PoE++ Vs VDSL: Strengths in Digital Network Operations
SEP 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PoE++ and VDSL Technology Evolution and Objectives
Power over Ethernet (PoE++) and Very High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) represent two significant technological advancements in digital network infrastructure. These technologies have evolved through distinct trajectories to address specific networking challenges in modern digital environments.
PoE technology originated in the early 2000s with IEEE 802.3af standard (PoE), delivering up to 15.4W of power. The evolution continued with IEEE 802.3at (PoE+) in 2009, increasing power delivery to 30W. The latest iteration, IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++), introduced in 2018, represents a significant leap forward with power delivery capabilities of up to 90W, enabling support for more power-intensive devices.
VDSL technology emerged as an enhancement to ADSL in the early 2000s, offering speeds up to 52 Mbps downstream and 16 Mbps upstream. VDSL2, standardized in 2006, dramatically improved performance with theoretical speeds up to 100 Mbps symmetrical. Subsequent advancements like vectoring (2010) and bonding further enhanced VDSL capabilities, making it a viable solution for last-mile connectivity challenges.
The primary objective of PoE++ development has been to create a unified infrastructure that simultaneously delivers data and power over standard Ethernet cabling. This integration aims to reduce installation complexity, lower deployment costs, and increase flexibility in device placement. The technology targets environments where power outlets are limited or where centralized power management is advantageous.
VDSL technology, conversely, has focused on maximizing data transmission rates over existing copper telephone infrastructure. Its primary goal has been to extend the lifespan of legacy copper networks while delivering broadband speeds comparable to fiber optics in short-to-medium distances. This approach offers a cost-effective alternative to fiber deployment in certain scenarios.
Both technologies are evolving toward supporting the increasing demands of IoT ecosystems, smart buildings, and high-bandwidth applications. PoE++ is trending toward higher power efficiency, intelligent power management, and support for a broader range of devices. VDSL development is focusing on techniques to mitigate interference, increase spectral efficiency, and push the boundaries of what copper infrastructure can deliver.
The convergence of these technologies with other networking innovations like Wi-Fi 6, 5G, and edge computing is shaping a more integrated approach to network infrastructure. Future objectives include enhanced energy efficiency, simplified network management, and seamless integration with emerging technologies to support the growing demands of digital transformation initiatives across various industries.
PoE technology originated in the early 2000s with IEEE 802.3af standard (PoE), delivering up to 15.4W of power. The evolution continued with IEEE 802.3at (PoE+) in 2009, increasing power delivery to 30W. The latest iteration, IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++), introduced in 2018, represents a significant leap forward with power delivery capabilities of up to 90W, enabling support for more power-intensive devices.
VDSL technology emerged as an enhancement to ADSL in the early 2000s, offering speeds up to 52 Mbps downstream and 16 Mbps upstream. VDSL2, standardized in 2006, dramatically improved performance with theoretical speeds up to 100 Mbps symmetrical. Subsequent advancements like vectoring (2010) and bonding further enhanced VDSL capabilities, making it a viable solution for last-mile connectivity challenges.
The primary objective of PoE++ development has been to create a unified infrastructure that simultaneously delivers data and power over standard Ethernet cabling. This integration aims to reduce installation complexity, lower deployment costs, and increase flexibility in device placement. The technology targets environments where power outlets are limited or where centralized power management is advantageous.
VDSL technology, conversely, has focused on maximizing data transmission rates over existing copper telephone infrastructure. Its primary goal has been to extend the lifespan of legacy copper networks while delivering broadband speeds comparable to fiber optics in short-to-medium distances. This approach offers a cost-effective alternative to fiber deployment in certain scenarios.
Both technologies are evolving toward supporting the increasing demands of IoT ecosystems, smart buildings, and high-bandwidth applications. PoE++ is trending toward higher power efficiency, intelligent power management, and support for a broader range of devices. VDSL development is focusing on techniques to mitigate interference, increase spectral efficiency, and push the boundaries of what copper infrastructure can deliver.
The convergence of these technologies with other networking innovations like Wi-Fi 6, 5G, and edge computing is shaping a more integrated approach to network infrastructure. Future objectives include enhanced energy efficiency, simplified network management, and seamless integration with emerging technologies to support the growing demands of digital transformation initiatives across various industries.
Market Demand Analysis for Power and Data Transmission Solutions
The global market for power and data transmission solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing digitalization of industries and the expansion of network infrastructure. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for this sector is projected to exceed 7% through 2028, with particularly strong demand in enterprise networks, smart buildings, and industrial automation applications.
Power over Ethernet (PoE++) and Very High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) technologies represent two distinct approaches to addressing modern network requirements, each with specific market segments showing robust demand. PoE++ technology has seen accelerated adoption in commercial buildings, particularly for powering IP cameras, wireless access points, and IoT devices. Market research indicates that approximately 30% of new network installations now incorporate some form of PoE technology.
