Reliability metrics in harsh-condition AMOLED testing.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Testing Background and Objectives
Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode (AMOLED) technology has revolutionized the display industry since its inception in the late 1990s. This advanced display technology offers superior image quality, energy efficiency, and flexibility compared to traditional LCD displays. As AMOLED displays have become increasingly prevalent in consumer electronics, automotive interfaces, and industrial applications, the need for robust reliability testing has grown exponentially.
The harsh conditions under which AMOLED displays are expected to operate present unique challenges for reliability testing. These conditions may include extreme temperatures, high humidity, mechanical stress, and exposure to various environmental contaminants. The primary objective of harsh-condition AMOLED testing is to ensure that these displays maintain their performance and longevity under such demanding circumstances.
Reliability metrics in harsh-condition AMOLED testing encompass a wide range of parameters that are critical to display performance and durability. These metrics typically include luminance degradation, color shift, pixel defects, power consumption changes, and response time variations. The goal is to quantify how these parameters evolve over time and under different stress conditions, providing valuable insights into the display's long-term reliability.
The evolution of AMOLED technology has been marked by significant improvements in materials science, manufacturing processes, and device architectures. These advancements have contributed to enhanced reliability, but they have also necessitated more sophisticated testing methodologies. The industry has moved from simple accelerated life tests to more comprehensive multi-factor stress testing regimes that better simulate real-world usage scenarios.
As AMOLED displays find applications in increasingly diverse and demanding environments, the importance of standardized reliability metrics has become paramount. Organizations such as the Society for Information Display (SID) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have been working towards establishing industry-wide standards for AMOLED reliability testing. These efforts aim to create a common language for manufacturers, researchers, and end-users to assess and compare display performance under harsh conditions.
The technological trajectory of AMOLED displays points towards even more challenging applications, such as foldable and rollable devices, transparent displays, and large-area lighting panels. These emerging form factors introduce additional reliability concerns and require the development of new testing protocols and metrics. The industry's focus is shifting towards predictive reliability models that can accurately forecast display performance over extended periods based on accelerated testing data.
The harsh conditions under which AMOLED displays are expected to operate present unique challenges for reliability testing. These conditions may include extreme temperatures, high humidity, mechanical stress, and exposure to various environmental contaminants. The primary objective of harsh-condition AMOLED testing is to ensure that these displays maintain their performance and longevity under such demanding circumstances.
Reliability metrics in harsh-condition AMOLED testing encompass a wide range of parameters that are critical to display performance and durability. These metrics typically include luminance degradation, color shift, pixel defects, power consumption changes, and response time variations. The goal is to quantify how these parameters evolve over time and under different stress conditions, providing valuable insights into the display's long-term reliability.
The evolution of AMOLED technology has been marked by significant improvements in materials science, manufacturing processes, and device architectures. These advancements have contributed to enhanced reliability, but they have also necessitated more sophisticated testing methodologies. The industry has moved from simple accelerated life tests to more comprehensive multi-factor stress testing regimes that better simulate real-world usage scenarios.
As AMOLED displays find applications in increasingly diverse and demanding environments, the importance of standardized reliability metrics has become paramount. Organizations such as the Society for Information Display (SID) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have been working towards establishing industry-wide standards for AMOLED reliability testing. These efforts aim to create a common language for manufacturers, researchers, and end-users to assess and compare display performance under harsh conditions.
The technological trajectory of AMOLED displays points towards even more challenging applications, such as foldable and rollable devices, transparent displays, and large-area lighting panels. These emerging form factors introduce additional reliability concerns and require the development of new testing protocols and metrics. The industry's focus is shifting towards predictive reliability models that can accurately forecast display performance over extended periods based on accelerated testing data.
Market Demand for Harsh-Condition AMOLED Displays
The demand for harsh-condition AMOLED displays has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by the need for robust and reliable display technologies in challenging environments. These displays are particularly sought after in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, industrial automation, and outdoor digital signage, where traditional display technologies often fall short.
In the automotive industry, there is a growing trend towards larger, more sophisticated in-vehicle infotainment systems and digital instrument clusters. These displays must withstand extreme temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and exposure to sunlight while maintaining high visibility and longevity. The global automotive display market is expected to experience significant growth, with AMOLED technology playing a crucial role in meeting the demanding requirements of modern vehicles.
