramics manufacturing, and certain consumer product categories where lithium chloride offers performance advantages but has been historically cost-prohibitive.
Current Synthesis Methods and Technical Barriers
Lithium chloride synthesis currently employs several established methods, each with distinct advantages and limitations. The most common industrial approach involves the reaction of lithium carbonate with hydrochloric acid, producing lithium chloride, water, and carbon dioxide. While straightforward, this method requires high-purity reagents and generates CO2 emissions, raising both cost and environmental concerns.
Alternative methods include direct extraction from brine resources, where lithium-rich solutions undergo concentration and purification processes. This approach, though potentially cost-effective for regions with natural brine deposits, faces challenges in separation efficiency and requires substantial energy for evaporation stages, contributing significantly to production costs.
The electrolysis of lithium hydroxide with chlorine gas represents another synthesis route, offering high-purity products but demanding specialized equipment and precise process control. This method's energy intensity and safety requirements limit its widespread industrial adoption despite quality advantages.
Technical barriers to cost-efficient lithium chloride production span multiple dimensions. Energy consumption remains a primary concern across all synthesis methods, with heating, evaporation, and electrolysis processes consuming substantial resources. Current technologies typically require 4-6 kWh per kilogram of lithium chloride produced, representing 30-40% of total production costs.
Reagent purity presents another significant challenge. Impurities in starting materials can compromise product quality and necessitate additional purification steps. Current industrial standards require 99.5% purity for battery-grade lithium chloride, demanding sophisticated and costly purification processes.
Process efficiency limitations further constrain cost optimization. Conventional batch processing methods exhibit yield rates of 85-92%, with material losses occurring at multiple production stages. Continuous flow processes show promise but face implementation challenges in maintaining consistent product quality.
Water usage represents an often-overlooked barrier, with traditional methods consuming 50-70 liters of water per kilogram of lithium chloride. This creates sustainability concerns and additional costs, particularly in water-scarce regions where lithium resources are often concentrated.
Waste management adds another layer of complexity and cost. Current synthesis methods generate significant byproducts requiring treatment or disposal, with neutralization and filtration processes adding approximately 15-20% to production costs. Regulatory compliance regarding these waste streams varies globally, creating regional cost disparities.
Equipment corrosion from chloride-rich environments necessitates the use of specialized materials and frequent maintenance, adding capital and operational expenses that impact overall production economics.
Alternative methods include direct extraction from brine resources, where lithium-rich solutions undergo concentration and purification processes. This approach, though potentially cost-effective for regions with natural brine deposits, faces challenges in separation efficiency and requires substantial energy for evaporation stages, contributing significantly to production costs.
The electrolysis of lithium hydroxide with chlorine gas represents another synthesis route, offering high-purity products but demanding specialized equipment and precise process control. This method's energy intensity and safety requirements limit its widespread industrial adoption despite quality advantages.
Technical barriers to cost-efficient lithium chloride production span multiple dimensions. Energy consumption remains a primary concern across all synthesis methods, with heating, evaporation, and electrolysis processes consuming substantial resources. Current technologies typically require 4-6 kWh per kilogram of lithium chloride produced, representing 30-40% of total production costs.
Reagent purity presents another significant challenge. Impurities in starting materials can compromise product quality and necessitate additional purification steps. Current industrial standards require 99.5% purity for battery-grade lithium chloride, demanding sophisticated and costly purification processes.
Process efficiency limitations further constrain cost optimization. Conventional batch processing methods exhibit yield rates of 85-92%, with material losses occurring at multiple production stages. Continuous flow processes show promise but face implementation challenges in maintaining consistent product quality.
Water usage represents an often-overlooked barrier, with traditional methods consuming 50-70 liters of water per kilogram of lithium chloride. This creates sustainability concerns and additional costs, particularly in water-scarce regions where lithium resources are often concentrated.
Waste management adds another layer of complexity and cost. Current synthesis methods generate significant byproducts requiring treatment or disposal, with neutralization and filtration processes adding approximately 15-20% to production costs. Regulatory compliance regarding these waste streams varies globally, creating regional cost disparities.
Equipment corrosion from chloride-rich environments necessitates the use of specialized materials and frequent maintenance, adding capital and operational expenses that impact overall production economics.
