Optimizing Luteolin Extraction from Plant Sources
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Extraction Background and Objectives
Luteolin, a natural flavonoid compound found in various plant sources, has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its remarkable pharmacological properties. The history of luteolin research dates back to the early 20th century, but intensive scientific investigation began in the 1990s when researchers started to uncover its potential health benefits. This flavonoid belongs to the flavone subclass and is characterized by its C6-C3-C6 structure with hydroxyl groups at positions 5, 7, 3', and 4', which contribute to its potent antioxidant activity.
The evolution of luteolin extraction techniques has progressed from traditional methods such as maceration and Soxhlet extraction to more sophisticated approaches including ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), and supercritical fluid extraction (SFE). Each advancement has aimed to improve extraction efficiency, reduce solvent consumption, and preserve the bioactive properties of luteolin. The technological trajectory clearly indicates a shift toward greener, more sustainable extraction methodologies that align with current environmental concerns.
Plant sources rich in luteolin include Reseda luteola (dyer's weld), Achillea millefolium (yarrow), Petroselinum crispum (parsley), Capsicum annuum (pepper), and various species of the Lamiaceae family such as Thymus vulgaris (thyme) and Origanum vulgare (oregano). The concentration of luteolin varies significantly among these sources, influenced by factors including plant species, growth conditions, harvesting time, and plant part utilized.
The primary objective of optimizing luteolin extraction is to develop efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly methods that maximize yield while maintaining the compound's biological activity. This involves addressing several key challenges: enhancing extraction efficiency, reducing processing time, minimizing solvent usage, and ensuring the stability of the extracted luteolin during storage and application.
Current research trends focus on developing hybrid extraction technologies that combine multiple approaches to leverage their respective advantages. Additionally, there is growing interest in utilizing computational modeling and machine learning algorithms to predict optimal extraction parameters, thereby reducing experimental workload and accelerating process optimization.
The anticipated technological goals include establishing standardized extraction protocols for different plant matrices, developing continuous-flow extraction systems for industrial-scale production, and creating novel formulations that enhance the bioavailability and stability of luteolin. These advancements would significantly contribute to the commercial viability of luteolin-based products in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industries.
The evolution of luteolin extraction techniques has progressed from traditional methods such as maceration and Soxhlet extraction to more sophisticated approaches including ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), and supercritical fluid extraction (SFE). Each advancement has aimed to improve extraction efficiency, reduce solvent consumption, and preserve the bioactive properties of luteolin. The technological trajectory clearly indicates a shift toward greener, more sustainable extraction methodologies that align with current environmental concerns.
Plant sources rich in luteolin include Reseda luteola (dyer's weld), Achillea millefolium (yarrow), Petroselinum crispum (parsley), Capsicum annuum (pepper), and various species of the Lamiaceae family such as Thymus vulgaris (thyme) and Origanum vulgare (oregano). The concentration of luteolin varies significantly among these sources, influenced by factors including plant species, growth conditions, harvesting time, and plant part utilized.
The primary objective of optimizing luteolin extraction is to develop efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly methods that maximize yield while maintaining the compound's biological activity. This involves addressing several key challenges: enhancing extraction efficiency, reducing processing time, minimizing solvent usage, and ensuring the stability of the extracted luteolin during storage and application.
Current research trends focus on developing hybrid extraction technologies that combine multiple approaches to leverage their respective advantages. Additionally, there is growing interest in utilizing computational modeling and machine learning algorithms to predict optimal extraction parameters, thereby reducing experimental workload and accelerating process optimization.
The anticipated technological goals include establishing standardized extraction protocols for different plant matrices, developing continuous-flow extraction systems for industrial-scale production, and creating novel formulations that enhance the bioavailability and stability of luteolin. These advancements would significantly contribute to the commercial viability of luteolin-based products in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Market Analysis for Luteolin-based Products
The global market for luteolin-based products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing consumer awareness of its health benefits and expanding applications across multiple industries. The current market size for luteolin-based products is estimated at $320 million globally, with projections indicating growth to reach $580 million by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of approximately 8.9%.
The pharmaceutical sector currently dominates the luteolin market, accounting for approximately 45% of total consumption. This dominance stems from luteolin's demonstrated anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential anti-cancer properties, which have sparked extensive research into therapeutic applications. Clinical trials investigating luteolin's efficacy in treating various conditions have increased by 35% over the past five years.
