Realizing seamless interactive experiences with AMOLED advancements.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Evolution Goals
The evolution of AMOLED technology is driven by the pursuit of seamless interactive experiences, with several key goals shaping its development trajectory. One primary objective is to enhance display performance, focusing on improving brightness, contrast ratios, and color accuracy. This involves refining pixel structures and developing advanced organic materials to achieve more vibrant and lifelike visuals.
Another crucial goal is to increase energy efficiency, as AMOLED displays are known for their power-saving capabilities. Researchers and manufacturers are working on optimizing the power consumption of individual pixels and developing more efficient driving circuits. This not only extends battery life in mobile devices but also enables the integration of larger AMOLED displays in various applications without compromising energy efficiency.
Flexibility and form factor innovation represent another significant evolution goal for AMOLED technology. The ability to create flexible and foldable displays opens up new possibilities for device design and user interaction. Efforts are focused on improving the durability of flexible AMOLED panels and developing manufacturing processes that allow for mass production of bendable displays without sacrificing quality or longevity.
Response time and refresh rate improvements are also at the forefront of AMOLED evolution. As interactive experiences become more demanding, particularly in gaming and virtual reality applications, AMOLED displays aim to minimize motion blur and latency. This involves enhancing the switching speed of organic materials and developing advanced driving techniques to support higher refresh rates.
Integration of touch functionality directly into the display layer is another key goal. This approach, known as in-cell or on-cell touch, aims to reduce display thickness and improve touch responsiveness. By eliminating the need for a separate touch layer, AMOLED displays can become thinner and more responsive, contributing to a more seamless interactive experience.
Lastly, enhancing the longevity and reliability of AMOLED displays remains a constant focus. This includes developing more stable organic materials that resist degradation over time, as well as implementing advanced compensation algorithms to maintain consistent performance throughout the display's lifespan. By addressing these challenges, AMOLED technology aims to provide long-lasting, high-quality visual experiences across a wide range of devices and applications.
Another crucial goal is to increase energy efficiency, as AMOLED displays are known for their power-saving capabilities. Researchers and manufacturers are working on optimizing the power consumption of individual pixels and developing more efficient driving circuits. This not only extends battery life in mobile devices but also enables the integration of larger AMOLED displays in various applications without compromising energy efficiency.
Flexibility and form factor innovation represent another significant evolution goal for AMOLED technology. The ability to create flexible and foldable displays opens up new possibilities for device design and user interaction. Efforts are focused on improving the durability of flexible AMOLED panels and developing manufacturing processes that allow for mass production of bendable displays without sacrificing quality or longevity.
Response time and refresh rate improvements are also at the forefront of AMOLED evolution. As interactive experiences become more demanding, particularly in gaming and virtual reality applications, AMOLED displays aim to minimize motion blur and latency. This involves enhancing the switching speed of organic materials and developing advanced driving techniques to support higher refresh rates.
Integration of touch functionality directly into the display layer is another key goal. This approach, known as in-cell or on-cell touch, aims to reduce display thickness and improve touch responsiveness. By eliminating the need for a separate touch layer, AMOLED displays can become thinner and more responsive, contributing to a more seamless interactive experience.
Lastly, enhancing the longevity and reliability of AMOLED displays remains a constant focus. This includes developing more stable organic materials that resist degradation over time, as well as implementing advanced compensation algorithms to maintain consistent performance throughout the display's lifespan. By addressing these challenges, AMOLED technology aims to provide long-lasting, high-quality visual experiences across a wide range of devices and applications.
Interactive Display Demand
The demand for interactive displays has been steadily increasing across various sectors, driven by the growing need for more immersive and engaging user experiences. AMOLED technology, with its superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and response times, has emerged as a key enabler for advanced interactive displays. The market for interactive AMOLED displays spans multiple industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, healthcare, and education.
In the consumer electronics sector, smartphones and tablets are the primary drivers of interactive display demand. Users increasingly expect seamless touch interactions, high refresh rates, and vibrant visuals for gaming, multimedia consumption, and productivity applications. The integration of under-display fingerprint sensors and front-facing cameras in AMOLED panels has further enhanced the interactive capabilities of these devices.