Cost-Efficient Synthesis Solutions
01 Direct synthesis methods from lithium sources
Direct synthesis methods involve extracting lithium chloride directly from lithium-containing raw materials such as lithium ores, brines, or waste materials. These methods typically involve fewer processing steps, reducing energy consumption and production costs. Techniques include direct extraction from salt lakes, conversion of lithium carbonate with hydrochloric acid, and recovery from industrial waste streams. These approaches minimize the use of expensive reagents and simplify the production process.- Direct synthesis methods from lithium sources: Direct synthesis methods involve extracting lithium chloride directly from lithium-containing sources such as brines, ores, or waste materials. These methods typically involve fewer processing steps, reducing energy consumption and production costs. Techniques include selective precipitation, ion exchange, and direct extraction from natural brines, which can significantly improve cost efficiency by eliminating intermediate processing steps.
- Recycling and recovery processes: Cost-efficient methods for recovering lithium chloride from waste materials and spent batteries have been developed to address resource scarcity and environmental concerns. These processes involve leaching, precipitation, and purification steps to extract lithium compounds from various waste streams. By recycling lithium from end-of-life products, these methods reduce the need for primary raw materials and lower overall production costs.
- Continuous flow production systems: Continuous flow production systems for lithium chloride synthesis offer advantages over batch processes, including better process control, reduced labor costs, and higher throughput. These systems often incorporate automated monitoring and control mechanisms to optimize reaction conditions and minimize reagent consumption. The continuous nature of these processes reduces downtime between batches and improves overall production efficiency.
- Energy-efficient reaction pathways: Novel reaction pathways have been developed to reduce the energy requirements for lithium chloride synthesis. These approaches include catalytic processes, low-temperature reactions, and alternative reaction media that lower activation energies. By reducing the thermal energy needed for synthesis, these methods significantly decrease production costs while maintaining high product purity and yield.
- Purification and quality control innovations: Advanced purification techniques have been developed to efficiently remove impurities from lithium chloride products while minimizing material losses. These methods include selective crystallization, membrane filtration, and advanced separation technologies that can achieve high-purity products with fewer processing steps. Improved quality control systems ensure consistent product quality while reducing waste and rework, contributing to overall cost efficiency in the production process.
02 Continuous flow production systems
Continuous flow production systems for lithium chloride synthesis offer significant cost advantages over batch processes. These systems enable constant production with reduced labor costs, improved quality control, and more efficient use of energy and raw materials. The continuous nature of these processes allows for better heat recovery, reduced equipment footprint, and minimized waste generation. Advanced monitoring and control systems further optimize the production parameters in real-time.Expand Specific Solutions03 Recycling and recovery methods
Cost-efficient lithium chloride synthesis can be achieved through recycling and recovery methods from spent lithium batteries, industrial waste streams, and other lithium-containing materials. These approaches reduce dependency on primary lithium sources and lower overall production costs. Advanced separation techniques, including selective precipitation, ion exchange, and membrane processes, enable efficient recovery of lithium compounds that can be converted to lithium chloride with minimal additional processing.Expand Specific Solutions04 Energy-efficient reaction pathways
Energy-efficient reaction pathways for lithium chloride synthesis focus on reducing the thermal energy requirements and optimizing reaction conditions. These methods include low-temperature synthesis routes, catalytic processes that lower activation energy, and novel reactor designs that improve heat transfer efficiency. By minimizing energy inputs while maintaining high conversion rates and product purity, these approaches significantly reduce production costs and environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process integration and by-product utilization
Process integration and by-product utilization strategies enhance the cost efficiency of lithium chloride synthesis by creating value from waste streams and integrating multiple production processes. These approaches include co-production of valuable by-products such as magnesium compounds, recovery of heat energy from exothermic reactions, and integration with other chemical manufacturing processes. By maximizing resource utilization and creating additional revenue streams, these methods improve the overall economics of lithium chloride production.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The lithium chloride synthesis optimization market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by the expanding lithium-ion battery sector. The global market size for lithium compounds is projected to reach $8-10 billion by 2025, with lithium chloride representing a significant segment. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across different synthesis approaches. Leading players like POSCO Holdings and Ganfeng Lithium have developed advanced extraction and processing technologies, while SQM and Central Glass focus on cost-efficient production methods. Research institutions such as KRICT and Central South University are pioneering novel synthesis routes. Companies like Panasonic and Idemitsu Kosan are investing in recycling technologies to reduce production costs, while specialized firms like Adionics are developing selective extraction processes that promise significant cost advantages in lithium chloride production.