The demand for PoE++ solutions is particularly strong in smart building applications, where the ability to deliver both data and up to 100W of power over a single cable creates significant installation cost savings and deployment flexibility. Healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and retail environments represent the fastest-growing vertical markets for PoE++ technology, with security and surveillance applications leading specific use cases.
VDSL technology continues to maintain substantial market share in residential broadband and last-mile connectivity solutions, especially in regions where fiber deployment remains economically challenging. Telecommunications providers in developing markets are increasingly leveraging VDSL as a cost-effective alternative to fiber, with particular strength in multi-dwelling units and rural deployments.
Market analysis reveals distinct geographical patterns in technology adoption. North America and Western Europe show stronger preference for PoE++ solutions in commercial applications, while VDSL maintains stronger presence in Eastern Europe, parts of Asia, and Latin America where existing copper infrastructure can be leveraged for broadband delivery.
Customer surveys indicate that key purchasing factors for PoE++ solutions include power delivery capacity, ease of installation, and total cost of ownership benefits. For VDSL solutions, bandwidth capabilities, reliability, and compatibility with existing infrastructure rank as primary considerations. Both technologies face competitive pressure from fiber optic solutions, though each maintains distinct advantages in specific deployment scenarios.
Industry forecasts suggest the convergence of power and data transmission will continue to drive market growth, with particular emphasis on solutions that enhance energy efficiency and support remote management capabilities. The increasing deployment of edge computing infrastructure and IoT devices is expected to further accelerate demand for integrated power and data transmission technologies over the next five years.
Power over Ethernet (PoE++) and Very High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) technologies represent two distinct approaches to addressing modern network requirements, each with specific market segments showing robust demand. PoE++ technology has seen accelerated adoption in commercial buildings, particularly for powering IP cameras, wireless access points, and IoT devices. Market research indicates that approximately 30% of new network installations now incorporate some form of PoE technology.
The demand for PoE++ solutions is particularly strong in smart building applications, where the ability to deliver both data and up to 100W of power over a single cable creates significant installation cost savings and deployment flexibility. Healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and retail environments represent the fastest-growing vertical markets for PoE++ technology, with security and surveillance applications leading specific use cases.
VDSL technology continues to maintain substantial market share in residential broadband and last-mile connectivity solutions, especially in regions where fiber deployment remains economically challenging. Telecommunications providers in developing markets are increasingly leveraging VDSL as a cost-effective alternative to fiber, with particular strength in multi-dwelling units and rural deployments.
Market analysis reveals distinct geographical patterns in technology adoption. North America and Western Europe show stronger preference for PoE++ solutions in commercial applications, while VDSL maintains stronger presence in Eastern Europe, parts of Asia, and Latin America where existing copper infrastructure can be leveraged for broadband delivery.
Customer surveys indicate that key purchasing factors for PoE++ solutions include power delivery capacity, ease of installation, and total cost of ownership benefits. For VDSL solutions, bandwidth capabilities, reliability, and compatibility with existing infrastructure rank as primary considerations. Both technologies face competitive pressure from fiber optic solutions, though each maintains distinct advantages in specific deployment scenarios.
Industry forecasts suggest the convergence of power and data transmission will continue to drive market growth, with particular emphasis on solutions that enhance energy efficiency and support remote management capabilities. The increasing deployment of edge computing infrastructure and IoT devices is expected to further accelerate demand for integrated power and data transmission technologies over the next five years.
Current Technological Landscape and Implementation Challenges
The global digital network infrastructure landscape is currently experiencing a significant transformation, with Power over Ethernet Plus Plus (PoE++) and Very High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) technologies playing pivotal roles. PoE++ (IEEE 802.3bt) represents the latest evolution in the Power over Ethernet family, capable of delivering up to 90W of power alongside data transmission over standard Ethernet cables. Meanwhile, VDSL technology continues to serve as a critical last-mile solution, offering broadband speeds up to 100 Mbps over existing copper telephone infrastructure.
The implementation of PoE++ has gained substantial traction in enterprise environments, particularly for powering devices such as high-performance wireless access points, pan-tilt-zoom cameras, and digital signage. Market adoption has accelerated with approximately 30% year-over-year growth in PoE-enabled switch ports. However, significant challenges persist, including heat dissipation issues in high-density deployments and compatibility concerns with legacy infrastructure.
VDSL deployment continues to be widespread in regions where fiber-to-the-home remains economically unfeasible. Telecommunications providers leverage VDSL's ability to utilize existing copper infrastructure while delivering improved bandwidth. The technology faces challenges related to distance limitations, with performance degrading significantly beyond 1-1.5 kilometers from the distribution point, and susceptibility to electromagnetic interference in industrial environments.