The nutraceutical and dietary supplement industry represents the fastest-growing segment for luteolin products, with a current growth rate of 12.3% annually. Consumer demand for natural health solutions has created a robust market for luteolin supplements, particularly in North America and Europe where health-conscious demographics are willing to pay premium prices for plant-derived bioactives.
Cosmetic and personal care applications constitute approximately 18% of the luteolin market, with particular focus on anti-aging and skin protection formulations. Market research indicates that consumers increasingly prefer products containing natural antioxidants like luteolin over synthetic alternatives, creating significant opportunities for expansion in this sector.
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently leads the global market with a 38% share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to demonstrate the highest growth rate over the next five years due to increasing disposable income, growing health awareness, and the region's traditional use of plant-based medicines.
Key market challenges include supply chain inconsistencies, price volatility due to seasonal availability of plant sources, and regulatory hurdles regarding health claims. The average price for pharmaceutical-grade luteolin currently ranges from $2,000 to $3,500 per kilogram, highlighting the economic incentive for optimizing extraction methods.
Consumer trend analysis indicates growing demand for products with transparent sourcing, sustainable production methods, and clinically validated benefits. This presents both challenges and opportunities for companies investing in optimized luteolin extraction technologies, as improved yield and purity can directly translate to market advantage and premium positioning.
The pharmaceutical sector currently dominates the luteolin market, accounting for approximately 45% of total consumption. This dominance stems from luteolin's demonstrated anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential anti-cancer properties, which have sparked extensive research into therapeutic applications. Clinical trials investigating luteolin's efficacy in treating various conditions have increased by 35% over the past five years.
The nutraceutical and dietary supplement industry represents the fastest-growing segment for luteolin products, with a current growth rate of 12.3% annually. Consumer demand for natural health solutions has created a robust market for luteolin supplements, particularly in North America and Europe where health-conscious demographics are willing to pay premium prices for plant-derived bioactives.
Cosmetic and personal care applications constitute approximately 18% of the luteolin market, with particular focus on anti-aging and skin protection formulations. Market research indicates that consumers increasingly prefer products containing natural antioxidants like luteolin over synthetic alternatives, creating significant opportunities for expansion in this sector.
Regional analysis reveals that North America currently leads the global market with a 38% share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to demonstrate the highest growth rate over the next five years due to increasing disposable income, growing health awareness, and the region's traditional use of plant-based medicines.
Key market challenges include supply chain inconsistencies, price volatility due to seasonal availability of plant sources, and regulatory hurdles regarding health claims. The average price for pharmaceutical-grade luteolin currently ranges from $2,000 to $3,500 per kilogram, highlighting the economic incentive for optimizing extraction methods.
Consumer trend analysis indicates growing demand for products with transparent sourcing, sustainable production methods, and clinically validated benefits. This presents both challenges and opportunities for companies investing in optimized luteolin extraction technologies, as improved yield and purity can directly translate to market advantage and premium positioning.
Current Extraction Technologies and Challenges
Luteolin extraction from plant sources currently employs several established technologies, each with specific advantages and limitations. Conventional solvent extraction remains the most widely used method, utilizing organic solvents such as ethanol, methanol, and acetone. This approach offers simplicity and scalability but suffers from high solvent consumption, potential thermal degradation of luteolin, and environmental concerns associated with organic solvent disposal.
Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) has emerged as an enhancement to conventional methods, using acoustic cavitation to disrupt plant cell walls and improve solvent penetration. Studies indicate UAE can reduce extraction time by 30-70% while increasing luteolin yields by 15-25% compared to conventional methods. However, challenges include equipment scaling limitations and potential degradation of heat-sensitive compounds during prolonged sonication.
Microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) utilizes electromagnetic radiation to heat the solvent and plant material simultaneously, creating localized superheating that facilitates rapid extraction. MAE demonstrates 40-60% reduction in extraction time with comparable or superior yields to conventional methods. The primary challenges include non-uniform heating patterns and difficulty in industrial-scale implementation.
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE), predominantly using CO2, offers a green alternative that produces solvent-free extracts. SFE operates at lower temperatures, preserving thermolabile compounds like luteolin. While environmentally superior, SFE requires significant capital investment and specialized expertise, limiting widespread adoption despite its technical advantages.
Enzyme-assisted extraction has gained attention for its specificity and mild operating conditions. By employing cellulases, pectinases, and hemicellulases to break down plant cell walls, this method enhances luteolin release while operating at near-ambient temperatures. Challenges include enzyme cost, stability concerns, and optimization requirements for different plant matrices.
Pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) operates at elevated temperatures and pressures to maintain solvents in liquid state, enhancing extraction efficiency. PLE demonstrates 2-3 fold higher extraction rates than conventional methods but faces challenges in equipment complexity and energy consumption.
The primary technical challenges across extraction methods include selectivity limitations, co-extraction of interfering compounds, degradation of luteolin during processing, and difficulties in maintaining consistent quality across batches. Additionally, most current methods struggle with green chemistry principles, presenting sustainability concerns through high energy consumption or chemical waste generation.
Scale-up challenges persist across technologies, with laboratory-optimized protocols often failing to translate directly to industrial production. This creates significant barriers to commercial implementation, particularly for newer technologies like SFE and enzyme-assisted extraction.
Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) has emerged as an enhancement to conventional methods, using acoustic cavitation to disrupt plant cell walls and improve solvent penetration. Studies indicate UAE can reduce extraction time by 30-70% while increasing luteolin yields by 15-25% compared to conventional methods. However, challenges include equipment scaling limitations and potential degradation of heat-sensitive compounds during prolonged sonication.
Microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) utilizes electromagnetic radiation to heat the solvent and plant material simultaneously, creating localized superheating that facilitates rapid extraction. MAE demonstrates 40-60% reduction in extraction time with comparable or superior yields to conventional methods. The primary challenges include non-uniform heating patterns and difficulty in industrial-scale implementation.
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE), predominantly using CO2, offers a green alternative that produces solvent-free extracts. SFE operates at lower temperatures, preserving thermolabile compounds like luteolin. While environmentally superior, SFE requires significant capital investment and specialized expertise, limiting widespread adoption despite its technical advantages.
Enzyme-assisted extraction has gained attention for its specificity and mild operating conditions. By employing cellulases, pectinases, and hemicellulases to break down plant cell walls, this method enhances luteolin release while operating at near-ambient temperatures. Challenges include enzyme cost, stability concerns, and optimization requirements for different plant matrices.
Pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) operates at elevated temperatures and pressures to maintain solvents in liquid state, enhancing extraction efficiency. PLE demonstrates 2-3 fold higher extraction rates than conventional methods but faces challenges in equipment complexity and energy consumption.
The primary technical challenges across extraction methods include selectivity limitations, co-extraction of interfering compounds, degradation of luteolin during processing, and difficulties in maintaining consistent quality across batches. Additionally, most current methods struggle with green chemistry principles, presenting sustainability concerns through high energy consumption or chemical waste generation.
Scale-up challenges persist across technologies, with laboratory-optimized protocols often failing to translate directly to industrial production. This creates significant barriers to commercial implementation, particularly for newer technologies like SFE and enzyme-assisted extraction.
Mainstream Luteolin Extraction Techniques
01 Solvent-based extraction methods
Various solvents can be used to extract luteolin from plant materials, with different solvents yielding different extraction efficiencies. Common solvents include ethanol, methanol, water, and their combinations. The selection of appropriate solvents significantly impacts the extraction yield and purity of luteolin. Factors such as solvent polarity, temperature, and extraction time play crucial roles in optimizing the extraction process.- Solvent extraction methods for luteolin: Various solvents can be used to extract luteolin from plant materials, with different solvents yielding different extraction efficiencies. Common solvents include ethanol, methanol, water, and their combinations. The choice of solvent significantly affects the extraction yield and purity of luteolin. Factors such as solvent polarity, extraction temperature, and extraction time play crucial roles in optimizing the extraction efficiency.
- Advanced extraction technologies: Advanced technologies have been developed to improve luteolin extraction efficiency. These include ultrasonic-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and pressurized liquid extraction. These methods can significantly reduce extraction time, lower solvent consumption, and increase extraction yield compared to conventional methods. The combination of different extraction technologies can further enhance the extraction efficiency of luteolin.
- Optimization of extraction parameters: Extraction efficiency of luteolin can be significantly improved by optimizing various parameters. These parameters include extraction temperature, extraction time, solid-to-liquid ratio, particle size of plant material, and pH of the extraction medium. Statistical experimental design methods such as response surface methodology can be employed to determine the optimal combination of these parameters for maximum luteolin yield.
- Purification and enrichment techniques: After initial extraction, various purification and enrichment techniques can be applied to increase the purity of luteolin. These techniques include liquid-liquid extraction, column chromatography, high-speed counter-current chromatography, and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. The selection of appropriate purification methods depends on the nature of the plant material and the desired purity of the final product.