The automotive industry is another significant market for interactive AMOLED displays. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, there is a growing demand for large, curved displays that can provide intuitive interfaces for infotainment systems, navigation, and vehicle controls. AMOLED technology's flexibility and ability to produce deep blacks make it particularly suitable for automotive applications, where glare reduction and readability in various lighting conditions are crucial.
In the healthcare sector, interactive AMOLED displays are finding applications in medical imaging equipment, patient monitoring systems, and surgical displays. The technology's high contrast ratio and wide color gamut enable more accurate representation of medical images, while its touch-sensitive capabilities allow for easier navigation of complex medical data.
The education sector is also embracing interactive AMOLED displays for smart boards and collaborative learning tools. These displays offer improved visibility, multi-touch capabilities, and integration with digital learning platforms, enhancing the overall educational experience.
The demand for larger interactive displays in public spaces, such as digital signage and information kiosks, is growing as well. AMOLED technology's ability to produce vivid colors and high brightness levels makes it ideal for these applications, where attracting attention and conveying information effectively are paramount.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart home technologies continue to evolve, there is an emerging demand for interactive AMOLED displays in household appliances and smart home control panels. These displays offer intuitive interfaces for managing connected devices and monitoring energy consumption.
The global pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote work and virtual collaboration tools, further driving the demand for high-quality interactive displays. AMOLED technology's superior visual performance and touch responsiveness make it well-suited for video conferencing and collaborative workspaces.
In the consumer electronics sector, smartphones and tablets are the primary drivers of interactive display demand. Users increasingly expect seamless touch interactions, high refresh rates, and vibrant visuals for gaming, multimedia consumption, and productivity applications. The integration of under-display fingerprint sensors and front-facing cameras in AMOLED panels has further enhanced the interactive capabilities of these devices.
The automotive industry is another significant market for interactive AMOLED displays. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, there is a growing demand for large, curved displays that can provide intuitive interfaces for infotainment systems, navigation, and vehicle controls. AMOLED technology's flexibility and ability to produce deep blacks make it particularly suitable for automotive applications, where glare reduction and readability in various lighting conditions are crucial.
In the healthcare sector, interactive AMOLED displays are finding applications in medical imaging equipment, patient monitoring systems, and surgical displays. The technology's high contrast ratio and wide color gamut enable more accurate representation of medical images, while its touch-sensitive capabilities allow for easier navigation of complex medical data.
The education sector is also embracing interactive AMOLED displays for smart boards and collaborative learning tools. These displays offer improved visibility, multi-touch capabilities, and integration with digital learning platforms, enhancing the overall educational experience.
The demand for larger interactive displays in public spaces, such as digital signage and information kiosks, is growing as well. AMOLED technology's ability to produce vivid colors and high brightness levels makes it ideal for these applications, where attracting attention and conveying information effectively are paramount.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart home technologies continue to evolve, there is an emerging demand for interactive AMOLED displays in household appliances and smart home control panels. These displays offer intuitive interfaces for managing connected devices and monitoring energy consumption.
The global pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote work and virtual collaboration tools, further driving the demand for high-quality interactive displays. AMOLED technology's superior visual performance and touch responsiveness make it well-suited for video conferencing and collaborative workspaces.
AMOLED Tech Challenges
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has revolutionized display systems, offering superior image quality, energy efficiency, and flexibility. However, as the demand for seamless interactive experiences grows, AMOLED faces several technical challenges that need to be addressed to realize its full potential.
One of the primary challenges is the improvement of touch sensitivity and response time. While AMOLED displays offer excellent visual quality, integrating touch functionality without compromising display performance remains a significant hurdle. Current in-cell and on-cell touch solutions often result in increased display thickness and reduced light transmission, affecting the overall user experience.
Another critical challenge lies in enhancing the durability and lifespan of AMOLED displays. The organic materials used in these displays are susceptible to degradation over time, leading to issues such as burn-in and color shift. This is particularly problematic for devices intended for long-term use or those exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Power consumption optimization presents another significant challenge. Although AMOLED displays are generally more energy-efficient than their LCD counterparts, there is still room for improvement, especially in high-brightness scenarios and when displaying predominantly white content. Balancing power efficiency with display performance is crucial for extending battery life in mobile devices and reducing energy consumption in larger displays.
The manufacturing process for AMOLED displays also poses challenges, particularly in terms of yield rates and cost-effectiveness. The complexity of producing large-scale AMOLED panels with consistent quality and performance across the entire display area remains a significant obstacle to wider adoption, especially in larger form factors such as televisions and monitors.