The aerospace sector also presents a substantial market opportunity for harsh-condition AMOLED displays. Cockpit displays, passenger entertainment systems, and maintenance equipment all require displays that can operate reliably in high-altitude environments with varying pressure and temperature conditions. The ability of AMOLED technology to deliver high contrast ratios and wide viewing angles makes it particularly attractive for these applications.
Industrial automation is another key market driver for harsh-condition AMOLED displays. Factory floors, oil rigs, and mining operations often involve exposure to dust, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. The demand for durable, high-performance displays in these settings is fueling the adoption of AMOLED technology, which offers superior readability and touch responsiveness even in challenging conditions.
The outdoor digital signage market is also contributing to the increased demand for harsh-condition AMOLED displays. These displays must withstand exposure to direct sunlight, rain, and temperature extremes while maintaining high brightness and color accuracy. The superior contrast and power efficiency of AMOLED technology make it an attractive option for outdoor advertising and information displays.
As smart cities and Internet of Things (IoT) applications continue to evolve, there is a growing need for robust display solutions in public spaces and infrastructure. This includes applications such as interactive kiosks, traffic management systems, and environmental monitoring displays, all of which benefit from the durability and performance characteristics of harsh-condition AMOLED technology.
The market demand for harsh-condition AMOLED displays is further bolstered by the increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency. The lower power consumption of AMOLED displays compared to traditional LCD technology aligns well with the global push for more environmentally friendly solutions across industries.
In the automotive industry, there is a growing trend towards larger, more sophisticated in-vehicle infotainment systems and digital instrument clusters. These displays must withstand extreme temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and exposure to sunlight while maintaining high visibility and longevity. The global automotive display market is expected to experience significant growth, with AMOLED technology playing a crucial role in meeting the demanding requirements of modern vehicles.
The aerospace sector also presents a substantial market opportunity for harsh-condition AMOLED displays. Cockpit displays, passenger entertainment systems, and maintenance equipment all require displays that can operate reliably in high-altitude environments with varying pressure and temperature conditions. The ability of AMOLED technology to deliver high contrast ratios and wide viewing angles makes it particularly attractive for these applications.
Industrial automation is another key market driver for harsh-condition AMOLED displays. Factory floors, oil rigs, and mining operations often involve exposure to dust, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. The demand for durable, high-performance displays in these settings is fueling the adoption of AMOLED technology, which offers superior readability and touch responsiveness even in challenging conditions.
The outdoor digital signage market is also contributing to the increased demand for harsh-condition AMOLED displays. These displays must withstand exposure to direct sunlight, rain, and temperature extremes while maintaining high brightness and color accuracy. The superior contrast and power efficiency of AMOLED technology make it an attractive option for outdoor advertising and information displays.
As smart cities and Internet of Things (IoT) applications continue to evolve, there is a growing need for robust display solutions in public spaces and infrastructure. This includes applications such as interactive kiosks, traffic management systems, and environmental monitoring displays, all of which benefit from the durability and performance characteristics of harsh-condition AMOLED technology.
The market demand for harsh-condition AMOLED displays is further bolstered by the increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency. The lower power consumption of AMOLED displays compared to traditional LCD technology aligns well with the global push for more environmentally friendly solutions across industries.
Current Challenges in AMOLED Reliability Testing
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays have become increasingly prevalent in modern electronic devices, particularly in smartphones and wearables. However, ensuring their reliability under harsh conditions remains a significant challenge for manufacturers and researchers alike. The current challenges in AMOLED reliability testing stem from the complex nature of these displays and the diverse environmental factors they must withstand.
One of the primary challenges is the development of standardized testing protocols that accurately simulate real-world harsh conditions. These conditions may include extreme temperatures, high humidity, mechanical stress, and exposure to various chemicals. Creating test environments that can consistently replicate these conditions while allowing for precise measurements is a formidable task. Moreover, the interaction between different environmental factors can lead to compound effects on AMOLED performance, further complicating the testing process.
Another significant challenge lies in the selection and implementation of appropriate reliability metrics. Traditional display metrics such as brightness, color accuracy, and contrast ratio may not fully capture the degradation patterns specific to AMOLEDs under harsh conditions. New metrics need to be developed and validated to assess factors such as organic material degradation, electrode corrosion, and encapsulation integrity. These metrics must be sensitive enough to detect early signs of failure while also being reproducible across different testing facilities.