Central South University
Technical Solution: Central South University has developed an electrochemical process for lithium chloride synthesis that significantly reduces production costs. Their approach utilizes a membrane electrolysis system that selectively extracts lithium ions from various feedstocks, including low-grade ores and industrial waste streams. The process employs specially designed electrodes with high selectivity for lithium, achieving separation efficiencies of over 90% while minimizing energy consumption. Their research has demonstrated that the electrochemical method reduces processing time by approximately 60% compared to conventional hydrometallurgical techniques. The university's technology incorporates a novel electrolyte recycling system that recovers and reuses over 85% of the process chemicals, substantially reducing raw material costs. Their approach operates at near-ambient temperatures (30-40°C), requiring approximately 40% less energy than traditional high-temperature processes. The system produces high-purity lithium chloride (>99.7%) through a continuous flow process that maintains consistent quality while minimizing labor requirements.
Strengths: Ability to process low-grade and unconventional lithium sources economically; reduced chemical consumption through recycling; precise control over product purity through electrochemical parameters. Weaknesses: Higher electricity requirements compared to some conventional methods; more complex equipment maintenance needs; technology still in transition from laboratory to industrial scale.
POSCO Holdings, Inc.
Technical Solution: POSCO has developed an innovative lithium extraction and conversion technology called "PosLX" specifically designed for cost-efficient lithium chloride production. Their process employs a selective lithium adsorption technique using proprietary adsorbent materials that can extract lithium from diverse sources including low-concentration brines and seawater. The PosLX system operates through a continuous adsorption-desorption cycle that achieves lithium recovery rates exceeding 80% while maintaining operational stability. POSCO's technology reduces processing time from months to just hours, with their pilot plants demonstrating production cycles of approximately 8 hours from extraction to lithium chloride formation. The process incorporates an energy-efficient precipitation method that minimizes chemical reagent usage by approximately 30% compared to conventional techniques. Their system includes a closed-loop water management approach that recycles over 95% of process water, significantly reducing freshwater requirements and environmental impact.
Strengths: Versatility in processing various lithium sources including low-grade resources; compact plant footprint requiring minimal land area; rapid production cycle enabling quick market response. Weaknesses: Higher energy consumption for adsorption-desorption cycles compared to solar evaporation; requires specialized adsorbent materials that need periodic replacement; technology still scaling to full commercial implementation.
Critical Patents and Technical Innovations
Process for producing lithium hydroxide monohydrate
PatentWO2025036769A1
Innovation
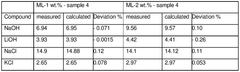
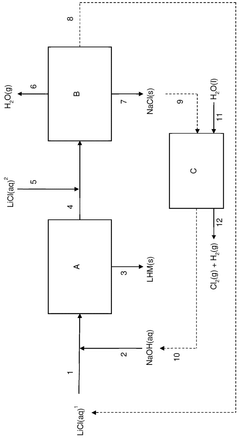
- A process involving the addition of an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to a lithium chloride solution, followed by cooling to precipitate lithium hydroxide monohydrate, and subsequent separation and purification steps to achieve high purity and efficiency.
Method for manufacturing metal lithium
PatentActiveUS20190264343A1
Innovation
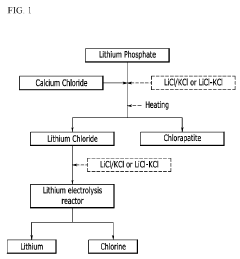
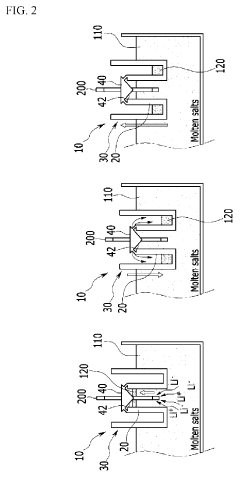
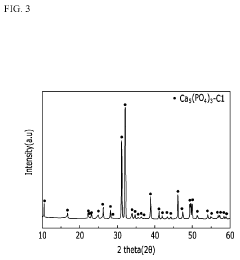
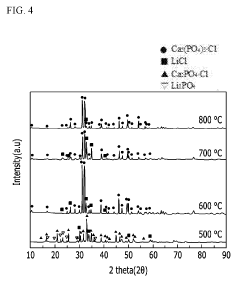
- A method involving the use of lithium phosphate as a raw material to produce lithium chloride through reaction with a chloride compound, followed by electrolysis to recover lithium metal, reducing the complexity and energy requirements of the process.