Addressing color accuracy and uniformity across the display is another ongoing challenge. While AMOLED technology offers vibrant colors and deep blacks, maintaining consistent color reproduction across different viewing angles and throughout the display's lifespan requires continuous innovation in materials science and display calibration techniques.
The development of flexible and foldable AMOLED displays introduces additional challenges related to durability, touch sensitivity, and visual quality when the display is bent or folded. Ensuring consistent performance and longevity in these dynamic form factors requires advancements in materials, manufacturing processes, and structural design.
Lastly, the challenge of reducing motion blur and improving response times for high-refresh-rate displays is crucial for realizing truly seamless interactive experiences, particularly in gaming and virtual reality applications. While AMOLED displays generally offer faster response times than LCDs, further improvements are necessary to eliminate any perceivable lag or motion artifacts in fast-moving content.
One of the primary challenges is the improvement of touch sensitivity and response time. While AMOLED displays offer excellent visual quality, integrating touch functionality without compromising display performance remains a significant hurdle. Current in-cell and on-cell touch solutions often result in increased display thickness and reduced light transmission, affecting the overall user experience.
Another critical challenge lies in enhancing the durability and lifespan of AMOLED displays. The organic materials used in these displays are susceptible to degradation over time, leading to issues such as burn-in and color shift. This is particularly problematic for devices intended for long-term use or those exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Power consumption optimization presents another significant challenge. Although AMOLED displays are generally more energy-efficient than their LCD counterparts, there is still room for improvement, especially in high-brightness scenarios and when displaying predominantly white content. Balancing power efficiency with display performance is crucial for extending battery life in mobile devices and reducing energy consumption in larger displays.
The manufacturing process for AMOLED displays also poses challenges, particularly in terms of yield rates and cost-effectiveness. The complexity of producing large-scale AMOLED panels with consistent quality and performance across the entire display area remains a significant obstacle to wider adoption, especially in larger form factors such as televisions and monitors.
Addressing color accuracy and uniformity across the display is another ongoing challenge. While AMOLED technology offers vibrant colors and deep blacks, maintaining consistent color reproduction across different viewing angles and throughout the display's lifespan requires continuous innovation in materials science and display calibration techniques.
The development of flexible and foldable AMOLED displays introduces additional challenges related to durability, touch sensitivity, and visual quality when the display is bent or folded. Ensuring consistent performance and longevity in these dynamic form factors requires advancements in materials, manufacturing processes, and structural design.
Lastly, the challenge of reducing motion blur and improving response times for high-refresh-rate displays is crucial for realizing truly seamless interactive experiences, particularly in gaming and virtual reality applications. While AMOLED displays generally offer faster response times than LCDs, further improvements are necessary to eliminate any perceivable lag or motion artifacts in fast-moving content.
Current Interactive Solutions
01 AMOLED display technology for interactive experiences
AMOLED displays are utilized to create immersive and interactive user experiences. These displays offer high contrast ratios, vibrant colors, and fast response times, making them ideal for interactive applications. The technology enables the development of touch-sensitive interfaces and dynamic content presentation, enhancing user engagement across various devices and platforms.- AMOLED display technology for interactive experiences: AMOLED displays are utilized to create immersive and interactive user experiences. These displays offer high contrast ratios, vibrant colors, and fast response times, making them ideal for interactive applications. The technology enables the development of responsive touch interfaces and visually appealing content presentation.
- User interface design for AMOLED devices: Specialized user interface designs are created to take advantage of AMOLED display capabilities. These interfaces focus on optimizing content layout, color schemes, and interactive elements to enhance user engagement and improve overall user experience on AMOLED-equipped devices.
- Interactive content creation for AMOLED displays: Methods and systems are developed for creating interactive content specifically tailored for AMOLED displays. This includes techniques for optimizing graphics, animations, and interactive elements to leverage the unique characteristics of AMOLED technology, resulting in more engaging and visually striking interactive experiences.
- AMOLED-based gaming experiences: AMOLED technology is applied to gaming applications, enhancing the visual quality and interactivity of mobile and console games. The high refresh rates and deep blacks of AMOLED displays contribute to more immersive gaming experiences, with improved graphics rendering and responsive touch controls.