The time-dependent nature of AMOLED degradation poses another challenge for reliability testing. Accelerated life testing is often employed to predict long-term reliability within a reasonable timeframe. However, determining the correlation between accelerated test results and real-world performance remains a complex issue. Researchers must develop accurate models that can extrapolate short-term test data to predict long-term reliability under various usage scenarios and environmental conditions.
Furthermore, the miniaturization and integration of AMOLEDs into flexible and foldable devices introduce additional complexities in reliability testing. These form factors subject the displays to unique stress patterns and failure modes that may not be adequately addressed by conventional testing methods. Developing specialized test equipment and procedures for these emerging display technologies is an ongoing challenge in the field.
Lastly, the rapid pace of innovation in AMOLED technology itself presents a moving target for reliability testing. As new materials, structures, and manufacturing processes are introduced, testing methodologies must evolve to address the specific vulnerabilities and failure modes associated with these advancements. This requires continuous research and development in testing techniques, as well as close collaboration between display manufacturers, testing equipment providers, and standardization bodies.
One of the primary challenges is the development of standardized testing protocols that accurately simulate real-world harsh conditions. These conditions may include extreme temperatures, high humidity, mechanical stress, and exposure to various chemicals. Creating test environments that can consistently replicate these conditions while allowing for precise measurements is a formidable task. Moreover, the interaction between different environmental factors can lead to compound effects on AMOLED performance, further complicating the testing process.
Another significant challenge lies in the selection and implementation of appropriate reliability metrics. Traditional display metrics such as brightness, color accuracy, and contrast ratio may not fully capture the degradation patterns specific to AMOLEDs under harsh conditions. New metrics need to be developed and validated to assess factors such as organic material degradation, electrode corrosion, and encapsulation integrity. These metrics must be sensitive enough to detect early signs of failure while also being reproducible across different testing facilities.
The time-dependent nature of AMOLED degradation poses another challenge for reliability testing. Accelerated life testing is often employed to predict long-term reliability within a reasonable timeframe. However, determining the correlation between accelerated test results and real-world performance remains a complex issue. Researchers must develop accurate models that can extrapolate short-term test data to predict long-term reliability under various usage scenarios and environmental conditions.
Furthermore, the miniaturization and integration of AMOLEDs into flexible and foldable devices introduce additional complexities in reliability testing. These form factors subject the displays to unique stress patterns and failure modes that may not be adequately addressed by conventional testing methods. Developing specialized test equipment and procedures for these emerging display technologies is an ongoing challenge in the field.
Lastly, the rapid pace of innovation in AMOLED technology itself presents a moving target for reliability testing. As new materials, structures, and manufacturing processes are introduced, testing methodologies must evolve to address the specific vulnerabilities and failure modes associated with these advancements. This requires continuous research and development in testing techniques, as well as close collaboration between display manufacturers, testing equipment providers, and standardization bodies.
Existing Reliability Metrics for Harsh Conditions
01 Compensation techniques for AMOLED display reliability
Various compensation techniques are employed to enhance AMOLED display reliability. These include methods for compensating pixel degradation, adjusting driving currents, and implementing voltage compensation schemes. Such techniques help maintain consistent brightness and color accuracy over the lifespan of the display, improving overall reliability and longevity.- Compensation techniques for AMOLED display reliability: Various compensation techniques are employed to improve the reliability of AMOLED displays. These include methods for compensating for pixel degradation, voltage drops, and temperature variations. Such techniques help maintain consistent image quality and extend the lifespan of AMOLED displays.
- Pixel circuit designs for enhanced AMOLED reliability: Advanced pixel circuit designs are developed to enhance the reliability of AMOLED displays. These circuits may include additional transistors or capacitors to improve stability, reduce current leakage, and minimize the effects of threshold voltage shifts in driving transistors.
- Driving schemes for AMOLED longevity: Innovative driving schemes are implemented to extend the longevity of AMOLED displays. These may include optimized voltage and current control methods, as well as techniques for reducing stress on organic light-emitting materials and driving transistors during operation.
- Material improvements for AMOLED durability: Advancements in materials used in AMOLED displays contribute to improved durability and reliability. This includes the development of more stable organic light-emitting materials, enhanced encapsulation techniques, and improved electrode materials to prevent degradation and increase device lifespan.
- Sensing and feedback systems for AMOLED reliability: Sensing and feedback systems are integrated into AMOLED displays to monitor and adjust performance in real-time. These systems may include temperature sensors, light sensors, and current sensing circuits to detect and compensate for variations in display performance, ensuring long-term reliability.