From a geographical perspective, PoE++ adoption is most prominent in North America and Western Europe, where enterprise network refreshes and IoT initiatives drive implementation. VDSL maintains stronger presence in Eastern Europe, parts of Asia, and developing markets where the cost of fiber deployment remains prohibitive. This regional disparity creates unique integration challenges for multinational organizations seeking consistent network performance across global operations.
Technical standardization presents another significant challenge. While PoE++ is governed by the IEEE 802.3bt standard, various proprietary implementations exist that may offer enhanced features but potentially compromise interoperability. VDSL implementations vary between ITU-T G.993.1 (VDSL) and G.993.2 (VDSL2) standards, with different profiles optimized for specific deployment scenarios.
Security considerations have emerged as critical factors in both technologies' implementation. PoE++ networks must address potential vulnerabilities in power negotiation protocols that could lead to denial-of-service conditions. VDSL deployments face challenges related to securing the data stream against interception, particularly in multi-tenant buildings where physical access to connection points may be possible.
Cost-efficiency analysis reveals that while PoE++ requires higher initial investment in compatible infrastructure, it typically delivers lower total cost of ownership through reduced installation complexity and operational expenses. VDSL offers lower upfront costs by leveraging existing infrastructure but may incur higher maintenance expenses and eventual replacement costs as bandwidth demands increase.
The implementation of PoE++ has gained substantial traction in enterprise environments, particularly for powering devices such as high-performance wireless access points, pan-tilt-zoom cameras, and digital signage. Market adoption has accelerated with approximately 30% year-over-year growth in PoE-enabled switch ports. However, significant challenges persist, including heat dissipation issues in high-density deployments and compatibility concerns with legacy infrastructure.
VDSL deployment continues to be widespread in regions where fiber-to-the-home remains economically unfeasible. Telecommunications providers leverage VDSL's ability to utilize existing copper infrastructure while delivering improved bandwidth. The technology faces challenges related to distance limitations, with performance degrading significantly beyond 1-1.5 kilometers from the distribution point, and susceptibility to electromagnetic interference in industrial environments.
From a geographical perspective, PoE++ adoption is most prominent in North America and Western Europe, where enterprise network refreshes and IoT initiatives drive implementation. VDSL maintains stronger presence in Eastern Europe, parts of Asia, and developing markets where the cost of fiber deployment remains prohibitive. This regional disparity creates unique integration challenges for multinational organizations seeking consistent network performance across global operations.
Technical standardization presents another significant challenge. While PoE++ is governed by the IEEE 802.3bt standard, various proprietary implementations exist that may offer enhanced features but potentially compromise interoperability. VDSL implementations vary between ITU-T G.993.1 (VDSL) and G.993.2 (VDSL2) standards, with different profiles optimized for specific deployment scenarios.
Security considerations have emerged as critical factors in both technologies' implementation. PoE++ networks must address potential vulnerabilities in power negotiation protocols that could lead to denial-of-service conditions. VDSL deployments face challenges related to securing the data stream against interception, particularly in multi-tenant buildings where physical access to connection points may be possible.
Cost-efficiency analysis reveals that while PoE++ requires higher initial investment in compatible infrastructure, it typically delivers lower total cost of ownership through reduced installation complexity and operational expenses. VDSL offers lower upfront costs by leveraging existing infrastructure but may incur higher maintenance expenses and eventual replacement costs as bandwidth demands increase.
Comparative Analysis of PoE++ and VDSL Implementation Approaches
01 Power over Ethernet (PoE++) capabilities and advantages
PoE++ technology provides enhanced power delivery capabilities over Ethernet cables, allowing for up to 90W of power to connected devices. This technology enables powering of higher-consumption devices like PTZ cameras, digital signage, and advanced network equipment through the same cables that carry data. The key strengths include simplified installation by eliminating separate power cables, reduced infrastructure costs, centralized power management, and improved reliability through backup power systems.- Power over Ethernet (PoE++) enhanced power delivery capabilities: PoE++ technology (IEEE 802.3bt) provides significantly higher power delivery capabilities over standard Ethernet cables, allowing up to 90W of power to network devices. This enables powering of more energy-demanding devices such as advanced IP cameras, wireless access points, and thin clients through a single cable, reducing installation complexity and costs while improving deployment flexibility in network infrastructure.
- VDSL high-speed data transmission over copper infrastructure: Very High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) technology enables high-bandwidth data transmission over existing copper telephone lines, achieving speeds up to 100 Mbps downstream and 50 Mbps upstream depending on line conditions. This technology allows telecommunications providers to deliver broadband services without the need for complete fiber infrastructure deployment, making it a cost-effective solution for last-mile connectivity in areas where fiber installation is challenging.
- Integration of PoE++ with network management systems: The integration of PoE++ technology with advanced network management systems enables intelligent power allocation, monitoring, and control across network infrastructure. This integration allows for remote power cycling, scheduled power management, and power consumption analytics, resulting in improved operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs. The system can automatically prioritize power distribution during outages and optimize energy usage based on device requirements and network conditions.