- Energy-efficient interactive experiences on AMOLED devices: Techniques are developed to create energy-efficient interactive experiences on AMOLED devices. These methods focus on optimizing content display and user interactions to take advantage of AMOLED's ability to turn off individual pixels, resulting in power savings while maintaining high-quality visual experiences.
02 User interface design for AMOLED screens
Specialized user interface designs are created to take advantage of AMOLED screen capabilities. These interfaces focus on optimizing visual elements, touch interactions, and gesture controls to provide intuitive and responsive user experiences. The designs consider factors such as power efficiency, color management, and adaptability to different screen sizes and resolutions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Interactive content creation for AMOLED displays
Content creation tools and techniques are developed specifically for AMOLED displays to maximize their interactive potential. These tools enable designers and developers to create dynamic, responsive content that leverages the unique characteristics of AMOLED technology. The focus is on producing visually striking and engaging interactive experiences across various applications and devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of AMOLED technology in gaming experiences
AMOLED displays are incorporated into gaming devices and applications to enhance the overall gaming experience. The technology's high refresh rates, deep blacks, and vivid colors contribute to more immersive gameplay. Interactive elements are designed to take advantage of AMOLED's capabilities, resulting in responsive controls and visually stunning game environments.Expand Specific Solutions05 AMOLED-based augmented and virtual reality experiences
AMOLED technology is utilized in the development of augmented and virtual reality systems to create more immersive and interactive experiences. The displays' high pixel density and low latency contribute to reduced motion sickness and improved visual fidelity in AR and VR applications. Interactive elements are designed to leverage AMOLED's strengths, enhancing user engagement and presence in virtual environments.Expand Specific Solutions
AMOLED Industry Leaders
The AMOLED advancements for seamless interactive experiences are in a growth phase, with the market expanding rapidly due to increasing demand for high-quality displays in smartphones, wearables, and other devices. The global AMOLED market is projected to reach significant size in the coming years. Technologically, AMOLED is maturing, with key players like Samsung Display, BOE Technology, and LG Display leading innovation. These companies, along with others like Tianma Microelectronics and Everdisplay Optronics, are investing heavily in R&D to improve AMOLED performance, efficiency, and manufacturing processes. The competition is intensifying as more manufacturers enter the market, driving further advancements in AMOLED technology.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has made significant strides in AMOLED technology, focusing on flexible and foldable displays to create seamless interactive experiences. Their latest flexible AMOLED panels feature a 360-degree folding radius, allowing for innovative device form factors[4]. BOE has also developed touch-integrated AMOLED displays, reducing the overall thickness of the display stack and improving touch responsiveness. The company's AMOLED panels incorporate high refresh rates up to 144Hz, enhancing the smoothness of animations and touch interactions[5]. BOE has also introduced advanced color management systems in their AMOLED displays, supporting wide color gamuts like DCI-P3 for more vibrant and accurate color reproduction.
Strengths: Advanced flexible display technology, high refresh rates, and integrated touch solutions. Weaknesses: Slightly behind Samsung in terms of overall market share and some cutting-edge features.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has been at the forefront of AMOLED technology, pioneering advancements in display quality and interactive experiences. Their latest AMOLED displays feature Dynamic AMOLED 2X technology, offering a 120Hz refresh rate for smoother scrolling and more responsive touch interactions[1]. The company has also developed an under-display camera technology for AMOLED screens, allowing for truly bezel-less designs without compromising on front-facing camera functionality[2]. Samsung's AMOLED panels incorporate advanced touch sensitivity and pressure detection, enabling more nuanced and intuitive user interactions. Additionally, they have implemented variable refresh rate technology, which can scale from 1Hz to 120Hz depending on the content, significantly improving power efficiency while maintaining smooth visuals[3].
Strengths: Industry-leading display quality, advanced touch sensitivity, and power-efficient variable refresh rate technology. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to LCD, potential for screen burn-in over extended periods of use.