02 Pixel circuit designs for improved AMOLED reliability
Advanced pixel circuit designs are developed to enhance AMOLED reliability. These circuits may incorporate additional transistors, capacitors, or sensing elements to monitor and adjust pixel performance. Such designs aim to mitigate issues like threshold voltage shifts and current variations, thereby improving the overall stability and lifespan of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions03 Thermal management for AMOLED reliability
Effective thermal management strategies are crucial for maintaining AMOLED reliability. These may include heat dissipation structures, temperature sensing mechanisms, and adaptive brightness control based on thermal conditions. By managing heat generation and distribution, these approaches help prevent thermal degradation and extend the operational life of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions04 Encapsulation and protection techniques for AMOLED displays
Advanced encapsulation and protection techniques are employed to enhance AMOLED reliability. These may include multi-layer barrier films, getter materials, and specialized packaging designs to prevent moisture and oxygen ingress. Such methods help protect sensitive organic materials from environmental factors, thereby improving the long-term stability and performance of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions05 Aging compensation and lifespan prediction for AMOLED displays
Sophisticated aging compensation algorithms and lifespan prediction models are developed to enhance AMOLED reliability. These techniques may involve real-time monitoring of pixel characteristics, historical usage data analysis, and adaptive compensation strategies. By anticipating and mitigating aging effects, these approaches help maintain consistent display performance over extended periods of use.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in AMOLED Testing Industry
The reliability metrics for AMOLED testing in harsh conditions represent a critical area of focus in the display technology industry, which is currently in a mature yet evolving stage. The market for AMOLED displays is substantial and growing, driven by increasing demand in smartphones, televisions, and other consumer electronics. Key players like Samsung Display, BOE Technology, and LG Display are at the forefront of technological advancements, investing heavily in research and development to improve AMOLED performance and durability. These companies are continuously refining their testing methodologies to ensure reliability under various environmental stresses, reflecting the industry's commitment to enhancing product quality and longevity in challenging conditions.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed advanced AMOLED testing methodologies for harsh conditions, incorporating multi-parameter stress testing and accelerated aging techniques. Their approach includes thermal cycling (-40°C to 85°C), high humidity exposure (up to 95% RH), and mechanical stress simulations. BOE utilizes AI-driven image analysis to detect subtle defects and employs in-situ monitoring systems for real-time reliability assessment[1][3]. The company has also implemented a comprehensive reliability prediction model that combines historical data with machine learning algorithms to forecast AMOLED panel longevity under various environmental stresses[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive testing suite, AI-enhanced defect detection, and predictive modeling capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential for over-reliance on predictive models, high costs associated with extensive testing procedures.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed innovative reliability metrics and testing methodologies for AMOLED displays in harsh conditions, leveraging its expertise in materials science and optical technologies. Their approach includes advanced accelerated aging tests that simulate multiple environmental stressors simultaneously, such as UV exposure, temperature cycling, and high humidity. 3M has pioneered the use of specialized optical films and coatings to enhance AMOLED durability, incorporating these materials into their testing protocols[12]. The company employs high-precision optical measurement systems to assess minute changes in display performance over time, including color gamut shift, contrast ratio degradation, and luminance decay[13]. 3M has also developed a unique environmental chamber system that allows for in-situ electrical and optical characterization of AMOLED panels under extreme conditions.
Strengths: Strong materials science foundation, innovative protective technologies, and comprehensive optical performance assessment capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential focus on material solutions may overlook some system-level reliability issues, specialized testing equipment may limit widespread adoption.
Core Innovations in AMOLED Testing Technologies
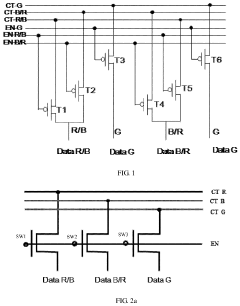
Active-matrix organic light emitting diode (amoled) panel cell testing circuit and method for repairing data lines via same
PatentActiveUS20200342807A1
Innovation
- An active-matrix organic light emitting diode (AMOLED) panel cell testing circuit with a modified configuration that includes three switches connected to detection control signals, allowing for the connection of parallel lines to repair open circuits in data lines, enabling both screen detection and data line repair.