- Novel extraction systems and materials: Innovative extraction systems and materials have been developed to enhance luteolin extraction efficiency. These include deep eutectic solvents, ionic liquids, molecularly imprinted polymers, and enzyme-assisted extraction. These novel approaches can offer advantages such as higher selectivity, environmental friendliness, and improved extraction yields compared to conventional methods. Additionally, the use of nanotechnology and smart materials in extraction processes shows promising results for luteolin recovery.
02 Advanced extraction technologies
Modern extraction technologies have been developed to improve luteolin extraction efficiency. These include ultrasonic-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, and pressurized liquid extraction. These technologies can significantly reduce extraction time, lower solvent consumption, and increase extraction yield compared to conventional methods. The combination of these technologies with optimized parameters can further enhance luteolin extraction efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Enzymatic and biological extraction methods
Enzymatic and biological approaches offer environmentally friendly alternatives for luteolin extraction. These methods utilize specific enzymes or microorganisms to break down plant cell walls, facilitating the release of luteolin. Enzymatic hydrolysis can be performed under mild conditions, preserving the bioactivity of luteolin while achieving high extraction efficiency. The selection of appropriate enzymes and optimization of reaction conditions are critical for maximizing extraction yield.Expand Specific Solutions04 Purification and enrichment techniques
After initial extraction, various purification and enrichment techniques can be employed to increase the purity and concentration of luteolin. These include column chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), macroporous resin adsorption, and membrane filtration. The selection of appropriate purification methods depends on the source material and desired purity level. Sequential purification steps can significantly enhance the final luteolin content and overall extraction efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process parameter optimization
Optimization of process parameters is crucial for maximizing luteolin extraction efficiency. Key parameters include extraction temperature, time, solid-to-liquid ratio, pH, and particle size of the plant material. Statistical experimental design methods such as response surface methodology can be employed to identify optimal extraction conditions. The development of continuous extraction processes and scale-up strategies also contributes to improved extraction efficiency at industrial scales.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Flavonoid Extraction
Luteolin extraction technology is currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding due to increasing applications in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmetics. The global market size for plant-derived luteolin is projected to reach significant value as consumer demand for natural ingredients rises. Technologically, extraction methods are advancing from traditional solvent-based approaches to more sophisticated techniques. Leading players demonstrate varying levels of technical maturity: established chemical companies like BASF's Cognis IP, Merck Patent GmbH, and Unilever have developed proprietary extraction technologies, while specialized firms such as Chenguang Biotech, India Glycols, and Kemin Industries focus on optimizing yield and purity. Academic institutions including Louisiana State University, Zhejiang University, and University of Tokyo are advancing fundamental research, creating a competitive landscape balanced between industrial innovation and scientific exploration.
Cognis IP Management GmbH
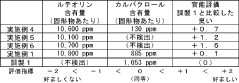
Technical Solution: Cognis has developed an advanced multi-solvent fractionation technology for luteolin extraction that achieves exceptional purity levels. Their process begins with a primary extraction using a proprietary blend of bio-based solvents derived from renewable resources, followed by a series of counter-current fractionation steps that progressively isolate luteolin from similar flavonoids. The company employs specialized low-temperature crystallization techniques that exploit the differential solubility properties of luteolin and its glycosides across varying solvent compositions and temperatures. Cognis has also implemented ultrasound-assisted extraction technology that reduces extraction time by approximately 60% while increasing yield by up to 25% compared to conventional methods. Their integrated production system includes continuous monitoring of critical quality attributes using advanced analytical techniques such as HPLC-MS/MS, ensuring consistent purity exceeding 95%. The company has optimized their process for multiple plant sources including Reseda luteola, Artemisia annua, and citrus peels.
Strengths: Exceptional purity levels with minimal processing steps; reduced extraction time and increased yield through ultrasound assistance; versatile technology applicable to multiple plant sources. Weaknesses: Complex process control requirements; higher energy consumption during fractionation steps; specialized analytical expertise required for quality control.
Chenguang Biotech Group Co., Ltd.