- VDSL profile optimization and noise mitigation techniques: Advanced VDSL implementations incorporate sophisticated profile optimization and noise mitigation techniques that dynamically adjust transmission parameters based on line conditions. These include vectoring technology to cancel crosstalk between adjacent lines, dynamic spectrum management, and adaptive bit loading. These enhancements significantly improve connection stability, extend effective range, and maximize achievable data rates even in challenging environments with electromagnetic interference or varying line quality.
- Hybrid PoE++ and VDSL deployment solutions: Hybrid solutions combining PoE++ and VDSL technologies enable comprehensive network deployments that leverage the strengths of both technologies. These integrated systems allow for power and high-speed data delivery over existing infrastructure, creating cost-effective solutions for smart building applications, surveillance systems, and industrial IoT deployments. The hybrid approach reduces installation complexity by minimizing cabling requirements while providing reliable power and connectivity to distributed network endpoints.
02 VDSL technology performance and bandwidth capabilities
Very High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) technology offers significant bandwidth improvements over traditional DSL connections, providing asymmetric data rates with downstream speeds up to 100 Mbps and upstream speeds up to 50 Mbps over existing copper telephone lines. VDSL's strengths include utilizing existing infrastructure while delivering broadband speeds suitable for high-definition video streaming, online gaming, and other bandwidth-intensive applications, making it cost-effective for service providers and accessible for consumers.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of PoE++ and VDSL for network solutions
The combination of PoE++ and VDSL technologies creates powerful integrated network solutions that can simultaneously deliver high-speed data and sufficient power over existing infrastructure. This integration enables deployment of advanced network devices in locations without dedicated power sources, simplifies cabling requirements, and reduces installation costs. The combined technologies support applications such as remote surveillance systems, distributed access points, and IoT deployments in challenging environments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Enhanced reliability and distance capabilities
Both PoE++ and VDSL technologies offer improved reliability and extended distance capabilities compared to their predecessors. VDSL employs advanced modulation techniques and noise cancellation to maintain signal integrity over longer distances, while PoE++ includes sophisticated power management features that ensure stable power delivery with protection against overloads and short circuits. These technologies can operate reliably in various environmental conditions and provide consistent performance even in challenging deployment scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions05 Network management and compatibility features
PoE++ and VDSL technologies incorporate advanced network management capabilities and backward compatibility features. PoE++ is compatible with earlier PoE standards while offering enhanced power negotiation protocols that prevent damage to non-PoE devices. VDSL systems include sophisticated line monitoring, dynamic rate adaptation, and quality of service features that optimize performance based on line conditions. Both technologies support remote management and diagnostics, reducing operational costs and simplifying maintenance for network administrators.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in PoE++ and VDSL Technologies
The Power over Ethernet Plus Plus (PoE++) and Very High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) technologies are currently in a mature growth phase, with the global digital network infrastructure market expanding at approximately 6-8% annually. PoE++ offers superior power delivery capabilities (up to 100W) compared to VDSL's limited power transmission, making it increasingly preferred for IoT and smart building applications. Leading the PoE++ innovation are Cisco, Huawei, and ZTE, who have developed advanced power management solutions, while Broadcom (Avago), Nokia, and Ericsson maintain strong positions in VDSL technology with enhanced bandwidth optimization. The competitive landscape is evolving as companies like Palo Alto Networks integrate these technologies into comprehensive network security frameworks, indicating a shift toward converged network solutions.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei has developed comprehensive solutions for both PoE++ and VDSL technologies. For PoE++, Huawei offers IEEE 802.3bt compliant switches delivering up to 90W per port, enabling power-hungry applications like PTZ cameras and wireless access points. Their S5700-SI series switches feature intelligent power management with real-time monitoring and prioritization capabilities. For VDSL, Huawei's SingleFAN solution utilizes vectoring technology to achieve speeds up to 100Mbps over existing copper infrastructure. Their MA5600T/MA5800 multi-service access platforms support VDSL2 with profiles up to 35b, allowing operators to maximize bandwidth while maintaining backward compatibility with ADSL deployments. Huawei has implemented these technologies in over 100 countries, demonstrating their scalability across diverse network environments.
Strengths: Huawei offers end-to-end solutions for both technologies with strong integration capabilities between access and core networks. Their equipment demonstrates superior power efficiency and heat dissipation. Weaknesses: Higher initial investment costs compared to some competitors, and potential security concerns have limited deployment in certain markets.
Cisco Technology, Inc.