Active matrix organic light emitting diode display
PatentInactiveUS20120044235A1
Innovation
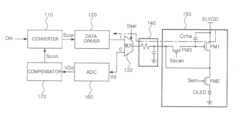
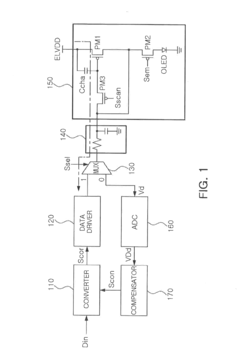
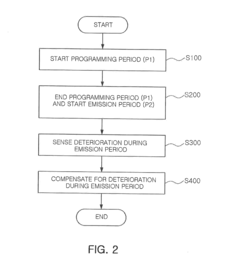
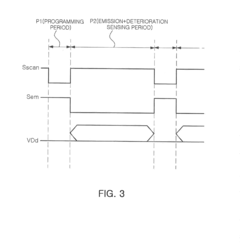
- An active matrix organic light-emitting diode display that includes a data driver generating correction signals, a selector for programming and deterioration detection paths, a pixel unit with MOS transistors and a charging capacitor, and an analog-to-digital converter to detect deterioration voltage during the emission period, enabling rapid sensing and compensation of deterioration.
Environmental Impact of AMOLED Testing Procedures
The environmental impact of AMOLED testing procedures is a critical consideration in the development and production of these advanced display technologies. As AMOLED displays become increasingly prevalent in consumer electronics, the need for rigorous testing under harsh conditions has grown. However, these testing procedures can have significant environmental implications that must be carefully managed.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with AMOLED testing is the energy consumption involved. Harsh-condition testing often requires extended periods of operation at high brightness levels and extreme temperatures, leading to substantial power usage. This increased energy demand contributes to higher carbon emissions, particularly if the testing facilities rely on non-renewable energy sources.
Chemical waste generation is another notable environmental issue in AMOLED testing. The use of various solvents, cleaning agents, and other chemicals during the testing process can result in hazardous waste that requires proper disposal. Improper handling of these substances may lead to soil and water contamination, posing risks to local ecosystems and human health.
The production of test samples and prototypes also contributes to electronic waste. As multiple iterations of displays are tested and discarded, the accumulation of electronic components containing potentially harmful materials such as heavy metals becomes a concern. Proper recycling and disposal protocols are essential to mitigate the environmental impact of this waste stream.
Temperature control systems used in harsh-condition testing can have indirect environmental effects. The use of refrigerants and heating elements in climate chambers may contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly if older, less environmentally friendly systems are employed. Additionally, the production and transportation of specialized testing equipment can have a carbon footprint that should be considered in the overall environmental assessment.
To address these environmental challenges, many AMOLED manufacturers and testing facilities are implementing more sustainable practices. These include the use of renewable energy sources to power testing equipment, the adoption of more efficient testing protocols to reduce energy consumption, and the implementation of comprehensive recycling programs for test samples and chemical waste.
Furthermore, there is a growing trend towards the development of eco-friendly testing materials and procedures. This includes the use of biodegradable cleaning agents, the design of reusable test fixtures, and the optimization of test cycles to minimize resource consumption without compromising the reliability of results.
As the industry continues to evolve, balancing the need for thorough reliability testing with environmental responsibility remains a key challenge. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on creating more sustainable testing methodologies that can maintain the high standards required for AMOLED quality assurance while reducing the overall environmental footprint of the testing process.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with AMOLED testing is the energy consumption involved. Harsh-condition testing often requires extended periods of operation at high brightness levels and extreme temperatures, leading to substantial power usage. This increased energy demand contributes to higher carbon emissions, particularly if the testing facilities rely on non-renewable energy sources.
Chemical waste generation is another notable environmental issue in AMOLED testing. The use of various solvents, cleaning agents, and other chemicals during the testing process can result in hazardous waste that requires proper disposal. Improper handling of these substances may lead to soil and water contamination, posing risks to local ecosystems and human health.
The production of test samples and prototypes also contributes to electronic waste. As multiple iterations of displays are tested and discarded, the accumulation of electronic components containing potentially harmful materials such as heavy metals becomes a concern. Proper recycling and disposal protocols are essential to mitigate the environmental impact of this waste stream.
Temperature control systems used in harsh-condition testing can have indirect environmental effects. The use of refrigerants and heating elements in climate chambers may contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly if older, less environmentally friendly systems are employed. Additionally, the production and transportation of specialized testing equipment can have a carbon footprint that should be considered in the overall environmental assessment.