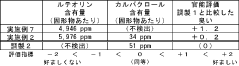
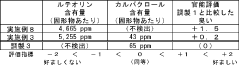
Technical Solution: Chenguang Biotech has developed a comprehensive luteolin extraction platform utilizing supercritical CO2 extraction technology combined with macroporous resin purification. Their process begins with careful selection of plant materials (primarily from Reseda luteola and marigold flowers) with high luteolin content, followed by ultrasonic-assisted extraction using environmentally friendly solvents. The company employs a multi-stage purification process involving molecular distillation and chromatographic separation to achieve luteolin purity exceeding 98%. Their proprietary temperature-controlled extraction system prevents degradation of heat-sensitive luteolin compounds while maximizing yield. Chenguang has also implemented continuous flow extraction technology that reduces processing time by approximately 40% compared to traditional batch methods, while maintaining consistent product quality.
Strengths: Industry-leading purity levels (>98%) with scalable production capacity; environmentally sustainable extraction methods with reduced solvent usage; comprehensive quality control system ensuring batch-to-batch consistency. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional methods; energy-intensive purification processes; requires specialized equipment and technical expertise for operation.
Critical Patents and Research in Extraction Optimization
Labiate plant extract production method
PatentActiveJP2015063493A
Innovation
- An enzymatic treatment using β-glucosidase enzymes is applied to plant materials from the Lamiaceae family, followed by the addition of fats and oils, stirring, and subsequent oil separation to produce a luteolin-rich extract with reduced odor.
Feral Hog Toxicant
PatentActiveUS20230329239A1
Innovation
- A composition of sodium nitrite in a bait with a high pH to inhibit decomposition, eliminating the need for encapsulation and avoiding acidic conditions that cause bitterness, combined with optional anti-emetic and luteolin to enhance toxicity and palatability.
Sustainability and Eco-friendly Extraction Approaches
The growing emphasis on environmental sustainability has significantly influenced extraction methodologies for bioactive compounds like luteolin. Traditional extraction techniques often involve substantial use of organic solvents, high energy consumption, and generate considerable waste, raising serious environmental concerns. In response, the industry has been actively developing and implementing more sustainable and eco-friendly extraction approaches that minimize environmental impact while maintaining extraction efficiency.
Green solvents represent a pivotal advancement in sustainable extraction. Water-based extraction systems, deep eutectic solvents (DES), and bio-derived solvents such as ethanol from renewable sources have emerged as viable alternatives to conventional petroleum-based solvents. These alternatives significantly reduce toxicity and environmental footprint while offering comparable extraction yields for luteolin from various plant matrices.
Energy-efficient extraction technologies have also gained prominence in sustainable luteolin extraction. Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) substantially reduce processing time and energy consumption compared to conventional methods. Studies indicate that UAE can reduce extraction time by up to 70% while maintaining or even improving luteolin yields from plant sources like celery and parsley.
Waste valorization represents another critical dimension of sustainable extraction. Integrated biorefinery approaches enable the extraction of luteolin from agricultural by-products and food processing waste streams, transforming what was once considered waste into valuable resources. This circular economy approach not only reduces waste but also creates additional value chains from existing agricultural operations.
Process intensification strategies further enhance sustainability by combining multiple unit operations into more efficient integrated systems. Continuous flow extraction systems, for instance, optimize solvent usage and energy consumption while improving extraction consistency and reducing operational footprint. These systems have demonstrated up to 40% reduction in solvent consumption for flavonoid extraction processes.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies are increasingly being applied to evaluate the environmental impact of different luteolin extraction methods. Recent LCA studies comparing conventional solvent extraction with green extraction techniques have demonstrated that supercritical CO2 extraction can reduce the carbon footprint by approximately 35% compared to traditional methods, despite higher initial capital investment requirements.
Regulatory frameworks and industry standards are evolving to encourage adoption of these sustainable practices. Organizations like the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have established guidelines promoting green extraction technologies, while certification systems are emerging to recognize environmentally responsible production methods for natural extracts including luteolin.
Green solvents represent a pivotal advancement in sustainable extraction. Water-based extraction systems, deep eutectic solvents (DES), and bio-derived solvents such as ethanol from renewable sources have emerged as viable alternatives to conventional petroleum-based solvents. These alternatives significantly reduce toxicity and environmental footprint while offering comparable extraction yields for luteolin from various plant matrices.
Energy-efficient extraction technologies have also gained prominence in sustainable luteolin extraction. Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) substantially reduce processing time and energy consumption compared to conventional methods. Studies indicate that UAE can reduce extraction time by up to 70% while maintaining or even improving luteolin yields from plant sources like celery and parsley.
Waste valorization represents another critical dimension of sustainable extraction. Integrated biorefinery approaches enable the extraction of luteolin from agricultural by-products and food processing waste streams, transforming what was once considered waste into valuable resources. This circular economy approach not only reduces waste but also creates additional value chains from existing agricultural operations.