AMOLED Innovation Analysis
Active matrix organic light emitting diode display
PatentInactiveUS20090201235A1
Innovation
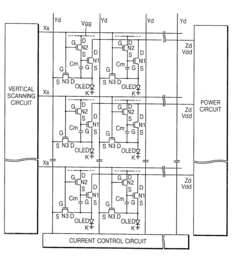
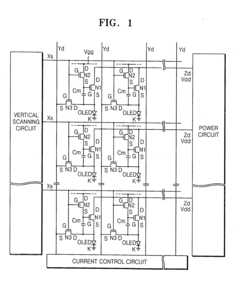
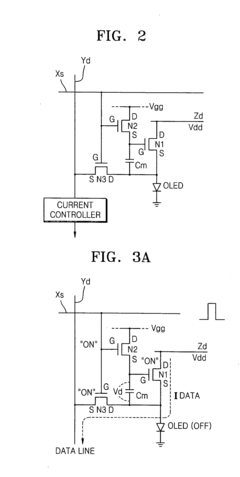
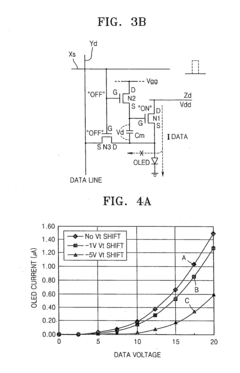
- An AMOLED display with a 3-transistor-1-capacitor structure using N-channel transistors, including a driving transistor, a switching transistor, and a programming transistor, along with a current controller, which determines the current flowing through the transistors to maintain uniform brightness by compensating for threshold voltage shifts, allowing for the use of amorphous silicon and simplifying the pixel structure.
Active-matrix organic light-emitting diode (AMOLED) display module
PatentActiveUS11257882B2
Innovation
- A second conductive layer is uniformly arranged across the AMOLED display panel to ensure consistent common ground voltage distribution to the cathode, maintaining a uniform voltage difference across each OLED element, thereby enhancing luminance uniformity.
Supply Chain Dynamics
The supply chain dynamics for AMOLED technology play a crucial role in realizing seamless interactive experiences. As the demand for high-quality displays in smartphones, tablets, and other consumer electronics continues to grow, the AMOLED supply chain has become increasingly complex and competitive.
Key players in the AMOLED supply chain include panel manufacturers, raw material suppliers, and equipment providers. Samsung Display and LG Display dominate the market, with emerging competitors from China, such as BOE and CSOT, rapidly gaining ground. These manufacturers rely on a network of suppliers for critical components like organic materials, glass substrates, and thin-film transistors.
The AMOLED supply chain faces several challenges, including capacity constraints, yield issues, and fluctuating material costs. As manufacturers strive to meet the growing demand for larger, higher-resolution displays, they must invest heavily in new production facilities and technologies. This has led to periodic supply shortages and price volatility in the market.
Advancements in AMOLED technology, such as flexible and foldable displays, have further complicated the supply chain. These innovations require specialized materials and manufacturing processes, creating new opportunities for suppliers while also introducing potential bottlenecks.
The geographical distribution of the AMOLED supply chain is primarily concentrated in East Asia, with South Korea, China, and Japan being the major hubs. This concentration has implications for global supply chain resilience, as evidenced by recent disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions.
To address these challenges and support the realization of seamless interactive experiences, the AMOLED supply chain is evolving in several ways. Vertical integration is becoming more common, with some panel manufacturers investing in their own material production capabilities to ensure a stable supply. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on diversifying supplier networks and exploring alternative materials to reduce dependency on specific sources.
The development of more efficient production techniques, such as inkjet printing for OLED materials, is also reshaping the supply chain. These advancements promise to reduce manufacturing costs and increase production flexibility, potentially enabling a wider range of companies to enter the market and accelerate innovation in interactive display technologies.
Key players in the AMOLED supply chain include panel manufacturers, raw material suppliers, and equipment providers. Samsung Display and LG Display dominate the market, with emerging competitors from China, such as BOE and CSOT, rapidly gaining ground. These manufacturers rely on a network of suppliers for critical components like organic materials, glass substrates, and thin-film transistors.
The AMOLED supply chain faces several challenges, including capacity constraints, yield issues, and fluctuating material costs. As manufacturers strive to meet the growing demand for larger, higher-resolution displays, they must invest heavily in new production facilities and technologies. This has led to periodic supply shortages and price volatility in the market.
Advancements in AMOLED technology, such as flexible and foldable displays, have further complicated the supply chain. These innovations require specialized materials and manufacturing processes, creating new opportunities for suppliers while also introducing potential bottlenecks.
The geographical distribution of the AMOLED supply chain is primarily concentrated in East Asia, with South Korea, China, and Japan being the major hubs. This concentration has implications for global supply chain resilience, as evidenced by recent disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions.