Raw Material Supply Chain Analysis
The global lithium supply chain represents a critical component in optimizing lithium chloride synthesis for cost efficiency. Currently, lithium raw materials are predominantly sourced from two distinct extraction methods: hard rock mining (primarily spodumene) and brine operations, with Australia, Chile, China, and Argentina controlling approximately 85% of global production capacity.
Supply chain analysis reveals significant volatility in lithium raw material pricing over the past five years, with prices fluctuating between $5,000 and $78,000 per metric ton of lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE). This volatility creates substantial challenges for maintaining consistent production costs in lithium chloride synthesis operations, necessitating strategic procurement approaches and long-term supplier agreements.
Transportation logistics constitute approximately 8-15% of total raw material costs, with geographical disparities creating notable cost differentials. Australian spodumene typically requires shipping to conversion facilities in China, while South American brine operations benefit from more vertically integrated processing capabilities but face political stability concerns that can disrupt supply continuity.
Quality variations in lithium feedstock significantly impact downstream synthesis efficiency. Spodumene concentrates typically contain 4.8-6.0% Li₂O, while brine-derived lithium carbonate purity ranges from 99.0-99.9%. Higher purity inputs directly correlate with reduced purification costs during lithium chloride synthesis, potentially decreasing overall production costs by 7-12%.
Emerging alternative sources, including direct lithium extraction (DLE) technologies and lithium clay deposits, show promise for diversifying the supply chain. DLE methods potentially reduce water consumption by 50-90% compared to traditional evaporation ponds while accelerating extraction timeframes from 18 months to mere days. However, these technologies remain predominantly in pilot stages with limited commercial implementation.
Recycling initiatives are gradually expanding, with current recovery rates of lithium from end-of-life batteries ranging between 5-15%. Industry projections suggest recycled lithium could constitute up to 25% of the supply chain by 2030, potentially stabilizing raw material costs through reduced dependency on primary extraction.
Strategic considerations for optimizing the lithium chloride synthesis supply chain include vertical integration opportunities, geographical diversification of suppliers, implementation of price hedging mechanisms, and investment in preprocessing technologies to accommodate lower-grade feedstock materials while maintaining synthesis efficiency.
Supply chain analysis reveals significant volatility in lithium raw material pricing over the past five years, with prices fluctuating between $5,000 and $78,000 per metric ton of lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE). This volatility creates substantial challenges for maintaining consistent production costs in lithium chloride synthesis operations, necessitating strategic procurement approaches and long-term supplier agreements.
Transportation logistics constitute approximately 8-15% of total raw material costs, with geographical disparities creating notable cost differentials. Australian spodumene typically requires shipping to conversion facilities in China, while South American brine operations benefit from more vertically integrated processing capabilities but face political stability concerns that can disrupt supply continuity.
Quality variations in lithium feedstock significantly impact downstream synthesis efficiency. Spodumene concentrates typically contain 4.8-6.0% Li₂O, while brine-derived lithium carbonate purity ranges from 99.0-99.9%. Higher purity inputs directly correlate with reduced purification costs during lithium chloride synthesis, potentially decreasing overall production costs by 7-12%.
Emerging alternative sources, including direct lithium extraction (DLE) technologies and lithium clay deposits, show promise for diversifying the supply chain. DLE methods potentially reduce water consumption by 50-90% compared to traditional evaporation ponds while accelerating extraction timeframes from 18 months to mere days. However, these technologies remain predominantly in pilot stages with limited commercial implementation.
Recycling initiatives are gradually expanding, with current recovery rates of lithium from end-of-life batteries ranging between 5-15%. Industry projections suggest recycled lithium could constitute up to 25% of the supply chain by 2030, potentially stabilizing raw material costs through reduced dependency on primary extraction.