To address these environmental challenges, many AMOLED manufacturers and testing facilities are implementing more sustainable practices. These include the use of renewable energy sources to power testing equipment, the adoption of more efficient testing protocols to reduce energy consumption, and the implementation of comprehensive recycling programs for test samples and chemical waste.
Furthermore, there is a growing trend towards the development of eco-friendly testing materials and procedures. This includes the use of biodegradable cleaning agents, the design of reusable test fixtures, and the optimization of test cycles to minimize resource consumption without compromising the reliability of results.
As the industry continues to evolve, balancing the need for thorough reliability testing with environmental responsibility remains a key challenge. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on creating more sustainable testing methodologies that can maintain the high standards required for AMOLED quality assurance while reducing the overall environmental footprint of the testing process.
Standardization Efforts in AMOLED Reliability Metrics
Standardization efforts in AMOLED reliability metrics have become increasingly crucial as the technology gains widespread adoption in harsh-condition applications. These efforts aim to establish uniform testing procedures and performance benchmarks, ensuring consistency across the industry and facilitating meaningful comparisons between different AMOLED displays.
One of the primary initiatives in this area is the development of standardized test protocols for harsh-condition environments. These protocols define specific temperature ranges, humidity levels, and mechanical stress conditions that AMOLED displays must withstand. By establishing these common testing parameters, manufacturers and researchers can more accurately assess the reliability of their displays under extreme conditions.
Another key aspect of standardization is the definition of key performance indicators (KPIs) for AMOLED reliability. These KPIs typically include metrics such as luminance degradation rate, color shift, and pixel failure rate. Standardizing these metrics allows for more objective evaluations of display performance and longevity across different manufacturers and applications.
International organizations, such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Society for Information Display (SID), play a crucial role in driving these standardization efforts. These bodies bring together experts from academia, industry, and regulatory agencies to develop consensus-based standards that address the unique challenges of AMOLED technology in harsh environments.
One significant outcome of these standardization efforts is the creation of reliability prediction models. These models, based on accelerated life testing data and statistical analysis, help predict the long-term performance of AMOLED displays under various environmental conditions. Standardizing these prediction models ensures that all stakeholders in the industry are working with consistent and reliable data.
Efforts are also underway to standardize the reporting of reliability test results. This includes defining common formats for data presentation, specifying required information in test reports, and establishing guidelines for interpreting results. Such standardization not only facilitates better communication between display manufacturers and their customers but also aids in regulatory compliance and quality assurance processes.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, these standardization efforts must remain dynamic and responsive to new developments. Regular reviews and updates of standards ensure that they remain relevant and effective in addressing the latest challenges in harsh-condition AMOLED testing. This ongoing process of refinement and adaptation is essential for maintaining the reliability and performance of AMOLED displays in demanding applications.
One of the primary initiatives in this area is the development of standardized test protocols for harsh-condition environments. These protocols define specific temperature ranges, humidity levels, and mechanical stress conditions that AMOLED displays must withstand. By establishing these common testing parameters, manufacturers and researchers can more accurately assess the reliability of their displays under extreme conditions.
Another key aspect of standardization is the definition of key performance indicators (KPIs) for AMOLED reliability. These KPIs typically include metrics such as luminance degradation rate, color shift, and pixel failure rate. Standardizing these metrics allows for more objective evaluations of display performance and longevity across different manufacturers and applications.
International organizations, such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Society for Information Display (SID), play a crucial role in driving these standardization efforts. These bodies bring together experts from academia, industry, and regulatory agencies to develop consensus-based standards that address the unique challenges of AMOLED technology in harsh environments.
One significant outcome of these standardization efforts is the creation of reliability prediction models. These models, based on accelerated life testing data and statistical analysis, help predict the long-term performance of AMOLED displays under various environmental conditions. Standardizing these prediction models ensures that all stakeholders in the industry are working with consistent and reliable data.
Efforts are also underway to standardize the reporting of reliability test results. This includes defining common formats for data presentation, specifying required information in test reports, and establishing guidelines for interpreting results. Such standardization not only facilitates better communication between display manufacturers and their customers but also aids in regulatory compliance and quality assurance processes.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, these standardization efforts must remain dynamic and responsive to new developments. Regular reviews and updates of standards ensure that they remain relevant and effective in addressing the latest challenges in harsh-condition AMOLED testing. This ongoing process of refinement and adaptation is essential for maintaining the reliability and performance of AMOLED displays in demanding applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!