Technical Solution: Cisco has pioneered advanced implementations of PoE++ technology through their Catalyst and Nexus switch portfolios. Their Universal Power Over Ethernet (UPOE+) extends beyond the IEEE 802.3bt standard to deliver up to 90W per port across all ports simultaneously without power degradation. Cisco's Perpetual PoE feature maintains power to devices during switch reboots, ensuring critical systems remain operational. For VDSL deployments, Cisco offers the 800 Series Integrated Services Routers with VDSL2 capabilities supporting profiles up to 35b with vectoring. Their Digital Network Architecture (DNA) provides unified management for both technologies, allowing centralized policy enforcement and analytics. Cisco's EnergyWise technology optimizes power consumption by scheduling and monitoring connected devices, reducing operational costs by up to 30% in large deployments. Their solutions incorporate advanced security features including MACsec encryption and identity-based networking to protect both data and power infrastructure.
Strengths: Cisco offers superior network management tools with DNA Center providing comprehensive visibility and control. Their solutions feature industry-leading security capabilities and high reliability with redundant power systems. Weaknesses: Premium pricing structure creates higher TCO compared to competitors, and their proprietary features can sometimes limit interoperability with third-party equipment.
Technical Deep Dive: Power Efficiency and Data Rate Capabilities
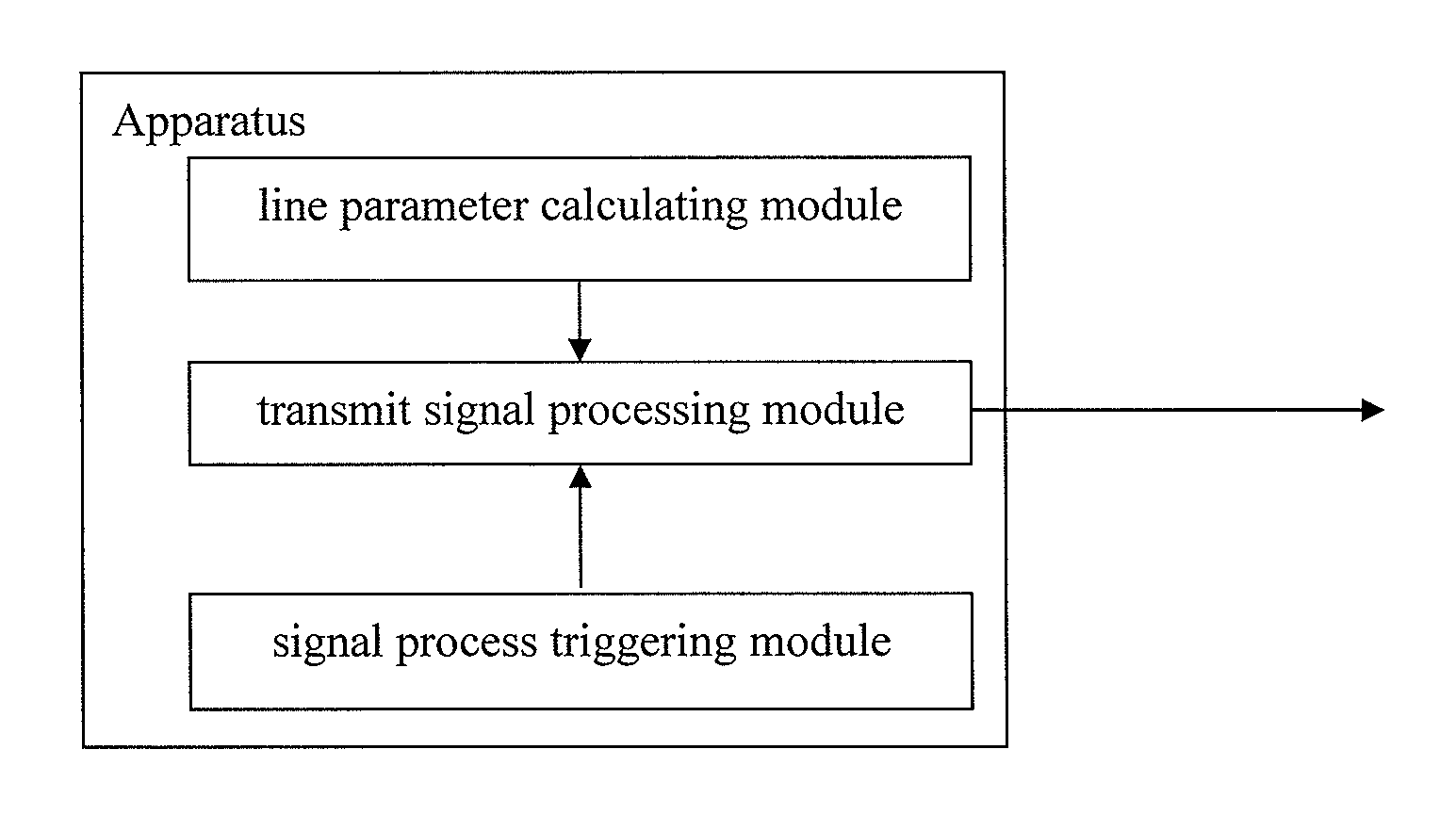
Method and apparatus for reducing crosstalk between digital subscriber lines
PatentActiveUS8081752B2
Innovation
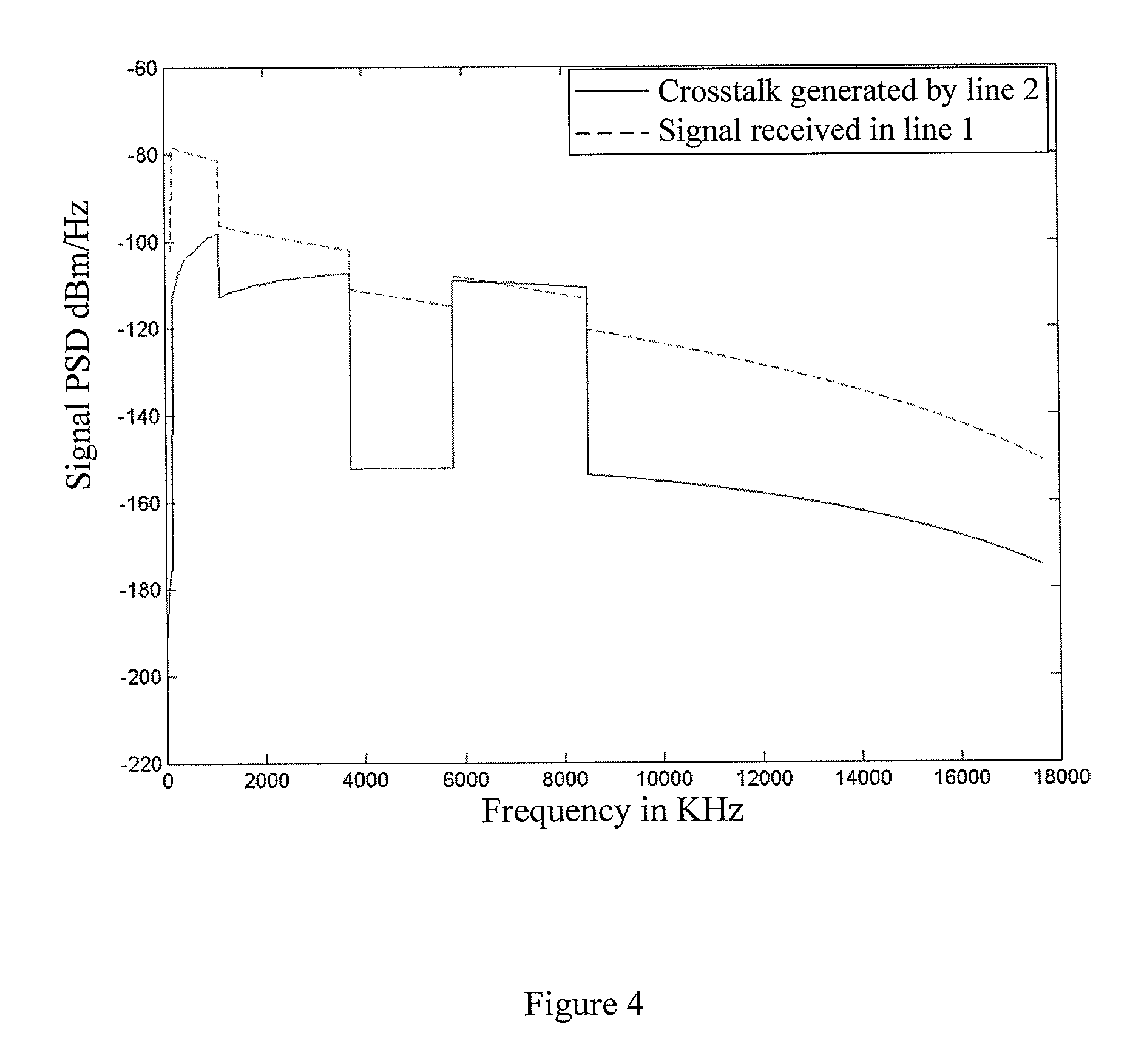
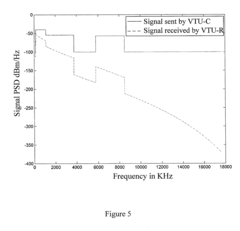
- A method and apparatus that determine line parameters through handshake signals to adjust signal transmit power and frequency, reducing high frequency crosstalk by turning off high frequency signals and transmitting only low frequency signals when the line length exceeds a predetermined threshold, thereby minimizing interference between neighboring VDSL lines.