Strategic considerations for optimizing the lithium chloride synthesis supply chain include vertical integration opportunities, geographical diversification of suppliers, implementation of price hedging mechanisms, and investment in preprocessing technologies to accommodate lower-grade feedstock materials while maintaining synthesis efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The optimization of lithium chloride synthesis processes must carefully consider environmental impacts and sustainability factors, as these aspects are increasingly critical in the chemical manufacturing industry. Traditional lithium chloride production methods often involve significant water consumption, energy usage, and generate considerable waste streams that can contain harmful chemicals. The environmental footprint of lithium chloride synthesis extends beyond immediate production facilities to affect surrounding ecosystems and communities.
Water usage represents one of the most pressing environmental concerns in lithium chloride production, particularly when extracted from brine operations. These processes can deplete local water resources in often arid regions where lithium deposits are found, creating competition with agricultural needs and threatening biodiversity. Advanced water recycling systems and closed-loop processing technologies offer promising solutions to reduce freshwater consumption by up to 30-50%, significantly improving the sustainability profile of production operations.
Energy consumption during lithium chloride synthesis contributes substantially to the carbon footprint of the final product. Conventional heating methods and electrolysis processes are energy-intensive, often relying on fossil fuel sources. Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power for production facilities can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 40-70% depending on the specific process configuration and energy mix. Additionally, process intensification techniques that optimize reaction conditions can further reduce energy requirements.
Chemical waste management presents another significant environmental challenge. Effluents from lithium chloride production may contain high concentrations of sodium, calcium, magnesium, and other potentially harmful elements. Implementation of advanced filtration systems, precipitation techniques, and selective recovery processes can minimize discharge of these contaminants while simultaneously recovering valuable by-products, creating additional revenue streams while reducing environmental impact.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that optimized lithium chloride synthesis can achieve a 25-35% reduction in overall environmental impact compared to conventional methods. These improvements come from combined enhancements in resource efficiency, waste reduction, and energy optimization. Furthermore, implementing circular economy principles by recovering and reusing reagents and by-products can extend these benefits throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory compliance and certification standards are increasingly stringent regarding chemical manufacturing processes. Companies investing in environmentally optimized lithium chloride synthesis not only reduce potential remediation costs and regulatory penalties but also position themselves advantageously in markets where sustainability credentials influence purchasing decisions. This alignment with global sustainability goals can provide significant competitive advantages in the rapidly evolving lithium market.
Water usage represents one of the most pressing environmental concerns in lithium chloride production, particularly when extracted from brine operations. These processes can deplete local water resources in often arid regions where lithium deposits are found, creating competition with agricultural needs and threatening biodiversity. Advanced water recycling systems and closed-loop processing technologies offer promising solutions to reduce freshwater consumption by up to 30-50%, significantly improving the sustainability profile of production operations.
Energy consumption during lithium chloride synthesis contributes substantially to the carbon footprint of the final product. Conventional heating methods and electrolysis processes are energy-intensive, often relying on fossil fuel sources. Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power for production facilities can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 40-70% depending on the specific process configuration and energy mix. Additionally, process intensification techniques that optimize reaction conditions can further reduce energy requirements.
Chemical waste management presents another significant environmental challenge. Effluents from lithium chloride production may contain high concentrations of sodium, calcium, magnesium, and other potentially harmful elements. Implementation of advanced filtration systems, precipitation techniques, and selective recovery processes can minimize discharge of these contaminants while simultaneously recovering valuable by-products, creating additional revenue streams while reducing environmental impact.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that optimized lithium chloride synthesis can achieve a 25-35% reduction in overall environmental impact compared to conventional methods. These improvements come from combined enhancements in resource efficiency, waste reduction, and energy optimization. Furthermore, implementing circular economy principles by recovering and reusing reagents and by-products can extend these benefits throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory compliance and certification standards are increasingly stringent regarding chemical manufacturing processes. Companies investing in environmentally optimized lithium chloride synthesis not only reduce potential remediation costs and regulatory penalties but also position themselves advantageously in markets where sustainability credentials influence purchasing decisions. This alignment with global sustainability goals can provide significant competitive advantages in the rapidly evolving lithium market.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!