Process intensification strategies further enhance sustainability by combining multiple unit operations into more efficient integrated systems. Continuous flow extraction systems, for instance, optimize solvent usage and energy consumption while improving extraction consistency and reducing operational footprint. These systems have demonstrated up to 40% reduction in solvent consumption for flavonoid extraction processes.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies are increasingly being applied to evaluate the environmental impact of different luteolin extraction methods. Recent LCA studies comparing conventional solvent extraction with green extraction techniques have demonstrated that supercritical CO2 extraction can reduce the carbon footprint by approximately 35% compared to traditional methods, despite higher initial capital investment requirements.
Regulatory frameworks and industry standards are evolving to encourage adoption of these sustainable practices. Organizations like the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have established guidelines promoting green extraction technologies, while certification systems are emerging to recognize environmentally responsible production methods for natural extracts including luteolin.
Quality Control and Standardization Methods
Quality control and standardization methods are critical components in the optimization of luteolin extraction processes, ensuring consistency, reliability, and efficacy of the final product. The implementation of robust quality control protocols begins with the establishment of validated analytical methods for luteolin identification and quantification. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with ultraviolet detection remains the gold standard, with recent advancements incorporating mass spectrometry for enhanced sensitivity and specificity.
Standardization of raw materials represents a fundamental quality control measure, requiring thorough botanical authentication of plant sources prior to extraction. This includes macroscopic and microscopic examination, genetic analysis through DNA barcoding, and chemical fingerprinting to confirm species identity and detect potential adulterants. Environmental factors affecting luteolin content, such as growing conditions, harvest time, and post-harvest handling, must be systematically documented and controlled.
Process validation protocols are essential for ensuring extraction reproducibility across batches. This encompasses the qualification of equipment, calibration of instruments, and validation of critical process parameters including temperature, pressure, solvent ratios, and extraction duration. Statistical process control methods, such as control charts and capability analyses, provide continuous monitoring of extraction performance and early detection of process drift.
The establishment of reference standards is paramount for accurate quantification of luteolin content. Certified reference materials with known purity and concentration enable precise calibration of analytical instruments and validation of testing methods. International organizations including USP, EP, and ISO have developed guidelines for reference standard preparation and usage, which should be incorporated into quality control frameworks.
Stability testing protocols must be implemented to evaluate the shelf-life of luteolin extracts under various storage conditions. Accelerated and real-time stability studies assess degradation patterns, identify appropriate packaging materials, and determine optimal storage parameters to maintain luteolin integrity throughout the product lifecycle.
Comprehensive documentation systems, including standard operating procedures (SOPs), batch records, and certificates of analysis, form the backbone of quality assurance. These systems facilitate traceability from raw material to finished product and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. The integration of quality-by-design principles further enhances product consistency by identifying critical quality attributes and establishing design spaces for extraction parameters.
Standardization of raw materials represents a fundamental quality control measure, requiring thorough botanical authentication of plant sources prior to extraction. This includes macroscopic and microscopic examination, genetic analysis through DNA barcoding, and chemical fingerprinting to confirm species identity and detect potential adulterants. Environmental factors affecting luteolin content, such as growing conditions, harvest time, and post-harvest handling, must be systematically documented and controlled.
Process validation protocols are essential for ensuring extraction reproducibility across batches. This encompasses the qualification of equipment, calibration of instruments, and validation of critical process parameters including temperature, pressure, solvent ratios, and extraction duration. Statistical process control methods, such as control charts and capability analyses, provide continuous monitoring of extraction performance and early detection of process drift.
The establishment of reference standards is paramount for accurate quantification of luteolin content. Certified reference materials with known purity and concentration enable precise calibration of analytical instruments and validation of testing methods. International organizations including USP, EP, and ISO have developed guidelines for reference standard preparation and usage, which should be incorporated into quality control frameworks.
Stability testing protocols must be implemented to evaluate the shelf-life of luteolin extracts under various storage conditions. Accelerated and real-time stability studies assess degradation patterns, identify appropriate packaging materials, and determine optimal storage parameters to maintain luteolin integrity throughout the product lifecycle.
Comprehensive documentation systems, including standard operating procedures (SOPs), batch records, and certificates of analysis, form the backbone of quality assurance. These systems facilitate traceability from raw material to finished product and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. The integration of quality-by-design principles further enhances product consistency by identifying critical quality attributes and establishing design spaces for extraction parameters.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!