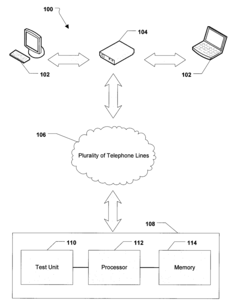
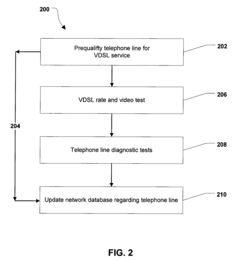
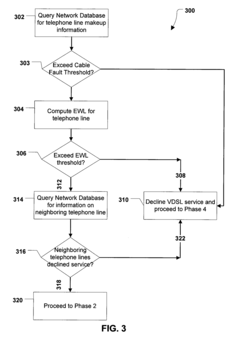
System and Method for Qualifying Telephone Lines for Very-High-Bit-Rate Digital Subscriber Line Service
PatentInactiveUS20090185664A1
Innovation
- A multi-step method involving prequalification, rate and video testing, diagnostic testing, and database updates to assess the suitability of telephone lines for VDSL service by measuring length, rate, and video quality, and identifying potential issues such as excessive Equivalent Working Length (EWL) and electrical faults.
Total Cost of Ownership and ROI Considerations
When evaluating the implementation of either PoE++ (Power over Ethernet Plus Plus) or VDSL (Very High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line) technologies, Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and Return on Investment (ROI) considerations become critical decision factors for organizations. These financial metrics extend beyond initial acquisition costs to encompass the complete lifecycle expenses and benefits.
For PoE++ deployments, the initial capital expenditure typically includes network switches with enhanced power capabilities, compatible cabling infrastructure, and potentially power management systems. While these upfront costs may be higher than traditional networking equipment, operational expenditures often demonstrate significant advantages. The elimination of separate power cabling and electrical outlets for connected devices can reduce installation costs by 50-60% compared to traditional power distribution methods.
VDSL implementations, conversely, often leverage existing copper telephone infrastructure, potentially reducing initial deployment costs in environments where this infrastructure already exists. However, maintenance of aging copper lines and the need for distribution points or street cabinets can increase long-term operational expenses. Studies indicate that fiber-to-the-cabinet VDSL deployments may cost 30-40% less initially than full fiber solutions but incur higher maintenance costs over a 10-year period.
Energy efficiency represents another significant TCO factor. PoE++ systems enable centralized power management with intelligent allocation features, potentially reducing energy consumption by 15-30% through scheduled power-downs and load balancing. VDSL systems typically consume more power per data unit transmitted, particularly at longer distances where signal boosting becomes necessary.
From an ROI perspective, PoE++ installations demonstrate compelling advantages in environments requiring both data and power delivery to multiple endpoints such as IP cameras, wireless access points, and IoT sensors. Organizations implementing PoE++ for campus-wide deployments report average ROI achievement within 24-36 months, primarily through reduced installation and maintenance costs, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced operational flexibility.
VDSL solutions typically show stronger ROI metrics in scenarios leveraging existing infrastructure for moderate bandwidth needs. Telecommunications providers report ROI periods of 18-30 months for VDSL deployments in residential areas with existing copper infrastructure, compared to 36-48 months for new fiber installations.
Scalability considerations also impact long-term TCO calculations. PoE++ systems offer modular expansion capabilities, allowing organizations to scale power delivery incrementally as needs evolve. VDSL deployments often face bandwidth and distance limitations that may necessitate complete infrastructure replacement as data requirements grow, potentially creating significant future capital expenditures that impact overall ROI calculations.
For PoE++ deployments, the initial capital expenditure typically includes network switches with enhanced power capabilities, compatible cabling infrastructure, and potentially power management systems. While these upfront costs may be higher than traditional networking equipment, operational expenditures often demonstrate significant advantages. The elimination of separate power cabling and electrical outlets for connected devices can reduce installation costs by 50-60% compared to traditional power distribution methods.
VDSL implementations, conversely, often leverage existing copper telephone infrastructure, potentially reducing initial deployment costs in environments where this infrastructure already exists. However, maintenance of aging copper lines and the need for distribution points or street cabinets can increase long-term operational expenses. Studies indicate that fiber-to-the-cabinet VDSL deployments may cost 30-40% less initially than full fiber solutions but incur higher maintenance costs over a 10-year period.
Energy efficiency represents another significant TCO factor. PoE++ systems enable centralized power management with intelligent allocation features, potentially reducing energy consumption by 15-30% through scheduled power-downs and load balancing. VDSL systems typically consume more power per data unit transmitted, particularly at longer distances where signal boosting becomes necessary.
From an ROI perspective, PoE++ installations demonstrate compelling advantages in environments requiring both data and power delivery to multiple endpoints such as IP cameras, wireless access points, and IoT sensors. Organizations implementing PoE++ for campus-wide deployments report average ROI achievement within 24-36 months, primarily through reduced installation and maintenance costs, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced operational flexibility.