To address these challenges and support the realization of seamless interactive experiences, the AMOLED supply chain is evolving in several ways. Vertical integration is becoming more common, with some panel manufacturers investing in their own material production capabilities to ensure a stable supply. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on diversifying supplier networks and exploring alternative materials to reduce dependency on specific sources.
The development of more efficient production techniques, such as inkjet printing for OLED materials, is also reshaping the supply chain. These advancements promise to reduce manufacturing costs and increase production flexibility, potentially enabling a wider range of companies to enter the market and accelerate innovation in interactive display technologies.
Energy Efficiency Strategies
Energy efficiency is a critical aspect of AMOLED technology advancement, particularly in the context of realizing seamless interactive experiences. As AMOLED displays continue to evolve, manufacturers are implementing various strategies to optimize power consumption without compromising visual quality or performance.
One key approach to enhancing energy efficiency in AMOLED displays is the implementation of adaptive brightness control. This technology dynamically adjusts the display's luminance based on ambient lighting conditions, reducing power consumption in low-light environments while maintaining visibility in bright settings. Advanced algorithms and light sensors work in tandem to provide a seamless transition between brightness levels, ensuring a consistent user experience.
Another significant strategy is the development of more efficient OLED materials. Researchers are focusing on creating emissive layers with higher quantum efficiency, which allows for the production of brighter displays that consume less power. These advancements in material science contribute to longer battery life and improved overall device performance.
Pixel-level power management is an innovative technique being explored to further reduce energy consumption. By selectively activating only the necessary pixels for displaying content, AMOLED screens can significantly decrease power usage, especially when displaying darker images or using dark mode interfaces. This approach takes advantage of the OLED technology's ability to completely turn off individual pixels when displaying black.
The integration of AI-driven power optimization algorithms is another promising avenue for energy efficiency. These intelligent systems can analyze user behavior patterns and content types to predict and adjust display parameters in real-time, maximizing power savings without noticeable impact on the user experience. Machine learning models continuously refine these predictions, leading to increasingly efficient power management over time.
Advancements in display driver ICs (Integrated Circuits) also play a crucial role in reducing power consumption. More efficient voltage regulation and charge pump designs help minimize power loss during the pixel driving process. Additionally, the implementation of low-power standby modes and fast wake-up capabilities contribute to overall energy savings in mobile devices and wearables.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, the focus on energy efficiency remains paramount. The combination of these strategies, along with ongoing research and development, promises to deliver increasingly power-efficient displays that can support more immersive and responsive interactive experiences while extending device battery life.
One key approach to enhancing energy efficiency in AMOLED displays is the implementation of adaptive brightness control. This technology dynamically adjusts the display's luminance based on ambient lighting conditions, reducing power consumption in low-light environments while maintaining visibility in bright settings. Advanced algorithms and light sensors work in tandem to provide a seamless transition between brightness levels, ensuring a consistent user experience.
Another significant strategy is the development of more efficient OLED materials. Researchers are focusing on creating emissive layers with higher quantum efficiency, which allows for the production of brighter displays that consume less power. These advancements in material science contribute to longer battery life and improved overall device performance.
Pixel-level power management is an innovative technique being explored to further reduce energy consumption. By selectively activating only the necessary pixels for displaying content, AMOLED screens can significantly decrease power usage, especially when displaying darker images or using dark mode interfaces. This approach takes advantage of the OLED technology's ability to completely turn off individual pixels when displaying black.
The integration of AI-driven power optimization algorithms is another promising avenue for energy efficiency. These intelligent systems can analyze user behavior patterns and content types to predict and adjust display parameters in real-time, maximizing power savings without noticeable impact on the user experience. Machine learning models continuously refine these predictions, leading to increasingly efficient power management over time.
Advancements in display driver ICs (Integrated Circuits) also play a crucial role in reducing power consumption. More efficient voltage regulation and charge pump designs help minimize power loss during the pixel driving process. Additionally, the implementation of low-power standby modes and fast wake-up capabilities contribute to overall energy savings in mobile devices and wearables.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, the focus on energy efficiency remains paramount. The combination of these strategies, along with ongoing research and development, promises to deliver increasingly power-efficient displays that can support more immersive and responsive interactive experiences while extending device battery life.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!