VDSL solutions typically show stronger ROI metrics in scenarios leveraging existing infrastructure for moderate bandwidth needs. Telecommunications providers report ROI periods of 18-30 months for VDSL deployments in residential areas with existing copper infrastructure, compared to 36-48 months for new fiber installations.
Scalability considerations also impact long-term TCO calculations. PoE++ systems offer modular expansion capabilities, allowing organizations to scale power delivery incrementally as needs evolve. VDSL deployments often face bandwidth and distance limitations that may necessitate complete infrastructure replacement as data requirements grow, potentially creating significant future capital expenditures that impact overall ROI calculations.
Environmental Impact and Energy Efficiency Metrics
The environmental impact and energy efficiency of networking technologies have become increasingly critical factors in technology selection for modern enterprises. When comparing Power over Ethernet Plus Plus (PoE++) and Very High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) technologies, several key metrics reveal significant differences in their ecological footprints and energy consumption patterns.
PoE++ (IEEE 802.3bt) demonstrates notable advantages in consolidated infrastructure deployment, delivering up to 90W of power alongside data through a single cable. This integration eliminates the need for separate power supplies and associated cabling, reducing material usage by approximately 30-40% compared to traditional network deployments. Studies from the Ethernet Alliance indicate that this consolidation can reduce electronic waste by up to 25% over the technology's lifecycle.
Energy consumption measurements reveal that PoE++ systems typically operate at 85-90% efficiency when delivering power to end devices. However, this efficiency decreases with distance, dropping approximately 0.5% per 10 meters due to transmission losses. The technology's intelligent power management capabilities enable dynamic power allocation, reducing unnecessary consumption by an estimated 15-20% compared to static power systems.
VDSL, conversely, leverages existing telephone infrastructure, minimizing the environmental impact of new deployments. The technology's carbon footprint during installation phase is approximately 60% lower than technologies requiring new cabling infrastructure. However, VDSL systems generally operate at lower energy efficiency rates of 70-75% due to signal processing requirements and line conditioning needs.
Thermal management represents another critical environmental consideration. PoE++ systems generate more concentrated heat in network closets, requiring additional cooling that increases overall energy consumption by 10-15%. VDSL distributes its heat generation across a wider area, reducing cooling requirements but potentially increasing the total energy footprint due to less efficient centralized management.
Lifecycle assessment data indicates that PoE++ equipment typically maintains operational efficiency for 7-8 years before requiring replacement, while VDSL infrastructure generally needs updates every 5-6 years due to compatibility issues with evolving standards. This difference translates to approximately 20% less electronic waste generation over a 15-year operational period for PoE++ deployments.
Carbon emissions calculations, accounting for both operational energy and embodied carbon, show that PoE++ networks produce approximately 15% lower lifetime emissions in scenarios where renewable energy sources power the network infrastructure. This advantage diminishes in regions heavily dependent on fossil fuels for electricity generation.
PoE++ (IEEE 802.3bt) demonstrates notable advantages in consolidated infrastructure deployment, delivering up to 90W of power alongside data through a single cable. This integration eliminates the need for separate power supplies and associated cabling, reducing material usage by approximately 30-40% compared to traditional network deployments. Studies from the Ethernet Alliance indicate that this consolidation can reduce electronic waste by up to 25% over the technology's lifecycle.
Energy consumption measurements reveal that PoE++ systems typically operate at 85-90% efficiency when delivering power to end devices. However, this efficiency decreases with distance, dropping approximately 0.5% per 10 meters due to transmission losses. The technology's intelligent power management capabilities enable dynamic power allocation, reducing unnecessary consumption by an estimated 15-20% compared to static power systems.
VDSL, conversely, leverages existing telephone infrastructure, minimizing the environmental impact of new deployments. The technology's carbon footprint during installation phase is approximately 60% lower than technologies requiring new cabling infrastructure. However, VDSL systems generally operate at lower energy efficiency rates of 70-75% due to signal processing requirements and line conditioning needs.
Thermal management represents another critical environmental consideration. PoE++ systems generate more concentrated heat in network closets, requiring additional cooling that increases overall energy consumption by 10-15%. VDSL distributes its heat generation across a wider area, reducing cooling requirements but potentially increasing the total energy footprint due to less efficient centralized management.
Lifecycle assessment data indicates that PoE++ equipment typically maintains operational efficiency for 7-8 years before requiring replacement, while VDSL infrastructure generally needs updates every 5-6 years due to compatibility issues with evolving standards. This difference translates to approximately 20% less electronic waste generation over a 15-year operational period for PoE++ deployments.
Carbon emissions calculations, accounting for both operational energy and embodied carbon, show that PoE++ networks produce approximately 15% lower lifetime emissions in scenarios where renewable energy sources power the network infrastructure. This advantage diminishes in regions heavily dependent on fossil fuels for electricity generation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!